Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Low-voltage 2D materials-based printed field-effect transistors for integrated digital and analog electronics on paper
Low-voltage 2D materials-based printed field-effect transistors for integrated digital and analog electronics on paper
Paper is a promising substrate for flexible and environmentally sustainable electronic devices. Here, the authors combine chemical vapor deposition of MoS2 with inkjet printing of a hexagonal boron nitride (hBN) dielectric and silver electrodes, to fabricate flexible MoS2 field-effect transistors on paper, and then combine the latter with printed graphene resistors and silver interconnects to create inverters, logic gates and current mirrors.
- Silvia Conti
- , Lorenzo Pimpolari
- & Gianluca Fiori
-
Article
| Open Access A high performance wearable strain sensor with advanced thermal management for motion monitoring
A high performance wearable strain sensor with advanced thermal management for motion monitoring
Though stretchable strain sensors are attractive for next-generation applications due to their high sensitivity, heat generated in these devices limits their reliability. Here, the authors report boron nitride nanosheet-based stretchable strain sensors with enhanced thermal management.
- Cenxiao Tan
- , Zhigang Dong
- & Bin Sun
-
Article
| Open Access All-printed nanomembrane wireless bioelectronics using a biocompatible solderable graphene for multimodal human-machine interfaces
All-printed nanomembrane wireless bioelectronics using a biocompatible solderable graphene for multimodal human-machine interfaces
Though wearable electronics remain an attractive technology for bioelectronics, fabrication methods that precisely print biocompatible materials for electronics are needed. Here, the authors report an additive manufacturing process that yields all-printed nanomaterial-based wireless electronics.
- Young-Tae Kwon
- , Yun-Soung Kim
- & Woon-Hong Yeo
-
Article
| Open Access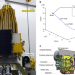 Design and flight results of the VHF/UHF communication system of Longjiang lunar microsatellites
Design and flight results of the VHF/UHF communication system of Longjiang lunar microsatellites
Satellites with amateur radio communication capabilities have not been operated in lunar orbit before. Here, the authors present the design and performance of a VHF/UHF software-defined radio developed for and tested on lunar microsatellites.
- Mingchuan Wei
- , Chaoran Hu
- & Feng Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Spiking neurons with spatiotemporal dynamics and gain modulation for monolithically integrated memristive neural networks
Spiking neurons with spatiotemporal dynamics and gain modulation for monolithically integrated memristive neural networks
Designing energy efficient and scalable artificial networks for neuromorphic computing remains a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate online learning in a monolithically integrated 4 × 4 fully memristive neural network consisting of volatile NbOx memristor neurons and nonvolatile TaOx memristor synapses.
- Qingxi Duan
- , Zhaokun Jing
- & Yuchao Yang
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time gap-free dynamic waveform spectral analysis with nanosecond resolutions through analog signal processing
Real-time gap-free dynamic waveform spectral analysis with nanosecond resolutions through analog signal processing
Real-time dynamic Fourier analysis of high-speed signals is difficult using either digital or analog schemes. Here, the authors present a universal analog approach that can track the changing frequency spectrum of waveforms in a real-time fashion at the nanosecond level, continuously and with no gaps.
- Saikrishna Reddy Konatham
- , Reza Maram
- & José Azaña
-
Article
| Open Access A framework for on-implant spike sorting based on salient feature selection
A framework for on-implant spike sorting based on salient feature selection
On-implant spike sorting methods utilize static waveform features for the classification. Here, the authors propose a framework based on dynamic selection of features that is more accurate and requires less memory.
- MohammadAli Shaeri
- & Amir M. Sodagar
-
Article
| Open Access Selective ion sensing with high resolution large area graphene field effect transistor arrays
Selective ion sensing with high resolution large area graphene field effect transistor arrays
The authors demonstrate wafer-scale, graphene-based ion sensitive field effect transistors arrays for simultaneous concentration measurement of K+, Na+, NH4+, NO3−, SO42−, HPO42− and Cl−, and use their technology for real-time ion concentration measurements in an aquarium with lemnoideae lemna over a period of three weeks.
- Ibrahim Fakih
- , Oliver Durnan
- & Thomas Szkopek
-
Article
| Open Access Employing a MEMS plasma switch for conditioning high-voltage kinetic energy harvesters
Employing a MEMS plasma switch for conditioning high-voltage kinetic energy harvesters
Conditioning efficiently high-voltage triboelectric nanogenerators for low-voltage applications remains a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate two orders of magnitude improvement of the energy harvesting efficiency by applying a conditioning circuit with self-sustained and automatic hysteresis MEMS micro-plasma switches.
- Hemin Zhang
- , Frédéric Marty
- & Philippe Basset
-
Article
| Open Access Parity-time symmetry in wavelength space within a single spatial resonator
Parity-time symmetry in wavelength space within a single spatial resonator
Most conventional PT-symmetric systems contain two physically separated modes. Here the authors proposed a PT-symmetric microwave optoelectronic oscillator, where the gain and loss modes are confined in a single spatial resonator, resulting in an increased structural simplicity, and long-term stability.
- Jiejun Zhang
- , Lingzhi Li
- & Jianping Yao
-
Article
| Open Access Optogenetics inspired transition metal dichalcogenide neuristors for in-memory deep recurrent neural networks
Optogenetics inspired transition metal dichalcogenide neuristors for in-memory deep recurrent neural networks
Accomplishing complex cognitive tasks such as speech recognition calls for artificial intelligence hardware with high computing precision. John et al. propose deep recurrent neural networks based on optoelectronic transition metal dichalcogenide memristors with high weight precision for in-memory computing.
- Rohit Abraham John
- , Jyotibdha Acharya
- & Nripan Mathews
-
Article
| Open Access Heterogeneously integrated flexible microwave amplifiers on a cellulose nanofibril substrate
Heterogeneously integrated flexible microwave amplifiers on a cellulose nanofibril substrate
Though flexible microwave integrated circuits (MICs) are desirable for the construction of functional microwave amplifier circuits, realizing low cost III-V-based MMICs remains a challenge. Here, the authors report a heterogeneous integration strategy for the fabrication of flexible low-cost MICs.
- Huilong Zhang
- , Jinghao Li
- & Zhenqiang Ma
-
Article
| Open Access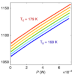 Non-thermal resistive switching in Mott insulator nanowires
Non-thermal resistive switching in Mott insulator nanowires
Despite intensive research on the electrically driven insulator-to-metal transition, this phenomenon is not well understood. Using quasi 1D nanowires of two Mott insulators, the authors reveal the central role of defects in enabling a non-thermal doping driven insulator-to metal transition.
- Yoav Kalcheim
- , Alberto Camjayi
- & Ivan K. Schuller
-
Article
| Open Access Control of criticality and computation in spiking neuromorphic networks with plasticity
Control of criticality and computation in spiking neuromorphic networks with plasticity
Designing efficient artificial networks able to quickly converge to optimal performance for a given task remains a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate a relation between criticality, task-performance and information theoretic fingerprint in a spiking neuromorphic network with synaptic plasticity.
- Benjamin Cramer
- , David Stöckel
- & Viola Priesemann
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-dense optical data transmission over standard fibre with a single chip source
Ultra-dense optical data transmission over standard fibre with a single chip source
Microcombs provide many opportunities for integration in optical communications systems. Here, the authors implement a soliton crystal microcomb as a tool to demonstrate more than 44 Tb/s communications with high spectral efficiency.
- Bill Corcoran
- , Mengxi Tan
- & David J. Moss
-
Article
| Open Access Finding the equilibrium of organic electrochemical transistors
Finding the equilibrium of organic electrochemical transistors
Though existing capacitive models describe the electronic transport in organic electrochemical transistors, these models do not provide an accurate steady-state solution. Here, the authors report a numerical model that describes the distribution and accumulation of ions in the transistor channel.
- Vikash Kaphle
- , Pushpa Raj Paudel
- & Björn Lüssem
-
Article
| Open Access Nature of power electronics and integration of power conversion with communication for talkative power
Nature of power electronics and integration of power conversion with communication for talkative power
Designing efficient power and communication electronics remains a challenge. Here, the authors reveal info characteristics of power electronics and propose a modulation strategy based on frequency hopping-differential phase shift keying to enable power converter design integrated with communication.
- Xiangning He
- , Ruichi Wang
- & Wuhua Li
-
Article
| Open Access Purely in-plane ferroelectricity in monolayer SnS at room temperature
Purely in-plane ferroelectricity in monolayer SnS at room temperature
Out-of-plane ferroelectricity is usually unstable in the two dimensional limit due to the presence of the depolarization field. Here, the authors successfully circumvent this issue by growing µm-sized SnS monolayers that exhibit in-plane ferroelectricity that is stable at room temperature.
- Naoki Higashitarumizu
- , Hayami Kawamoto
- & Kosuke Nagashio
-
Article
| Open Access Memristor networks for real-time neural activity analysis
Memristor networks for real-time neural activity analysis
Designing energy efficient artificial neural networks for real-time analysis remains a challenge. Here, the authors report the development of a perovskite halide (CsPbI3) memristor-based Reservoir Computing system for real-time recognition of neural firing patterns and neural synchronization states.
- Xiaojian Zhu
- , Qiwen Wang
- & Wei D. Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Randomized resonant metamaterials for single-sensor identification of elastic vibrations
Randomized resonant metamaterials for single-sensor identification of elastic vibrations
Designing efficient and flexible metamaterial with uncorrelated transmissions for spatial vibration encoding and identification remains a challenge. Here, the authors propose a randomized resonant metamaterial with randomly coupled local resonators for single-sensor identification of elastic vibrations.
- Tianxi Jiang
- , Chong Li
- & Zhi-Ke Peng
-
Article
| Open Access Epitaxial bulk acoustic wave resonators as highly coherent multi-phonon sources for quantum acoustodynamics
Epitaxial bulk acoustic wave resonators as highly coherent multi-phonon sources for quantum acoustodynamics
Acoustic resonators may find application for qubit coupling in compact quantum information and processing systems. Here the authors show a multi-phonon source with high quality factors and long phonon lifetimes via epitaxial high-overtone bulk acoustic resonators.
- Vikrant J. Gokhale
- , Brian P. Downey
- & David J. Meyer
-
Article
| Open Access Artifact-free and high-temporal-resolution in vivo opto-electrophysiology with microLED optoelectrodes
Artifact-free and high-temporal-resolution in vivo opto-electrophysiology with microLED optoelectrodes
Artifact-free opto-electrophysiology is key for precise modulation and monitoring of individual neurons at high spatio-temporal resolution. The authors present a method for eliminating stimulation artifacts in high-density micro-LED optoelectrodes for accurate functional mapping of local circuits.
- Kanghwan Kim
- , Mihály Vöröslakos
- & Euisik Yoon
-
Article
| Open Access Single-shot link discovery for terahertz wireless networks
Single-shot link discovery for terahertz wireless networks
At terahertz frequencies, link discovery by scanning is impractically slow. Here, the authors propose an alternative, single-shot link-finding method based on a leaky-wave device.
- Yasaman Ghasempour
- , Rabi Shrestha
- & Daniel M. Mittleman
-
Article
| Open Access Stepwise internal potential jumps caused by multiple-domain polarization flips in metal/ferroelectric/metal/paraelectric/metal stack
Stepwise internal potential jumps caused by multiple-domain polarization flips in metal/ferroelectric/metal/paraelectric/metal stack
Negative capacitance (NC) effects that could allow steep subthreshold swing (SS) in field-effect transistors (FETs) are still controversially discussed. Here the authors propose a model distinct from the NC concept, taking into account domain flips in multiple-domain ferroelectric/paraelectric gate stack FETs.
- Xiuyan Li
- & Akira Toriumi
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired bio-voltage memristors
Bioinspired bio-voltage memristors
Designing energy efficient systems capable to directly process signals at biological voltages remains a challenge. Here, the authors propose a bio-compatible memristor device based on protein-nanowire dielectric, harvested from the bacterium Geobactor sulfurreducens, working at biological voltages.
- Tianda Fu
- , Xiaomeng Liu
- & Jun Yao
-
Article
| Open Access Analog content-addressable memories with memristors
Analog content-addressable memories with memristors
Designing low power and high performance content-addressable memory remains a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate a content-addressable memory concept and circuit which leverages the analog conductance tunability of memristors, reduces power consumption, and enables new functionalities and applications.
- Can Li
- , Catherine E. Graves
- & John Paul Strachan
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrafast 27 GHz cutoff frequency in vertical WSe2 Schottky diodes with extremely low contact resistance
Ultrafast 27 GHz cutoff frequency in vertical WSe2 Schottky diodes with extremely low contact resistance
Two-dimensional materials show promise for 5G wireless communication applications. Here, the authors report vertical Schottky diodes based on thick mechanically exfoliated WSe2 flakes having low ohmic contact resistance of 50 Ω and ultrafast cutoff frequency of 27 GHz.
- Sung Jin Yang
- , Kyu-Tae Park
- & Seongil Im
-
Article
| Open Access Spiking neurons from tunable Gaussian heterojunction transistors
Spiking neurons from tunable Gaussian heterojunction transistors
Designing high performance, scalable, and energy efficient spiking neural networks remains a challenge. Here, the authors utilize mixed-dimensional dual-gated Gaussian heterojunction transistors from single-walled carbon nanotubes and monolayer MoS2 to realize simplified spiking neuron circuits.
- Megan E. Beck
- , Ahish Shylendra
- & Mark C. Hersam
-
Article
| Open Access Human activity recognition using magnetic induction-based motion signals and deep recurrent neural networks
Human activity recognition using magnetic induction-based motion signals and deep recurrent neural networks
Designing reliable, scalable and energy efficient sensor-based activity recognition system remains a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate low power wearable wireless network system based on magnetic induction which is integrated with deep recurrent neural networks for human activity recognition.
- Negar Golestani
- & Mahta Moghaddam
-
Article
| Open Access Toward a generalized Bienenstock-Cooper-Munro rule for spatiotemporal learning via triplet-STDP in memristive devices
Toward a generalized Bienenstock-Cooper-Munro rule for spatiotemporal learning via triplet-STDP in memristive devices
Designing reliable and energy efficient neuromorphic computing systems for spatiotemporal coding remains a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate a type of spike-rate-dependent plasticity based on a triplet learning scheme in a WO3−x-based second-order memristor network for spatiotemporal patterns.
- Zhongqiang Wang
- , Tao Zeng
- & Daniele Ielmini
-
Article
| Open Access Topological edge states of interacting photon pairs emulated in a topolectrical circuit
Topological edge states of interacting photon pairs emulated in a topolectrical circuit
Experimental studies of topological phenomena for interacting quantum systems are challenging. Here, the authors exploit the analogy between a quantum two-body problem in one dimension and a classical two-dimensional problem, emulating two-photon topological bound states in 1D using a 2D electrical circuit.
- Nikita A. Olekhno
- , Egor I. Kretov
- & Maxim A. Gorlach
-
Article
| Open Access Tunable rectification in a molecular heterojunction with two-dimensional semiconductors
Tunable rectification in a molecular heterojunction with two-dimensional semiconductors
Molecular electronics holds promise for device miniaturization yet can only be realized by choosing specially designed molecular species to date. Here, Shin et al. show tunable rectifying characteristics in a molecular heterojunction with non-functionalized molecules and two-dimensional semiconductors.
- Jaeho Shin
- , Seunghoon Yang
- & Gunuk Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Tactile sensory coding and learning with bio-inspired optoelectronic spiking afferent nerves
Tactile sensory coding and learning with bio-inspired optoelectronic spiking afferent nerves
Designing artificial somatosensory systems to efficiently emulate biological tactile information sensing, coding, and processing remains a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate a tactile sensory system based on optoelectronic spiking afferent nerves with both coding and learning capabilities.
- Hongwei Tan
- , Quanzheng Tao
- & Sebastiaan van Dijken
-
Article
| Open Access A highly CMOS compatible hafnia-based ferroelectric diode
A highly CMOS compatible hafnia-based ferroelectric diode
Designing reliable, scalable and high speed computing systems remains a challenge. Here, the authors identify noncentrosymmetric orthorhombic phase in HZO film and demonstrate a CMOS compatible 3D Vertical HZO-based ferroelectric diode array with self-selective property and 20 ns of speed operation.
- Qing Luo
- , Yan Cheng
- & Ming Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoelectromechanical relay without pull-in instability for high-temperature non-volatile memory
Nanoelectromechanical relay without pull-in instability for high-temperature non-volatile memory
Designing reliable, scalable and energy efficient data storage systems that can operate in extreme temperatures, remains a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate a nanoelectromechanical relay that does not exhibit pull-in instability for reliable reprogrammable non-volatile memory operation.
- Sunil Rana
- , João Mouro
- & Dinesh Pamunuwa
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanically and biologically skin-like elastomers for bio-integrated electronics
Mechanically and biologically skin-like elastomers for bio-integrated electronics
Designing biodegradable and biocompatible polymers to mimic both mechanical and biological properties of skins for emerging electronic devices remains a challenge. Here, the authors propose PSeD-U skin-like elastomers with both mechanical and biological properties for bio-integrated electronics.
- Shuo Chen
- , Lijie Sun
- & Zhengwei You
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoscale triboelectrification gated transistor
Nanoscale triboelectrification gated transistor
Though tribotronics, e.g., semiconductor electronics that utilize triboelectricity, is a promising technology, current devices have limited application in micro/nano electronics. Here, the authors report a triboelectrification-gated transistor with triboelectric modulation at the nanoscale.
- Tianzhao Bu
- , Liang Xu
- & Zhong Lin Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Nanofabrication for all-soft and high-density electronic devices based on liquid metal
Nanofabrication for all-soft and high-density electronic devices based on liquid metal
Though all-soft electronic devices with liquid metals are attractive due to the material’s compatibility with patterning methods, obtaining sub-micron patterns remains a challenge. Here, the authors report a hybrid lithography process to realize all-soft submicron-scale devices based on EGaIn.
- Min-gu Kim
- , Devin K. Brown
- & Oliver Brand
-
Article
| Open Access Regular perturbation on the group-velocity dispersion parameter for nonlinear fibre-optical communications
Regular perturbation on the group-velocity dispersion parameter for nonlinear fibre-optical communications
Nonlinear effects have been studied in optical fiber communications channels under various specified parameter regimes. Here, the authors develop an approximate model via perturbation that is more accurate for the highly nonlinear regime.
- Vinícius Oliari
- , Erik Agrell
- & Alex Alvarado
-
Article
| Open Access Ultraflexible and transparent electroluminescent skin for real-time and super-resolution imaging of pressure distribution
Ultraflexible and transparent electroluminescent skin for real-time and super-resolution imaging of pressure distribution
Electronic skin that spatially maps pressure distribution through imaging shows limited performance despite improvements to data acquisition. Here, the authors report ultraflexible, transparent electroluminescent skin capable of high-resolution imaging of pressure distribution over 3D surfaces.
- Byeongmoon Lee
- , Ji-Young Oh
- & Yongtaek Hong
-
Article
| Open Access Stretchable fabric generates electric power from woven thermoelectric fibers
Stretchable fabric generates electric power from woven thermoelectric fibers
Despite recent advances in flexible thermoelectric generators for wearable devices, current designs are unable to efficiently harvest heat flowing from human body. Here, the authors report high thermoelectric performance and stretchability in interlocked fiber-based modules for wearable devices.
- Tingting Sun
- , Beiying Zhou
- & Gerald Jeffrey Snyder
-
Article
| Open Access An all-optical technique enables instantaneous single-shot demodulation of images at high frequency
An all-optical technique enables instantaneous single-shot demodulation of images at high frequency
Traditional lock-in detection methods have been limited for wide-field imaging. Here, the authors present an all-optical design which enables four quadrature image channels to be recorded simultaneously, and show demodulation of wide-field images based on a single frame acquisition.
- Swapnesh Panigrahi
- , Julien Fade
- & Mehdi Alouini
-
Article
| Open Access Wireless battery-free body sensor networks using near-field-enabled clothing
Wireless battery-free body sensor networks using near-field-enabled clothing
Though wireless near-field communication (NFC) technologies that connect wearable sensors for health monitoring have been reported, the short range of NFC readers limits sensor functionality. Here, the authors report a wireless and battery-free body sensor network with near-field-enabled clothing.
- Rongzhou Lin
- , Han-Joon Kim
- & John S. Ho
-
Article
| Open Access Photonic integrated field-programmable disk array signal processor
Photonic integrated field-programmable disk array signal processor
FPGAs have long been of interest as reconfigurable circuits, but their electronic nature provides eventual limitations. Here the authors demonstrate a photonic digital signal processor that is field programmable using arrays of microdisk resonators.
- Weifeng Zhang
- & Jianping Yao
-
Article
| Open Access Strain-controlled power devices as inspired by human reflex
Strain-controlled power devices as inspired by human reflex
Designing intelligent power devices that can directly control the output power modulation responses to external stimuli at a rapid speed remains a challenge. Here, the authors report a strain-controlled power device by using the cantilever-structured AlGaN/AlN/GaN HEMT to emulate human reflex process.
- Shuo Zhang
- , Bei Ma
- & Zhong Lin Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Digitally virtualized atoms for acoustic metamaterials
Digitally virtualized atoms for acoustic metamaterials
Tuning the constitutive parameters of metamaterials in real time depends on the ability to modify the structure or external circuits attached to the metamaterials. Here, the authors propose virtualized metamaterials, allowing the tuning of acoustic parameters on-demand through software-defined frequency dispersion.
- Choonlae Cho
- , Xinhua Wen
- & Jensen Li
-
Article
| Open Access A bioinspired analogous nerve towards artificial intelligence
A bioinspired analogous nerve towards artificial intelligence
Designing artificial sensory neural system for neuroprosthetics and smart robotics applications remains a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate an all-in-one bionic sensory transmission nerve capable integrating the functions of perception, recognition and transmission of mechano-sensitive signal.
- Xinqin Liao
- , Weitao Song
- & Yuanjin Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Phase-coherent lightwave communications with frequency combs
Phase-coherent lightwave communications with frequency combs
Frequency combs have the potential to be used as multi-wavelength sources in future optical communications through fiber. Here the authors demonstrate joint phase processing of multi-wavelength comb transmission, and show two schemes to improve performance and reduce complexity.
- Lars Lundberg
- , Mikael Mazur
- & Peter A. Andrekson
-
Article
| Open Access Reversible displacive transformation in MnTe polymorphic semiconductor
Reversible displacive transformation in MnTe polymorphic semiconductor
Designing low power consumption and fast operation electronic phase-change devices remains a challenge. Here, the authors demonstrate the reversible displacive transformation in polycrystalline MnTe films to enable resistive switching via fast Joule heating for fast nonvolatile memory applications.
- Shunsuke Mori
- , Shogo Hatayama
- & Yuji Sutou

 A solution to the learning dilemma for recurrent networks of spiking neurons
A solution to the learning dilemma for recurrent networks of spiking neurons