Featured
-
-
Article |
 Design of active and stable Co–Mo–Sx chalcogels as pH-universal catalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction
Design of active and stable Co–Mo–Sx chalcogels as pH-universal catalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction
Low efficiency, short lifetime of catalysts and a lack of low-cost materials have limited electrochemical H2 production. Now, active and stable Co–Mo–Sx chalcogels for the efficient production of H2 in alkaline and acidic environments are reported.
- Jakub Staszak-Jirkovský
- , Christos D. Malliakas
- & Nenad M. Markovic
-
News & Views |
 Powered by porphyrin packing
Powered by porphyrin packing
Self-assembling covalent organic frameworks can boost electrode performance for the catalytic reduction of carbon dioxide.
- Idan Hod
- , Omar K. Farha
- & Joseph T. Hupp
-
Letter |
 Activating and optimizing MoS2 basal planes for hydrogen evolution through the formation of strained sulphur vacancies
Activating and optimizing MoS2 basal planes for hydrogen evolution through the formation of strained sulphur vacancies
Molybdenum disulphide is a promising non-precious catalyst for hydrogen evolution because it contains active edge sites and an inert basal plane. Introducing sulphur vacancies and strain now leads to activation and optimization of the basal plane.
- Hong Li
- , Charlie Tsai
- & Xiaolin Zheng
-
Article |
 An electrodeposited inhomogeneous metal–insulator–semiconductor junction for efficient photoelectrochemical water oxidation
An electrodeposited inhomogeneous metal–insulator–semiconductor junction for efficient photoelectrochemical water oxidation
Water splitting requires a semiconductor to absorb light and a catalyst to enhance the kinetics of electron transfer. An electrodeposition method to produce efficient photoanodes for the photoelectrochemical oxidation of water to oxygen is presented.
- James C. Hill
- , Alan T. Landers
- & Jay A. Switzer
-
Article |
 Efficient hydrogen evolution catalysis using ternary pyrite-type cobalt phosphosulphide
Efficient hydrogen evolution catalysis using ternary pyrite-type cobalt phosphosulphide
Production of hydrogen by water splitting demands efficient Earth-abundant catalysts for the hydrogen evolution reaction. An efficient ternary pyrite-type cobalt phosphosulphide catalyst for photoelectrochemical hydrogen production is now identified.
- Miguel Cabán-Acevedo
- , Michael L. Stone
- & Song Jin
-
Article |
 Identification of catalytic sites for oxygen reduction in iron- and nitrogen-doped graphene materials
Identification of catalytic sites for oxygen reduction in iron- and nitrogen-doped graphene materials
Although Fe–N–C materials are promising catalysts for oxygen electroreduction in polymer fuel cells, the structure of their active sites is unclear. Quantitative analysis of Fe–N–C now reveals the existence of porphyrin-like FeN4C12 moieties.
- Andrea Zitolo
- , Vincent Goellner
- & Frédéric Jaouen
-
Article |
 High H− ionic conductivity in barium hydride
High H− ionic conductivity in barium hydride
Heavy alkaline-earth hydrides could be of interest as ionically conducting electrolytes for electrochemical applications. Barium hydride is now shown to exhibit fast ionic transport of hydride ions in a high-temperature and high-symmetry phase.
- Maarten C. Verbraeken
- , Chaksum Cheung
- & John T. S. Irvine
-
Article |
 Proton switch for modulating oxygen reduction by a copper electrocatalyst embedded in a hybrid bilayer membrane
Proton switch for modulating oxygen reduction by a copper electrocatalyst embedded in a hybrid bilayer membrane
Molecular switches regulate many fundamental processes in natural and artificial systems. An electrochemical platform in which a proton carrier switches the activity of a catalyst is now presented. A hybrid bilayer membrane allows the regulation of proton transport to a Cu-based molecular oxygen reduction reaction catalyst.
- Christopher J. Barile
- , Edmund C. M. Tse
- & Andrew A. Gewirth
-
Article |
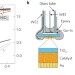 Adaptive semiconductor/electrocatalyst junctions in water-splitting photoanodes
Adaptive semiconductor/electrocatalyst junctions in water-splitting photoanodes
Photoelectrochemical water-splitting devices require integrating electrocatalysts with light-absorbing semiconductors, but understanding charge-transfer processes at interfaces has proved difficult. Ion-permeable electrocatalysts deposited onto TiO2 photoelectrodes now result in adaptive semiconductor/electrocatalyst junctions where both the effective interface barrier height and the photovoltage output change depending on the oxidation state of the electrocatalyst.
- Fuding Lin
- & Shannon W. Boettcher
-
-
Article |
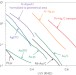 Enabling direct H2O2 production through rational electrocatalyst design
Enabling direct H2O2 production through rational electrocatalyst design
The electrochemical reduction of oxygen to hydrogen peroxide requires selective and stable electrocatalysts. It is now shown that Pt–Hg nanoparticles display an order of magnitude improvement in the mass activity for hydrogen peroxide production compared with the best performing catalyst.
- Samira Siahrostami
- , Arnau Verdaguer-Casadevall
- & Jan Rossmeisl
-
Article |
 The effect of particle proximity on the oxygen reduction rate of size-selected platinum clusters
The effect of particle proximity on the oxygen reduction rate of size-selected platinum clusters
The catalytic activity of highly dispersed platinum nanoparticles is not yet well understood. Now, a unique approach that allows precise control of both the size and coverage of platinum nanoclusters reveals that particle proximity influences the oxygen reduction rate of these size-selected clusters, especially in terms of mass normalized activity.
- Markus Nesselberger
- , Melanie Roefzaad
- & Matthias Arenz
-
Article |
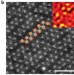 Enhanced catalytic activity in strained chemically exfoliated WS2 nanosheets for hydrogen evolution
Enhanced catalytic activity in strained chemically exfoliated WS2 nanosheets for hydrogen evolution
Efficient evolution of hydrogen via electrocatalysis at low overpotentials is promising for clean energy production. Monolayered nanosheets of chemically exfoliated WS2 are shown to be efficient catalysts for hydrogen evolution at very low overpotentials. The enhanced catalytic performance is associated with the high concentration of the strained metallic octahedral phase in the exfoliated nanosheets.
- Damien Voiry
- , Hisato Yamaguchi
- & Manish Chhowalla
-
Article |
 Compositional segregation in shaped Pt alloy nanoparticles and their structural behaviour during electrocatalysis
Compositional segregation in shaped Pt alloy nanoparticles and their structural behaviour during electrocatalysis
Although site-dependent metal surface segregation in bimetallic nanoalloys affects catalytic activity and stability, segregation on shaped nanocatalysts and their atomic-scale evolution is largely unexplored. PtxNi1−x alloy nanoparticle electrocatalysts with unique activity for oxygen reduction reactions exhibit an unexpected compositional segregation structure across the {111} facets.
- Chunhua Cui
- , Lin Gan
- & Peter Strasser
-
News & Views |
 Interfacing electrochemistry
Interfacing electrochemistry
Electrocatalysis lies at the heart of the chemical phenomena that take place at electrochemical interfaces. In the future it will be the key to driving technological innovations that are urgently needed to deliver reliable, affordable and environmentally friendly energy.
- Nenad M. Markovic
-
Article |
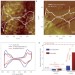 Mesostructured thin films as electrocatalysts with tunable composition and surface morphology
Mesostructured thin films as electrocatalysts with tunable composition and surface morphology
Some of the most challenging issues in energy conversion are the insufficient activity of the catalysts for the oxygen-reduction reaction, catalyst degradation and carbon-support corrosion. A class of mesostructured carbon-free metallic catalysts based on thin films and with tunable near-surface composition, morphology and structure that lead to an improved affinity for the electrochemical reduction of oxygen are now reported.
- Dennis F. van der Vliet
- , Chao Wang
- & Vojislav R. Stamenkovic
-
Article |
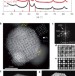 Structurally ordered intermetallic platinum–cobalt core–shell nanoparticles with enhanced activity and stability as oxygen reduction electrocatalysts
Structurally ordered intermetallic platinum–cobalt core–shell nanoparticles with enhanced activity and stability as oxygen reduction electrocatalysts
Enhancing and optimizing the performance and durability of nanocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction is crucial for fuel-cell applications. A class of Pt–Co nanocatalysts consisting of ordered Pt3Co intermetallic cores with a 2–3 atomic-layer-thick platinum shell now exhibit a large increase in mass activity and specific activity when compared with disordered alloy nanoparticles.
- Deli Wang
- , Huolin L. Xin
- & Héctor D. Abruña
-
Article |
 Engineering the surface structure of MoS2 to preferentially expose active edge sites for electrocatalysis
Engineering the surface structure of MoS2 to preferentially expose active edge sites for electrocatalysis
Controlling surface structure at the atomic scale is paramount to developing effective catalysts. The surface structure of MoS2 is now engineered to preferentially expose edge sites by successfully synthesizing contiguous large-area thin films of a highly ordered double-gyroid MoS2 bicontinuous network with nanoscale pores.
- Jakob Kibsgaard
- , Zhebo Chen
- & Thomas F. Jaramillo
-
Article |
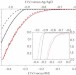 A Janus cobalt-based catalytic material for electro-splitting of water
A Janus cobalt-based catalytic material for electro-splitting of water
Innovative solutions for the design of sustainable and efficient systems for the conversion and storage of renewable energy sources are needed, and one promising option is the production of hydrogen through water splitting. A nanoparticulate electrocatalytic material consisting of metallic cobalt coated with a cobalt-oxo/hydroxo-phosphate layer is now found to exhibit active hydrogen evolution, and can also be converted into a cobalt oxide film catalysing oxygen evolution.
- Saioa Cobo
- , Jonathan Heidkamp
- & Vincent Artero
-
Article |
 Trends in activity for the water electrolyser reactions on 3d M(Ni,Co,Fe,Mn) hydr(oxy)oxide catalysts
Trends in activity for the water electrolyser reactions on 3d M(Ni,Co,Fe,Mn) hydr(oxy)oxide catalysts
Efficient electrochemical transformation of water to molecular hydrogen and of hydroxyl ions to oxygen in alkaline environments is important for reducing energy losses in water–alkali electrolysers. Insight into the activities of hydr(oxy)oxides on platinum catalyst surfaces for hydrogen and oxygen evolution reactions should prove significant for designing practical alkaline electrocatalysts.
- Ram Subbaraman
- , Dusan Tripkovic
- & Nenad M. Markovic
-
Article |
 High electrochemical activity of the oxide phase in model ceria–Pt and ceria–Ni composite anodes
High electrochemical activity of the oxide phase in model ceria–Pt and ceria–Ni composite anodes
A key step in fuel-cell energy-conversion processes is electro-oxidation of the fuel at the anode, but ways to improve electrocatalytic activity remain unclear. Using ceria–metal structures, H2-oxidation reactions are shown to be dominated by electrocatalysis at the oxide/gas interface with minimal contributions from the oxide/metal/gas triple-phase boundaries.
- William C. Chueh
- , Yong Hao
- & Sossina M. Haile
-
Letter |
 Oxygen reduction in nanoporous metal–ionic liquid composite electrocatalysts
Oxygen reduction in nanoporous metal–ionic liquid composite electrocatalysts
The improvement of catalysts for the oxygen-reduction reaction is an important challenge for fuel cells and other electrochemical-energy technologies. A composite nanoporous Ni–Pt alloy with a tailored geometric architecture is now shown to exhibit high mass activity for oxygen reduction.
- J. Snyder
- , T. Fujita
- & J. Erlebacher

 Water reduction by a p-GaInP2 photoelectrode stabilized by an amorphous TiO2 coating and a molecular cobalt catalyst
Water reduction by a p-GaInP2 photoelectrode stabilized by an amorphous TiO2 coating and a molecular cobalt catalyst