Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid inundation of southern Florida coastline despite low relative sea-level rise rates during the late-Holocene
Rapid inundation of southern Florida coastline despite low relative sea-level rise rates during the late-Holocene
Sea-level rise threatens coastal mangroves, with global consequences for these important blue carbon sinks. Here the authors analyse four Holocene sediment cores from islands in Florida Bay and find that mangroves that comprised the South Florida coastline 4–3000 years ago rapidly transitioned to estuarine conditions, despite low rates of sea-level rise, and propose that their demise was driven by high climate variability.
- Miriam C. Jones
- , G. Lynn Wingard
- & Christopher E. Bernhardt
-
Article
| Open Access Coral bacterial community structure responds to environmental change in a host-specific manner
Coral bacterial community structure responds to environmental change in a host-specific manner
The flexibility of corals to associate with different bacteria in different environments has not been systematically investigated. Here, the authors study bacterial community dynamics for two coral species and show that bacterial community structure responds to environmental changes in a host-specific manner.
- Maren Ziegler
- , Carsten G. B. Grupstra
- & Christian R. Voolstra
-
Article
| Open Access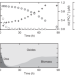 Anoxygenic photosynthesis and the delayed oxygenation of Earth’s atmosphere
Anoxygenic photosynthesis and the delayed oxygenation of Earth’s atmosphere
Competition dynamics between early Earth photosynthetic microorganisms are unclear. Here, the authors demonstrate that competition for light and nutrients between oxygenic phototrophs and Fe-based photosynthesizers in surface oceans provides a novel ecophysiological mechanism for the protracted oxygenation of Earth’s atmosphere.
- Kazumi Ozaki
- , Katharine J. Thompson
- & Christopher T. Reinhard
-
Article
| Open Access Divergent changes in the elevational gradient of vegetation activities over the last 30 years
Divergent changes in the elevational gradient of vegetation activities over the last 30 years
Climate change may lead to changes in elevational patterns of vegetation activitities. Here, the authors analyze global remotely sensing data collected during 1982–2015 to investigate the spatio-temporal dynamics of the elevational gradient in vegetation activities.
- Mengdi Gao
- , Shilong Piao
- & Ivan A. Janssens
-
Article
| Open Access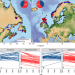 Genomic signatures and correlates of widespread population declines in salmon
Genomic signatures and correlates of widespread population declines in salmon
The Atlantic salmon has suffered widespread population declines over the last century. Here, Lehnert et al. reconstruct changes in effective population size of 172 populations based on genomic linkage information revealing mostly temperature-associated population declines with over 60% of populations in decline since 1975.
- S. J. Lehnert
- , T. Kess
- & I. R. Bradbury
-
Article
| Open Access European mushroom assemblages are darker in cold climates
European mushroom assemblages are darker in cold climates
The functions of color in fungi are not well characterized. Here, Krah and colleagues investigate the color of mushroom assemblages across Europe and show relationships with climate, nutritional mode (saprotrophic and ectomycorrhizal) and seasonality.
- Franz-Sebastian Krah
- , Ulf Büntgen
- & Claus Bässler
-
Article
| Open Access Early evidence of molariform hypsodonty in a Triassic stem-mammal
Early evidence of molariform hypsodonty in a Triassic stem-mammal
Hypsodonty is a durable pattern of dentition seen in mammals with abrasive diets. Here, Melo and colleagues describe new fossils of the stem-mammal Menadon besairiei from the Late Triassic, which show the convergent evolution of hypsodonty before mammals.
- Tomaz P. Melo
- , Ana Maria Ribeiro
- & Marina Bento Soares
-
Article
| Open Access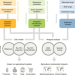 Global impacts of future cropland expansion and intensification on agricultural markets and biodiversity
Global impacts of future cropland expansion and intensification on agricultural markets and biodiversity
The increase in needs for agricultural commodities is projected to outpace the growth of farmland production globally, leading to high pressure on farming systems in the next decades. Here, the authors investigate the future impact of cropland expansion and intensification on agricultural markets and biodiversity, and suggest the need for balancing agricultural production with conservation goals.
- Florian Zabel
- , Ruth Delzeit
- & Tomáš Václavík
-
Article
| Open Access Improving risk assessments in conservation ecology
Improving risk assessments in conservation ecology
Risk estimates are important measures for the study and practice of conservation ecology. Here, the authors show that such estimates can be substantially biased, and propose an approach to improve accuracy.
- Kotaro Ono
- , Øystein Langangen
- & Nils Chr. Stenseth
-
Article
| Open Access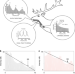 Coevolution of vocal signal characteristics and hearing sensitivity in forest mammals
Coevolution of vocal signal characteristics and hearing sensitivity in forest mammals
Sensory drive theory predicts that vocal signalling coevolves with auditory sensitivity, but empirical evidence is limited. Here, Charlton et al. show that vocal characteristics and hearing have coevolved in forest mammals, due to constraints imposed by the local signalling environment.
- Benjamin D. Charlton
- , Megan A. Owen
- & Ronald R. Swaisgood
-
Article
| Open Access Probing the active fraction of soil microbiomes using BONCAT-FACS
Probing the active fraction of soil microbiomes using BONCAT-FACS
Standard DNA-based analyses of microbial communities cannot distinguish between active microbes and dead or dormant cells. Here, Couradeau et al. use BONCAT (bioorthogonal non-canonical amino acid tagging), flow cytometry, and 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing to identify active microbial cells in soils.
- Estelle Couradeau
- , Joelle Sasse
- & Trent R. Northen
-
Article
| Open Access Regional influences on community structure across the tropical-temperate divide
Regional influences on community structure across the tropical-temperate divide
Multiple drivers maintain unique species assemblages at multiple biogeographic scales. Here, the authors show that the freezing line is a key barrier generating evolutionary differences in temperate and tropical bird communities across a steep elevational gradient in the Himalaya.
- Alexander E. White
- , Kushal K. Dey
- & Trevor D. Price
-
Article
| Open Access A Lévy expansion strategy optimizes early dune building by beach grasses
A Lévy expansion strategy optimizes early dune building by beach grasses
Random walk movement patterns with specific step size distributions are commonly associated with resource search optimization strategies in mobile organisms. Here, the authors show that clonal expansion of beach grasses follows a Lévy-type step size strategy that optimizes early dune building.
- Valérie C. Reijers
- , Koen Siteur
- & Tjisse van der Heide
-
Article
| Open Access Deterministic processes structure bacterial genetic communities across an urban landscape
Deterministic processes structure bacterial genetic communities across an urban landscape
Disease transmission is particularly complex at the human-livestock-wildlife interface. Here the authors sample E. coli from wild birds near households in Nairobi and show that antimicrobial resistance gene diversity is correlated with human and lifestock density, while virulence gene diversity is correlated with avian species richness.
- J. M. Hassell
- , M. J. Ward
- & E. M. Fèvre
-
Article
| Open Access Convergent eusocial evolution is based on a shared reproductive groundplan plus lineage-specific plastic genes
Convergent eusocial evolution is based on a shared reproductive groundplan plus lineage-specific plastic genes
Eusocial caste systems have evolved independently multiple times. Here, Warner et al. investigate the amount of shared vs. lineage-specific genes involved in the evolution of caste in pharaoh ants and honey bees by comparing transcriptomes across tissues, developmental stages, and castes.
- Michael R. Warner
- , Lijun Qiu
- & Timothy A. Linksvayer
-
Article
| Open Access Functional traits and phenotypic plasticity modulate species coexistence across contrasting climatic conditions
Functional traits and phenotypic plasticity modulate species coexistence across contrasting climatic conditions
The response of traits and their plasticity to different environments within plant communities is incompletely understood. Here, the authors use field experiments under two climatic conditions to describe the dynamic relationship between ten annual plant species in association with 19 functional traits.
- Ignacio M. Pérez-Ramos
- , Luis Matías
- & Óscar Godoy
-
Article
| Open Access Feather moult and bird appearance are correlated with global warming over the last 200 years
Feather moult and bird appearance are correlated with global warming over the last 200 years
Most passerine bird species replace part of their plumage within the first year of life. Here, using data from 4,012 individuals of 19 species, Kiat et al. find that the extent of post-juvenile moult has increased over the past 212 years and this correlated with the global temperature increase in this period.
- Y. Kiat
- , Y. Vortman
- & N. Sapir
-
Article
| Open Access Phylogenetic conservation of bacterial responses to soil nitrogen addition across continents
Phylogenetic conservation of bacterial responses to soil nitrogen addition across continents
Developing a predictive understanding of bacterial community responses to environmental change is an ongoing challenge. Here, Isobe et al. reanalyze data on soil microbial responses to nitrogen addition across 5 continents, finding that responses are predictable based on phylogeny.
- Kazuo Isobe
- , Steven D. Allison
- & Jennifer B. H. Martiny
-
Article
| Open Access Fruit scent and observer colour vision shape food-selection strategies in wild capuchin monkeys
Fruit scent and observer colour vision shape food-selection strategies in wild capuchin monkeys
We know little about the relative contributions of visual and olfactory senses for wild, frugivorous mammals. Here, the authors show that in capuchin monkeys, frequency of olfactory evaluation of fruits is higher when scent production increases with ripening, and among monkeys with red-green colorblindness.
- Amanda D. Melin
- , Omer Nevo
- & Shoji Kawamura
-
Article
| Open Access No trends in spring and autumn phenology during the global warming hiatus
No trends in spring and autumn phenology during the global warming hiatus
A global warming hiatus occurred during 1998 and 2012 but its effects on phenology are unclear. Here the authors examine the trends in spring and autumn phenology in the northern hemisphere and the effects of the warming hiatus and show that phenology change rate in the northern hemisphere slowed down during the warming hiatus.
- Xufeng Wang
- , Jingfeng Xiao
- & Rachhpal S. Jassal
-
Review Article
| Open Access The reach of gene–culture coevolution in animals
The reach of gene–culture coevolution in animals
The reciprocal interaction between genetic and cultural evolution is well recognised in humans. Here, Whitehead and colleagues review the growing body of evidence that culture is also a major driver of both neutral and adaptive genetic evolution in non-human animals.
- Hal Whitehead
- , Kevin N. Laland
- & Andrew Whiten
-
Article
| Open Access A few Ascomycota taxa dominate soil fungal communities worldwide
A few Ascomycota taxa dominate soil fungal communities worldwide
Soil fungi play essential roles in ecosystems worldwide. Here, the authors sequence and analyze 235 soil samples collected from across the globe, and identify dominant fungal taxa and their associated environmental attributes.
- Eleonora Egidi
- , Manuel Delgado-Baquerizo
- & Brajesh K. Singh
-
Article
| Open Access Inter-outbreak stability reflects the size of the susceptible pool and forecasts magnitudes of seasonal epidemics
Inter-outbreak stability reflects the size of the susceptible pool and forecasts magnitudes of seasonal epidemics
Directly measuring the size of the susceptible population is usually unfeasible before dengue outbreaks. Here, the authors show that the stability of low-incidence periods provides a proxy measure, which can be estimated from incidence data, and show its utility for forecasting outbreaks.
- Martin Rypdal
- & George Sugihara
-
Article
| Open Access Synergistic and antagonistic impacts of suspended sediments and thermal stress on corals
Synergistic and antagonistic impacts of suspended sediments and thermal stress on corals
Multiple aspects of anthropogenic change threaten coral reefs. Here, the authors show that bleaching associated with thermal stress was low when local dredging released moderate amounts of suspended sediments, but high sediment loads coupled with high temperatures had synergistic negative effects on coral survival.
- Rebecca Fisher
- , Pia Bessell-Browne
- & Ross Jones
-
Article
| Open Access African elephant poaching rates correlate with local poverty, national corruption and global ivory price
African elephant poaching rates correlate with local poverty, national corruption and global ivory price
Ivory poaching has decreased since 2011, and understanding why may help to further prevent losses to elephant populations. Here the authors show correlations between poaching rates and poverty and corruption-related indices, and proxies of ivory demand.
- Severin Hauenstein
- , Mrigesh Kshatriya
- & Colin M. Beale
-
Article
| Open Access The stability of multitrophic communities under habitat loss
The stability of multitrophic communities under habitat loss
Habitat loss could affect ecological communities in variable ways depending on its structure. Here, the authors show that contiguous rather than random loss is more damaging to the stability of multitrophic communities, regardless of the fraction of mutualistic interactions within the community.
- Chris McWilliams
- , Miguel Lurgi
- & Daniel Montoya
-
Article
| Open Access Increasing species sampling in chelicerate genomic-scale datasets provides support for monophyly of Acari and Arachnida
Increasing species sampling in chelicerate genomic-scale datasets provides support for monophyly of Acari and Arachnida
Morphological and molecular data have led to conflicting phylogenetic hypotheses for the Chelicerata. Here, the authors reconstruct the phylogeny of the Chelicerata using genomic-scale datasets, finding evidence for a monophyletic Acari and a single terrestrialisation of Arachnida.
- Jesus Lozano-Fernandez
- , Alastair R. Tanner
- & Davide Pisani
-
Article
| Open Access Projected losses of global mammal and bird ecological strategies
Projected losses of global mammal and bird ecological strategies
Animal diversity, measured in numbers of species, is rapidly being lost to extinction. Here, Cooke et al. show that the diversity of ecological strategies employed by land mammals and birds is also expected to narrow towards small, fecund, insect-eating generalists with fast-paced life histories.
- Robert S. C. Cooke
- , Felix Eigenbrod
- & Amanda E. Bates
-
Article
| Open Access The composition of British bird communities is associated with long-term garden bird feeding
The composition of British bird communities is associated with long-term garden bird feeding
Garden bird feeding is a prolific human activity that provides a reliable foraging opportunity to wild birds. Here the authors use a 40-year data set to show that large-scale restructuring of garden bird communities and growth in urban bird populations can be linked to changing feeding practices.
- Kate E. Plummer
- , Kate Risely
- & Gavin M. Siriwardena
-
Article
| Open Access Artisanal fish fences pose broad and unexpected threats to the tropical coastal seascape
Artisanal fish fences pose broad and unexpected threats to the tropical coastal seascape
Artisanal fish fences are used for fishing along many tropical coastlines. Here, Exton et al. examine the impact footprint of artisanal fish fences, showing that they are highly non-selective, cause direct harm across the tropical seascape, disrupt ecological connectivity and create social conflict.
- Dan A. Exton
- , Gabby N. Ahmadia
- & David J. Smith
-
Article
| Open Access Elevational differences in hydrogeomorphic disturbance regime influence sediment residence times within mountain river corridors
Elevational differences in hydrogeomorphic disturbance regime influence sediment residence times within mountain river corridors
Extreme climatic events and wildfires can potentially influence sediment residence times in rivers, although the effect is not clear. Here, the authors present radiocarbon ages to show mountain streams as stable retentive reservoirs poised to change under shifting hydrologic and fire regimes.
- Nicholas A. Sutfin
- & Ellen Wohl
-
Article
| Open Access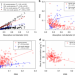 Nonlinearity of root trait relationships and the root economics spectrum
Nonlinearity of root trait relationships and the root economics spectrum
Kong et al. use a global trait dataset of 800 plant species to examine the root economics spectrum in relation to root diameter, tissue density and root nitrogen concentration. Nonlinear trait relationships were observed, suggesting allometry-based nonlinearity in root trait relationships.
- Deliang Kong
- , Junjian Wang
- & Yulong Feng
-
Article
| Open Access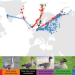 Stochastic simulations reveal few green wave surfing populations among spring migrating herbivorous waterfowl
Stochastic simulations reveal few green wave surfing populations among spring migrating herbivorous waterfowl
The green wave hypothesis is often considered a key driver of spring migration in avian herbivores. Here the authors employ a multispecies comparison and find that migration did not track the green wave better than simulated stochastic migrations.
- Xin Wang
- , Lei Cao
- & Ran Nathan
-
Article
| Open Access Limited capacity of tree growth to mitigate the global greenhouse effect under predicted warming
Limited capacity of tree growth to mitigate the global greenhouse effect under predicted warming
Fertilization under greenhouse warming conditions is expected to accelerate tree growth and potentially increase the biological storage of CO2. Here the authors analyse ring width measurements from 1768 conifers from the Spanish and Russian mountains and demonstrate that longevity requires slow growth rates at least in mountainous regions.
- Ulf Büntgen
- , Paul J. Krusic
- & Christian Körner
-
Article
| Open Access Mortality causes universal changes in microbial community composition
Mortality causes universal changes in microbial community composition
Environmental stress can affect the outcome of ecological competition. Here, the authors use theory and experiments with a synthetic microbial community to show that a tradeoff between growth rate and competitive ability determines which species prevails when the population faces variable mortality rates.
- Clare I. Abreu
- , Jonathan Friedman
- & Jeff Gore
-
Article
| Open Access Microbial coexistence through chemical-mediated interactions
Microbial coexistence through chemical-mediated interactions
The drivers of coexistence between species with different growth rates are of interest in both ecology and applied microbial science. The authors show, via modelling, that species interactions moderated by consumption or degradation of chemicals can allow coexistence.
- Lori Niehaus
- , Ian Boland
- & Babak Momeni
-
Article
| Open Access The ecological drivers of variation in global language diversity
The ecological drivers of variation in global language diversity
Could similar ecological and biogeographic drivers explain the distributions of biological diversity and human cultural diversity? The authors explore ecological correlates of human language diversity, finding strong support for a role of high year-round productivity but less support for landscape features.
- Xia Hua
- , Simon J. Greenhill
- & Lindell Bromham
-
Article
| Open Access Social-ecological alignment and ecological conditions in coral reefs
Social-ecological alignment and ecological conditions in coral reefs
The relationships between people can have important consequences for the systems they depend on. Here the authors show that when coral reef fishers face commons dilemmas, the formation of cooperative communication with competitors can lead to positive gains in reef fish biomass and functional richness.
- Michele L. Barnes
- , Örjan Bodin
- & Nicholas A. J. Graham
-
Article
| Open Access Coral carbon isotope sensitivity to growth rate and water depth with paleo-sea level implications
Coral carbon isotope sensitivity to growth rate and water depth with paleo-sea level implications
Rising anthropogenic CO2 levels in the atmosphere are resulting in ocean acidification which may impact coral growth rates. Here, the authors quantify the relationship between water depth and δ13C compositions of South Pacific corals from the pre-industrial era, and their results should lead to improvements in the precision of sea level reconstructions using fossil corals.
- Braddock K. Linsley
- , Robert B. Dunbar
- & Gerard M. Wellington
-
Article
| Open Access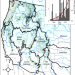 Four-fold increase in solar forcing on snow in western U.S. burned forests since 1999
Four-fold increase in solar forcing on snow in western U.S. burned forests since 1999
The impacts of forest fire activity in the western US on snow melt are poorly quantified. Here the authors use satellite and field-based observations to document a four-fold increase in the solar forcing on snow in western burned forests from 1999 to 2018.
- Kelly E. Gleason
- , Joseph R. McConnell
- & Wendy M. Calvin
-
Article
| Open Access Meta-analytic evidence that sexual selection improves population fitness
Meta-analytic evidence that sexual selection improves population fitness
Sexual selection has the potential to either increase or decrease absolute fitness. Here, Cally et al. perform a meta-analysis of 65 experimental evolution studies and find that sexual selection on males tends to increase fitness, especially in females evolving under stressful conditions.
- Justin G. Cally
- , Devi Stuart-Fox
- & Luke Holman
-
Article
| Open Access Light-dependent grazing can drive formation and deepening of deep chlorophyll maxima
Light-dependent grazing can drive formation and deepening of deep chlorophyll maxima
Previous work on the mechanisms responsible for the formation of deep chlorophyll maxima (DCM) has focused on phytoplankton physiology and behaviour. Here the authors used mathematical models informed by laboratory grazing studies to show that microzooplankton has a mechanism that can reduce phytoplankton biomass but allows accumulation at depth.
- Holly V. Moeller
- , Charlotte Laufkötter
- & Matthew D. Johnson
-
Article
| Open Access Water quality improvements offset the climatic debt for stream macroinvertebrates over twenty years
Water quality improvements offset the climatic debt for stream macroinvertebrates over twenty years
Both climate change and environmental degradation pose harm to freshwaters. Here the authors find that macroinvertebrate communities in England and Wales maintained equilibrium with the environment from 1991 to 2011, and attribute this to water quality improvements offsetting rising temperatures.
- Ian P. Vaughan
- & Nicholas J. Gotelli
-
Article
| Open Access Bacterial chemotaxis in a microfluidic T-maze reveals strong phenotypic heterogeneity in chemotactic sensitivity
Bacterial chemotaxis in a microfluidic T-maze reveals strong phenotypic heterogeneity in chemotactic sensitivity
Chemotaxis is usually considered as a trait of a species or population. Here, the authors use a microfluidics device to reveal that clonal E. coli show individual variation in a key aspect of chemotactic behavior.
- M. Mehdi Salek
- , Francesco Carrara
- & Roman Stocker
-
Article
| Open Access Low yield and abiotic origin of N2O formed by the complete nitrifier Nitrospira inopinata
Low yield and abiotic origin of N2O formed by the complete nitrifier Nitrospira inopinata
Ammonia-oxidizing bacteria and archaea are major producers of the gases nitrous oxide and nitric oxide. Here, Kits et al. show that a complete ammonia-oxidizing (comammox) bacterium emits nitrous oxide at levels that are comparable to those produced by ammonia-oxidizing archaea.
- K. Dimitri Kits
- , Man-Young Jung
- & Holger Daims
-
Article
| Open Access Genetics and evidence for balancing selection of a sex-linked colour polymorphism in a songbird
Genetics and evidence for balancing selection of a sex-linked colour polymorphism in a songbird
Gouldian finches have a head colour polymorphism that is also associated with physiological and behavioural differentiation. Here, the authors map this colour polymorphism to a putative regulatory region for follistatin on the Z chromosome and suggest it is maintained by balancing selection.
- Kang-Wook Kim
- , Benjamin C. Jackson
- & Terry Burke
-
Article
| Open Access Metabolic potential of uncultured bacteria and archaea associated with petroleum seepage in deep-sea sediments
Metabolic potential of uncultured bacteria and archaea associated with petroleum seepage in deep-sea sediments
Little is known about the microbial ecology of the deep seabed. Here, Dong et al. predict metabolic capabilities and microbial interactions in deep seabed petroleum seeps using shotgun metagenomics, sediment geochemistry, metabolomics, and thermodynamic modelling.
- Xiyang Dong
- , Chris Greening
- & Casey R. J. Hubert
-
Article
| Open Access Optimizing the conservation of migratory species over their full annual cycle
Optimizing the conservation of migratory species over their full annual cycle
Conservation decisions to protect land used by migratory birds rely on understanding species’ dynamic habitat associations. Here the authors identify conservation scenarios needed to maintain >30% of the abundances of 117 migratory birds across the Americas, considering spatial and temporal patterns of species abundance.
- Richard Schuster
- , Scott Wilson
- & Joseph. R. Bennett
-
Article
| Open Access Closing yield gaps for rice self-sufficiency in China
Closing yield gaps for rice self-sufficiency in China
Whether or not China can be rice self-sufficient in the future is in question. Here the authors provide a spatially explicit yield-gap analysis of Chinese rice production under future scenarios, identifying priority areas for improving yields to meet demands by 2030.
- Nanyan Deng
- , Patricio Grassini
- & Shaobing Peng
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Agroecology
- Animal migration
- Behavioural ecology
- Biodiversity
- Biogeochemistry
- Biogeography
- Biooceanography
- Boreal ecology
- Climate-change ecology
- Community ecology
- Conservation biology
- Ecological epidemiology
- Ecological genetics
- Ecological modelling
- Ecological networks
- Ecophysiology
- Ecosystem ecology
- Ecosystem services
- Environmental economics
- Evolutionary ecology
- Fire ecology
- Forest ecology
- Forestry
- Freshwater ecology
- Grassland ecology
- Invasive species
- Macroecology
- Microbial ecology
- Molecular ecology
- Palaeoecology
- Population dynamics
- Restoration ecology
- Riparian ecology
- Stable isotope analysis
- Theoretical ecology
- Tropical ecology
- Urban ecology
- Wetlands ecology

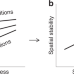 Global evidence of positive biodiversity effects on spatial ecosystem stability in natural grasslands
Global evidence of positive biodiversity effects on spatial ecosystem stability in natural grasslands