Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access SHQ1 regulation of RNA splicing is required for T-lymphoblastic leukemia cell survival
SHQ1 regulation of RNA splicing is required for T-lymphoblastic leukemia cell survival
T-acute lymphoblastic leukemia is an aggressive cancer. Here the authors provide insights into the functional role of SHQ1, an H/ACA snoRNP assembly factor involved in snRNA pseudouridylation, in T-lymphoblastic leukemia cell survival through regulating the maturation of MYC mRNA.
- Hexiu Su
- , Juncheng Hu
- & Hudan Liu
-
Article
| Open AccessGene expression imputation identifies candidate genes and susceptibility loci associated with cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma
Genetic loci linked to susceptibility for the common skin cancer cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) have been identified by genome wide association studies (GWAS). Here, the authors impute gene expression levels from GWAS data to perform a transcriptome wide association study (TWAS), identifying five novel genetic loci linked to cSCC susceptibility.
- Nilah M. Ioannidis
- , Wei Wang
- & Alice S. Whittemore
-
Article
| Open Access ATRX, DAXX or MEN1 mutant pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors are a distinct alpha-cell signature subgroup
ATRX, DAXX or MEN1 mutant pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors are a distinct alpha-cell signature subgroup
In pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors (PanNETs) ATRX, DAXX, and MEN1 are commonly mutated (A-D-M mutant PanNETs). Here, the authors find in a cohort of PanNETS 58% are A-D-M mutant PanNETs, with a worse clinical outcome and differences in gene expression and methylation compared to A-D-M wild type cases- these gene expression differences suggest that A-D-M mutant PanNETs potentially originate from a cell type similar to alpha cells.
- Chang S. Chan
- , Saurabh V. Laddha
- & Laura H. Tang
-
Article
| Open Access EVI1 overexpression reprograms hematopoiesis via upregulation of Spi1 transcription
EVI1 overexpression reprograms hematopoiesis via upregulation of Spi1 transcription
Chr3q26 rearrangements cause overexpression of EVI1 and associate with myeloid neoplasms, but the mechanism behind this association is unclear. Here, using a novel mouse model they show that EVI1 causes premalignant myeloid expansion with suppression of other lineages through upregulation of Spi1/PU.1.
- Edward Ayoub
- , Michael P. Wilson
- & Archibald S. Perkins
-
Article
| Open Access Variants in exons 5 and 6 of ACTB cause syndromic thrombocytopenia
Variants in exons 5 and 6 of ACTB cause syndromic thrombocytopenia
Genetic variants in ACTB and ACTG1 have been associated with Baraitser-Winter Cerebrofrontofacial syndrome. Here, the authors report of a syndromic thrombocytopenia caused by variants in ACTB exons 5 or 6 that compromise the organization and coupling of the cytoskeleton, leading to impaired platelet maturation.
- Sharissa L. Latham
- , Nadja Ehmke
- & Nataliya Di Donato
-
Article
| Open Access A conserved HH-Gli1-Mycn network regulates heart regeneration from newt to human
A conserved HH-Gli1-Mycn network regulates heart regeneration from newt to human
Due to the limited proliferation capacity of adult mammalian cardiomyocytes, the human heart has negligible regenerative capacity after injury. Here the authors show that a Hedgehog-Gli1-Mycn signaling cascade regulates cardiomyocyte proliferation and cardiac regeneration from amphibians to mammals.
- Bhairab N. Singh
- , Naoko Koyano-Nakagawa
- & Daniel J. Garry
-
Article
| Open Access REV-ERBα integrates colon clock with experimental colitis through regulation of NF-κB/NLRP3 axis
REV-ERBα integrates colon clock with experimental colitis through regulation of NF-κB/NLRP3 axis
REV-ERBα is a nuclear receptor that links the circadian pathways with those of metabolism. Here the authors show REV-ERBα is also involved with linking the circadian system with the inflammatory pathways of an experimental model of colitis through regulation of the NF-κB/NLRP3 axis.
- Shuai Wang
- , Yanke Lin
- & Baojian Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Precisely measured protein lifetimes in the mouse brain reveal differences across tissues and subcellular fractions
Precisely measured protein lifetimes in the mouse brain reveal differences across tissues and subcellular fractions
Measuring precise protein turnover rates in animals is technically challenging at the proteomic level. Here, Fornasiero and colleagues use isotopic labeling with mass spectrometry and mathematical modeling to accurately determine protein lifetimes in the mouse brain
- Eugenio F. Fornasiero
- , Sunit Mandad
- & Silvio O. Rizzoli
-
Article
| Open Access Epistasis studies reveal redundancy among calcium-dependent protein kinases in motility and invasion of malaria parasites
Epistasis studies reveal redundancy among calcium-dependent protein kinases in motility and invasion of malaria parasites
Despite functional optimisation during evolution of parasitism, most members of a calcium dependent protein kinase (CDPK) family show genetic redundancy in Plasmodium. Here, the authors screen 294 genetic interactions among protein kinases in Plasmodium and show how some CDPKs functionally interact to control motility and host cell invasion.
- Hanwei Fang
- , Ana Rita Gomes
- & Mathieu Brochet
-
Article
| Open Access Large-scale whole-exome sequencing association studies identify rare functional variants influencing serum urate levels
Large-scale whole-exome sequencing association studies identify rare functional variants influencing serum urate levels
Elevated serum urate levels are a risk factor for gout. Here, Tin et al. perform whole-exome sequencing in 19,517 individuals and detect low-frequency genetic variants in urate transporter genes, SLC22A12 and SLC2A9, associated with serum urate levels and confirm their damaging nature in vitro and in silico.
- Adrienne Tin
- , Yong Li
- & Anna Köttgen
-
Article
| Open Access Non-neutralizing antibodies elicited by recombinant Lassa–Rabies vaccine are critical for protection against Lassa fever
Non-neutralizing antibodies elicited by recombinant Lassa–Rabies vaccine are critical for protection against Lassa fever
There is currently no approved vaccine for Lassa fever virus (LASV). Here, Abreu-Mota et al. develop an inactivated, adjuvanted vaccine candidate expressing LASV glycoprotein (GPC) in a rabies virus vector, and show that non-neutralizing LASV GPC-specific antibodies are a major mechanism of protection.
- Tiago Abreu-Mota
- , Katie R. Hagen
- & Matthias J. Schnell
-
Article
| Open Access Prevention of pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma by Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Surgery
Prevention of pancreatic acinar cell carcinoma by Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Surgery
Pancreatic cancer risk increases in obese and diabetic people. In this manuscript, the authors show that Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery (RYGB) decreases the impact of pancreatic cancer in a mouse model; this effect seems independent of weight loss or decreased hyperglycemia pointing to an involvement of mTOR pathway.
- Rui He
- , Yue Yin
- & Weizhen Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access LRH-1 mitigates intestinal inflammatory disease by maintaining epithelial homeostasis and cell survival
LRH-1 mitigates intestinal inflammatory disease by maintaining epithelial homeostasis and cell survival
Inflammatory bowel disease is characterised by epithelial dysfunction. Here the authors show that loss of the nuclear receptor LRH-1 leads to epithelial disruption by altering Notch signaling in mouse intestinal organoids, and that LRH-1 overexpression ameliorates immune-mediated colitis in a mouse model.
- James R. Bayrer
- , Hongtao Wang
- & Holly A. Ingraham
-
Article
| Open Access MiR-34 inhibits polycomb repressive complex 2 to modulate chaperone expression and promote healthy brain aging
MiR-34 inhibits polycomb repressive complex 2 to modulate chaperone expression and promote healthy brain aging
miR-34 is known to regulate age-related gene expression in the Drosophila brain, and miR-34 overexpression can attenuate neurodegeneration induced by polyQ-expanded proteins. Here, Kennerdell and colleagues show that miR-34 confers longevity and neuroprotection via an epigenetic regulator Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 and molecular chaperone expression.
- Jason R. Kennerdell
- , Nan Liu
- & Nancy M. Bonini
-
Article
| Open Access SIRT1 mediates obesity- and nutrient-dependent perturbation of pubertal timing by epigenetically controlling Kiss1 expression
SIRT1 mediates obesity- and nutrient-dependent perturbation of pubertal timing by epigenetically controlling Kiss1 expression
The onset of mammalian puberty is sensitive to metabolic changes and nutritional status, but the mechanisms underlying this phenomenon are poorly understood. Here the authors show that the epigenetic regulator of transcription, SIRT1, mediates the effects of under and overnutrition on pubertal timing by controlling the expression of Kiss1 in hypothalamic neurons.
- M. J. Vazquez
- , C. A. Toro
- & M. Tena-Sempere
-
Article
| Open Access Metastatic adrenocortical carcinoma displays higher mutation rate and tumor heterogeneity than primary tumors
Metastatic adrenocortical carcinoma displays higher mutation rate and tumor heterogeneity than primary tumors
Adrenocortical cancer (ACC) is a rarely diagnosed and aggressive cancer whose metastatic form has been scarcely studied. Here, the authors study primary and metastatic ACC to investigate genomic heterogeneity, discovering higher mutation rates in metastatic lesions and novel recurrent mutations.
- Sudheer Kumar Gara
- , Justin Lack
- & Electron Kebebew
-
Article
| Open Access Long non-coding RNA CCRR controls cardiac conduction via regulating intercellular coupling
Long non-coding RNA CCRR controls cardiac conduction via regulating intercellular coupling
Long noncoding RNAs have been shown to play a role in cardiovascular disease. Here, the authors identify a lncRNA named CCRR, whose downregulation in failing hearts causes cardiac conduction disturbances by altering the endocytic trafficking of Cx43.
- Yong Zhang
- , Lihua Sun
- & Baofeng Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Meta-analysis of effects of exclusive breastfeeding on infant gut microbiota across populations
Meta-analysis of effects of exclusive breastfeeding on infant gut microbiota across populations
Studies on the effects of breastfeeding on the infant gut microbiota have provided inconsistent results. Here, Ho et al. perform a meta-analysis of seven studies across different populations, supporting that exclusive breastfeeding is associated with short-term and long-term alterations in the infant gut microbiota.
- Nhan T. Ho
- , Fan Li
- & Louise Kuhn
-
Article
| Open Access Genetic signature to provide robust risk assessment of psoriatic arthritis development in psoriasis patients
Genetic signature to provide robust risk assessment of psoriatic arthritis development in psoriasis patients
Approximately 30% of psoriasis patients develop psoriatic arthritis (PsA) and early diagnosis is crucial for the management of PsA. Here, Patrick et al. develop a computational pipeline involving statistical and machine-learning methods that can assess the risk of progression to PsA based on genetic markers.
- Matthew T. Patrick
- , Philip E. Stuart
- & Lam C. Tsoi
-
Article
| Open Access Patchwork of contrasting medication cultures across the USA
Patchwork of contrasting medication cultures across the USA
Health care in the United States is heterogeneous with respect to factors like disease incidence, treatment choices and health care spending. Here, the authors use insurance claims data from over 150 million patients to compare prescription rates of over 600 drugs, and uncover patterns of geographical variation that suggest an influence of race, health care laws and wealth.
- Rachel D. Melamed
- & Andrey Rzhetsky
-
Article
| Open Access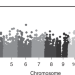 A missense variant in SLC39A8 is associated with severe idiopathic scoliosis
A missense variant in SLC39A8 is associated with severe idiopathic scoliosis
The majority of scoliosis is considered idiopathic with onset in adolescence (AIS) and has a genetic contribution. Here, the authors perform an exome wide association study of data from 457 severe AIS cases and 987 controls, and find a missense variant in SLC39A8 is associated with AIS.
- Gabe Haller
- , Kevin McCall
- & Christina A. Gurnett
-
Article
| Open Access A comprehensive overview of genomic imprinting in breast and its deregulation in cancer
A comprehensive overview of genomic imprinting in breast and its deregulation in cancer
In growth and development genomic imprinting is important in regulating gene expression. Here, the authors study loss of imprinting (LOI) in cancer, developing a mixture model to detect monoallelically expressed loci without genotyping data - applying this novel methodology to TCGA breast cancer data they find massive deregulation of imprinting.
- Tine Goovaerts
- , Sandra Steyaert
- & Tim De Meyer
-
Article
| Open Access Modulation of proteoglycan receptor PTPσ enhances MMP-2 activity to promote recovery from multiple sclerosis
Modulation of proteoglycan receptor PTPσ enhances MMP-2 activity to promote recovery from multiple sclerosis
Demyelination failure in multiple sclerosis (MS) may contribute to the disease progression. This study shows that chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans (CSPGs) can inhibit remyelination in an animal model of MS via CSPG binding with the receptor PTPσ on oligodendrocyte progenitor cells, and disruption of this interaction can promote recovery in the animal models of MS.
- Fucheng Luo
- , Amanda Phuong Tran
- & Yan Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-long-acting removable drug delivery system for HIV treatment and prevention
Ultra-long-acting removable drug delivery system for HIV treatment and prevention
Long-acting (LA) formulations of antiretroviral (ARV) drugs are an alternative approach to improve adherence for HIV treatment and prevention. Here the authors show a removable biodegradable ultra-LA-ARV drug system that effectively delivers drug, controls viremia and prevents infection in animal models of HIV infection.
- Martina Kovarova
- , S. Rahima Benhabbour
- & J. Victor Garcia
-
Article
| Open Access Epigenomic map of human liver reveals principles of zonated morphogenic and metabolic control
Epigenomic map of human liver reveals principles of zonated morphogenic and metabolic control
Spatial mapping of genomic programs in tissue cells is an important step in the understanding of organ function and disease. Here, the authors provide a spatially resolved epigenomic and transcriptomic map of human liver and show porto-central gradients in metabolic and morphogen networks and transcription factor binding sites as a basis to better understand liver regeneration and function.
- Mario Brosch
- , Kathrin Kattler
- & Jochen Hampe
-
Article
| Open Access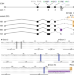 Genetic and mechanistic basis for APOBEC3H alternative splicing, retrovirus restriction, and counteraction by HIV-1 protease
Genetic and mechanistic basis for APOBEC3H alternative splicing, retrovirus restriction, and counteraction by HIV-1 protease
Human APOBEC3H has several haplotypes and splice variants with distinct anti-HIV-1 activities, but the genetics underlying the expression of these variants are unclear. Here, the authors identify an intronic deletion in A3H haplotype II resulting in production of the most active splice variant, which is counteracted by HIV-1 protease.
- Diako Ebrahimi
- , Christopher M. Richards
- & Reuben S. Harris
-
Article
| Open Access Bone protection by inhibition of microRNA-182
Bone protection by inhibition of microRNA-182
Osteoclasts mediate bone disruption in a number of degenerative bone diseases. Here, the authors show that miR-182 regulates osteoclastogenesis via PKR and IFN-beta signaling, is correlated with rheumatoid arthritis, and that its ablation or inhibition is protective against bone erosion in mouse models of osteoporosis or inflammatory arthritis.
- Kazuki Inoue
- , Zhonghao Deng
- & Baohong Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access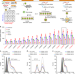 Targeting of NLRP3 inflammasome with gene editing for the amelioration of inflammatory diseases
Targeting of NLRP3 inflammasome with gene editing for the amelioration of inflammatory diseases
Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome triggers the production of inflammatory cytokines. Here, the authors inactivate NLRP3 in macrophages using CRISPR/Cas9 encapsulated in nanoparticles, and show that administration in mice is effective in preventing septic shock and peritonitis, and in improving diabetes-associated inflammation and insulin resistance.
- Congfei Xu
- , Zidong Lu
- & Jun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide association study identifies two risk loci for tuberculosis in Han Chinese
Genome-wide association study identifies two risk loci for tuberculosis in Han Chinese
Genetic risk loci for tuberculosis (TB) have so far been identified in African and Russian populations. Here, the authors perform a three-stage GWAS for TB in Han Chinese populations and find two risk loci near ESRRB and TGM6 and further demonstrate that tgm6 protects mice from Mtb infection.
- Ruijuan Zheng
- , Zhiqiang Li
- & Baoxue Ge
-
Article
| Open Access Pathogenic variants in glutamyl-tRNAGln amidotransferase subunits cause a lethal mitochondrial cardiomyopathy disorder
Pathogenic variants in glutamyl-tRNAGln amidotransferase subunits cause a lethal mitochondrial cardiomyopathy disorder
Mitochondrial protein synthesis requires charging a mitochondrial tRNA with its amino acid. Here, the authors describe pathogenic variants in the GatCAB protein complex genes required for the generation of glutaminyl-mt-tRNAGln, that impairs mitochondrial translation and presents with cardiomyopathy.
- Marisa W. Friederich
- , Sharita Timal
- & Johan L. K. Van Hove
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo neutralization of dendrotoxin-mediated neurotoxicity of black mamba venom by oligoclonal human IgG antibodies
In vivo neutralization of dendrotoxin-mediated neurotoxicity of black mamba venom by oligoclonal human IgG antibodies
Current anti-venoms against black mamba (Dendroaspis polylepis) bites are animal-derived and associated with several limitations. Here, Laustsen and colleagues develop an experimental recombinant anti-venom based on oligoclonal human IgG antibodies and establish its potential protective value in neutralizing dendrotoxin-mediated neurotoxicity using venom challenge in vivo models.
- Andreas H. Laustsen
- , Aneesh Karatt-Vellatt
- & John McCafferty
-
Article
| Open Access Correcting glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency with a small-molecule activator
Correcting glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency with a small-molecule activator
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency provides insufficient protection from oxidative stress, contributing to diverse human pathologies. Here, the authors identify a small molecule that increases the activity and/or stability of mutant G6PD and show that it reduces oxidative stress in zebrafish and hemolysis in isolated human erythrocytes.
- Sunhee Hwang
- , Karen Mruk
- & Daria Mochly-Rosen
-
Article
| Open Access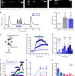 Preventing acute asthmatic symptoms by targeting a neuronal mechanism involving carotid body lysophosphatidic acid receptors
Preventing acute asthmatic symptoms by targeting a neuronal mechanism involving carotid body lysophosphatidic acid receptors
Acute bronchoconstriction is the leading cause of asthmatic sudden death following allergen exposure. The authors show that the systemic increase of LPA following inhaled allergen or bradykinin challenge activates the carotid bodies through TRPV1 and LPA-specific receptors and that systemic TRPV1 and LPA-specific receptor antagonists ameliorate acute bronchoconstriction.
- Nicholas G. Jendzjowsky
- , Arijit Roy
- & Richard J. A. Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access Chemogenetic generation of hydrogen peroxide in the heart induces severe cardiac dysfunction
Chemogenetic generation of hydrogen peroxide in the heart induces severe cardiac dysfunction
Excessive production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) is associated with cardiac dysfunction, but the causal role of ROS remains poorly understood. Here the authors use an in vivo chemogenetic approach to develop a heart failure model in which generation of hydrogen peroxide in the heart leads to systolic heart failure without fibrotic remodeling.
- Benjamin Steinhorn
- , Andrea Sorrentino
- & Thomas Michel
-
Article
| Open Access Ebola viral dynamics in nonhuman primates provides insights into virus immuno-pathogenesis and antiviral strategies
Ebola viral dynamics in nonhuman primates provides insights into virus immuno-pathogenesis and antiviral strategies
Optimization of antiviral therapy can be crucial in the management of Ebola virus outbreaks. Here, Madelain et al. use an integrative mathematical model to correlate the dose and the time of treatment initiation with survival rate, enhanced immune response and viral clearance.
- Vincent Madelain
- , Sylvain Baize
- & Jérémie Guedj
-
Article
| Open Access Engineered mRNA-expressed antibodies prevent respiratory syncytial virus infection
Engineered mRNA-expressed antibodies prevent respiratory syncytial virus infection
Engineered neutralizing antibodies are potential therapeutics for numerous viruses, such as respiratory syncytial virus (RSV). Here, the authors develop an mRNA-based approach to express membrane-anchored neutralizing antibodies in the lung and demonstrate that it inhibits RSV infections in mice.
- Pooja Munnilal Tiwari
- , Daryll Vanover
- & Philip J. Santangelo
-
Article
| Open Access Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy disease results from disparate impairments of cardiac myosin function and auto-inhibition
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy disease results from disparate impairments of cardiac myosin function and auto-inhibition
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is caused by point mutations in sarcomeric proteins. Here the authors develop an optimized model of the sequestered state of cardiac myosin and define the features affecting the lever arm compliance, allowing them to group mutations in classes and to elucidate the molecular mechanisms leading to cardiac dysfunction in HCM.
- Julien Robert-Paganin
- , Daniel Auguin
- & Anne Houdusse
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide discovery of somatic regulatory variants in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Genome-wide discovery of somatic regulatory variants in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
The driver mutations for the two main molecular subgroups of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) are poorly defined. Here, an integrative genomics analysis identifies 3′ UTR NFKBIZ mutations within the activated B-cell DLBCL subgroup and small FCGR2B amplifications in the germinal centre B-cell DLBCL subgroup.
- Sarah E. Arthur
- , Aixiang Jiang
- & Ryan D. Morin
-
Article
| Open Access Clonal dynamics in osteosarcoma defined by RGB marking
Clonal dynamics in osteosarcoma defined by RGB marking
Osteosarcoma is a heterogeneous bone tumour with a high mutational rate. Here the authors use an RGB-based single-cell tracking system to track clonal dynamics in a mouse model of osteosarcoma, which their findings indicate follows a neutral evolution model in which different clones simultaneously coexist and propagate.
- Stefano Gambera
- , Ander Abarrategi
- & Javier García-Castro
-
Article
| Open Access A Mendelian randomization study of the effects of blood lipids on breast cancer risk
A Mendelian randomization study of the effects of blood lipids on breast cancer risk
The link between circulating lipids and breast cancer risk is complex. Here, the authors utilise data from more than 400,000 participants in two-sample Mendelian randomization to assess the link between blood lipids and breast cancer risk, and they find risk-promoting effects of raised LDL-cholesterol and CETP-mediated raised HDL-cholesterol.
- Christoph Nowak
- & Johan Ärnlöv
-
Article
| Open Access High-resolution NMR studies of antibiotics in cellular membranes
High-resolution NMR studies of antibiotics in cellular membranes
Antibiotics that target the peptidoglycan precursor lipid II are promising templates for next-generation antibiotics. Here authors use solid-state NMR and monitor lipid II-binding antibiotics, such as nisin, directly in cell membranes.
- João Medeiros-Silva
- , Shehrazade Jekhmane
- & Markus Weingarth
-
Article
| Open Access Genetic and pharmacological regulation of the endocannabinoid CB1 receptor in Duchenne muscular dystrophy
Genetic and pharmacological regulation of the endocannabinoid CB1 receptor in Duchenne muscular dystrophy
The regenerative capacity of muscle stem cells is impaired in Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD). Here, the authors show that the endocannabinoid receptor CB1 is activated by PAX7 in muscle stem cells, and that pharmacological inhibition of CB1 promotes stem cell activation and ameliorates symptoms in DMD mouse models.
- Fabio A. Iannotti
- , Ester Pagano
- & Vincenzo Di Marzo
-
Article
| Open Access A distal centriolar protein network controls organelle maturation and asymmetry
A distal centriolar protein network controls organelle maturation and asymmetry
Removal of daughter centriole-specific/enriched proteins (DCPs) and assembly of distal appendages (DA) are important for centrosome asymmetry. Here, the authors report that a centriolar distal end protein network regulates DCP removal, DA assembly, and ciliary vesicle docking.
- Lei Wang
- , Marion Failler
- & Brian D. Dynlacht
-
Article
| Open Access Mitochondrial uncoupling reveals a novel therapeutic opportunity for p53-defective cancers
Mitochondrial uncoupling reveals a novel therapeutic opportunity for p53-defective cancers
Several challenges are involved in direct targeting of mutant p53, while targeting altered fitness of cells with loss of wild type p53 is an alternative approach. Here they identify niclosamide to be selectively toxic to p53 deficient cells through a previously unknown mitochondrial uncoupling mechanism.
- R. Kumar
- , L. Coronel
- & C. F. Cheok
-
Article
| Open Access A scalable online tool for quantitative social network assessment reveals potentially modifiable social environmental risks
A scalable online tool for quantitative social network assessment reveals potentially modifiable social environmental risks
An individual’s social network—their friends, family, and acquaintances—is important for their health, but existing tools for assessing social networks have limitations. Here, the authors introduce a quantitative social network assessment tool on a secure open-source web platform and show its utility in a nation-wide study.
- Amar Dhand
- , Charles C. White
- & Philip L. De Jager
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of small-molecule ion channel modulators in C. elegans channelopathy models
Identification of small-molecule ion channel modulators in C. elegans channelopathy models
Mutations in the voltage-gated K+ channel human ether-a-go-go-related gene (hERG) lead to Long-QT syndrome, causing life-threatening cardiac arrhythmia. Here the authors use C. elegans as a platform to run a channelopathy drug screen, identifying drugs to target hERG mutants.
- Qiang Jiang
- , Kai Li
- & Shi-Qing Cai
-
Article
| Open Access Analysis of extracellular mRNA in human urine reveals splice variant biomarkers of muscular dystrophies
Analysis of extracellular mRNA in human urine reveals splice variant biomarkers of muscular dystrophies
Patients with myotonic dystrophy need to undergo invasive muscle biopsies to monitor disease progression and response to therapy. Here, the authors show that extracellular RNAs in human urine can be used as biomarkers to differentiate patients from unaffected controls, and to monitor exon skipping in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy taking the drug eteplirsen.
- Layal Antoury
- , Ningyan Hu
- & Thurman M. Wheeler
-
Article
| Open Access Plasmodium co-infection protects against chikungunya virus-induced pathologies
Plasmodium co-infection protects against chikungunya virus-induced pathologies
Chikungunya virus (CHIKV) and Plasmodium co-infections have been reported in humans, but effects of the two pathogens on each other are unclear. Here, Teo et al. show in mice that Plasmodium infection affects CHIKV-specific T and B cell responses, leading to reduced joint inflammation.
- Teck-Hui Teo
- , Fok-Moon Lum
- & Lisa F. P. Ng
-
Article
| Open Access Fine mapping of MHC region in lung cancer highlights independent susceptibility loci by ethnicity
Fine mapping of MHC region in lung cancer highlights independent susceptibility loci by ethnicity
The basis for associations between lung cancer and major histocompatibility complex genes is not completely understood. Here the authors further consider genetic variation within the MHC region in lung cancer patients and identify independent associations within HLA genes that explain MHC lung cancer associations in Europeans and Asian populations.
- Aida Ferreiro-Iglesias
- , Corina Lesseur
- & Paul Brennan

 HIV-1 Tat interactions with cellular 7SK and viral TAR RNAs identifies dual structural mimicry
HIV-1 Tat interactions with cellular 7SK and viral TAR RNAs identifies dual structural mimicry