Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Bipolar charge collecting structure enables overall water splitting on ferroelectric photocatalysts
Bipolar charge collecting structure enables overall water splitting on ferroelectric photocatalysts
While ferroelectric materials are promising candidates for solar water splitting, most examples show poor activities. Here, authors prepare charge-collecting nanostructures on the positive and negative domains of BaTiO3 and demonstrate photocatalytic overall water splitting.
- Yong Liu
- , Mingjian Zhang
- & Fengtao Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Origin of giant electric-field-induced strain in faulted alkali niobate films
Origin of giant electric-field-induced strain in faulted alkali niobate films
Maximizing the electromechanical response is crucial for developing piezoelectric devices. Here, the authors demonstrate a giant electric-field-induced strain and its origin in alkali niobate epitaxial thin films with self-assembled planar faults.
- Moaz Waqar
- , Haijun Wu
- & John Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Soliton walls paired by polar surface interactions in a ferroelectric nematic liquid crystal
Soliton walls paired by polar surface interactions in a ferroelectric nematic liquid crystal
Surface interactions are usually polar along the normal to the interface and apolar within the interface. Here, the authors find that polar in-plane surface interactions produce domain structures in the bulk of a ferroelectric nematic liquid crystal.
- Bijaya Basnet
- , Mojtaba Rajabi
- & Oleg D. Lavrentovich
-
Article
| Open Access Dielectric magnetochiral anisotropy
Dielectric magnetochiral anisotropy
The interplay between chirality and magnetism has been attracting much. Here, the authors show that the movement of bound charges in a chiral dielectric depends on the relative orientation between this movement and an external magnetic field.
- Geert L. J. A. Rikken
- & Narcis Avarvari
-
Article
| Open Access Deciphering the phase transition-induced ultrahigh piezoresponse in (K,Na)NbO3-based piezoceramics
Deciphering the phase transition-induced ultrahigh piezoresponse in (K,Na)NbO3-based piezoceramics
Functional oxides with coexisting states of comparable energy typically exhibit extraordinary responses to external stimuli. Here, the authors demonstrate that coexisting phase structures provide large electric field-triggered volume change.
- Mao-Hua Zhang
- , Chen Shen
- & Manuel Hinterstein
-
Article
| Open Access Multilevel polarization switching in ferroelectric thin films
Multilevel polarization switching in ferroelectric thin films
Setting any polarization value in ferroelectric thin films is a key step for their implementation in neuromorphic devices. Here, the authors demonstrate continuous modulation of the remanent polarization at the nanoscale in PbZr0.52Ti0.48O3 films.
- Martin F. Sarott
- , Marta D. Rossell
- & Morgan Trassin
-
Article
| Open Access Ferroelectric domain-wall logic units
Ferroelectric domain-wall logic units
Ferroelectric domain walls have been extensively explored for nanoelectronics, but the logic devices are still challenging. Here, the authors propose programmable logic gates and circuits based on electric-field controllable conductive domain walls.
- Jing Wang
- , Jing Ma
- & Ce-Wen Nan
-
Article
| Open Access Intercalation-driven ferroelectric-to-ferroelastic conversion in a layered hybrid perovskite crystal
Intercalation-driven ferroelectric-to-ferroelastic conversion in a layered hybrid perovskite crystal
There are few examples of tunable ferroic orders in two-dimensional layered hybrid perovskites. Here, the authors demonstrate tunable ferroic orders from ferroelectricity to ferroelasticity in such system by intercalation chemistry.
- Zhenyue Wu
- , Shunning Li
- & Kian Ping Loh
-
Article
| Open Access Giant energy-storage density with ultrahigh efficiency in lead-free relaxors via high-entropy design
Giant energy-storage density with ultrahigh efficiency in lead-free relaxors via high-entropy design
Dielectric ceramics are widely used in advanced high/pulsed power capacitors. Here, the authors propose a high-entropy strategy to design “local polymorphic distortion” in lead-free ceramics, achieving high energy storage performance.
- Liang Chen
- , Shiqing Deng
- & Jun Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Exceptionally high work density of a ferroelectric dynamic organic crystal around room temperature
Exceptionally high work density of a ferroelectric dynamic organic crystal around room temperature
Organic electronics requires dynamic materials, however, most of them have small strokes and operate at high temperatures. Here, the authors describe organic crystal that repeatedly expands and contracts nearly half its length around room temperature.
- Durga Prasad Karothu
- , Rodrigo Ferreira
- & Panče Naumov
-
Article
| Open Access Twisted oxide lateral homostructures with conjunction tunability
Twisted oxide lateral homostructures with conjunction tunability
It is challenging to construct lateral homostructures with controllable geometry and repeated alternating configurations. Here the authors develop a generic approach for fabricating twisted lateral homostructures with tunable crystal orientation, epitaxial constrain, and phase stability.
- Ping-Chun Wu
- , Chia-Chun Wei
- & Jan-Chi Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Deterministic control of ferroelectric polarization by ultrafast laser pulses
Deterministic control of ferroelectric polarization by ultrafast laser pulses
Controlling the electric polarization in ferroelectric materials at room temperature is an important aspect in the design of novel ferroelectric-based devices. Simulations of a typical ferroelectric material now provide insights into why and how its ferroelectric polarization can be partially reversed.
- Peng Chen
- , Charles Paillard
- & Laurent Bellaiche
-
Article
| Open Access Simultaneously achieving giant piezoelectricity and record coercive field enhancement in relaxor-based ferroelectric crystals
Simultaneously achieving giant piezoelectricity and record coercive field enhancement in relaxor-based ferroelectric crystals
High-drive electromechanical applications require ferroelectrics accounting for a large coercive field and high piezoelectricity simultaneously but it is still a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate it in a relaxor-based ferroelectric crystal.
- Liya Yang
- , Houbing Huang
- & Gang Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Emergent multiferroism with magnetodielectric coupling in EuTiO3 created by a negative pressure control of strong spin-phonon coupling
Emergent multiferroism with magnetodielectric coupling in EuTiO3 created by a negative pressure control of strong spin-phonon coupling
Negative pressure tailors the physical properties of functional oxide materials. Here, the authors demonstrate an emergent multiferroism with magnetodielectric coupling in EuTiO3 created by a negative pressure control of strong spin-phonon coupling.
- Run Zhao
- , Chao Yang
- & Hao Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Physical realization of topological Roman surface by spin-induced ferroelectric polarization in cubic lattice
Physical realization of topological Roman surface by spin-induced ferroelectric polarization in cubic lattice
A non-orientable surface can mirror reflecting the man travelling on it. Realizing such topological object is fascinating. Here, the authors discover that antiferromagnetic-induced polarization in a solid can realize a non-orientable Roman surface.
- Guangxiu Liu
- , Maocai Pi
- & Youwen Long
-
Article
| Open Access Chiral structures of electric polarization vectors quantified by X-ray resonant scattering
Chiral structures of electric polarization vectors quantified by X-ray resonant scattering
The polar chiral texture of the vortex or skyrmion structure in ferroelectric oxide PbTiO3/SrTiO3 superlattice attracts attention. Here, the authors report a theoretical framework to probe emergent chirality of electrical polarization textures.
- Kook Tae Kim
- , Margaret R. McCarter
- & Dong Ryeol Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Ferroelectric photosensor network: an advanced hardware solution to real-time machine vision
Ferroelectric photosensor network: an advanced hardware solution to real-time machine vision
Robust, fast, and low-power hardware platforms are desirable for the implementation of real-time machine vision. Here the authors develop a computing-in-sensor network using ferroelectric photo sensors with remanent-polarization-controlled photo responsivities.
- Boyuan Cui
- , Zhen Fan
- & Jun-Ming Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic reconfiguration among tri-state transition at ferroelectric/antiferroelectric phase boundaries in Pb(Zr,Ti)O3
Atomic reconfiguration among tri-state transition at ferroelectric/antiferroelectric phase boundaries in Pb(Zr,Ti)O3
Ferroelectric/antiferroelectric phase boundary is both technologically and scientifically important. Here, the authors reveal the structure of intermediate phase involved in classical Pb(Zr1-xTix)O3.
- Zhengqian Fu
- , Xuefeng Chen
- & Fangfang Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Antiferroelectric negative capacitance from a structural phase transition in zirconia
Antiferroelectric negative capacitance from a structural phase transition in zirconia
Applying an electric field to an antiferroelectric material transforms its non-polar crystal structure into a polar one. Here, the authors show that the antiferroelectric transition in zirconia causes a negative capacitance, useful for electronics.
- Michael Hoffmann
- , Zheng Wang
- & Asif Islam Khan
-
Article
| Open Access The role of lattice dynamics in ferroelectric switching
The role of lattice dynamics in ferroelectric switching
Reducing the switching energy of ferroelectric films remains an important goal. Here, the authors elucidate the fundamental role of lattice dynamics in ferroelectric switching on both freestanding BiFeO3 membranes and films clamped to a substrate.
- Qiwu Shi
- , Eric Parsonnet
- & Ramamoorthy Ramesh
-
Article
| Open Access High-precision and linear weight updates by subnanosecond pulses in ferroelectric tunnel junction for neuro-inspired computing
High-precision and linear weight updates by subnanosecond pulses in ferroelectric tunnel junction for neuro-inspired computing
Brain-inspired computing demands high-performance synapses. Here, the authors report a subnanosecond ferroelectric tunnel junction with 256 conductance states, 109 endurance, and 5.3 fJ/bit energy consumption, satisfactory to build synaptic devices.
- Zhen Luo
- , Zijian Wang
- & Xiaoguang Li
-
Article
| Open Access Manipulation of current rectification in van der Waals ferroionic CuInP2S6
Manipulation of current rectification in van der Waals ferroionic CuInP2S6
Developing a single-phase self-rectifying memristor is desirable and functionally adaptive to dynamic environmental stimuli variations. Here, the authors report a single phase CuInP2S6 based memristor with continuously tunable current rectifying.
- Xingan Jiang
- , Xueyun Wang
- & Jiawang Hong
-
Article
| Open Access Emerging spin–phonon coupling through cross-talk of two magnetic sublattices
Emerging spin–phonon coupling through cross-talk of two magnetic sublattices
Typically, magnetic phenomena result from the spontaneous order of the sublattices. Here, the cross-talk of two magnetic ions gives rise to an intrinsic, yet non-spontaneous ordering and manifests as emergent strong spin–phonon coupling in SmFeO3.
- Mads C. Weber
- , Mael Guennou
- & Jens Kreisel
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering of atomic-scale flexoelectricity at grain boundaries
Engineering of atomic-scale flexoelectricity at grain boundaries
Large strain gradient is crucial for flexoelectricity. Here, the authors reveal the generality and tunability of large strain gradients at grain boundaries in oxides, explaining the possible effects on the electrical activities of ceramics.
- Mei Wu
- , Xiaowei Zhang
- & Peng Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Signatures of enhanced out-of-plane polarization in asymmetric BaTiO3 superlattices integrated on silicon
Signatures of enhanced out-of-plane polarization in asymmetric BaTiO3 superlattices integrated on silicon
Integrating multifunctional oxides on silicon is highly desirable. Here, the authors present asymmetric BaTiO3 superlattices on silicon exhibiting enhanced out-of-plane polarization by harnessing the interfacial strain and broken inversion symmetry.
- Binbin Chen
- , Nicolas Gauquelin
- & Gertjan Koster
-
Article
| Open Access Piezoelectricity in hafnia
Piezoelectricity in hafnia
HfO2 is a promising ferroelectric material for applications in electronics but knowledge on its ferroic and electromechanical response properties is still lacking. Here, the authors demonstrate the peculiar piezoresponse of HfO2, predicting on how to reverse its sign by means of a biaxial strain.
- Sangita Dutta
- , Pratyush Buragohain
- & Jorge Íñiguez
-
Article
| Open Access Unraveling the origin of ferroelectric resistance switching through the interfacial engineering of layered ferroelectric-metal junctions
Unraveling the origin of ferroelectric resistance switching through the interfacial engineering of layered ferroelectric-metal junctions
The mechanism of ferroelectric resistance switching is still under debate. Here, the authors propose an interfacial engineering approach to demonstrate its origin and find that it is governed by three independent variables: polarization, barrier change, and initial barrier.
- Fei Xue
- , Xin He
- & Xixiang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access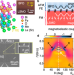 Long decay length of magnon-polarons in BiFeO3/La0.67Sr0.33MnO3 heterostructures
Long decay length of magnon-polarons in BiFeO3/La0.67Sr0.33MnO3 heterostructures
Long-distance magnon transport is highly desired for magnonics. Here, the authors demonstrate a millimetre-long magnon decay length in multiferroic heterostructures, which is attributed to magnon-polarons induced by the magnetoelastic coupling.
- Jianyu Zhang
- , Mingfeng Chen
- & Haiming Yu
-
Article
| Open Access Electroresistance in multipolar antiferroelectric Cu2Se semiconductor
Electroresistance in multipolar antiferroelectric Cu2Se semiconductor
The reaction of a conductive ferroelectric matter to external electric field remains largely unknown. Here, the authors reveal the relationship between the electrically-driven crystalline domain transition along the multiple-polar directions and the resistance change.
- Hui Bai
- , Jinsong Wu
- & Xinfeng Tang
-
Article
| Open Access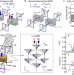 Enhanced gyrotropic birefringence and natural optical activity on electromagnon resonance in a helimagnet
Enhanced gyrotropic birefringence and natural optical activity on electromagnon resonance in a helimagnet
Gyrotropic birefringence is expected to emerge from the magnetoelectric coupling. Here, the authors find polarity and chirality arising from the helical spin order exhibit enhanced optical activities, gyrotropic birefringence and natural optical activity, on the electromagnon resonance.
- S. Iguchi
- , R. Masuda
- & Y. Takahashi
-
Article
| Open Access Ferroelectric 2D ice under graphene confinement
Ferroelectric 2D ice under graphene confinement
Ferroelectric ordering of water has been at the heart of intense debates due to its importance in enhancing our understanding of the condensed matter. Here, the authors observe ferroelectric properties of water ice in a two dimensional phase under confinement between two graphene layers.
- Hao-Ting Chin
- , Jiri Klimes
- & Ya-Ping Hsieh
-
Article
| Open Access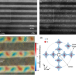 Atomic scale crystal field mapping of polar vortices in oxide superlattices
Atomic scale crystal field mapping of polar vortices in oxide superlattices
The response of the electronic structure to the non-trivial polarization texture in PbTiO3/SrTiO3 superlattices has not been explored. Here, the authors reveal how the peaks of the spectra shift and change their local electronic structure depending on the position of the Ti cation.
- Sandhya Susarla
- , Pablo García-Fernández
- & Javier Junquera
-
Article
| Open Access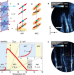 Writing of strain-controlled multiferroic ribbons into MnWO4
Writing of strain-controlled multiferroic ribbons into MnWO4
It is difficult to find magnetoelectric low-dimensional structures partly due to the lack of experimental techniques locally probing their physical nature. Here, the authors observe multiferroic ribbon-like domains in a non-multiferroic environment in MnWO4 by optical second harmonic generation.
- Shingo Toyoda
- , Manfred Fiebig
- & Naoki Ogawa
-
Article
| Open Access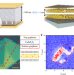 Enhanced bulk photovoltaic effect in two-dimensional ferroelectric CuInP2S6
Enhanced bulk photovoltaic effect in two-dimensional ferroelectric CuInP2S6
While magnetism, hyperferroelectricity, and topological phases in the two-dimensional limit have been widely explored, the direct experimental study on bulk photovoltaic effect in 2D materials remains unimplemented. Here, the authors find bulk photovoltaic effect in 2D ferroelectric CuInP2S6.
- Yue Li
- , Jun Fu
- & Hualing Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access Chemically driven energetic molecular ferroelectrics
Chemically driven energetic molecular ferroelectrics
An interest arises if energetic molecules and molecular ferroelectrics can be integrated together to obtain a chemically driven electricity conversion. Here, the authors explore energetic molecular ferroelectrics consisting of imidazolium cations and perchlorate anions with a high-power density.
- Yong Hu
- , Zhiyu Liu
- & Shenqiang Ren
-
Article
| Open Access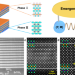 Magnetoelectric phase transition driven by interfacial-engineered Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction
Magnetoelectric phase transition driven by interfacial-engineered Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction
A controllable magnetoelectric phase based on symmetry engineering is challenge in natural bulk crystals. Here, via engineering of interfacial Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya interaction, the authors design a magnetoelectric phase transition in oxide superlattices of correlated electron systems.
- Xin Liu
- , Wenjie Song
- & Jinxing Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access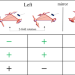 Field-tunable toroidal moment in a chiral-lattice magnet
Field-tunable toroidal moment in a chiral-lattice magnet
Toroidal moments arise from vortex like spin arrangements. These moments can then interact, giving rise to ferri- or ferro-toroidal order, though controlling such order is difficult. Here, the authors demonstrate a ferri-toroidal state in BaCoSiO4, which under an applied magnetic field exhibits multiple toroidal and metamagnetic transitions.
- Lei Ding
- , Xianghan Xu
- & Huibo Cao
-
Article
| Open Access Ferroelectric phase-transition frustration near a tricritical composition point
Ferroelectric phase-transition frustration near a tricritical composition point
Phase transition brings a plethora of exotic phenomena and intriguing effects such as spin and charge frustration. However, the phase transition order is not always explicit. Here, the authors discover phase transition frustration near a tricritical composition point in ferroelectric Pb(Zr,Ti)O3.
- Xian-Kui Wei
- , Sergei Prokhorenko
- & Zuo-Guang Ye
-
Article
| Open Access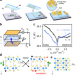 Direct measurement of ferroelectric polarization in a tunable semimetal
Direct measurement of ferroelectric polarization in a tunable semimetal
Free carriers and electrical polarization coexist in ferroelectric metals. Here, the authors use a capacitive method to probe the electronic compressibility of free carriers in a tunable semimetal, extract the polarized contribution, and study the carrier dependence of the ferroelectric state.
- Sergio C. de la Barrera
- , Qingrui Cao
- & Benjamin M. Hunt
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering polar vortex from topologically trivial domain architecture
Engineering polar vortex from topologically trivial domain architecture
The majority of polar structures emerging naturally in ferroelectrics are topologically trivial. Here, the authors demonstrate reconstruction of topologically trivial strip-like domain architecture into arrays of polar vortex in (PbTiO3)10/(SrTiO3)10 superlattice.
- Congbing Tan
- , Yongqi Dong
- & Jiangyu Li
-
Article
| Open Access Proton switching molecular magnetoelectricity
Proton switching molecular magnetoelectricity
Compared to inorganic materials, the magnetoelectric coupling in macromolecules is still hidden. Here, the authors describe machine learning coupled with additive manufacturing to accelerate the discovery of multiferroic macromolecules with a proton-mediated magnetoelectric coupling effect.
- Yong Hu
- , Scott Broderick
- & Shenqiang Ren
-
Article
| Open Access An antisite defect mechanism for room temperature ferroelectricity in orthoferrites
An antisite defect mechanism for room temperature ferroelectricity in orthoferrites
Ferroelectricity in orthoferrite perovskites has stimulated intense research, but the mechanism remains unclear. Here, the authors propose an antisite defect mechanism for introducing ferroelectricity in magnetically ordered YFeO3 and the family of rare earth orthoferrites.
- Shuai Ning
- , Abinash Kumar
- & Caroline A. Ross
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of negative capacitance in antiferroelectric PbZrO3 Films
Observation of negative capacitance in antiferroelectric PbZrO3 Films
The observation of negative capacitance effect is focused on the ferroelectrics, while the antiferroelectrics based on Landau switches may have negative capacitance effect. Here, the authors report the static and transient negative capacitance effect in antiferroelectric PbZrO3 and reveal its origin.
- Leilei Qiao
- , Cheng Song
- & Feng Pan
-
Article
| Open Access Giant conductivity of mobile non-oxide domain walls
Giant conductivity of mobile non-oxide domain walls
Conductive domain walls have been usually found in ferroelectric oxides. Here, the authors report on giant conductivity of domain walls and their magnetically avalanche-like expulsion event in non-oxide ferroelectric GaV4S8, extending the source of phenomena beyond the realm of oxide electronics.
- S. Ghara
- , K. Geirhos
- & I. Kézsmárki
-
Article
| Open Access Two-dimensional ferroelasticity in van der Waals β’-In2Se3
Two-dimensional ferroelasticity in van der Waals β’-In2Se3
Ferroelasticity is predicted theoretically in 2D materials, but it lacks experimental validation. Here, the authors find 2D ferroelasticity in both exfoliated and CVD-grown β’-In2Se3 down to few-layer thickness by atomic-resolution electron microscopy, in situ X-ray diffraction, and polarized-light microscopy.
- Chao Xu
- , Jianfeng Mao
- & Ye Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscale bubble domains with polar topologies in bulk ferroelectrics
Nanoscale bubble domains with polar topologies in bulk ferroelectrics
Experimentally manipulating bubble domains remains elusive especially in the bulk form of ferroelectrics. Here, the authors achieve self-confined bubble domains with multiple polar topologies in bulk Bi0.5Na0.5TiO3 ferroelectrics, demonstrating reversible and donut-like domain morphology evolution.
- Jie Yin
- , Hongxiang Zong
- & Stephen J. Pennycook
-
Article
| Open Access Atomic scale symmetry and polar nanoclusters in the paraelectric phase of ferroelectric materials
Atomic scale symmetry and polar nanoclusters in the paraelectric phase of ferroelectric materials
The existence and atomic-level structure of the hypothetical polar nanoclusters above the Curie temperature is one of the oldest open questions in the physics of ferroelectrics. Here, the authors find the polar nanoclusters in the paraelectric phases of classical perovskite ferroelectrics.
- Andreja Bencan
- , Emad Oveisi
- & Dragan Damjanovic
-
Article
| Open Access Giant electrocaloric materials energy efficiency in highly ordered lead scandium tantalate
Giant electrocaloric materials energy efficiency in highly ordered lead scandium tantalate
The intrinsic efficiency of electrocaloric materials has been largely overlooked. Here, the authors use the parameter materials efficiency as the figure of merit to rank caloric materials, reporting on the materials efficiency of highly ordered bulk lead scandium tantalate PST.
- Youri Nouchokgwe
- , Pierre Lheritier
- & Emmanuel Defay
-
Article
| Open Access Magnetoelectric coupling of domains, domain walls and vortices in a multiferroic with independent magnetic and electric order
Magnetoelectric coupling of domains, domain walls and vortices in a multiferroic with independent magnetic and electric order
In h-RMnO3, the linear magnetoelectric effect is symmetry forbidden. Here, the authors show a pronounced magnetoelectric coupling driven by superexchange interaction giving rise to types of topological defects like magnetoelectric domain walls and vortex-like singularities.
- Marcela Giraldo
- , Quintin N. Meier
- & Thomas Lottermoser

 Competing electronic states emerging on polar surfaces
Competing electronic states emerging on polar surfaces