Research Highlight |
Featured
-
-
-
Research Highlight |
 Long-term dual antiplatelet therapy and bleeding in stable patients—insights from CHARISMA
Long-term dual antiplatelet therapy and bleeding in stable patients—insights from CHARISMA
- Joana Osório
-
Research Highlight |
Eating for two? Maternal weight gain and offspring cardiovascular risk
- Alexandra King
-
Research Highlight |
 Autologous delipidated HDL infusion is safe and feasible in patients with ACS
Autologous delipidated HDL infusion is safe and feasible in patients with ACS
- Alexandra King
-
-
-
News & Views |
 Percent stenosis in CAD—a flaw in current practice
Percent stenosis in CAD—a flaw in current practice
The optimum strategy to treat patients with coronary artery disease (CAD) has been under debate. New data show that revascularization guided by fractional flow measurements leads to better outcomes than revascularization guided by arteriography. We call for a paradigm shift in CAD care, with coronary flow measurements by PET as key to diagnosis and clinical decision-making.
- K. Lance Gould
- & Nils P. Johnson
-
News & Views |
No-reflow—an ominous sign of cardiac dysfunction
Mechanical reperfusion in acute myocardial infarction does not always result in desirable optimal microvascular perfusion. Failure to achieve a normal myocardial blush in the infarcted region by contrast injection immediately after percutaneous coronary intervention—the 'no-reflow' phenomenon—is an ominous sign whose prognostic importance may go beyond its intimate association with infarct size.
- Michael Magro
- & Patrick W. Serruys
-
News & Views |
 Reducing the risk of CVD in patients with periodontitis
Reducing the risk of CVD in patients with periodontitis
The association between periodontitis and other chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular disease (CVD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus, could be related to systemic inflammation initiated by a local inflammatory challenge. Oliveira et al. have added lack of oral hygiene, and its link with systemic inflammation, to the spectrum of risk factors for CVD.
- Robert J. Genco
- & Thomas E. Van Dyke
-
-
Review Article |
 Stenting of complex lesions: an overview
Stenting of complex lesions: an overview
Percutaneous coronary intervention can be performed successfully in most lesions; however, some specific types of lesion continue to present unique technical challenges. In this Review, stenting of bifurcations, fibrocalcific and undilatable lesions, chronic total occlusions, unprotected left main coronary artery stenoses, thrombotic lesions, and saphenous vein grafts are discussed in detail.
- Usman Baber
- , Annapoorna S. Kini
- & Samin K. Sharma
-
Review Article |
 Cardiotoxicity of anticancer treatments: what the cardiologist needs to know
Cardiotoxicity of anticancer treatments: what the cardiologist needs to know
Cancer therapies can have a profound, and often permanent, effect on the cardiovascular system. Patients at high risk of cardiotoxicity should be identified before treatment, closely monitored, and given cardioprotective agents to reduce adverse events. The authors of this Review discuss the complications that can occur as a result of cancer therapy, and emphasize the importance of assessing both the cardiotoxicity and benefits of cancer treatment.
- Michael S. Ewer
- & Steven M. Ewer
-
Review Article |
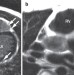 Imaging the right ventricle—current state of the art
Imaging the right ventricle—current state of the art
The morphology, structure and position of the right ventricle differ substantially from those of the left ventricle and have posed difficulties in the assessment of right ventricular function. Imaging techniques, notably echocardiography and MRI, have enabled a better understanding of right ventricular performance. Mertens and Friedberg discuss the advantages and disadvantages of established and new methods of right ventricular imaging and their potential in the clinical setting.
- Luc L. Mertens
- & Mark K. Friedberg
-
-
Research Highlight |
 New blood tests improve risk assessment and early diagnosis of AMI
New blood tests improve risk assessment and early diagnosis of AMI
- Bryony M. Mearns
-
Research Highlight |
 A noninvasive strategy to monitor rejection in patients with a heart transplant
A noninvasive strategy to monitor rejection in patients with a heart transplant
- Helene Myrvang
-
-
-
News & Views |
Treating pediatric DCM—great expectations unfulfilled
Kantor and colleagues from the Hospital for Sick Children in Toronto, Canada have reported that outcomes for medically treated pediatric patients with dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM) have not changed over a 30-year period, despite institution of neurohormonal inhibition therapy. These findings are placed in the context of the worldwide experience of pediatric DCM and the limited number of studies of neurohormonal inhibition therapy in children with heart failure.
- Charles E. Canter
-
News & Views |
 Blockade of the renin–angiotensin system in atrial fibrillation
Blockade of the renin–angiotensin system in atrial fibrillation
The effectiveness of existing strategies for management of atrial fibrillation is limited, which has stimulated research into novel therapeutic approaches. A new meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of inhibitors of the renin–angiotensin system highlights the clinical benefits of these agents and underscores their potential in the prevention and treatment of this disease.
- Nadzeya Kuzniatsova
- , Eduard Shantsila
- & Gregory Y. H. Lip
-
Research Highlight |
 Endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm—the importance of long-term follow-up data
Endovascular repair of abdominal aortic aneurysm—the importance of long-term follow-up data
- Joana Osório
-
News & Views |
Identifying high-risk patients from carotid plaque composition
The ability to identify which patients with atherosclerosis are at higher risk of future cardiovascular events is important not only for decisions about medical therapy, but also for decisions about surgical or percutaneous intervention. Pathological findings of plaque features that predict cardiovascular events may point the way to noninvasive imaging approaches to identify high-risk plaques.
- J. David Spence
-
News & Views |
 The private life of tissue valves
The private life of tissue valves
Although the majority of implanted valves used in aortic valve surgery are tissue valves (bioprostheses), the mechanisms by which they interact with the host are not well understood. A new study by Flameng et al. gives insight into the structural and functional changes that result from patient–bioprosthesis mismatch.
- Magdi H. Yacoub
- & Ismail El-Hamamsy
-
News & Views |
Transport for PCI versus fibrinolysis—long-term data scrutinized
The optimal reperfusion strategy for patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction who are admitted to community hospitals without a catheterization laboratory is still a matter of debate. The long-term results of the DANAMI-2 study contribute to the evidence base for optimal reperfusion, but should be interpreted with caution and in the context of the wider literature on this subject.
- Frans Van de Werf
-
Review Article |
 Arterial aging—hemodynamic changes and therapeutic options
Arterial aging—hemodynamic changes and therapeutic options
Aging is accompanied by changes in vascular structure and function leading to arterial stiffness, which is an important predictor of cardiovascular disease. Hemodynamic changes associated with arterial aging include increased pulse pressure, pulse wave velocity, and wave reflection. In this Review, Michel Safar describes the features of arterial aging, and how blockade of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system may ameliorate the effects of this process.
- Michel E. Safar
-
Review Article |
 Acute pulmonary embolism. Part 1: epidemiology and diagnosis
Acute pulmonary embolism. Part 1: epidemiology and diagnosis
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a frequently occurring, acute, and potentially fatal condition. Numerous risk factors for PE have been identified. The diagnostic work-up for PE should comprise safe, efficient and noninvasive methods. In this Review, Renée Douma and colleagues discuss the epidemiology of PE, its risk factors and clinical presentation, together with the latest advances in the diagnostic approach to this condition.
- Renée A. Douma
- , Pieter W. Kamphuisen
- & Harry R. Büller
-
Review Article |
 Epigenetics and cardiovascular disease
Epigenetics and cardiovascular disease
Epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation and histone acetylation, are crucial for homeostasis, and enable cells to respond quickly to environmental changes. However, epigenetic alterations are also associated with the development and progression of disease. The authors of this Review outline how epigenetics may contribute to cardiovascular disease, and highlight potential therapeutic agents that modify the epigenetic state, which could be used in the prevention or treatment of cardiovascular disease.
- José M. Ordovás
- & Caren E. Smith
-
-
Research Highlight |
 New D-dimer cut-off value helps rule out pulmonary embolism in the elderly
New D-dimer cut-off value helps rule out pulmonary embolism in the elderly
- Joana Osório
-
-
-
-
-
Research Highlight |
 Cardiac device therapy in elderly patients—insights from 'real world' practice
Cardiac device therapy in elderly patients—insights from 'real world' practice
- Alexandra King
-
-
News & Views |
Revascularization strategies for patients with CAD and diabetes
CABG surgery has been considered the optimal revascularization strategy for patients with diabetes mellitus who have left main and/or multivessel coronary artery disease. The results of a new analysis of data from the SYNTAX trial challenge this conventional wisdom and highlight additional coronary revascularization options to physicians and patients.
- G. Robert Myers
- & William S. Weintraub
-
News & Views |
Does stent overlap make a difference to clinical outcome?
The impact of overlap of drug-eluting stents on clinical and angiographic outcomes is controversial. Individuals with long coronary lesions requiring implantation of multiple stents are an important patient subgroup for whom careful evaluation and decision-making with optimal stent deployment is needed to ensure the best possible short-term and long-term results.
- Antonio Colombo
- & Rasha Al-Lamee
-
Review Article |
 New antithrombotic agents—insights from clinical trials
New antithrombotic agents—insights from clinical trials
Antithrombotic therapy with ADP-receptor antagonists or anticoagulant agents improves outcomes in patients with acute coronary syndromes and/or undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention. However, the current standard-of-care ADP-receptor antagonist for dual antiplatelet therapy, clopidogrel, and the currently available oral anticoagulants, the coumarins, have several limitations. In this Review, the authors discuss the pharmacology and clinical potential of new antithrombotic drugs, with an emphasis on data from phase III clinical trials.
- Jeremy S. Paikin
- , John W. Eikelboom
- & Jack Hirsh
-
Review Article |
 Four decades of Fontan palliation
Four decades of Fontan palliation
The Fontan palliation was introduced in 1968 for congenital heart defects with a single dominant ventricle. Although considerable technical improvements have meant that this procedure can be applied to a wide range of patients, the Fontan circulation has intrinsic limitations. Professors de Leval and Deanfield consider the past four decades of Fontan palliation and describe how developments have moved practice closer to the 'perfect' Fontan. Future challenges and possible solutions are also discussed.
- Marc R. de Leval
- & John E. Deanfield
-
Review Article |
 Novel therapeutic targets for hypertension
Novel therapeutic targets for hypertension
Although effective therapies for hypertension exist, the prevalence of elevated blood pressure and resistant hypertension is increasing and novel treatment strategies are needed. In this Review, Drs. Paulis and Unger discuss new targets for antihypertensive therapy, many of which, including renalase and the (pro)renin receptor, are based on modulation of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone system. Invasive strategies, such as renal denervation, are also explored.
- Ludovit Paulis
- & Thomas Unger
-
-
-
-
-
-
News & Views |
Antihypertensive class matters for combination therapy
Combination therapy is used to lower blood pressure in the majority of patients with hypertension, yet there has been little evidence as to which classes of antihypertensive agents are most effective. The publication of findings from the ACCOMPLISH trial provides an opportunity to explore the merits of various combination therapies, with a focus on renal risk reduction.
- William B. White
-
News & Views |
Carotid endarterectomy versus stenting—long live the king?
Carotid endarterectomy (CEA) is considered the gold standard for treatment of stenosis, but carotid artery stenting (CAS) is a less invasive procedure that offers a promising alternative. Short-term data from ICASS suggest that CEA is superior to CAS; however, features of the study design may have affected the results, and long-term data are needed before conclusions can be made.
- Sandra Narayanan
- & Seemant Chaturvedi
-
News & Views |
 Aspirin for asymptomatic atherosclerosis?
Aspirin for asymptomatic atherosclerosis?
The ankle–brachial index (ABI) can be used to assess the risk of cardiovascular events. The AAA trial aimed to determine whether low-dose aspirin was of net benefit among apparently healthy people with an ABI ≤0.95. The largely negative findings of this study raise important mechanistic and practical questions.
- Carlo Patrono
- & Colin Baigent
-
Research Highlight |
 A new scoring system for simple risk prediction in patients with unprovoked venous thromboembolism
A new scoring system for simple risk prediction in patients with unprovoked venous thromboembolism
- Bryony M. Mearns

 Group medical clinics to manage diabetes and hypertension
Group medical clinics to manage diabetes and hypertension Poor health literacy: a 'hidden' risk factor
Poor health literacy: a 'hidden' risk factor Promising improvements in DES technology
Promising improvements in DES technology Fibrates reduce risk of coronary events
Fibrates reduce risk of coronary events Continuous-flow LVAD improves quality of life
Continuous-flow LVAD improves quality of life Should AMI care be regionalized?
Should AMI care be regionalized? Magnetic resonance angiography in pulmonary embolism diagnosis
Magnetic resonance angiography in pulmonary embolism diagnosis Children are key to CVD prevention
Children are key to CVD prevention