Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Whole-genome resequencing reveals world-wide ancestry and adaptive introgression events of domesticated cattle in East Asia
Whole-genome resequencing reveals world-wide ancestry and adaptive introgression events of domesticated cattle in East Asia
There are various indigenous cattle breeds in East Asia which have a complex history. Here, the authors analyse the genomes of 49 modern breeds and eight ancient samples and identify three distinct ancestries and multiple adaptive introgressions from other bovine species.
- Ningbo Chen
- , Yudong Cai
- & Chuzhao Lei
-
Article
| Open Access High-throughput screening of prostate cancer risk loci by single nucleotide polymorphisms sequencing
High-throughput screening of prostate cancer risk loci by single nucleotide polymorphisms sequencing
Functional characterization of disease-causing variants at risk loci in cancer is challenging. Here, in prostate cancer the authors report a pipeline for high-throughput single-nucleotide polymorphisms sequencing (SNPs-seq) for large scale screening of functional SNPs at disease risk loci.
- Peng Zhang
- , Ji-Han Xia
- & Liang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Analysis of predicted loss-of-function variants in UK Biobank identifies variants protective for disease
Analysis of predicted loss-of-function variants in UK Biobank identifies variants protective for disease
Examination of predicted loss-of-function (pLOF) genetic variants allows direct identification of genes with therapeutic potential. Here, Emdin et al. perform association analysis for 3759 pLOF variants with 24 traits and highlight protective variants against cardiometabolic and immune phenotypes.
- Connor A. Emdin
- , Amit V. Khera
- & Sekar Kathiresan
-
Article
| Open Access Repeated evolution of self-compatibility for reproductive assurance
Repeated evolution of self-compatibility for reproductive assurance
Mating-type switching enables self-compatible reproduction in fungi, but switching ability is variable even within species. Here, the authors find de novo evolution of switching genotypes in experimentally evolved fission yeast populations and show a trade-off between mating success and growth.
- Bart P. S. Nieuwenhuis
- , Sergio Tusso
- & Simone Immler
-
Article
| Open Access Medical relevance of protein-truncating variants across 337,205 individuals in the UK Biobank study
Medical relevance of protein-truncating variants across 337,205 individuals in the UK Biobank study
Protein-truncating variants (PTVs) are predicted to significantly affect a gene’s function and, thus, human traits. Here, DeBoever et al. systematically analyze PTVs in more than 300,000 individuals across 135 phenotypes and identify 27 associations between PTVs and medical conditions.
- Christopher DeBoever
- , Yosuke Tanigawa
- & Manuel A. Rivas
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of rare sequence variation underlying heritable pulmonary arterial hypertension
Identification of rare sequence variation underlying heritable pulmonary arterial hypertension
Pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) is a rare lung disorder characterised by narrowing and obliteration of small pulmonary arteries ultimately leading to right heart failure. Here, the authors sequence whole genomes of over 1000 PAH patients and identify likely causal variants in GDF2, ATP13A3, AQP1 and SOX17.
- Stefan Gräf
- , Matthias Haimel
- & Nicholas W. Morrell
-
Article
| Open Access Circular DNA elements of chromosomal origin are common in healthy human somatic tissue
Circular DNA elements of chromosomal origin are common in healthy human somatic tissue
Somatic cells can accumulate structural variations such as deletions. Here, Møller et al. show that normal human cells generate large extrachromosomal circular DNAs (eccDNAs), most likely the products of excised DNA, that can be transcriptionally active and, thus, may have phenotypic consequences.
- Henrik Devitt Møller
- , Marghoob Mohiyuddin
- & Birgitte Regenberg
-
Article
| Open Access Convergent genomic signatures of domestication in sheep and goats
Convergent genomic signatures of domestication in sheep and goats
The sheep and goat were domesticated ~10,500 years ago in the same region of the Middle-East. Here, Alberto et al compare the genomes of wild Asiatic mouflon and Bezoar ibex with that of domestics from local, traditional and improved breeds and find common targets of selection related to domestication and improvement in sheep and goats.
- Florian J. Alberto
- , Frédéric Boyer
- & François Pompanon
-
Article
| Open Access High contiguity Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly with a single nanopore flow cell
High contiguity Arabidopsis thaliana genome assembly with a single nanopore flow cell
Long-read sequencing technologies facilitate efficient and high quality genome assembly. Here Michael et al. achieve a fast reference assembly for Arabidopsis thaliana KBS-Mac-74 accession using the handheld Oxford Nanopore MinION sequencer and consumer computing hardware, and demonstrate its usefulness in resolving complex structural variation.
- Todd P. Michael
- , Florian Jupe
- & Joseph R. Ecker
-
Article
| Open Access RNA sequencing provides insights into the evolution of lettuce and the regulation of flavonoid biosynthesis
RNA sequencing provides insights into the evolution of lettuce and the regulation of flavonoid biosynthesis
Horticultural lettuce varieties vary considerably in phenotype. Here, via RNA-seq of 240 different lettuce accessions, the authors identify loci and expression patterns associated with flavonoid and anthocyanin content and show that cultivated lettuce likely arose via a single domestication event.
- Lei Zhang
- , Wenqing Su
- & Hanhui Kuang
-
Article
| Open Access Extensive gene content variation in the Brachypodium distachyon pan-genome correlates with population structure
Extensive gene content variation in the Brachypodium distachyon pan-genome correlates with population structure
The role of differential gene content in the evolution and function of eukaryotic genomes remains poorly explored. Here the authors assemble and annotate the Brachypodium distachyon pan-genome consisting of 54 diverse lines and reveal the differential present genes as a major driver of phenotypic variation.
- Sean P. Gordon
- , Bruno Contreras-Moreira
- & John P. Vogel
-
Article
| Open Access Whole-genome sequencing for an enhanced understanding of genetic variation among South Africans
Whole-genome sequencing for an enhanced understanding of genetic variation among South Africans
African populations show a high level of genetic diversity and extensive regional admixture. Here, the authors sequence the whole genomes of 24 South African individuals of different ethnolinguistic origin and find substantive genomic divergence between two southeastern Bantu-speaking groups.
- Ananyo Choudhury
- , Michèle Ramsay
- & Michael S. Pepper
-
Article
| Open Access 3D genome of multiple myeloma reveals spatial genome disorganization associated with copy number variations
3D genome of multiple myeloma reveals spatial genome disorganization associated with copy number variations
Chromosome conformation capture techniques enable the study of genome organization in cancer cells. Here, the authors use Hi-C, WGS, and RNA-seq to study the 3D genome of multiple myeloma and find that genome disorganization is associated with copy number variations and changes in gene expression.
- Pengze Wu
- , Tingting Li
- & Cheng Li
-
Article
| Open Access A soft selective sweep during rapid evolution of gentle behaviour in an Africanized honeybee
A soft selective sweep during rapid evolution of gentle behaviour in an Africanized honeybee
Africanized honey bees (AHB) are notoriously aggressive, but in Puerto Rico they have a ‘gentle’ phenotype. Here, Avalos et al. show that there has been a soft selective sweep at several loci in the Puerto Rican AHB population and suggest a role in the rapid evolution of gentle behaviour.
- Arian Avalos
- , Hailin Pan
- & Guojie Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access The effect of artificial selection on phenotypic plasticity in maize
The effect of artificial selection on phenotypic plasticity in maize
Breeding has increased crop productivity, but whether it has also changed phenotypic plasticity is unclear. Here, the authors find maize genomic regions selected for high productivity show reduced contribution to genotype by environment variation and provide evidence for regulatory control of phenotypic stability.
- Joseph L. Gage
- , Diego Jarquin
- & Natalia de Leon
-
Article
| Open Access The effect of genetic variation on promoter usage and enhancer activity
The effect of genetic variation on promoter usage and enhancer activity
Expression quantitative trait loci (eQTL) are widely studied, yet the mechanisms by which they exert their effects are largely unknown. Here, performing CAGE-seq on 154 lymphoblastoid cell lines, the authors map regulatory variants associated with promoter usage (puQTLs) and enhancer activity (eaQTLs).
- Marco Garieri
- , Olivier Delaneau
- & Alexandre Fort
-
Article
| Open Access Mapping and phasing of structural variation in patient genomes using nanopore sequencing
Mapping and phasing of structural variation in patient genomes using nanopore sequencing
The detection of structural variants can be difficult with short-read sequencing technology, especially when variants are highly complex. Here, the authors use a MinION nanopore sequencer to analyse two patient genomes and develop NanoSV to map known and novel structural variants in long read data.
- Mircea Cretu Stancu
- , Markus J. van Roosmalen
- & Wigard P. Kloosterman
-
Article
| Open Access High-frequency recombination between members of an LTR retrotransposon family during transposition bursts
High-frequency recombination between members of an LTR retrotransposon family during transposition bursts
Retrotransposons are abundant in eukaryotic genomes. Here, Sanchez et al. show evidence of high-frequency recombination between members of an LTR retrotransposon family during transposition bursts in Arabidopsis.
- Diego H. Sanchez
- , Hervé Gaubert
- & Jerzy Paszkowski
-
Article
| Open Access Demographic history and biologically relevant genetic variation of Native Mexicans inferred from whole-genome sequencing
Demographic history and biologically relevant genetic variation of Native Mexicans inferred from whole-genome sequencing
People of Mexico have diverse historical and genetic background. Here, Romero-Hidalgo and colleagues sequence whole genomes of Native Americans of Mexico, and show demographic history and genetic variation shared among subgroups of Native Americans.
- Sandra Romero-Hidalgo
- , Adrián Ochoa-Leyva
- & Xavier Soberón
-
Article
| Open Access Integrating evolutionary and regulatory information with a multispecies approach implicates genes and pathways in obsessive-compulsive disorder
Integrating evolutionary and regulatory information with a multispecies approach implicates genes and pathways in obsessive-compulsive disorder
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is a neuropsychiatric disorder with symptoms including intrusive thoughts and time-consuming repetitive behaviors. Here Noh and colleagues identify genes enriched for functional variants associated with increased risk of OCD.
- Hyun Ji Noh
- , Ruqi Tang
- & Kerstin Lindblad-Toh
-
Article
| Open Access The genetic basis of natural variation in a phoretic behavior
The genetic basis of natural variation in a phoretic behavior
Nematodes use a characteristic set of movements, called nictation, to hitchhike on more mobile animals. Here, Lee et al. identify a genetic locus in the nematode Caenorhabditis elegans that underlies nictation and contributes to successful hitchhiking, but at expense of reduced offspring production.
- Daehan Lee
- , Heeseung Yang
- & Junho Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Whole genome sequencing and imputation in isolated populations identify genetic associations with medically-relevant complex traits
Whole genome sequencing and imputation in isolated populations identify genetic associations with medically-relevant complex traits
Isolated populations can provide useful information on low-frequency variants for dissecting genetic architecture of complex traits. Here, Zeggini and colleagues show enrichment of rare and low-frequency variants and 8 novel low-frequency variant signals for cardiometabolic traits in two Greek isolated populations
- Lorraine Southam
- , Arthur Gilly
- & Eleftheria Zeggini
-
Article
| Open Access Meta-analysis identifies five novel loci associated with endometriosis highlighting key genes involved in hormone metabolism
Meta-analysis identifies five novel loci associated with endometriosis highlighting key genes involved in hormone metabolism
Endometriosis is a major cause of infertility. Molecular mechanisms underlying the disease involve genetic and environmental risk factors. In a meta-analysis of eleven GWA studies, Sapkota and colleagues identify five novel risk loci, implicating steroid sex hormone pathways in the pathogenesis.
- Yadav Sapkota
- , Valgerdur Steinthorsdottir
- & Dale R. Nyholt
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasensitive and high-efficiency screen of de novo low-frequency mutations by o2n-seq
Ultrasensitive and high-efficiency screen of de novo low-frequency mutations by o2n-seq
Detection ofde novo, low frequency mutations is important for characterising heterogeneous cell populations, such as those found in cancer cell populations. Here the authors present o2n-seq, an ultrasensitive method with highly efficient data usage for detection of rare mutations.
- Kaile Wang
- , Shujuan Lai
- & Jue Ruan
-
Article
| Open Access Refined genetic maps reveal sexual dimorphism in human meiotic recombination at multiple scales
Refined genetic maps reveal sexual dimorphism in human meiotic recombination at multiple scales
It is known that males have lower recombination rates than females over much of the genome but little is known about differences at a fine scale. Here the authors combine data from over 100,000 meioses and show that the majority of differences can be explained by variation in hotspot magnitude.
- Claude Bhérer
- , Christopher L. Campbell
- & Adam Auton
-
Article
| Open Access Archaeogenomic evidence reveals prehistoric matrilineal dynasty
Archaeogenomic evidence reveals prehistoric matrilineal dynasty
In ancient cultures without a writing system, it is difficult to infer the basis of status and rank. Here the authors analyse ancient DNA from nine presumed elite individuals buried successively over a 300-year period at Chaco Canyon, and show evidence of matrilineal relationships.
- Douglas J. Kennett
- , Stephen Plog
- & George H. Perry
-
Article
| Open Access Clustering of 770,000 genomes reveals post-colonial population structure of North America
Clustering of 770,000 genomes reveals post-colonial population structure of North America
Genetic data has led to great advances in our understanding of human evolution and dispersal, but information on more recent events is limited. Here, the authors analyse genotypes from 770,000 US individuals to map the fine-scale population structure of North America after European settlement.
- Eunjung Han
- , Peter Carbonetto
- & Catherine A. Ball
-
Article
| Open Access Convergent recombination suppression suggests role of sexual selection in guppy sex chromosome formation
Convergent recombination suppression suggests role of sexual selection in guppy sex chromosome formation
It has been suggested that sex chromosomes arise as a result of sexual conflict, resulting in selection against recombination between chromosomes. Here, the authors resequence laboratory and wild guppy populations with differing levels of sexual antagonism, providing support for this long-held view.
- Alison E. Wright
- , Iulia Darolti
- & Judith E. Mank
-
Article
| Open Access A polychromatic ‘greenbeard’ locus determines patterns of cooperation in a social amoeba
A polychromatic ‘greenbeard’ locus determines patterns of cooperation in a social amoeba
Cooperation can be stabilized against exploitation if cooperators can reliably recognize each other. Here, Gruenheit and colleagues show that different alleles of the Tgr locus of the social amoebaDictyostelium discoideumunderlie the ability of different strains to recognize and cooperate with socially compatible individuals.
- Nicole Gruenheit
- , Katie Parkinson
- & Christopher R. L. Thompson
-
Article
| Open Access Transient structural variations have strong effects on quantitative traits and reproductive isolation in fission yeast
Transient structural variations have strong effects on quantitative traits and reproductive isolation in fission yeast
Fission yeastSchizosaccharomyces pombe has diverse traits. Jeffares et al. characterize large copy number variations (CNVs) and rearrangements in S. pombe, and show that CNVs are transient with effects on quantitative traits and gene expression, whereas rearrangements influence intrinsic reproductive isolation.
- Daniel C. Jeffares
- , Clemency Jolly
- & Fritz J. Sedlazeck
-
Article
| Open Access Global and local selection acting on the pathogen Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in the human lung
Global and local selection acting on the pathogen Stenotrophomonas maltophilia in the human lung
The authors sequence the genomes of 552 bacterial isolates sampled across 23 sites of the lungs of a patient with cystic fibrosis, and identify bacterial genes under global and location-specific adaptation.
- Hattie Chung
- , Tami D. Lieberman
- & Roy Kishony
-
Article
| Open Access A time transect of exomes from a Native American population before and after European contact
A time transect of exomes from a Native American population before and after European contact
A First Nation population declined after European contact, likely as a result of infectious disease. Here, researchers partner with indigenous communities to analyse ancient and modern Native American exomes, and find a shift in selection pressure on immune genes, correlated to European-borne epidemics.
- John Lindo
- , Emilia Huerta-Sánchez
- & Ripan S. Malhi
-
Article
| Open Access The pangenome of an agronomically important crop plant Brassica oleracea
The pangenome of an agronomically important crop plant Brassica oleracea
Brassica oleracea is a single species that includes diverse crops such as cabbage, broccoli and Brussels sprouts. Here, the authors identify genes not captured in existing B. oleraceareference genomes by the assembly of a pangenome and show variations in gene content that may be related to important agronomic traits
- Agnieszka A. Golicz
- , Philipp E. Bayer
- & David Edwards
-
Article
| Open Access A multi-marker association method for genome-wide association studies without the need for population structure correction
A multi-marker association method for genome-wide association studies without the need for population structure correction
Currently available methods for phenotype to genetic markers association need to account for population structure. Here, Klasen et al. devise a statistical method called Quantitative Trait Cluster Association Test (QTCAT) that overcomes the need for population structure correction.
- Jonas R. Klasen
- , Elke Barbez
- & Korbinian Schneeberger
-
Article
| Open Access Powerful decomposition of complex traits in a diploid model
Powerful decomposition of complex traits in a diploid model
Dissecting the architecture of complex trait is challenging. Here, Hallin, Märtens et al. devises Phased Outbred Lines (POLs) in order to accurately decompose growth trait variation in diploid yeast across different environments.
- Johan Hallin
- , Kaspar Märtens
- & Gianni Liti
-
Article
| Open Access A continuum of admixture in the Western Hemisphere revealed by the African Diaspora genome
A continuum of admixture in the Western Hemisphere revealed by the African Diaspora genome
The Consortium on Asthma among African-ancestry Populations in the Americas (CAAPA) aims to better understand population genetics of the African diaspora. Here, it uses deeply sequenced whole-genomes to describe the impact of admixture and potential disease burden of deleterious variants.
- Rasika Ann Mathias
- , Margaret A. Taub
- & Kathleen C. Barnes
-
Article
| Open Access A high-quality human reference panel reveals the complexity and distribution of genomic structural variants
A high-quality human reference panel reveals the complexity and distribution of genomic structural variants
Structural variants (SVs) are prevalent in genomes of the general population. Here, Guryev and The Genome of the Netherlands Consortium describe the reference panel of haplotype-resolved SVs from 769 individuals from 250 Dutch families and show its utility for studying heritable traits.
- Jayne Y. Hehir-Kwa
- , Tobias Marschall
- & Victor Guryev
-
Article
| Open Access Excess of mutational jackpot events in expanding populations revealed by spatial Luria–Delbrück experiments
Excess of mutational jackpot events in expanding populations revealed by spatial Luria–Delbrück experiments
Large mutant clones arising from early mutations in growing cell populations facilitate short-term evolution in microbes and in tumours. Here the authors analyse spatially expanding colonies, and show that large mutant clones can also arise late when they surf at expanding frontiers.
- Diana Fusco
- , Matti Gralka
- & Oskar Hallatschek
-
Article
| Open Access An exome array study of the plasma metabolome
An exome array study of the plasma metabolome
Several GWAS have identified many common variants associated with blood metabolites. Here, the authors use an exome array to identify low frequency, potentially functional variants that impact human metabolism.
- Eugene P. Rhee
- , Qiong Yang
- & Robert E. Gerszten
-
Article
| Open Access RUBIC identifies driver genes by detecting recurrent DNA copy number breaks
RUBIC identifies driver genes by detecting recurrent DNA copy number breaks
Analysis of cancer genome sequencing data has been used to predict genes associated with the pathogenesis of cancer. Here, the authors propose a new algorithm entitled RUBIC that predicts breaks in DNA as opposed to previously published methods that predict amplifications and deletions of DNA.
- Ewald van Dyk
- , Marlous Hoogstraat
- & Lodewyk F. A. Wessels
-
Article
| Open Access A heavy metal P-type ATPase OsHMA4 prevents copper accumulation in rice grain
A heavy metal P-type ATPase OsHMA4 prevents copper accumulation in rice grain
Copper (Cu) is an essential mineral nutrient but high concentrations in rice grain can cause toxicity. Here the authors provide evidence that natural variation in rice grain Cu concentration is caused by altered sequestration of Cu into root vacuoles due to a single amino acid substitution in the OsHMA4 transporter.
- Xin-Yuan Huang
- , Fenglin Deng
- & Jian Feng Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Spatial niche formation but not malignant progression is a driving force for intratumoural heterogeneity
Spatial niche formation but not malignant progression is a driving force for intratumoural heterogeneity
It has been increasingly recognised that tumours are not made up of a homogeneous population of cells. Here, the authors show heterogeneous expression of five protein markers in renal cell cancer and demonstrate that the progression of the tumour does not influence the degree of heterogeneity in the tumour.
- Rouven Hoefflin
- , Bernd Lahrmann
- & Stefan Duensing
-
Article
| Open Access SURVIV for survival analysis of mRNA isoform variation
SURVIV for survival analysis of mRNA isoform variation
Clinical RNA-seq datasets can predict clinical outcomes. Here, Shen et al. report a statistical method for survival analysis of mRNA isoform variation using clinical RNA-seq datasets, and the identified isoform based survival predictors outperform gene expression based survival predictors using TCGA data on six cancer types.
- Shihao Shen
- , Yuanyuan Wang
- & Yi Xing
-
Article
| Open Access The T300A Crohn’s disease risk polymorphism impairs function of the WD40 domain of ATG16L1
The T300A Crohn’s disease risk polymorphism impairs function of the WD40 domain of ATG16L1
The T300A substitution in ATG16L is associated with Crohn’s disease risk and disrupts clearance of intracellular pathogens by autophagy. Here the authors show that the mutation impairs interaction of ATG16L with TMEM59 and disrupts unconventional TMEM-induced autophagy, an aspect of innate immunity.
- Emilio Boada-Romero
- , Inmaculada Serramito-Gómez
- & Felipe X. Pimentel-Muiños
-
Article
| Open Access Rebalancing gene haploinsufficiency in vivo by targeting chromatin
Rebalancing gene haploinsufficiency in vivo by targeting chromatin
Deficit in transcription factor Tbx1 causes heart defects in humans and mice. Here the authors show that Tbx1 regulates gene expression by recruiting histone methyltransferases that affect chromatin marks, and that a drug inhibiting histone demethylation ameliorates the cardiovascular phenotype in Tbx1 haploinsufficient or hypomorphic mice.
- Filomena Gabriella Fulcoli
- , Monica Franzese
- & Antonio Baldini
-
Article
| Open Access Diverse genetic architectures lead to the same cryptic phenotype in a yeast cross
Diverse genetic architectures lead to the same cryptic phenotype in a yeast cross
Cryptic genetic variants may not individually show discernible phenotypic effects, but collectively, these polymorphisms can lead to unexpected, genetically complex traits that might be relevant to evolution and disease. Here, the authors use large yeast populations to comprehensively dissect the genetic bases of 17 independent occurrences of a phenotype that arises due to combinations of epistatically interacting cryptic variants.
- Matthew B. Taylor
- , Joann Phan
- & Ian M. Ehrenreich
-
Article
| Open Access Common genetic variation in ETV6 is associated with colorectal cancer susceptibility
Common genetic variation in ETV6 is associated with colorectal cancer susceptibility
Genome-wide association studies have been performed to identify genetic variants that are associated with susceptibility to colorectal cancer. Here, the authors expand on these studies and identify a variant that regulates the expression of ETV6 and find that over-expression of ETV6 blocks cell proliferation in vitro.
- Meilin Wang
- , Dongying Gu
- & Jinfei Chen
-
Article
| Open Access A genetic basis for the variation in the vulnerability of cancer to DNA damage
A genetic basis for the variation in the vulnerability of cancer to DNA damage
The variability in patient response to radiation treatment is difficult to predict. Here, using more than 500 cell lines the authors measure response to radiation exposure and a large panel of compounds, and show that response can be predicted by genetic alterations of the cells.
- Brian D. Yard
- , Drew J. Adams
- & Mohamed E. Abazeed
-
Article
| Open Access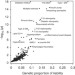 Identifying genetically driven clinical phenotypes using linear mixed models
Identifying genetically driven clinical phenotypes using linear mixed models
Use of general linear mixed models (GLMMs) in genetic variance analysis can quantify the relative contribution of additive effects from genetic variation on a given trait. Here, Jonathan Mosley and colleagues apply GLMM in a phenome-wide analysis and show that genetic variations in the HLA region are associated with 44 phenotypes, 5 phenotypes which were not previously reported in GWASes.
- Jonathan D. Mosley
- , John S. Witte
- & Joshua C. Denny

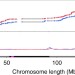 High-resolution crossover mapping reveals similarities and differences of male and female recombination in maize
High-resolution crossover mapping reveals similarities and differences of male and female recombination in maize