Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Antigen-selective modulation of AAV immunogenicity with tolerogenic rapamycin nanoparticles enables successful vector re-administration
Antigen-selective modulation of AAV immunogenicity with tolerogenic rapamycin nanoparticles enables successful vector re-administration
Immunogenicity of AAV vectors renders repeated AAV dosing ineffective. Here the authors show that coadministration of nanoparticle-encapsulated rapamycin overcomes AAV immunogenicity through Treg induction, enabling efficient AAV redosing in mice and nonhuman primates.
- Amine Meliani
- , Florence Boisgerault
- & Federico Mingozzi
-
Article
| Open Access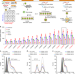 Targeting of NLRP3 inflammasome with gene editing for the amelioration of inflammatory diseases
Targeting of NLRP3 inflammasome with gene editing for the amelioration of inflammatory diseases
Activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome triggers the production of inflammatory cytokines. Here, the authors inactivate NLRP3 in macrophages using CRISPR/Cas9 encapsulated in nanoparticles, and show that administration in mice is effective in preventing septic shock and peritonitis, and in improving diabetes-associated inflammation and insulin resistance.
- Congfei Xu
- , Zidong Lu
- & Jun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access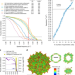 Sub-2 Å Ewald curvature corrected structure of an AAV2 capsid variant
Sub-2 Å Ewald curvature corrected structure of an AAV2 capsid variant
Single-particle cryo-EM is a powerful method for macromolecular structure determination. Here the authors demonstrate that Ewald sphere curvature correction, sub-Angstrom pixilation and per-particle CTF refinement can improve map quality and resolution and present the 1.86 Å cryo-EM structure of an adeno-associated virus serotype 2 variant.
- Yong Zi Tan
- , Sriram Aiyer
- & Dmitry Lyumkis
-
Article
| Open Access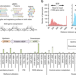 Engineered bidirectional promoters enable rapid multi-gene co-expression optimization
Engineered bidirectional promoters enable rapid multi-gene co-expression optimization
Classic monodirectional promoters are of limited use for multiple gene co-expression. Here the authors generate a library of 168 bidirectional promoters for the yeast K. phaffii (syn. P. pastoris) with diverse expression profiles to optimize metabolic pathway design.
- Thomas Vogl
- , Thomas Kickenweiz
- & Anton Glieder
-
Article
| Open Access Nanomedicines reveal how PBOV1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma for effective gene therapy
Nanomedicines reveal how PBOV1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma for effective gene therapy
Novel therapeutic strategies are needed to improve the treatment outcome of hepatocellular carcinoma. Here, the authors develop a theranostical targeted nanomedicine platform that reveals the key oncogenic role of PBOV1 in hepatocellular carcinoma.
- Yu Guo
- , Zhiqiang Wu
- & Xintao Shuai
-
Article
| Open Access Controlled gene and drug release from a liposomal delivery platform triggered by X-ray radiation
Controlled gene and drug release from a liposomal delivery platform triggered by X-ray radiation
X-ray radiation has excellent tissue penetration depth, making it a useful trigger for deep tissue cancer therapy. Here, the authors design X-ray triggered drug/gene-loaded liposomes by embedding photosensitizers and gold nanoparticles in the liposome bilayer, and demonstrate their efficacy in cancer and gene therapy.
- Wei Deng
- , Wenjie Chen
- & Ewa M. Goldys
-
Article
| Open Access AAV vector-mediated in vivo reprogramming into pluripotency
AAV vector-mediated in vivo reprogramming into pluripotency
In vivo reprogramming of somatic cells is hampered by the need for vectors to express the OKSM factors in selected organs. Here the authors report new AAV-based vectors capable of in vivo reprogramming at low doses.
- Elena Senís
- , Lluc Mosteiro
- & Dirk Grimm
-
Article
| Open Access Immunogene therapy with fusogenic nanoparticles modulates macrophage response to Staphylococcus aureus
Immunogene therapy with fusogenic nanoparticles modulates macrophage response to Staphylococcus aureus
In the context of increasing bacterial antibiotic-resistance, gene therapy that targets the immune system to clear infection is a major goal. Here the authors show a silicon based nanosystem that modulates the macrophage response in an in vivo model of Staphylococcal pneumonia.
- Byungji Kim
- , Hong-Bo Pang
- & Michael J. Sailor
-
Article
| Open Access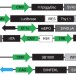 Transposon-modified antigen-specific T lymphocytes for sustained therapeutic protein delivery in vivo
Transposon-modified antigen-specific T lymphocytes for sustained therapeutic protein delivery in vivo
Delivery of therapeutic proteins to patients may be costly to administer, and often requires repeated injections. Here, the authors use antigen-specific T cells expressing erythropoietin, and show that following transfer in mice, cell expansion and erythropoietin production can be boosted by vaccination, raising the haematocrit.
- Richard T. O’Neil
- , Sunandan Saha
- & Matthew H. Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access Metal-organic frameworks for precise inclusion of single-stranded DNA and transfection in immune cells
Metal-organic frameworks for precise inclusion of single-stranded DNA and transfection in immune cells
Non-viral vectors are important for transfection but can be limited in the uptake, protection and release of ssDNA. Here, the authors report on the design of metal-organic-framework vectors with precisely controlled pore geometry and demonstrate the vector in the transfection of immune cells.
- Shuang Peng
- , Binglin Bie
- & Xiang Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Adenoviral vector with shield and adapter increases tumor specificity and escapes liver and immune control
Adenoviral vector with shield and adapter increases tumor specificity and escapes liver and immune control
Viral gene therapy can be limited by the efficacy of virion sequestration, immune responses and the silencing of genetic payloads. Here the authors engineer an advenovirus protein coat which shields the virion from the immune system while targeting cancer cells.
- Markus Schmid
- , Patrick Ernst
- & Andreas Plückthun
-
Article
| Open Access Estrogen-related receptor γ causes osteoarthritis by upregulating extracellular matrix-degrading enzymes
Estrogen-related receptor γ causes osteoarthritis by upregulating extracellular matrix-degrading enzymes
The pathogenesis of osteoarthritis is unclear. The authors show that estrogen-related receptor gamma is upregulated in cartilage from patients and mouse models, where it drives production of matrix-degrading MMPs in chondrocytes, and that its downregulation ameliorates pathology in mice.
- Young-Ok Son
- , Seulki Park
- & Jang-Soo Chun
-
Article
| Open Access Hit-and-run programming of therapeutic cytoreagents using mRNA nanocarriers
Hit-and-run programming of therapeutic cytoreagents using mRNA nanocarriers
Current widely used viral and electroporation methods for creating therapeutic cell-based products are complex and expensive. Here, the authors develop targeted mRNA nanocarriers that can transiently program gene expression by simply mixing them with cells, to improve their therapeutic potential.
- H. F. Moffett
- , M. E. Coon
- & M. T. Stephan
-
Article
| Open Access PUMA gene delivery to synoviocytes reduces inflammation and degeneration of arthritic joints
PUMA gene delivery to synoviocytes reduces inflammation and degeneration of arthritic joints
Proliferation of synoviocytes contributes to joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis. Here the authors show that targeting of these cells by a vector, consisting of a baculovirus conjugated to an adenovirus carrying the pro-apoptotic gene PUMA, has therapeutic efficacy in a rat arthritis model.
- Saw-See Hong
- , Hubert Marotte
- & Pierre Miossec
-
Article
| Open Access A robot for high yield electrophysiology and morphology of single neurons in vivo
A robot for high yield electrophysiology and morphology of single neurons in vivo
Single-cell characterization and perturbation of neurons is critical for revealing the structure-function relationship of brain cells. Here the authors develop a robot that performs single-cell electroporation and extracellular electrophysiology and can be used for performingin vivosingle-cell experiments in deep brain tissues optically difficult to access.
- Lu Li
- , Benjamin Ouellette
- & Hongkui Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access Enhancing titres of therapeutic viral vectors using the transgene repression in vector production (TRiP) system
Enhancing titres of therapeutic viral vectors using the transgene repression in vector production (TRiP) system
The maximum titre of therapeutic viral vectors can be adversely affected by the encoded transgene. Here the authors repress transgene expression in producing cells by employing the tryptophan RNA-binding attenuation protein and show that it improves titre of RNA- and DNA-based viral vectors expressing toxic transgenes.
- H. E. Maunder
- , J. Wright
- & D. C. Farley
-
Article
| Open Access PolyMetformin combines carrier and anticancer activities for in vivo siRNA delivery
PolyMetformin combines carrier and anticancer activities for in vivo siRNA delivery
The anti-diabetic drug Metformin also possesses anti-tumour activity. Here, the authors synthesize polymeric Metformin-based nanoparticles that still exert intrinsic biological activity through AMPK and mTOR regulation and can systematically deliver VEGF siRNA, significantly reducing lung cancer growth in mice.
- Yi Zhao
- , Wei Wang
- & Leaf Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Highly efficient baculovirus-mediated multigene delivery in primary cells
Highly efficient baculovirus-mediated multigene delivery in primary cells
Current viral gene delivery systems are limited in the amount of foreign DNA they can deliver to cells. Here the authors develop MultiPrime, a baculovirus-based vector system capable of multigene delivery into a wide variety of cells, and use Multiprime for genome engineering by CRISPR/Cas9.
- Maysam Mansouri
- , Itxaso Bellon-Echeverria
- & Philipp Berger
-
Article
| Open Access Designer diatom episomes delivered by bacterial conjugation
Designer diatom episomes delivered by bacterial conjugation
Algae hold great promise for biofuel and chemical production but their use as model systems is hampered by the absence of suitable genetic tools. Here Karas et al. present a nuclear episomal vector for diatoms that is maintained in the absence of antibiotics, and a plasmid delivery method via conjugation with E. coli.
- Bogumil J. Karas
- , Rachel E. Diner
- & Philip D. Weyman
-
Article
| Open Access Modelling breast cancer requires identification and correction of a critical cell lineage-dependent transduction bias
Modelling breast cancer requires identification and correction of a critical cell lineage-dependent transduction bias
Clinical breast cancers predominantly present luminal features, but experimental models are essentially basal. Here the authors show that luminal cells are significantly less susceptible to viral transduction, and present methods to analyse and overcome the bias in heterogeneous populations.
- William C. Hines
- , Paul Yaswen
- & Mina J. Bissell
-
Article
| Open Access Highly specific in vivo gene delivery for p53-mediated apoptosis and genetic photodynamic therapies of tumour
Highly specific in vivo gene delivery for p53-mediated apoptosis and genetic photodynamic therapies of tumour
Alterations of p53 are associated with more than half of all human cancers. Here the authors present a new pH-sensitive nanoparticle that is delivered via systemic circulation and combines gene delivery to restore p53 with expression of Killerred protein to induce photosensitization.
- S.-Ja Tseng
- , Zi-Xian Liao
- & Ivan M. Kempson
-
Article |
 Off-target-free gene delivery by affinity-purified receptor-targeted viral vectors
Off-target-free gene delivery by affinity-purified receptor-targeted viral vectors
The clinical use of adeno-associated virus vectors (AAVs) has been limited by the lack of transduction specificity. Here the authors show that receptor-targeted, affinity-tagged, and purified AVVs reach tumours in mouse models with high selectivity and efficiency, outperforming therapeutic antibodies.
- Robert C. Münch
- , Anke Muth
- & Christian J. Buchholz
-
Article |
 Poking cells for efficient vector-free intracellular delivery
Poking cells for efficient vector-free intracellular delivery
The incorporation of foreign objects into cells can be used in various avenues of biological research, although crossing the cell membrane can be challenging. Here, the authors use a diamond nanoneedle array for enhanced delivery of various particles into cells, including neurons.
- Ying Wang
- , Yang Yang
- & Peng Shi
-
Article |
 Degradable lipid nanoparticles with predictable in vivo siRNA delivery activity
Degradable lipid nanoparticles with predictable in vivo siRNA delivery activity
Robust and reliable structure–function relationships are valuable for the development of potent drug delivery systems. Here, the authors use a library of lipid-like materials to predict in vivosiRNA delivery efficacy without any biological testing.
- Kathryn A. Whitehead
- , J. Robert Dorkin
- & Daniel G. Anderson
-
Article |
 Three-layered polyplex micelle as a multifunctional nanocarrier platform for light-induced systemic gene transfer
Three-layered polyplex micelle as a multifunctional nanocarrier platform for light-induced systemic gene transfer
Light-controlled mechanisms for the delivery of drug molecules to cells is a promising route for non-invasive disease therapy. Here, the authors develop a photosensitive polymeric micelle for light-induced gene transfection and show its effectiveness in vivovia systemic administration.
- Takahiro Nomoto
- , Shigeto Fukushima
- & Kazunori Kataoka
-
Article |
 A fluorinated dendrimer achieves excellent gene transfection efficacy at extremely low nitrogen to phosphorus ratios
A fluorinated dendrimer achieves excellent gene transfection efficacy at extremely low nitrogen to phosphorus ratios
Polymers represent promising gene vectors due to their high efficiency and low cytotoxicity. Here, the authors show that fluorination increases gene transfection efficacy, while reducing cytotoxicity, and suggest an important role for this strategy in the design of efficient gene vectors.
- Mingming Wang
- , Hongmei Liu
- & Yiyun Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Arginine clustering on calix[4]arene macrocycles for improved cell penetration and DNA delivery
Arginine clustering on calix[4]arene macrocycles for improved cell penetration and DNA delivery
Arginine-rich peptides act as delivery systems for the internalization of cargoes in cells. Here, the clustering of arginine units in a parallel array on a macrocyclic scaffold produces a vector with high efficiency in DNA delivery and transfection.
- Valentina Bagnacani
- , Valentina Franceschi
- & Rocco Ungaro
-
Article
| Open Access High-performance and site-directed in utero electroporation by a triple-electrode probe
High-performance and site-directed in utero electroporation by a triple-electrode probe
In uteroelectroporation allows the labelling of specific populations of neurons in the developing mouse brain. The authors of this paper present a simple modification of this method that increases labelling efficiency and allows, for the first time, transfection of Purkinje cells in the rat cerebellum.
- Marco dal Maschio
- , Diego Ghezzi
- & Laura Cancedda
-
Article |
 A plasmid-based multigene expression system for mammalian cells
A plasmid-based multigene expression system for mammalian cells
Fluorescent proteins are widely used in molecular biology to visualize protein expression and localization. Here, Krizet al. describe an efficient and flexible modular plasmid-based eukaryotic expression cloning strategy for the homogeneous expression of several fluorescent proteins in one cell.
- Andrijana Kriz
- , Katharina Schmid
- & Philipp Berger

 A RNA producing DNA hydrogel as a platform for a high performance RNA interference system
A RNA producing DNA hydrogel as a platform for a high performance RNA interference system