Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Mutualism increases diversity, stability, and function of multiplex networks that integrate pollinators into food webs
Mutualism increases diversity, stability, and function of multiplex networks that integrate pollinators into food webs
Aside from their pollination function, pollinators consume and are consumed by other members of ecological communities; these relationships could explain the controversial effects of pollinators on ecological networks. Here the authors show that when mutualists such as pollinators are introduced into food webs, they increase ecosystem biodiversity, stability, and function.
- Kayla R. S. Hale
- , Fernanda S. Valdovinos
- & Neo D. Martinez
-
Article
| Open Access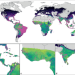 Accelerating invasion potential of disease vector Aedes aegypti under climate change
Accelerating invasion potential of disease vector Aedes aegypti under climate change
Understanding how life cycles of vectors respond to climatic factors is important to predict potential shifts in vector-borne disease risk in the coming decades. Here the authors develop a mechanistic phenological model for the invasive mosquito Aedes aegypti and apply it to project shifts under climate change scenarios.
- Takuya Iwamura
- , Adriana Guzman-Holst
- & Kris A. Murray
-
Article
| Open Access Fire deficit increases wildfire risk for many communities in the Canadian boreal forest
Fire deficit increases wildfire risk for many communities in the Canadian boreal forest
A primary element of modern wildfire management is to aggressively suppress small fires before they become large, but benefits can be offset by the fact that these practices promote older forests that are more ‘flammable’. Here the authors show that this downside puts numerous human communities at elevated risk of fires in boreal Canada.
- Marc-André Parisien
- , Quinn E. Barber
- & Sean A. Parks
-
Article
| Open Access Endemism patterns are scale dependent
Endemism patterns are scale dependent
Endemism is an important metric for conservation, but it may be sensitive to the measurement approach. Here Daru et al analyze global datasets of birds and amphibians and show that both weighted and phylogenetic endemism are scale dependent, across grain sizes, spatial extent and taxonomic treatment.
- Barnabas H. Daru
- , Harith Farooq
- & Søren Faurby
-
Article
| Open Access The impact of antimalarial resistance on the genetic structure of Plasmodium falciparum in the DRC
The impact of antimalarial resistance on the genetic structure of Plasmodium falciparum in the DRC
The genome of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum contains a record of past evolutionary forces. Here, using 2537 parasite sequences from the Democratic Republic of the Congo, the authors demonstrate how drug pressure and human movement have shaped the present-day parasite population.
- Robert Verity
- , Ozkan Aydemir
- & Jonathan J. Juliano
-
Article
| Open Access Local conditions and policy design determine whether ecological compensation can achieve No Net Loss goals
Local conditions and policy design determine whether ecological compensation can achieve No Net Loss goals
Countries are adopting ecological compensation policies aimed at achieving no net loss of biodiversity and ecosystem services. Here, Sonter and colleagues apply spatial simulation models to case studies in Australia, Brazil, Indonesia, and Mozambique to show that compensation alone is not sufficient to preserve biodiversity.
- Laura J. Sonter
- , Jeremy S. Simmonds
- & Martine Maron
-
Article
| Open Access The intensification of Arctic warming as a result of CO2 physiological forcing
The intensification of Arctic warming as a result of CO2 physiological forcing
Plants respond to increasing CO2 concentrations in the atmosphere by stomatal closure which causes a reduction of evapotranspiration and thus latent heat flux. Here, the authors show that this CO2 physiological forcing strengthens Arctic warming through increasing sea ice loss and local feedbacks.
- So-Won Park
- , Jin-Soo Kim
- & Jong-Seong Kug
-
Article
| Open Access Marine resource abundance drove pre-agricultural population increase in Stone Age Scandinavia
Marine resource abundance drove pre-agricultural population increase in Stone Age Scandinavia
How the development of human societies is influenced through their ecological environment and climatic conditions has been the subject of intensive debate. Here, the authors present multi-proxy data from southern Scandinavia which suggests that pre-agricultural population growth there was likely influenced by enhanced marine production.
- J. P. Lewis
- , D. B. Ryves
- & S. Juggins
-
Article
| Open Access Topography and human pressure in mountain ranges alter expected species responses to climate change
Topography and human pressure in mountain ranges alter expected species responses to climate change
It is often assumed that many species will move upslope in mountainous regions as the climate warms. However, the authors show here that as many species move to higher elevations they will enter areas of lower human footprint but potentially more constraining topography.
- Paul R. Elsen
- , William B. Monahan
- & Adina M. Merenlender
-
Article
| Open Access Changing role of coral reef marine reserves in a warming climate
Changing role of coral reef marine reserves in a warming climate
It is unclear whether rapid climate change will alter the effectiveness of marine reserves. Here Graham et al. use a 20-year time-series from the Seychelles to show that marine reserves may not prevent climate-driven shifts in community composition, and that ecological responses to reserves are substantially altered.
- Nicholas A. J. Graham
- , James P. W. Robinson
- & Shaun K. Wilson
-
Article
| Open Access Long-term isolation of European steppe outposts boosts the biome’s conservation value
Long-term isolation of European steppe outposts boosts the biome’s conservation value
Europe hosts isolated remnants of the steppe belt that once covered much of Eurasia. Here the authors combine genomic data and ecological niche modelling on three plant and three insect species to show evolution independent of the zonal steppe and high conservation value of these extrazonal steppes.
- Philipp Kirschner
- , Eliška Záveská
- & Peter Schönswetter
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell bacterial transcription measurements reveal the importance of dimethylsulfoniopropionate (DMSP) hotspots in ocean sulfur cycling
Single-cell bacterial transcription measurements reveal the importance of dimethylsulfoniopropionate (DMSP) hotspots in ocean sulfur cycling
DMSP is a ubiquitous organosulfur compound in the ocean that, once degraded by bacteria, plays key roles in global biogeochemical cycles and climate regulation. Here, the authors use single-cell measurements of transcription to investigate the intricate dynamics of bacterial DMSP degradation.
- Cherry Gao
- , Vicente I. Fernandez
- & Roman Stocker
-
Article
| Open Access Biological weed control to relieve millions from Ambrosia allergies in Europe
Biological weed control to relieve millions from Ambrosia allergies in Europe
Invasive plants can adversely affect ecosystems and economic costs. Here, the authors quantify the impact of the invasive plant Ambrosia artemisiifolia on seasonal allergies and health costs across Europe, finding that the costs are considerably higher than what previously reported, and estimate also the reduction in the number of patients and health costs that may be obtained with biological control
- Urs Schaffner
- , Sandro Steinbach
- & Heinz Müller-Schärer
-
Article
| Open Access Cable bacteria reduce methane emissions from rice-vegetated soils
Cable bacteria reduce methane emissions from rice-vegetated soils
Rice paddies are a major source of the Earth’s atmospheric methane, making these important food crops potent contributors to greenhouse gas emissions. Here the authors show that inoculation of paddies with a particular bacterium could significantly curb methane production.
- Vincent V. Scholz
- , Rainer U. Meckenstock
- & Nils Risgaard-Petersen
-
Article
| Open Access Stochasticity constrained by deterministic effects of diet and age drive rumen microbiome assembly dynamics
Stochasticity constrained by deterministic effects of diet and age drive rumen microbiome assembly dynamics
How complex microbial communities assemble through the animal’s life, and how predictable the assembly process is, remains poorly understood. Here, the authors profile the cow gut microbiome from birth to adulthood in animals born in C-section or natural birth and show that chance events early in life have a strong impact on microbiome development.
- Ori Furman
- , Liat Shenhav
- & Itzhak Mizrahi
-
Article
| Open Access Fire decline in dry tropical ecosystems enhances decadal land carbon sink
Fire decline in dry tropical ecosystems enhances decadal land carbon sink
In recent history the amount of carbon captured by terrestrial systems has increased, but the processes driving this process has remained poorly constrained. Here the authors use a global carbon model to show that a decrease in wildfires has caused the land carbon sink to increase in the past few decades.
- Yi Yin
- , A. Anthony Bloom
- & David Schimel
-
Article
| Open Access Aquaculture at the crossroads of global warming and antimicrobial resistance
Aquaculture at the crossroads of global warming and antimicrobial resistance
Global environmental changes threaten many food-producing sectors, including aquaculture. Here the authors show that countries most vulnerable to climate change will probably face the highest antimicrobial resistance in aquaculture-related bacteria, and that infected aquatic animals have higher mortality at warmer temperatures.
- Miriam Reverter
- , Samira Sarter
- & Rodolphe E. Gozlan
-
Article
| Open Access Drought alters the biogeochemistry of boreal stream networks
Drought alters the biogeochemistry of boreal stream networks
High latitude droughts are increasing, but their effects on freshwater systems are poorly understood. Here the authors investigate Sweden’s most severe drought in the last century and show that these dry conditions induce hypoxia and elevated methane production from streams.
- Lluís Gómez-Gener
- , Anna Lupon
- & Ryan A. Sponseller
-
Article
| Open Access Invasive earthworms unlock arctic plant nitrogen limitation
Invasive earthworms unlock arctic plant nitrogen limitation
Arctic plant growth is predominantly nitrogen limited, where the slow nitrogen turnover in the soil is commonly attributed to the cold arctic climate. Here the authors show that the arctic plant-soil nitrogen cycling is also constrained by the lack of larger detritivores like earthworms.
- Gesche Blume-Werry
- , Eveline J. Krab
- & Jonatan Klaminder
-
Article
| Open Access The morphology, molecular development and ecological function of pseudonectaries on Nigella damascena (Ranunculaceae) petals
The morphology, molecular development and ecological function of pseudonectaries on Nigella damascena (Ranunculaceae) petals
Interspecies interactions, including those between plants and pollinators, can involve deception. The authors characterize the molecular development of Nigella damascena pseudonectaries, and their adaptive function in attracting specific pollinators to concealed nectaries with visual cues.
- Hong Liao
- , Xuehao Fu
- & Hongzhi Kong
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic genome evolution and complex virocell metabolism of globally-distributed giant viruses
Dynamic genome evolution and complex virocell metabolism of globally-distributed giant viruses
Nucleocytoplasmic large DNA viruses (NCLDV) exhibit a large genomic repertoire and complex evolutionary history. Here, the authors generate 501 metagenome-assembled genomes from diverse environments and show NCLDVs to harbor a wide range of potential metabolic capabilities.
- Mohammad Moniruzzaman
- , Carolina A. Martinez-Gutierrez
- & Frank O. Aylward
-
Article
| Open Access Integrating multiple sources of ecological data to unveil macroscale species abundance
Integrating multiple sources of ecological data to unveil macroscale species abundance
Measurement of species abundance is fundamental in ecology, yet challenging at large spatial scales. Here, the authors show estimates of abundance of 1248 woody plant species over the East Asian islands that highlight macroevolutionary processes of biodiversity and the status of the national red listing.
- Keiichi Fukaya
- , Buntarou Kusumoto
- & Yasuhiro Kubota
-
Article
| Open Access Prompt rewetting of drained peatlands reduces climate warming despite methane emissions
Prompt rewetting of drained peatlands reduces climate warming despite methane emissions
Drained peatlands are sources of CO2, and though rewetting could curb emissions, this strategy results in elevated methane release. Here, the authors model peatland emissions scenarios and show that rewetting is a critical way to mitigate climate change despite potential methane increases.
- Anke Günther
- , Alexandra Barthelmes
- & John Couwenberg
-
Article
| Open Access Pelagic fish predation is stronger at temperate latitudes than near the equator
Pelagic fish predation is stronger at temperate latitudes than near the equator
One hypothesis for the latitudinal diversity gradient is based on an assumption of stronger species interactions at lower latitudes. Here, Roesti et al. estimate pelagic fish predation from long-term fishing records and find evidence of stronger predation at higher latitudes and with lower fish species richness.
- Marius Roesti
- , Daniel N. Anstett
- & Roi Holzman
-
Article
| Open Access Estimating the size distribution of plastics ingested by animals
Estimating the size distribution of plastics ingested by animals
Plastic pollution is an escalating problem and there is a need to predict the range of plastic sizes that an organism of interest could feasibly ingest. Here the authors use previously published data to develop an allometric equation for plastic size ingested as a function of animal body size, a relationship which could help predict risk of plastic introduction into food webs.
- Ifan B. Jâms
- , Fredric M. Windsor
- & Isabelle Durance
-
Article
| Open Access Downsizing of animal communities triggers stronger functional than structural decay in seed-dispersal networks
Downsizing of animal communities triggers stronger functional than structural decay in seed-dispersal networks
Species loss from ecological networks can impair network stability and ecosystem function. Here the authors simulate animal extinctions in interaction networks between plants and avian frugivores, showing that frugivore extinctions have comparatively weak effects on network structure, but strongly reduce seed-dispersal distance.
- Isabel Donoso
- , Marjorie C. Sorensen
- & Matthias Schleuning
-
Article
| Open Access The base of the Lystrosaurus Assemblage Zone, Karoo Basin, predates the end-Permian marine extinction
The base of the Lystrosaurus Assemblage Zone, Karoo Basin, predates the end-Permian marine extinction
The end-Permian is associated with major changes in both marine and terrestrial biodiversity. Here, Gastaldo et al. present high resolution dating of the Lystrosaurus Assemblage Zone in the Karoo Basin, South Africa, demonstrating that the marine crisis did not mirror a coeval event on land.
- Robert A. Gastaldo
- , Sandra L. Kamo
- & Anna M. Martini
-
Article
| Open Access Context-dependent dynamics lead to the assembly of functionally distinct microbial communities
Context-dependent dynamics lead to the assembly of functionally distinct microbial communities
Historical contingency can affect community composition and function, but the extent to which this occurs is unclear. Here the authors use pitcher plant microbial communities to demonstrate that community dynamics and key metabolic functions at equilibrium depend on history and initial composition.
- Leonora S. Bittleston
- , Matti Gralka
- & Otto X. Cordero
-
Article
| Open Access Locally-adapted reproductive photoperiodism determines population vulnerability to climate change in burying beetles
Locally-adapted reproductive photoperiodism determines population vulnerability to climate change in burying beetles
Understanding whether intraspecific trait variation results from local adaptation or phenotypic plasticity is crucial to predict species responses to climate change. Here the authors investigate geographically distinct burying beetle populations, showing that photoperiodism is a locally adapted, not phenotypically plastic, trait.
- Hsiang-Yu Tsai
- , Dustin R. Rubenstein
- & Sheng-Feng Shen
-
Article
| Open Access Global plant trait relationships extend to the climatic extremes of the tundra biome
Global plant trait relationships extend to the climatic extremes of the tundra biome
It is unclear whether plant trait relationships found at the global scale extend to climatic extremes. Here the authors analyse six major aboveground traits to show that known plant trait relationships extend to the tundra biomes and exhibit the same two dimensions of variation detected at the global scale.
- H. J. D. Thomas
- , A. D. Bjorkman
- & F. T. de Vries
-
Article
| Open Access Regime shifts occur disproportionately faster in larger ecosystems
Regime shifts occur disproportionately faster in larger ecosystems
Little is known about how the speed of ecosystem collapse depends on ecosystem size. Here, Cooper, Willcock et al. analyse empirical data and models finding that although regime shift duration increases with ecosystem size, this relationship saturates and even large ecosystems can collapse in a few decades.
- Gregory S. Cooper
- , Simon Willcock
- & John A. Dearing
-
Article
| Open Access Global consumption and international trade in deforestation-associated commodities could influence malaria risk
Global consumption and international trade in deforestation-associated commodities could influence malaria risk
Because many primary commodities cause deforestation and deforestation can increase malaria transmission, international trade can thus indirectly influence malaria risk. Here the authors use trade databases for commodites associated with deforestation to demonstrate that consumption of such commodities in developed nations could increase malaria risk in developing nations.
- Leonardo Suveges Moreira Chaves
- , Jacob Fry
- & Manfred Lenzen
-
Article
| Open Access Aggravation of reactive nitrogen flow driven by human production and consumption in Guangzhou City China
Aggravation of reactive nitrogen flow driven by human production and consumption in Guangzhou City China
There lacks research to figure out the variations in sources, magnitude, and spatiotemporal patterns of Nr flows in urban system. Here the authors develop a coupled human-natural urban nitrogen flow analysis model and show that anthropogenic perturbations not only intensify Nr input to sustain increasing demands for production and consumption of cities, but also greatly change the Nr distribution pattern in the urban system.
- Yue Dong
- , Linyu Xu
- & Lei Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Enhanced heat tolerance of viral-infected aphids leads to niche expansion and reduced interspecific competition
Enhanced heat tolerance of viral-infected aphids leads to niche expansion and reduced interspecific competition
Organisms living on and inside of plants—such as microbes and herbivorous insects—can interact in complex ways. Here the authors show that a plant virus increases the temperature of the plant and also the thermal tolerance of an aphid species feeding on the plant; this change in thermal tolerance also affects competition with another aphid species.
- Mitzy F. Porras
- , Carlos A. Navas
- & Tomás A. Carlo
-
Article
| Open Access Trade-offs between multifunctionality and profit in tropical smallholder landscapes
Trade-offs between multifunctionality and profit in tropical smallholder landscapes
Identifying economic and ecological trade-offs of land-use transitions is important to ensure sustainability. Here, Grass et al. find biodiversity-profit trade-offs in tropical land-use transitions in Sumatra, and show that targeted landscape planning is needed to increase land-use efficiency while ensuring socio-ecological sustainability.
- Ingo Grass
- , Christoph Kubitza
- & Meike Wollni
-
Article
| Open Access Juvenile cleaner fish can socially learn the consequences of cheating
Juvenile cleaner fish can socially learn the consequences of cheating
Cleaner fish can cheat clients for higher rewards but this comes with a risk of punishment. Here, Truskanov et al. show that juvenile cleaner fish can learn by observing adults to behave more cooperatively themselves but also to prefer clients that are more tolerant to cheating.
- Noa Truskanov
- , Yasmin Emery
- & Redouan Bshary
-
Article
| Open Access DNA metabarcoding and spatial modelling link diet diversification with distribution homogeneity in European bats
DNA metabarcoding and spatial modelling link diet diversification with distribution homogeneity in European bats
Ecological niche breadth may help explain spatial distribution patterns in animals. In this study on European bats, Alberdi et al. combine DNA metabarcoding and species distribution modelling to show that dietary niche breadth is related to hunting flexibility and broad-scale spatial patterns in species distribution.
- Antton Alberdi
- , Orly Razgour
- & M. Thomas P. Gilbert
-
Article
| Open Access Conservation prioritization can resolve the flagship species conundrum
Conservation prioritization can resolve the flagship species conundrum
Conservation actions focused on flagship species are effective at raising funds and awareness. Here, McGowan et al. show that prioritizing areas for conservation based on the presence of flagship species results in the selection of areas with ~ 79-89% of the total species that would be selected by maximizing biodiversity representation only.
- Jennifer McGowan
- , Linda J. Beaumont
- & Hugh P. Possingham
-
Article
| Open Access Purging of highly deleterious mutations through severe bottlenecks in Alpine ibex
Purging of highly deleterious mutations through severe bottlenecks in Alpine ibex
Although there is extensive theory predicting the effects of population bottlenecks on mutation load, there is little empirical evidence from recent bottlenecks. Here, Grossen et al. compare the consequences of population bottlenecks in six ibex species for genome-wide variation and mutation load.
- Christine Grossen
- , Frédéric Guillaume
- & Daniel Croll
-
Article
| Open Access Impact of two of the world's largest protected areas on longline fishery catch rates
Impact of two of the world's largest protected areas on longline fishery catch rates
There are concerns that expansion of marine protected areas could have negative effects on the fishing industry. Here Lynham et al. demonstrate that the expansion of two of the world’s largest protected areas did not have a negative impact on catch rates in the Hawaii longline fishery.
- John Lynham
- , Anton Nikolaev
- & Juan Carlos Villaseñor-Derbez
-
Article
| Open Access A global assessment of the drivers of threatened terrestrial species richness
A global assessment of the drivers of threatened terrestrial species richness
Understanding to what extent geographic patterns in threatened species diversity are driven by environmental features or human activities could aid conservation. Here, Howard et al. investigate broad scale patterns in species richness of threatened vertebrates and test the role of environmental and anthropogenic drivers.
- Christine Howard
- , Curtis H. Flather
- & Philip A. Stephens
-
Article
| Open Access Migration, hotspots, and dispersal of HIV infection in Rakai, Uganda
Migration, hotspots, and dispersal of HIV infection in Rakai, Uganda
HIV prevalence varies throughout Africa, but the contribution of migration remains unclear. Using population-based data from ~22,000 persons, Grabowski et al. show that HIV-positive migrants selectively migrate to high prevalence areas and that out-migrants from these areas geographically disperse.
- Mary Kate Grabowski
- , Justin Lessler
- & Ronald H. Gray
-
Article
| Open Access Simulation-based reconstruction of global bird migration over the past 50,000 years
Simulation-based reconstruction of global bird migration over the past 50,000 years
It is unclear whether bird migration patterns are restricted to interglacial periods or are maintained during glacial maxima. Somveille et al. apply a global migration simulation model to climate reconstruction to show that the prevalence of this phenomenon has likely been largely maintained up to 50,000 years ago.
- Marius Somveille
- , Martin Wikelski
- & Walter Jetz
-
Article
| Open Access Evolutionary conservation of within-family biodiversity patterns
Evolutionary conservation of within-family biodiversity patterns
Little is known about the phylogenetic conservation of higher-level properties. Here, the authors analyse the species distributions of 14 lichen families, 9 insect families, and 9 bird families in the Cantabrian mountains and show phylogenetic conservation of within-family biodiversity patterns.
- Paola Laiolo
- , Joaquina Pato
- & José Ramón Obeso
-
Article
| Open Access Evolutionary games with environmental feedbacks
Evolutionary games with environmental feedbacks
Strategic game payoffs often depend on the state of the environment, which in turn can be influenced by game strategies. Here, Tilman et al. develop a general framework for modeling strategic games with environmental feedbacks and analyze case studies from decision-making, ecology, and economics.
- Andrew R. Tilman
- , Joshua B. Plotkin
- & Erol Akçay
-
Article
| Open Access Systematic selection between age and household structure for models aimed at emerging epidemic predictions
Systematic selection between age and household structure for models aimed at emerging epidemic predictions
Models of emerging epidemics can be exceedingly helpful in planning the response, but early on model selection is a difficult task. Here, the authors explore the joint contribution of age stratification and household structure on epidemic spread, and provides a rule of thumb to guide model choice.
- Lorenzo Pellis
- , Simon Cauchemez
- & Christophe Fraser
-
Article
| Open Access Global determinants of freshwater and marine fish genetic diversity
Global determinants of freshwater and marine fish genetic diversity
Biogeographic patterns of genetic diversity are poorly documented, especially for fish species. Here the authors show that (mitochondrial) genetic diversity has global spatial organization patterns with different environmental drivers for marine and freshwater fishes, where genetic diversity is only partly congruent with species richness.
- Stéphanie Manel
- , Pierre-Edouard Guerin
- & Loïc Pellissier
-
Article
| Open Access Plant diversity effects on forage quality, yield and revenues of semi-natural grasslands
Plant diversity effects on forage quality, yield and revenues of semi-natural grasslands
Higher plant diversity in agricultural settings is often associated with lower biomass yield and with lower forage quality. Here, Schaub et al. show positive effects of plant diversity on biomass yield, quality-adjusted yield and revenues in semi-natural grassland across a range of management intensities.
- Sergei Schaub
- , Robert Finger
- & Michael Scherer-Lorenzen
-
Article
| Open Access Single cell analyses reveal contrasting life strategies of the two main nitrifiers in the ocean
Single cell analyses reveal contrasting life strategies of the two main nitrifiers in the ocean
Ammonia oxidizing archaea and Nitrospinae are the main known nitrifiers in the ocean, but the much greater abundance of the former is puzzling. Here, the authors show that differences in mortality, rather than thermodynamics, cell size or biomass yield, explain the discrepancy, without the need to invoke yet undiscovered, abundant nitrite oxidizers.
- Katharina Kitzinger
- , Hannah K. Marchant
- & Marcel M. M. Kuypers
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Agroecology
- Animal migration
- Behavioural ecology
- Biodiversity
- Biogeochemistry
- Biogeography
- Biooceanography
- Boreal ecology
- Climate-change ecology
- Community ecology
- Conservation biology
- Ecological epidemiology
- Ecological genetics
- Ecological modelling
- Ecological networks
- Ecophysiology
- Ecosystem ecology
- Ecosystem services
- Environmental economics
- Evolutionary ecology
- Fire ecology
- Forest ecology
- Forestry
- Freshwater ecology
- Grassland ecology
- Invasive species
- Macroecology
- Microbial ecology
- Molecular ecology
- Palaeoecology
- Population dynamics
- Restoration ecology
- Riparian ecology
- Stable isotope analysis
- Theoretical ecology
- Tropical ecology
- Urban ecology
- Wetlands ecology

 Turbulent coherent structures and early life below the Kolmogorov scale
Turbulent coherent structures and early life below the Kolmogorov scale