Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Time-lapse crystallography snapshots of a double-strand break repair polymerase in action
Time-lapse crystallography snapshots of a double-strand break repair polymerase in action
DNA polymerase (pol) μ functions in DNA double-strand break repair. Here the authors use time-lapse X-ray crystallography to capture the states of pol µ during the conversion from pre-catalytic to product complex and observe a third transiently bound metal ion in the product state.
- Joonas A. Jamsen
- , William A. Beard
- & Samuel H. Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insights into the mechanism and E2 specificity of the RBR E3 ubiquitin ligase HHARI
Structural insights into the mechanism and E2 specificity of the RBR E3 ubiquitin ligase HHARI
HHARI is a RING-in-between-RING (RBR) ubiquitin (Ub) E3 ligase. Here the authors present the crystal structure of HHARI with the UbcH7 ~ Ub thioester intermediate mimetic, which reveals that HHARI binds this E2 ~ Ub in an open conformation and explains the specificity of this cognate RBR E3/E2 pair.
- Lingmin Yuan
- , Zongyang Lv
- & Shaun K. Olsen
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of Notch O-glucosylation and O–xylosylation by mammalian protein–O-glucosyltransferase 1 (POGLUT1)
Structural basis of Notch O-glucosylation and O–xylosylation by mammalian protein–O-glucosyltransferase 1 (POGLUT1)
POGLUT1 is a protein-O-glucosyltransferase that transfers glucose and xylose to the EGF-like domains of Notch and other signaling receptors. Here the authors report the structure of human POGLUT1 in complexes with 3 different EGF-like domains and donor substrates and shed light on the enzyme’s substrate specificity and catalytic mechanism
- Zhijie Li
- , Michael Fischer
- & James M. Rini
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for dolichylphosphate mannose biosynthesis
Structural basis for dolichylphosphate mannose biosynthesis
The generation of glycolipid dolichylphosphate mannose (Dol-P-Man) is a critical step for protein glycosylation and GPI anchor synthesis. Here the authors report the structure of dolichylphosphate mannose synthase in complex with bound nucleotide and donor to provide insight into the mechanism of Dol-P-Man synthesis.
- Rosaria Gandini
- , Tom Reichenbach
- & Christina Divne
-
Article
| Open Access Accumulating the hydride state in the catalytic cycle of [FeFe]-hydrogenases
Accumulating the hydride state in the catalytic cycle of [FeFe]-hydrogenases
Of the four intermediates in the catalytic cycle of [FeFe]-hydrogenases, the hydride state still has eluded characterization. Here, the authors shift the reaction equilibrium for three hydrogenases and enrich the hydride-bound species, characterizing them using a real-time IR spectroscopic technique.
- Martin Winkler
- , Moritz Senger
- & Thomas Happe
-
Article
| Open Access Redox-dependent substrate-cofactor interactions in the Michaelis-complex of a flavin-dependent oxidoreductase
Redox-dependent substrate-cofactor interactions in the Michaelis-complex of a flavin-dependent oxidoreductase
Due to their transient nature, enzyme-substrate complexes are difficult to characterize structurally. Here, the authors capture the reactive reduced form of xenobiotic reductase A bound to its substrate and show that the oxidation state of the flavin cofactor affects the interaction of the substrate with the enzyme.
- Tobias Werther
- , Stefan Wahlefeld
- & Holger Dobbek
-
Article
| Open Access Structural insights into the mechanism of the membrane integral N-acyltransferase step in bacterial lipoprotein synthesis
Structural insights into the mechanism of the membrane integral N-acyltransferase step in bacterial lipoprotein synthesis
Lipoproteins are essential components of bacterial membranes. Here the authors present the crystal structures ofPseudomonas aeruginosa and Escherichia coliapolipoprotein N-acyltransferase, which catalyses the final step in the lipoprotein synthesis pathway, and give insights into its mechanism.
- Maciej Wiktor
- , Dietmar Weichert
- & Martin Caffrey
-
Article
| Open Access Cobamide-mediated enzymatic reductive dehalogenation via long-range electron transfer
Cobamide-mediated enzymatic reductive dehalogenation via long-range electron transfer
Cobalamin-containing reductive dehalogenases from organohalide-respiring bacteria play a key role in the degradation of halogenated organic compounds. Here the authors proposed a catalytic mechanism for dehalogenation that relies on a long-range electron transfer from the cobalt in the centre of the enzyme’s cofactor to the substrate.
- Cindy Kunze
- , Martin Bommer
- & Gabriele Diekert
-
Article
| Open Access Phosphate steering by Flap Endonuclease 1 promotes 5′-flap specificity and incision to prevent genome instability
Phosphate steering by Flap Endonuclease 1 promotes 5′-flap specificity and incision to prevent genome instability
Flap Endonuclease 1 is a DNA replication and repair enzyme indispensable for maintaining genomic stability. Here the authors provide mechanistic details on how FEN1 selects for 5′-flaps and promotes catalysis to avoid large-scale repeat expansion by a process termed ‘phosphate steering’.
- Susan E. Tsutakawa
- , Mark J. Thompson
- & John A. Tainer
-
Article
| Open Access INO80 exchanges H2A.Z for H2A by translocating on DNA proximal to histone dimers
INO80 exchanges H2A.Z for H2A by translocating on DNA proximal to histone dimers
Chromatin remodellers usually mobilize or disassemble nucleosomes by translocating along the nucleosomal DNA at the H3-H4 interface. Here, the authors provide evidence chromatin remodeller INO80 translocates along DNA at the H2A-H2B interface and displaces DNA from the surface of H2A-H2B.
- Sandipan Brahma
- , Maheshi I. Udugama
- & Blaine Bartholomew
-
Article
| Open Access The CaMKII holoenzyme structure in activation-competent conformations
The CaMKII holoenzyme structure in activation-competent conformations
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) forms a 12 subunit holoenzyme central to synaptic plasticity. Here the authors report a 3D structure of the CaMKII holoenzyme in an activation-competent state obtained by single particle EM, and suggest a role for the intrinsically disordered linker domain in facilitating cooperative activation.
- Janette B. Myers
- , Vincent Zaegel
- & Steve L. Reichow
-
Article
| Open Access Single-peptide DNA-dependent RNA polymerase homologous to multi-subunit RNA polymerase
Single-peptide DNA-dependent RNA polymerase homologous to multi-subunit RNA polymerase
Although all known RNA polymerases have multiple subunits, unrelated single-subunit polymerases have also been described. Here, the authors describe a single-subunit RNA polymerase from the SPβ prophage ofBacillus subtilis, which shares homology to multi-subunit enzymes.
- David Forrest
- , Katherine James
- & Nikolay Zenkin
-
Article
| Open Access Conformational dynamics of dynamin-like MxA revealed by single-molecule FRET
Conformational dynamics of dynamin-like MxA revealed by single-molecule FRET
MxA (myxovirus resistance protein A) is a viral restriction factor whose activity depends on self-assembly into polymeric rings and helical filaments. Here the authors reveal the conformational movements involved in generating torque within polymeric MxA molecules and the dynamic conformational changes that occur upon GTP loading and hydrolysis.
- Yang Chen
- , Lei Zhang
- & Song Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Decoding and reprogramming fungal iterative nonribosomal peptide synthetases
Decoding and reprogramming fungal iterative nonribosomal peptide synthetases
Nonribosomal peptides are important bioactive molecules that are synthetized by enzymes containing several catalytic domains. Here the authors describe the catalytic mechanism of fungal nonribosomal peptide synthetases and present an approach to modify these enzymes to produce specific nonribosomal peptides.
- Dayu Yu
- , Fuchao Xu
- & Jixun Zhan
-
Article
| Open Access Improving 10-deacetylbaccatin III-10-β-O-acetyltransferase catalytic fitness for Taxol production
Improving 10-deacetylbaccatin III-10-β-O-acetyltransferase catalytic fitness for Taxol production
Taxol is a widely used anticancer drug that is found in very low amounts in the bark of Taxus plants. Here, the authors improve the catalytic fitness of DBAT, an enzyme that catalyses the conversion of tree by products into taxol, enabling the design of anin vitrobiochemical systems for taxol production.
- Bing-Juan Li
- , Hao Wang
- & Ping Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Histone deacetylase 10 structure and molecular function as a polyamine deacetylase
Histone deacetylase 10 structure and molecular function as a polyamine deacetylase
Polyamines bind to nucleic acids and their function is regulated by reversible acetylation. Here, the authors show that histone deacetylase 10 is a polyamine deacetylase and present its crystal structure with a bound polyamine transition state analogue inhibitor.
- Yang Hai
- , Stephen A. Shinsky
- & David W. Christianson
-
Article
| Open Access Sirt1 carboxyl-domain is an ATP-repressible domain that is transferrable to other proteins
Sirt1 carboxyl-domain is an ATP-repressible domain that is transferrable to other proteins
The deacetylase Sirt1, known to regulate many cellular functions, can be activated by energy deprivation, however the mechanism is unclear. Here, the authors show that ATP inhibits Sirt1 by binding to the C-terminal domain, and energy deprivation derepresses Sirt1 activity by lowering the ATP level.
- Hyeog Kang
- , Shinichi Oka
- & Jay H. Chung
-
Article
| Open Access The molecular mechanism of the type IVa pilus motors
The molecular mechanism of the type IVa pilus motors
Bacterial type IVa pili are protein filaments used for motility and protein secretion. Here the authors present crystal structures of theGeobacter metallireducensPilB ATPase in two nucleotide states, and suggest a clockwise rotation of the central sub-pores of PilB that would support the assembly of a right-handed helical pilus.
- Matthew McCallum
- , Stephanie Tammam
- & P. Lynne Howell
-
Article
| Open Access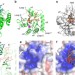 Crystal structure of APOBEC3A bound to single-stranded DNA reveals structural basis for cytidine deamination and specificity
Crystal structure of APOBEC3A bound to single-stranded DNA reveals structural basis for cytidine deamination and specificity
Cytidine deaminases are evolutionarily conserved enzymes that edit genomes by deaminating cytidine to uridine. Here the authors present the crystal structure of APOBEC3A with a single-stranded DNA substrate bound in the active site to shed light on the mechanism and specificity of substrate recognition.
- Takahide Kouno
- , Tania V. Silvas
- & Celia A. Schiffer
-
Article
| Open Access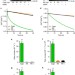 Cytoglobin regulates blood pressure and vascular tone through nitric oxide metabolism in the vascular wall
Cytoglobin regulates blood pressure and vascular tone through nitric oxide metabolism in the vascular wall
The gaseous signalling molecule nitric oxide regulates vascular tone. Here, the authors show that nitric oxide is degraded by the enzyme cytoglobin in the vascular wall, and that mice lacking cytoglobin have reduced blood pressure and are less sensitive to angiotensin-mediated hypertension.
- Xiaoping Liu
- , Mohamed A. El-Mahdy
- & Jay L. Zweier
-
Article
| Open Access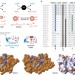 Glutaredoxin catalysis requires two distinct glutathione interaction sites
Glutaredoxin catalysis requires two distinct glutathione interaction sites
Glutaredoxins have important roles in redox processes. Here the authors show that the enzymatic activity of glutaredoxins requires two distinct glutathione interactions sites, one recognizing the glutathione disulfide substrate and one activating glutathione as a reducing agent.
- Patricia Begas
- , Linda Liedgens
- & Marcel Deponte
-
Article
| Open Access Macrocycle peptides delineate locked-open inhibition mechanism for microorganism phosphoglycerate mutases
Macrocycle peptides delineate locked-open inhibition mechanism for microorganism phosphoglycerate mutases
River blindness, a disease affecting millions throughout the tropics, is caused by parasitic worms. Here, Yuet al. report the discovery and structural characterization of potent macrocyclic peptide inhibitors of iPGM, a nematode-specific phosphoglycerate mutase, as potential leads for novel antimicrobial agents.
- Hao Yu
- , Patricia Dranchak
- & James Inglese
-
Article
| Open Access A redox-mediated Kemp eliminase
A redox-mediated Kemp eliminase
The majority of enzymatic Kemp elimination reactions proceed via a well-established acid-base mechanism. Here, the authors show that cytochrome P450 is able to metabolize the leflunomide drug via a redox Kemp elimination, offering new insights into enzyme catalysis.
- Aitao Li
- , Binju Wang
- & Manfred T. Reetz
-
Article
| Open Access Plant cysteine oxidases are dioxygenases that directly enable arginyl transferase-catalysed arginylation of N-end rule targets
Plant cysteine oxidases are dioxygenases that directly enable arginyl transferase-catalysed arginylation of N-end rule targets
The N-end rule pathway targets substrate proteins for proteasomal degradation. Here, Whiteet al. show that ArabidopsisPLANT CYSTEINE OXIDASEs show dioxygenase activity producing Cys-sulfinic acid at the N-terminus of target proteins, which then act as direct substrates for arginyl transferase.
- Mark D. White
- , Maria Klecker
- & Emily Flashman
-
Article
| Open Access Structure-guided mutagenesis reveals a hierarchical mechanism of Parkin activation
Structure-guided mutagenesis reveals a hierarchical mechanism of Parkin activation
Parkin and PINK1 are involved in damaged mitochondria clearance; however the sequence of events of Parkin activation is not clear. Here, the authors show that binding to phospho-ubiquitin on mitochondria enables Parkin phosphorylation, which allows Repressor Element of Parkin removal, E3 ligase activation and mitophagy.
- Matthew Y. Tang
- , Marta Vranas
- & Edward A. Fon
-
Article
| Open Access A substrate-bound structure of cyanobacterial biliverdin reductase identifies stacked substrates as critical for activity
A substrate-bound structure of cyanobacterial biliverdin reductase identifies stacked substrates as critical for activity
Biliverdin reductase (BVR) catalyses the last step in haem degradation. Here the authors present the crystal structure of cyanobacterial BVR bound to its substrate biliverdin and oxidised cofactor NADP+, which was used to propose the catalytic mechanism of this enzyme.
- Haruna Takao
- , Kei Hirabayashi
- & Kei Wada
-
Correspondence
| Open Access Correspondence: Spontaneous secondary mutations confound analysis of the essential two-component system WalKR in Staphylococcus aureus
Correspondence: Spontaneous secondary mutations confound analysis of the essential two-component system WalKR in Staphylococcus aureus
- Ian R. Monk
- , Benjamin P. Howden
- & Timothy P. Stinear
-
Article
| Open Access Ufd2p synthesizes branched ubiquitin chains to promote the degradation of substrates modified with atypical chains
Ufd2p synthesizes branched ubiquitin chains to promote the degradation of substrates modified with atypical chains
How ubiquitination affects the proteins it modifies varies according to the type of linkage between ubiquitin moieties. Here, Liuet al. show how yeast Udf2p promotes K48 linkage formation onto K29-linked chains to generate branched K29-K48 ubiquitin chains that target its substrate to the proteasome.
- Chao Liu
- , Weixiao Liu
- & Wei Li
-
Article
| Open Access Human farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase is allosterically inhibited by its own product
Human farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase is allosterically inhibited by its own product
Farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP) is a key building block for the synthesis of many lipids. Here the authors determine the crystal structure of farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase (FPPS) with its bound product and use kinetic measurements to show that FPP is an allosteric effector of the enzyme.
- Jaeok Park
- , Michal Zielinski
- & Albert M. Berghuis
-
Article
| Open Access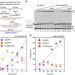 Oxidized nucleotide insertion by pol β confounds ligation during base excision repair
Oxidized nucleotide insertion by pol β confounds ligation during base excision repair
Oxidative stress in cells leads to the oxidations of DNA precursors. Here the authors show that these oxidized precursors can be incorporatedin vivoduring base excision repair, leading to DNA breaks and cytotoxicity.
- Melike Çağlayan
- , Julie K. Horton
- & Samuel H. Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access Evolutionary conservation and in vitro reconstitution of microsporidian iron–sulfur cluster biosynthesis
Evolutionary conservation and in vitro reconstitution of microsporidian iron–sulfur cluster biosynthesis
The functions of the highly reduced mitochondria (mitosomes) of microsporidians are not well-characterized. Here, the authors show that theTrachipleistophora hominismitosome is the site of iron–sulfur cluster assembly and that its retention is likely linked to its role in cytosolic and nuclear iron–sulfur protein maturation.
- Sven-A. Freibert
- , Alina V. Goldberg
- & Roland Lill
-
Article
| Open Access Kinetic disruption of lipid rafts is a mechanosensor for phospholipase D
Kinetic disruption of lipid rafts is a mechanosensor for phospholipase D
Mechanosensation by biological membranes can be relayed by mechanical tension to ion channels. Here the authors show that phospholipase D (PLD) is activated by mechanical disruption of lipid rafts which allows PLD to mix with its substrate in the lipid membrane, and propose a kinetic model of force transduction.
- E. Nicholas Petersen
- , Hae-Won Chung
- & Scott B. Hansen
-
Article
| Open Access Membrane pyrophosphatases from Thermotoga maritima and Vigna radiata suggest a conserved coupling mechanism
Membrane pyrophosphatases from Thermotoga maritima and Vigna radiata suggest a conserved coupling mechanism
In some parasites, membrane-bound pyrophosphatases, which couple proton and sodium ion transport across the membrane, are important for infectivity. Here, the authors report crystal structures of these proteins alongside biophysical analyses that allow them to propose a model for how the coupling is achieved.
- Kun-Mou Li
- , Craig Wilkinson
- & Adrian Goldman
-
Article
| Open Access Direct visualization of a Fe(IV)–OH intermediate in a heme enzyme
Direct visualization of a Fe(IV)–OH intermediate in a heme enzyme
The nature of the ferryl intermediate generated in reactions catalysed by heme-containing enzymes is uncertain, due to the ambiguity of X-ray crystallography data. Here, the authors apply neutron diffraction, kinetics and other spectroscopy to directly observe a protonated ferryl intermediate in a heme peroxidase.
- Hanna Kwon
- , Jaswir Basran
- & Emma L. Raven
-
Article
| Open Access Repression of RNA polymerase by the archaeo-viral regulator ORF145/RIP
Repression of RNA polymerase by the archaeo-viral regulator ORF145/RIP
How archaeal viruses perturb host transcription machinery is poorly understood. Here, the authors provide evidence that the archaeo-viral transcription factor ORF145/RIP targets host RNA polymerase, repressing its activity.
- Carol Sheppard
- , Fabian Blombach
- & Finn Werner
-
Article
| Open Access Reader domain specificity and lysine demethylase-4 family function
Reader domain specificity and lysine demethylase-4 family function
KDM4 histone demethylases target specific chromatin regions by a mechanism that is not fully characterised. Here, the authors identify trimethyl-lysine histone-binding preferences for closely related KDM4 double tudor domains and use structural and biochemical information to examine the molecular details of this interaction.
- Zhangli Su
- , Fengbin Wang
- & John M. Denu
-
Article
| Open Access Structural roles of guide RNAs in the nuclease activity of Cas9 endonuclease
Structural roles of guide RNAs in the nuclease activity of Cas9 endonuclease
In bacteria, CRISPR-Cas9 identifies and cleaves the target DNA with the assistance of a tracrRNA and a crRNA. Here the authors use single-molecule spectroscopy to investigate conformational changes and show that the tracrRNA keeps Cas9 in a functionally active form.
- Youngbin Lim
- , So Young Bak
- & Seong Keun Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Crystal structures of the ATP-binding and ADP-release dwells of the V1 rotary motor
Crystal structures of the ATP-binding and ADP-release dwells of the V1 rotary motor
V1-ATPases are rotary molecular motors that are powered by ATP hydrolysis. Here, the authors report two of the missing rotary states of this protein complex, and perform biochemical analysis to investigate the binding mode of the nucleotides.
- Kano Suzuki
- , Kenji Mizutani
- & Takeshi Murata
-
Article
| Open Access A substrate-driven allosteric switch that enhances PDI catalytic activity
A substrate-driven allosteric switch that enhances PDI catalytic activity
Protein Disulfide Isomerase (PDI) is a prothrombotic, multidomain enzyme with separate substrate binding and catalytic domains. Here, the authors identify a new class of compounds that target the PDI substrate binding site, inducing a conformational change in the catalytic domains and inhibiting thrombosis.
- Roelof H. Bekendam
- , Pavan K. Bendapudi
- & Robert Flaumenhaft
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis for oxygen degradation domain selectivity of the HIF prolyl hydroxylases
Structural basis for oxygen degradation domain selectivity of the HIF prolyl hydroxylases
The response to hypoxia involves multiple genes regulated by the hypoxia inducible transcription factors (HIFs), whose stability is regulated by prolyl hydroxylation. Here the authors provide a molecular basis for the substrate selectivity of the HIF prolyl hydroxylases that can be altered in erythrocytosis and cancer.
- Rasheduzzaman Chowdhury
- , Ivanhoe K. H. Leung
- & Christopher J. Schofield
-
Article
| Open Access Catalytic transformation of dinitrogen into ammonia and hydrazine by iron-dinitrogen complexes bearing pincer ligand
Catalytic transformation of dinitrogen into ammonia and hydrazine by iron-dinitrogen complexes bearing pincer ligand
Converting dinitrogen into other nitrogen compounds such as ammonia is a difficult task, especially under mild conditions. Here, the authors report a molecular iron complex capable of reducing dinitrogen to both ammonia and hydrazine in a catalytic process.
- Shogo Kuriyama
- , Kazuya Arashiba
- & Yoshiaki Nishibayashi
-
Correspondence
| Open Access Correspondence: On the enzymology and significance of HSPA1 lysine methylation
Correspondence: On the enzymology and significance of HSPA1 lysine methylation
- Magnus E. Jakobsson
- , Anders Moen
- & Pål Ø Falnes
-
Article
| Open Access NETosis and lack of DNase activity are key factors in Echis carinatus venom-induced tissue destruction
NETosis and lack of DNase activity are key factors in Echis carinatus venom-induced tissue destruction
The saw-scaled viper venom causes continued tissue damage that may cause death. Here the authors show that the venom attracts neutrophils to the bite site and induces neutrophil extracellular traps that capture venom components causing tissue damage, which can be prevented by enzymatic DNA degradation.
- Gajanan D. Katkar
- , Mahalingam S. Sundaram
- & Kempaiah Kemparaju
-
Article
| Open Access Structure and mechanism of the essential two-component signal-transduction system WalKR in Staphylococcus aureus
Structure and mechanism of the essential two-component signal-transduction system WalKR in Staphylococcus aureus
The WalKR signal transduction system is involved in extracellular signal recognition, but the details of this function are not well established. Here, the authors report the crystal structure of this two-component system alongside the characterisation of a small-molecule activator.
- Quanjiang Ji
- , Peter J. Chen
- & Chuan He
-
Article
| Open Access Subnanometre enzyme mechanics probed by single-molecule force spectroscopy
Subnanometre enzyme mechanics probed by single-molecule force spectroscopy
Adenylate kinase catalyses the interconversion of adenosine phosphates, and plays a crucial role in maintaining cellular energy homeostasis. Here, the authors use single molecule optical tweezers to understand how the enzyme’s conformation dynamics modulates catalysis.
- Benjamin Pelz
- , Gabriel Žoldák
- & Matthias Rief
-
Article
| Open Access BAP1/ASXL1 recruitment and activation for H2A deubiquitination
BAP1/ASXL1 recruitment and activation for H2A deubiquitination
The tumor suppressor BAP1 is activated by ASXL1 to deubiquitinate mono-ubiquitinated H2A at K119 in Polycomb gene repression. Here, the authors show how BAP1’s C-terminal extension auto-recruits it to nucleosomes, where the DEUBAD domain of ASXL1 increases BAP1’s affinity for ubiquitin to drive deubiquitination.
- Danny D. Sahtoe
- , Willem J. van Dijk
- & Titia K. Sixma
-
Article
| Open Access Rational engineering of a mesohalophilic carbonic anhydrase to an extreme halotolerant biocatalyst
Rational engineering of a mesohalophilic carbonic anhydrase to an extreme halotolerant biocatalyst
Halophilic organisms thrive in high salt conditions and express proteins that display desirable characteristics for industrial applications. Here, the authors use a rational design approach to transform wild-type carbonic anhydrase into a strongly halophilic enzyme.
- Andrew C. Warden
- , Michelle Williams
- & Victoria S. Haritos
-
Article
| Open Access Structure–function characterization reveals new catalytic diversity in the galactose oxidase and glyoxal oxidase family
Structure–function characterization reveals new catalytic diversity in the galactose oxidase and glyoxal oxidase family
Auxilliary Activity Family 5 (AA5) comprises mononuclear copper radical oxidases with catalytic diversity that is not well characterised. Here, structural, phylogenetic and biochemical analyses advance our understanding of the potential biological and biotechnology functions of these proteins.
- DeLu (Tyler) Yin
- , Saioa Urresti
- & Harry Brumer
-
Article
| Open Access Ternary structure reveals mechanism of a membrane diacylglycerol kinase
Ternary structure reveals mechanism of a membrane diacylglycerol kinase
Diacylglycerol kinase is a small bacterial membrane-bound trimer that catalyses diacylglycerol conversion to phosphatidic acid. Here, the authors solve the crystal structure of the kinase bound to a lipid substrate and an ATP analogue, and show that the active site arose through convergent evolution.
- Dianfan Li
- , Phillip J. Stansfeld
- & Martin Caffrey

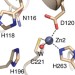 A general reaction mechanism for carbapenem hydrolysis by mononuclear and binuclear metallo-β-lactamases
A general reaction mechanism for carbapenem hydrolysis by mononuclear and binuclear metallo-β-lactamases