Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Spontaneous creation and annihilation dynamics and strain-limited stability of magnetic skyrmions
Spontaneous creation and annihilation dynamics and strain-limited stability of magnetic skyrmions
Skyrmions are spin textures which have integer topological charge. Typically they are very stable. Here, the authors observe the spontaneous creation and annihilation of skyrmions in regions of high exchange energy density, suggesting a limit to skyrmion stability.
- Frederic Rendell-Bhatti
- , Raymond J. Lamb
- & Damien McGrouther
-
Article
| Open Access Large magnetoelectric coupling in multiferroic oxide heterostructures assembled via epitaxial lift-off
Large magnetoelectric coupling in multiferroic oxide heterostructures assembled via epitaxial lift-off
Key properties of transition metal perovskite oxides are degraded after epitaxial growth on ferroelectric substrates due to lattice-mismatch strain. Here, the authors use epitaxial lift-off and transfer to overcome this problem and demonstrate electric field control of a bulk-like magnetization.
- D. Pesquera
- , E. Khestanova
- & N. D. Mathur
-
Article
| Open Access A flexible artificial intrinsic-synaptic tactile sensory organ
A flexible artificial intrinsic-synaptic tactile sensory organ
Emulating the preprocessing abilities of sensory organs and sensory memory at the device level remains a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate a flexible tactile sensor based on barium titanate nanoparticles in ferroelectric nanocomposite capable of emulating filtering and sensory memory functions.
- Yu Rim Lee
- , Tran Quang Trung
- & Nae-Eung Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic wrinkling pattern exhibiting tunable fluorescence for anticounterfeiting applications
Dynamic wrinkling pattern exhibiting tunable fluorescence for anticounterfeiting applications
Dynamic surface patterns are widely used in information security and anticounterfeiting technologies. Here, the authors demonstrated a dynamic wrinkled and fluorescent pattern using a supramolecular network in which both the wrinkle morphology and fluorescence color can be regulated by pH or light.
- Tianjiao Ma
- , Tiantian Li
- & Xuesong Jiang
-
Article
| Open Access Sub-nanosecond memristor based on ferroelectric tunnel junction
Sub-nanosecond memristor based on ferroelectric tunnel junction
Memristor devices based on ferroelectric tunnel junctions are promising, but suffer from quite slow switching times. Here, the authors report on ultrafast switching times at and above room temperature of 600ps in Ag/BaTiO3/Nb:SrTiO3 based ferroelectric tunnel junctions.
- Chao Ma
- , Zhen Luo
- & Xiaoguang Li
-
Article
| Open Access Superior polarization retention through engineered domain wall pinning
Superior polarization retention through engineered domain wall pinning
The use of ferroelectric materials in memory device applications is held back by low retention times. Here, the authors demonstrate that by intentionally introducing defective nanoregions which increase the activation field for domain wall motion, retention times larger than a year can be achieved.
- Dawei Zhang
- , Daniel Sando
- & Jan Seidel
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging and writing magnetic domains in the non-collinear antiferromagnet Mn3Sn
Imaging and writing magnetic domains in the non-collinear antiferromagnet Mn3Sn
Interpretation of the physical phenomena observed in non-collinear antiferromagnets is challenging; imaging and writing magnetic domains is important for applications. Here the authors show magnetic domain imaging and writing in a non-collinear antiferromagnet by recording anomalous Nernst voltage in response to a localized thermal gradient.
- Helena Reichlova
- , Tomas Janda
- & Sebastian T. B. Goennenwein
-
Article
| Open Access Direct atomic insight into the role of dopants in phase-change materials
Direct atomic insight into the role of dopants in phase-change materials
Quantitative imaging on the doping in phase-change materials for data storage remains scarce. Here, the authors combine electron microscopy, atom probe tomography, and simulations to determine the role of indium and silver dopants during recrystallization.
- Min Zhu
- , Wenxiong Song
- & Richard Dronskowski
-
Article
| Open Access Revealing the intrinsic nature of the mid-gap defects in amorphous Ge2Sb2Te5
Revealing the intrinsic nature of the mid-gap defects in amorphous Ge2Sb2Te5
The structural origin of the mid-gap states responsible for the time-dependent resistance drift in phase-change materials is still under debate. Here the authors use machine learning and density functional theory to identify the structural motifs of the mid-gap defects in the prototypical Ge2Sb2Te5 phase-change alloy.
- Konstantinos Konstantinou
- , Felix C. Mocanu
- & Stephen R. Elliott
-
Article
| Open Access Multiferroicity in atomic van der Waals heterostructures
Multiferroicity in atomic van der Waals heterostructures
Low dimensional multiferroic materials promise the technological advances in next generation spintronic and microwave magnetoelectric devices. Here the authors propose the multiferroicity in the atomically thin ferromagnetic Cr2Ge2Te6/ferroelectric In2Se3 van der Waals heterostructure due to the crosslayer magnetoelectric coupling.
- Cheng Gong
- , Eun Mi Kim
- & Xiang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Depolarization of multidomain ferroelectric materials
Depolarization of multidomain ferroelectric materials
The depolarization dynamics in ferroelectric materials is important for applications as it governs data loss. Here, the authors find a universal constant in ferroelectric materials that gives the boundary between a depolarizing and thermodynamically stable regime.
- Dong Zhao
- , Thomas Lenz
- & Ilias Katsouras
-
Article
| Open Access ZnO composite nanolayer with mobility edge quantization for multi-value logic transistors
ZnO composite nanolayer with mobility edge quantization for multi-value logic transistors
Designing multi-value logic transistors with stable and reliable intermediate states remains a challenge. Here, the authors report the mobility edge quantization phenomenon via resonant hybridization of ZnO QDs embedded in amorphous ZnO domains to enable adjustable multi-value intermediate states.
- Lynn Lee
- , Jeongwoon Hwang
- & Myung Mo Sung
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetization-polarization cross-control near room temperature in hexaferrite single crystals
Magnetization-polarization cross-control near room temperature in hexaferrite single crystals
Mutual control of the electric polarization and magnetization promises for low power consumption spintronic devices but remains challenging. Here the authors show reversal of non-volatile magnetization by electric field as well as the polarization switching by magnetic field in a single-component material, close to room temperature.
- V. Kocsis
- , T. Nakajima
- & Y. Taguchi
-
Article
| Open Access Redox gated polymer memristive processing memory unit
Redox gated polymer memristive processing memory unit
Though designing conductive polymers for memory devices is attractive for future low-cost flexible electronics, a proof-of-concept device has yet to be realized. Here, the authors report a redox-gated polymer memristive processing unit with programmable multilevel storage and logic functionalities.
- Bin Zhang
- , Fei Fan
- & Yu Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Spin–orbit torque switching in a T-type magnetic configuration with current orthogonal to easy axes
Spin–orbit torque switching in a T-type magnetic configuration with current orthogonal to easy axes
Spin-orbit torque (SOT) induced magnetization switching facilitates all electric multi-state spin memories and spin logic devices. Here the authors show a new SOT field-free switching mode where the perpendicular layer with tilted easy axis is coupled to an in-plane layer with a uniaxial easy axis.
- W. J. Kong
- , C. H. Wan
- & X. F. Han
-
Article
| Open Access Electric-field control of spin accumulation direction for spin-orbit torques
Electric-field control of spin accumulation direction for spin-orbit torques
Voltage control of spin-orbit torques (SOTs) provides additional degrees of freedom for spinmemory and -logic applications. Here the authors demonstrate a large voltage control of direction as well as amount of current-induced spin accumulation at the heavy metal/ferromagnet interface and effectively tune the SOTs in a Pt/Co/GdOx heterostructure.
- Rahul Mishra
- , Farzad Mahfouzi
- & Hyunsoo Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Giant nonvolatile manipulation of magnetoresistance in magnetic tunnel junctions by electric fields via magnetoelectric coupling
Giant nonvolatile manipulation of magnetoresistance in magnetic tunnel junctions by electric fields via magnetoelectric coupling
Electric field controlled magnetism provides an energy efficient way for the operations in the spintronic devices. Here the authors show strain induced, reversible, nonvolatile electric field control of magnetization and magnetoresistance in a magnetic tunnel junction on a ferroelectric substrate at room temperature and zero magnetic field.
- Aitian Chen
- , Yan Wen
- & Yonggang Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Physical reality of the Preisach model for organic ferroelectrics
Physical reality of the Preisach model for organic ferroelectrics
Though the Preisach model successfully describes hysteretic switching in ferroelectrics, the physical reality of the model remains elusive. Here, the authors explained the origin of the experimental Preisach distribution and its effect on switching kinetics and materials’ potential applications
- Indrė Urbanavičiūtė
- , Tim D. Cornelissen
- & Martijn Kemerink
-
Article
| Open Access A hardware Markov chain algorithm realized in a single device for machine learning
A hardware Markov chain algorithm realized in a single device for machine learning
Despite the need to develop resistive random access memory (RRAM) devices for machine learning, RRAM array-based hardware methods for algorithm require external electronics. Here, the authors realize a Markov chain algorithm in a single 2D multilayer SnSe device without external electronics.
- He Tian
- , Xue-Feng Wang
- & Tian-Ling Ren
-
Article
| Open Access Two-dimensional multibit optoelectronic memory with broadband spectrum distinction
Two-dimensional multibit optoelectronic memory with broadband spectrum distinction
Continued device miniaturization and feasibility of integrating two-dimensional materials into circuits have enabled flexible and transparent optoelectronic memories. Here, the authors show a WSe2–hBN-based heterostructure memory with switching ratio of ~1.1 × 106, ensuring over 128 distinct storage states and retention time of ~4.5 × 104 s.
- Du Xiang
- , Tao Liu
- & Wei Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic metal-ligand coordination for multicolour and water-jet rewritable paper
Dynamic metal-ligand coordination for multicolour and water-jet rewritable paper
Rewritable paper is environmentally favourable, but its practical realization is stifled by limited ink colour versatility and poor image retention times. Here, the authors exploit the relatively stable but reversible nature of metal–organic coordination bonds to produce long-lasting and multicoloured inks for rewritable paper.
- Yun Ma
- , Pengfei She
- & Wei Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Electrically reversible cracks in an intermetallic film controlled by an electric field
Electrically reversible cracks in an intermetallic film controlled by an electric field
Electric-field-induced cracks are generally detrimental to functionality of ferroelectric ceramics. Liu et al. use an intermetallic alloy and ferroelectric oxide junction to mediate the reversible formation of cracks at nanoscales, resulting in colossal electroresistance modulation for memory applications.
- Z. Q. Liu
- , J. H. Liu
- & R. Ramesh
-
Article
| Open Access Conversion of invisible metal-organic frameworks to luminescent perovskite nanocrystals for confidential information encryption and decryption
Conversion of invisible metal-organic frameworks to luminescent perovskite nanocrystals for confidential information encryption and decryption
Materials with switchable fluorescence possess great potential for information encryption applications, but systems where the off state is invisible are lacking. Here the authors print patterns of colourless metal organic frameworks and reversibly transform these inks into fluorescent perovskite nanocrystals
- Congyang Zhang
- , Bo Wang
- & Liang Li
-
Article
| Open Access Temporal correlation detection using computational phase-change memory
Temporal correlation detection using computational phase-change memory
New computing paradigms, such as in-memory computing, are expected to overcome the limitations of conventional computing approaches. Sebastian et al. report a large-scale demonstration of computational phase change memory (PCM) by performing high-level computational primitives using one million PCM devices.
- Abu Sebastian
- , Tomas Tuma
- & Evangelos Eleftheriou
-
Article
| Open Access Origami-based tunable truss structures for non-volatile mechanical memory operation
Origami-based tunable truss structures for non-volatile mechanical memory operation
Origami is a popular method to design building blocks for mechanical metamaterials. Here, the authors assemble a volumetric origami-based structure, predict its axial and rotational movements during folding, and demonstrate the operation of mechanical one- and two-bit memory storage.
- Hiromi Yasuda
- , Tomohiro Tachi
- & Jinkyu Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Antiferromagnetic CuMnAs multi-level memory cell with microelectronic compatibility
Antiferromagnetic CuMnAs multi-level memory cell with microelectronic compatibility
Devices based on antiferromagnetic materials have advantages of robustness to external magnetic fields and the potential for ultrafast operation. Here the authors present a multilevel antiferromagnetic memory cell that can be operated using standard electronic interfaces.
- K. Olejník
- , V. Schuler
- & T. Jungwirth
-
Article
| Open Access Adaptive microwave impedance memory effect in a ferromagnetic insulator
Adaptive microwave impedance memory effect in a ferromagnetic insulator
Dissipative systems may provide another platform towards adaptive electronics beyond adaptive biological systems. Here, Leeet al. report a non-volatile memristive microwave device based on adaptive tuning of the dissipative magnetic domains of a driven ferromagnetic system.
- Hanju Lee
- , Barry Friedman
- & Kiejin Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering the magnetic coupling and anisotropy at the molecule–magnetic surface interface in molecular spintronic devices
Engineering the magnetic coupling and anisotropy at the molecule–magnetic surface interface in molecular spintronic devices
Controlling the magnetic response of a molecular device is important for spintronic applications. Here the authors report the self-assembly, magnetic coupling, and anisotropy of two transition metal complexes bound to a ferrimagnetic surface, and probe the role of the nature of the transition metal ion.
- Victoria E. Campbell
- , Monica Tonelli
- & Talal Mallah
-
Article
| Open Access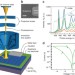 Quantifying redox-induced Schottky barrier variations in memristive devices via in operando spectromicroscopy with graphene electrodes
Quantifying redox-induced Schottky barrier variations in memristive devices via in operando spectromicroscopy with graphene electrodes
Resistive switching in metal oxides is related to the migration of donor defects. Here Baeumer et al. use in operandoX-ray spectromicroscopy to quantify the doping locally and show that small local variations in the donor concentration result in large variations in the device resistance.
- Christoph Baeumer
- , Christoph Schmitz
- & Regina Dittmann
-
Article
| Open Access Room-temperature ferroelectricity in CuInP2S6 ultrathin flakes
Room-temperature ferroelectricity in CuInP2S6 ultrathin flakes
Two dimensional materials are promising for electronic applications, which await the exploration of cooperative phenomena. Here, Liu et al. report switchable ferroelectric polarization in thin CuInP2S6film at room temperature, demonstrating good memory behaviour with on/off ratio of ∼100 based on two-dimensional ferroelectricity.
- Fucai Liu
- , Lu You
- & Zheng Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Design and synthesis of digitally encoded polymers that can be decoded and erased
Design and synthesis of digitally encoded polymers that can be decoded and erased
DNA and other biopolymers encode information based on a sequence of monomers. Here, the authors report a synthetic polymer capable of storing simple binary information which can subsequently be decoded by tandem mass spectroscopy, or permanently erased by heating.
- Raj Kumar Roy
- , Anna Meszynska
- & Jean-François Lutz
-
Article |
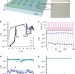 Highly transparent nonvolatile resistive memory devices from silicon oxide and graphene
Highly transparent nonvolatile resistive memory devices from silicon oxide and graphene
Flexible electronic devices are widely considered to have significant potential for a range of applications. Here the authors present a bendable and transparent memory based on graphene electrical contacts and silica as the memory element.
- Jun Yao
- , Jian Lin
- & James M. Tour
-
Article
| Open Access High-density magnetoresistive random access memory operating at ultralow voltage at room temperature
High-density magnetoresistive random access memory operating at ultralow voltage at room temperature
Magnetoresistive random access memory offers significant promise as a next-generation memory technology. Nan and colleagues present a design concept for a device that simultaneously possesses ultrahigh storage capacity, ultralow power dissipation, and high-speed operation at room temperature.
- Jia-Mian Hu
- , Zheng Li
- & Ce-Wen Nan

 Single pulse all-optical toggle switching of magnetization without gadolinium in the ferrimagnet Mn2RuxGa
Single pulse all-optical toggle switching of magnetization without gadolinium in the ferrimagnet Mn2RuxGa