Research Highlights |
Featured
-
-
Research Highlights |
Shielded cells treat diabetes
-
Research Highlights |
Personalized diets for health
-
Autumn Books |
Nutrition: Dominions of fizz
David Katz applauds an analysis of the carbonated-drinks industry and public health.
- David Katz
-
News & Views |
 A smart insulin patch
A smart insulin patch
A microneedle-containing patch that is designed to sense elevated blood glucose levels and to respond by releasing insulin could offer people with diabetes a less-painful and more-reliable way to manage their condition.
- Omid Veiseh
- & Robert Langer
-
Research Highlights |
Gene therapy halts type 1 diabetes
-
Research Highlights |
Stem cells tackle diabetes
-
News |
 An inside look at the first pig biobank
An inside look at the first pig biobank
Nature watches a porcine autopsy that will help create a powerful animal model of diabetes.
- Alison Abbott
-
Letter |
 Group 2 innate lymphoid cells promote beiging of white adipose tissue and limit obesity
Group 2 innate lymphoid cells promote beiging of white adipose tissue and limit obesity
Group 2 innate lymphoid cells are shown to have a critical role in energy homeostasis by producing methionine-enkephalin peptides in response to interleukin 33, thus promoting the beiging of white adipose tissue; increased numbers of beige (also known as brown-like or brite) fat cells in white adipose tissue leads to increased energy expenditure and decreased adiposity.
- Jonathan R. Brestoff
- , Brian S. Kim
- & David Artis
-
Article |
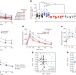 Artificial sweeteners induce glucose intolerance by altering the gut microbiota
Artificial sweeteners induce glucose intolerance by altering the gut microbiota
Non-caloric artificial sweeteners (NAS), widely used food additives considered to be safe and beneficial alternatives to sugars, are shown here to lead to the development of glucose intolerance through compositional and functional changes in the gut microbiota of mice, and the deleterious metabolic effects are transferred to germ-free mice by faecal transplant; NAS-induced dysbiosis and glucose intolerance are also demonstrated in healthy human subjects.
- Jotham Suez
- , Tal Korem
- & Eran Elinav
-
Letter |
 Diabetes recovery by age-dependent conversion of pancreatic δ-cells into insulin producers
Diabetes recovery by age-dependent conversion of pancreatic δ-cells into insulin producers
An investigation of the influence of age on the generation of insulin-producing cells after β-cell loss in mice reveals that, whereas α-cells can reprogram to produce insulin from puberty to adulthood, efficient reconstitution in the very young is through δ-cell reprogramming, leading to complete diabetes recovery.
- Simona Chera
- , Delphine Baronnier
- & Pedro L. Herrera
-
Letter |
 A common Greenlandic TBC1D4 variant confers muscle insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes
A common Greenlandic TBC1D4 variant confers muscle insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes
An association mapping study of type-2-diabetes-related quantitative traits in the Greenlandic population identified a common variant in TBC1D4 that increases plasma glucose levels and serum insulin levels after an oral glucose load and type 2 diabetes risk, with effect sizes several times larger than any previous findings of large-scale genome-wide association studies for these traits.
- Ida Moltke
- , Niels Grarup
- & Torben Hansen
-
Letter |
 Obesity-associated variants within FTO form long-range functional connections with IRX3
Obesity-associated variants within FTO form long-range functional connections with IRX3
Obesity-associated noncoding sequences within FTO are functionally connected with IRX3, and long-range enhancers in this region recapitulate aspects of IRX3 expression, suggesting that the obesity-associated interval is part of IRX3 regulation; Irx3-deficient mice have lower body weight and are resistant to diet-induced obesity, suggesting IRX3 as a novel determinant of body mass and composition.
- Scott Smemo
- , Juan J. Tena
- & Marcelo A. Nóbrega
-
Letter |
 Antidiabetic effects of glucokinase regulatory protein small-molecule disruptors
Antidiabetic effects of glucokinase regulatory protein small-molecule disruptors
Two small-molecule disruptors of the glucokinase–glucokinase-regulatory-protein complex, AMG-1694 and AMG-3969, are identified that decrease blood glucose levels in various models of hyperglycaemic rodents.
- David J. Lloyd
- , David J. St Jean Jr
- & Clarence Hale
-
Letter |
 Diabetic hyperglycaemia activates CaMKII and arrhythmias by O-linked glycosylation
Diabetic hyperglycaemia activates CaMKII and arrhythmias by O-linked glycosylation
CaMKII is known to be pathologically activated in heart failure and arrhythmias; here it is shown that glucose-induced CaMKII activation via O-linked glycosylation might contribute to cardiac pathology in diabetes.
- Jeffrey R. Erickson
- , Laetitia Pereira
- & Donald M. Bers
-
Letter |
 How insulin engages its primary binding site on the insulin receptor
How insulin engages its primary binding site on the insulin receptor
The three-dimensional structure of the insulin–insulin receptor complex has proved elusive, confounded by the complexity of producing the receptor protein; here is the first glimpse of the interaction between insulin and its primary binding site on the insulin receptor, a view based on four crystal structures of insulin bound to truncated insulin receptor complexes.
- John G. Menting
- , Jonathan Whittaker
- & Michael C. Lawrence
-
Letter |
 Biguanides suppress hepatic glucagon signalling by decreasing production of cyclic AMP
Biguanides suppress hepatic glucagon signalling by decreasing production of cyclic AMP
Biguanides such as metformin, which is the most widely prescribed drug for type-2 diabetes, are shown to antagonize the actions of glucagon by decreasing the levels of cyclic AMP.
- Russell A. Miller
- , Qingwei Chu
- & Morris J. Birnbaum
-
World View |
 Treat obesity as physiology, not physics
Treat obesity as physiology, not physics
The energy in–energy out hypothesis is not set in stone, argues Gary Taubes. It is time to test hormonal theories about why we get fat.
- Gary Taubes
-
Research Highlights |
Fat helps tumours to grow
-
News & Views |
 Resident risks
Resident risks
An innovative method for probing the genomes of the vast community of microorganisms that inhabit the human gut provides an alternative approach to identifying risk factors for type 2 diabetes. See Letter p.55
- Julia Oh
- & Julia A. Segre
-
Research Highlights |
 Cells turn back clock in diabetes
Cells turn back clock in diabetes
-
Article |
 A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes
A metagenome-wide association study of gut microbiota in type 2 diabetes
The authors have developed a new method, metagenome-wide association study (MGWAS), to compare the combined genetic content of the faecal microbiota of healthy people versus patients with type 2 diabetes; they identify multiple microbial species and metabolic pathways that are associated with either cohort and show that some of these may be used as biomarkers.
- Junjie Qin
- , Yingrui Li
- & Jun Wang
-
Letter |
 FTO genotype is associated with phenotypic variability of body mass index
FTO genotype is associated with phenotypic variability of body mass index
A meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies of phenotypic variation for height and body mass index in human populations using 170,000 samples shows that one single nucleotide polymorphism at the FTO locus, which is associated with obesity, is also associated with phenotypic variation.
- Jian Yang
- , Ruth J. F. Loos
- & Peter M. Visscher
-
Research Highlights |
Hunter-gatherer workout disproved
-
News |
 Law spurs regulators to heed patients’ priorities
Law spurs regulators to heed patients’ priorities
US FDA to consider risks and benefits more explicitly in drug approvals.
- Amy Maxmen
-
News |
 Weight-loss drug wins US approval
Weight-loss drug wins US approval
Obesity treatment shows promise for patients with diabetes despite concerns that it could cause heart complications.
- Brendan Borrell
-
-
Outlook |
 Diabetes in numbers
Diabetes in numbers
The number of people living with, and dying of, diabetes across the world is shocking: 90 million Chinese live with diabetes and 1.3 million died in 2011; 23% of Qatari adults have developed diabetes. Here we chart the extent of the global epidemic and present some of the implications for national governments by Tony Scully.
- Tony Scully
-
Outlook |
 Pathology: Cause and effect
Pathology: Cause and effect
Decades of study into the causes of diabetes have produced no definitive answers.
- Erika Jonietz
-
Outlook |
 Prevention: Nipped in the bud
Prevention: Nipped in the bud
While type 1 diabetes might be promising ground for a vaccine, the most effective way to avoid type 2 remains good old-fashioned diet and exercise.
- Scott P. Edwards
-
Outlook |
 Microbiome: The critters within
Microbiome: The critters within
Your gut microflora might be aiding and abetting diabetes.
- Lauren Gravitz
-
Outlook |
 Medical devices: Managed by machine
Medical devices: Managed by machine
Artificial pancreases promise to take the decision-making — and human mistakes — out of managing type 1 diabetes.
- Elie Dolgin
-
Outlook |
 Perspective: Testing failures
Perspective: Testing failures
Promising drugs to treat diabetes stumble in the latter stages of clinical testing. Thomas Mandrup-Poulsen explains why — and how to fix it.
- Thomas Mandrup-Poulsen
-
Outlook |
 Public health: India's diabetes time bomb
Public health: India's diabetes time bomb
Epigenetics and lifestyle are conspiring to inflict a massive epidemic of type 2 diabetes in the subcontinent.
- Priya Shetty
-
News & Views |
 Double protection for weakened bones
Double protection for weakened bones
The protein Sema3A both restrains bone degradation and stimulates bone building in mice, suggesting a potential therapy for conditions such as osteoporosis. See Article p.69
- Mone Zaidi
- & Jameel Iqbal
-
Letter |
 Inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor regulates hepatic gluconeogenesis in fasting and diabetes
Inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor regulates hepatic gluconeogenesis in fasting and diabetes
Interactions between cyclic AMP and calcium signalling pathways mediated by the inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor are shown to regulate hepatic gluconeogenesis in fasting and diabetes.
- Yiguo Wang
- , Gang Li
- & Marc Montminy
-
Article |
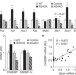 A novel ChREBP isoform in adipose tissue regulates systemic glucose metabolism
A novel ChREBP isoform in adipose tissue regulates systemic glucose metabolism
Downregulation of the glucose transporter GLUT4 in adipose tissue occurs early in the development of type 2 diabetes; here GLUT4-mediated glucose uptake is shown to induce a novel form of the transcription factor ChREBP, which regulates de novo lipogenesis and systemic glucose metabolism.
- Mark A. Herman
- , Odile D. Peroni
- & Barbara B. Kahn
-
News |
 The rise of the 'narciss-ome'
The rise of the 'narciss-ome'
Profiles of a researcher's genes, proteins and more show personalized genomic medicine in action.
- Carina Dennis
-
Letter |
 The BAH domain of ORC1 links H4K20me2 to DNA replication licensing and Meier–Gorlin syndrome
The BAH domain of ORC1 links H4K20me2 to DNA replication licensing and Meier–Gorlin syndrome
The ORC1 BAH domain is shown to be a module that recognizes a histone modification associated with replication origins, providing insight into the aetiology of Meier–Gorlin syndrome.
- Alex J. Kuo
- , Jikui Song
- & Or Gozani
-
-
Editorial |
On the up
The soaring incidence of diabetes is driving the United Arab Emirates' science ambitions.
-
Research Highlights |
Culprits in diabetic heart risk
-
Review Article |
 The contribution of bone to whole-organism physiology
The contribution of bone to whole-organism physiology
- Gérard Karsenty
- & Mathieu Ferron
-
Letter |
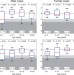 Mirror extreme BMI phenotypes associated with gene dosage at the chromosome 16p11.2 locus
Mirror extreme BMI phenotypes associated with gene dosage at the chromosome 16p11.2 locus
- Sébastien Jacquemont
- , Alexandre Reymond
- & Philippe Froguel
-
Letter |
 MicroRNAs 103 and 107 regulate insulin sensitivity
MicroRNAs 103 and 107 regulate insulin sensitivity
- Mirko Trajkovski
- , Jean Hausser
- & Markus Stoffel
-
Letter |
 Aberrant lipid metabolism disrupts calcium homeostasis causing liver endoplasmic reticulum stress in obesity
Aberrant lipid metabolism disrupts calcium homeostasis causing liver endoplasmic reticulum stress in obesity
- Suneng Fu
- , Ling Yang
- & Gökhan S. Hotamisligil
-
Research Highlights |
The roots of insulin production
-
News & Views Forum |
 Drugs, diabetes and cancer
Drugs, diabetes and cancer
Variation in a genomic region that contains the cancer-associated gene ATM affects a patient's response to the diabetes drug metformin. Two experts discuss the implications for understanding diabetes and the link to cancer.
- Morris J. Birnbaum
- & Reuben J. Shaw
-
Letter |
 9p21 DNA variants associated with coronary artery disease impair interferon-γ signalling response
9p21 DNA variants associated with coronary artery disease impair interferon-γ signalling response
A non-coding region on chromosome 9p21 was previously shown to associate with coronary artery disease and type 2 diabetes, and the region has been implicated in regulating neighbouring genes. Here, 33 distinct enhancers within this region are identified, showing that SNPs in one of the enhancers affect STAT1 binding. Furthermore, it is shown that in human vascular endothelial cells the enhancer interval physically interacts with a number of specific loci and that IFN-γ activation strongly affects the chromatin structure and transcriptional regulation of the 9p21 locus, including STAT1 binding, long-range enhancer interactions and expression of neighbouring genes.
- Olivier Harismendy
- , Dimple Notani
- & Kelly A. Frazer
-
News & Views |
 Diabetes in India
Diabetes in India
With the spread of fast-food outlets and more sedentary lifestyles, the prevalence of diabetes in India is rising alarmingly. But the subpopulations at risk and the symptoms of the disease differ from those in the West.
- Jared Diamond

 Insulin from mini stomach
Insulin from mini stomach