Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Transcriptional linkage analysis with in vivo AAV-Perturb-seq
Transcriptional linkage analysis with in vivo AAV-Perturb-seq
An in vivo single-cell CRISPR screening method identifies transcriptional phenotypes of 22q11.2 deletion syndrome associated with a broad dysregulation of a class of disease susceptibility genes that are important for RNA processing and synaptic function.
- Antonio J. Santinha
- , Esther Klingler
- & Randall J. Platt
-
Article
| Open Access Mega-scale experimental analysis of protein folding stability in biology and design
Mega-scale experimental analysis of protein folding stability in biology and design
Large-scale assays using cDNA display proteolysis are used to measure the folding stabilities of protein domains, providing a method to quantify the effects of mutations on protein folding, with applications in protein design.
- Kotaro Tsuboyama
- , Justas Dauparas
- & Gabriel J. Rocklin
-
Article |
 High-throughput Oligopaint screen identifies druggable 3D genome regulators
High-throughput Oligopaint screen identifies druggable 3D genome regulators
High-throughput DNA or RNA labelling with optimized Oligopaints (HiDRO) reveals more than 300 factors that influence genome folding during interphase, including 43 genes that were validated as either increasing or decreasing interactions between topologically associating domains.
- Daniel S. Park
- , Son C. Nguyen
- & Eric F. Joyce
-
Article |
 CRISPR screens in Drosophila cells identify Vsg as a Tc toxin receptor
CRISPR screens in Drosophila cells identify Vsg as a Tc toxin receptor
A genome-wide CRISPR–Cas9-mediated knockout screen in Drosophila cells identifies Visgun as a proteinaceous receptor for toxin complex toxins, demonstrating the utility of this approach for investigating insecticidal toxins and pathogens.
- Ying Xu
- , Raghuvir Viswanatha
- & Min Dong
-
Article |
 Differential cofactor dependencies define distinct types of human enhancers
Differential cofactor dependencies define distinct types of human enhancers
The systematic categorization of human enhancers by their cofactor dependencies provides a conceptual framework to understand the sequence and chromatin diversity of enhancers and their roles in different gene-regulatory programmes.
- Christoph Neumayr
- , Vanja Haberle
- & Alexander Stark
-
Article
| Open Access Design of protein-binding proteins from the target structure alone
Design of protein-binding proteins from the target structure alone
A design pipeline is presented whereby binding proteins can be designed de novo without the need for prior information on binding hotspots or fragments from structures of complexes with binding partners.
- Longxing Cao
- , Brian Coventry
- & David Baker
-
Article
| Open Access Effective drug combinations in breast, colon and pancreatic cancer cells
Effective drug combinations in breast, colon and pancreatic cancer cells
A survey of potency and efficacy of 2,025 clinically relevant two-drug combinations against 125 molecularly characterized breast, colorectal and pancreatic cancer cell lines identifies rare synergistic effects of anticancer drugs, informing rational combination treatments for specific cancer subtypes.
- Patricia Jaaks
- , Elizabeth A. Coker
- & Mathew J. Garnett
-
Article
| Open Access Omicron escapes the majority of existing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies
Omicron escapes the majority of existing SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies
A high-throughput yeast display platform is used to analyse the profiles of mutations in the SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain (RBD) that enable escape from antibodies, and suggests that most anti-RBD antibodies can be escaped by the Omicron variant.
- Yunlong Cao
- , Jing Wang
- & Xiaoliang Sunney Xie
-
Article |
 AKIRIN2 controls the nuclear import of proteasomes in vertebrates
AKIRIN2 controls the nuclear import of proteasomes in vertebrates
Using time-controlled CRISPR screens, the authors identify AKIRIN2 as a factor involved in the nuclear import of the proteasome.
- Melanie de Almeida
- , Matthias Hinterndorfer
- & Johannes Zuber
-
Article |
 ALDH4A1 is an atherosclerosis auto-antigen targeted by protective antibodies
ALDH4A1 is an atherosclerosis auto-antigen targeted by protective antibodies
An autoantibody found in a mouse model of atherosclerosis recognizses ALDH4A1, and infusion of the antibody delays plaque formation in mice.
- Cristina Lorenzo
- , Pilar Delgado
- & Almudena R. Ramiro
-
Article |
 Identification of SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors using lung and colonic organoids
Identification of SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors using lung and colonic organoids
The use of lung and colonic organoid systems to assess the susceptibility of lung and gut cells to SARS-CoV-2 and to screen FDA-approved drugs that have antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2 is demonstrated.
- Yuling Han
- , Xiaohua Duan
- & Shuibing Chen
-
Article |
 Single-particle cryo-EM at atomic resolution
Single-particle cryo-EM at atomic resolution
Advances in electron cryo-microscopy hardware allow proteins to be studied at atomic resolution.
- Takanori Nakane
- , Abhay Kotecha
- & Sjors H. W. Scheres
-
Article |
 Population genomics of the Viking world
Population genomics of the Viking world
Ancient DNA analyses reveal that Viking Age migrations from Scandinavia resulted in differential influxes of ancestry to different parts of Europe, and the increased presence of non-local ancestry within Scandinavia.
- Ashot Margaryan
- , Daniel J. Lawson
- & Eske Willerslev
-
Article |
 Discovery of SARS-CoV-2 antiviral drugs through large-scale compound repurposing
Discovery of SARS-CoV-2 antiviral drugs through large-scale compound repurposing
A screen of the ReFRAME library of approximately 12,000 known drugs for antiviral activity against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) identified several candidate compounds with suitable activities and pharmacological profiles, which could potentially expedite the deployment of therapies for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
- Laura Riva
- , Shuofeng Yuan
- & Sumit K. Chanda
-
Article |
 A reference map of the human binary protein interactome
A reference map of the human binary protein interactome
A human binary protein interactome map that includes around 53,000 protein–protein interactions involving more than 8,000 proteins provides a reference for the study of human cellular function in health and disease.
- Katja Luck
- , Dae-Kyum Kim
- & Michael A. Calderwood
-
Article |
 An open-source drug discovery platform enables ultra-large virtual screens
An open-source drug discovery platform enables ultra-large virtual screens
VirtualFlow, an open-source drug discovery platform, enables the efficient preparation and virtual screening of ultra-large ligand libraries to identify molecules that bind with high affinity to target proteins.
- Christoph Gorgulla
- , Andras Boeszoermenyi
- & Haribabu Arthanari
-
Article |
 Zucchini consensus motifs determine the mechanism of pre-piRNA production
Zucchini consensus motifs determine the mechanism of pre-piRNA production
A silkworm model recapitulates key steps of Zucchini-mediated cleavage of pre-pre-piRNA and provides insights into Zucchini-mediated and -independent pathways that generate pre-piRNAs, which converge to a common piRNA maturation step.
- Natsuko Izumi
- , Keisuke Shoji
- & Yukihide Tomari
-
Article |
 Allele-selective lowering of mutant HTT protein by HTT–LC3 linker compounds
Allele-selective lowering of mutant HTT protein by HTT–LC3 linker compounds
Compounds that interact with mutant huntingtin and an autophagosomal protein are able to reduce cellular levels of mutant huntingtin by targeting it for autophagic degradation, demonstrating an approach that may have potential for treating proteopathies.
- Zhaoyang Li
- , Cen Wang
- & Boxun Lu
-
Letter |
 Transcriptional cofactors display specificity for distinct types of core promoters
Transcriptional cofactors display specificity for distinct types of core promoters
A screen of 23 transcriptional cofactors for their ability to activate 72,000 candidate core promoters in Drosophila melanogaster identified distinct compatibility groups, providing insight into mechanisms that underlie the selective activation of transcriptional programs.
- Vanja Haberle
- , Cosmas D. Arnold
- & Alexander Stark
-
Article |
 The interaction landscape between transcription factors and the nucleosome
The interaction landscape between transcription factors and the nucleosome
A method for systematically exploring interactions between the nucleosome and transcription factors identifies five major interaction patterns.
- Fangjie Zhu
- , Lucas Farnung
- & Jussi Taipale
-
Letter |
 Single-cell mapping of the thymic stroma identifies IL-25-producing tuft epithelial cells
Single-cell mapping of the thymic stroma identifies IL-25-producing tuft epithelial cells
A comprehensive characterization of the thymic stroma identifies a tuft-cell-like thymic epithelial cell population that is critical for shaping the immune niche in the thymus.
- Chamutal Bornstein
- , Shir Nevo
- & Ido Amit
-
Letter |
 A new class of synthetic retinoid antibiotics effective against bacterial persisters
A new class of synthetic retinoid antibiotics effective against bacterial persisters
Synthetic retinoid compounds can kill both growing and persister MRSA cells by disrupting the membrane lipid bilayer, and are effective in a mouse model of chronic MRSA infection.
- Wooseong Kim
- , Wenpeng Zhu
- & Eleftherios Mylonakis
-
Article |
 Extensive impact of non-antibiotic drugs on human gut bacteria
Extensive impact of non-antibiotic drugs on human gut bacteria
A screen of more than 1,000 drugs shows that about a quarter of the non-antibiotic drugs inhibit the growth of at least one commensal bacterial strain in vitro.
- Lisa Maier
- , Mihaela Pruteanu
- & Athanasios Typas
-
Letter |
 Transcription elongation factors represent in vivo cancer dependencies in glioblastoma
Transcription elongation factors represent in vivo cancer dependencies in glioblastoma
An in vivo RNA interference screening strategy in glioblastoma enabled the identification of a host of epigenetic targets required for glioblastoma cell survival that were not identified by parallel standard screening in cell culture, including the transcription pause–release factor JMJD6, and could be a powerful tool to uncover new therapeutic targets in cancer.
- Tyler E. Miller
- , Brian B. Liau
- & Jeremy N. Rich
-
Letter |
 DHX9 suppresses RNA processing defects originating from the Alu invasion of the human genome
DHX9 suppresses RNA processing defects originating from the Alu invasion of the human genome
In the absence of DHX9, circular RNAs accumulate and transcription and translation are dysregulated—effects that are exacerbated by concomitant depletion of the RNA-editing enzyme ADAR.
- Tuğçe Aktaş
- , İbrahim Avşar Ilık
- & Asifa Akhtar
-
Article |
 An Argonaute phosphorylation cycle promotes microRNA-mediated silencing
An Argonaute phosphorylation cycle promotes microRNA-mediated silencing
The application of genome-wide CRISPR–Cas9 screening coupled with a fluorescent reporter to interrogate the microRNA pathway reveals that continual transient phosphorylation of Argonaute 2 is required to maintain the global efficiency of microRNA-mediated repression.
- Ryan J. Golden
- , Beibei Chen
- & Joshua T. Mendell
-
Letter |
 Genome-wide in vivo screen identifies novel host regulators of metastatic colonization
Genome-wide in vivo screen identifies novel host regulators of metastatic colonization
Screening mutant mouse lines using a genome-wide in vivo assay identifies microenvironmental regulators of metastatic colonization and defines SPNS2 as an important mediator of lung colonization.
- Louise van der Weyden
- , Mark J. Arends
- & David J. Adams
-
Brief Communications Arising |
Safikhani et al. reply
- Zhaleh Safikhani
- , Nehme El-Hachem
- & Benjamin Haibe-Kains
-
Brief Communications Arising |
 Consistency in large pharmacogenomic studies
Consistency in large pharmacogenomic studies
- Paul Geeleher
- , Eric R. Gamazon
- & R. Stephanie Huang
-
Outlook |
 Compound screening: Fresh hunting ground
Compound screening: Fresh hunting ground
In the search for novel therapies, drug developers have begun crowdsourcing molecules.
- Annabel McGilvray
-
Article |
 Interconnected microbiomes and resistomes in low-income human habitats
Interconnected microbiomes and resistomes in low-income human habitats
An analysis of bacterial community structure and antibiotic resistance gene content of interconnected human faecal and environmental samples from two low-income communities in Latin America was carried out using a combination of functional metagenomics, 16S sequencing and shotgun sequencing; resistomes across habitats are generally structured along ecological gradients, but key resistance genes can cross these boundaries, and the authors assessed the usefulness of excreta management protocols in the prevention of resistance gene dissemination.
- Erica C. Pehrsson
- , Pablo Tsukayama
- & Gautam Dantas
-
Letter |
 Live imaging RNAi screen reveals genes essential for meiosis in mammalian oocytes
Live imaging RNAi screen reveals genes essential for meiosis in mammalian oocytes
A high-content phenotypic screening method has been developed allowing the first systematic RNA interference screen for nearly 800 genes mediating mammalian meiosis.
- Sybille Pfender
- , Vitaliy Kuznetsov
- & Melina Schuh
-
Letter |
 Protein quality control at the inner nuclear membrane
Protein quality control at the inner nuclear membrane
A protein degradation pathway is found at the inner nuclear membrane that is distinct from, but complementary to, endoplasmic-reticulum-associated protein degradation, and which is mediated by the Asi protein complex; a genome-wide library screening of yeast identifies more than 20 substrates of this pathway, which is shown to target mislocalized integral membrane proteins for degradation.
- Anton Khmelinskii
- , Ewa Blaszczak
- & Michael Knop
-
Letter |
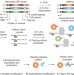 Multiplex single-molecule interaction profiling of DNA-barcoded proteins
Multiplex single-molecule interaction profiling of DNA-barcoded proteins
Single-molecular-interaction-sequencing involves attaching DNA barcodes to proteins, assaying these barcoded proteins en masse in an aqueous solution, followed by immobilization in a polyacrylamide film and amplifying and analysing the barcoding DNAs—the method allows for precise protein quantification and simultaneous interrogation of molecular binding affinity and specificity.
- Liangcai Gu
- , Chao Li
- & George M. Church
-
Technology Feature |
 Charting the brain's networks
Charting the brain's networks
The field of connectomics is pulling neuroscience into a speedy, high-throughput lane that is generating vast amounts of data.
- Vivien Marx
-
News & Views |
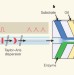 Analog-to-digital drug screening
Analog-to-digital drug screening
Current methods for screening libraries of compounds for biological activity are rather cumbersome, slow and imprecise. A method that breaks up a continuous flow of a compound's solution into droplets offers radical improvements.
- Robert C. R. Wootton
- & Andrew J. deMello
-
Research Highlights |
Genomics: Transposition trends

 Genetic determinants of micronucleus formation in vivo
Genetic determinants of micronucleus formation in vivo