Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article |
 Northern-hemispheric differential warming is the key to understanding the discrepancies in the projected Sahel rainfall
Northern-hemispheric differential warming is the key to understanding the discrepancies in the projected Sahel rainfall
Rainfall in the Sahel region has a decadal variability related to tropical sea-surface temperatures; however, models disagree regarding future changes in rainfall. Here the authors suggest that differential warming in the northern hemisphere is key to understanding this discrepancy.
- Jong-Yeon Park
- , Jürgen Bader
- & Daniela Matei
-
Article
| Open Access Upward electrical discharges observed above Tropical Depression Dorian
Upward electrical discharges observed above Tropical Depression Dorian
Upward electrical discharges from thunderstorms were discovered recently, and only a very limited set of observations exist because they are rare and unpredictable. Here, the authors present recordings of different types of the discharge above a storm, which contradict current theories of their origins.
- Ningyu Liu
- , Nicholas Spiva
- & Steven A. Cummer
-
Article
| Open Access Abundance of live 244Pu in deep-sea reservoirs on Earth points to rarity of actinide nucleosynthesis
Abundance of live 244Pu in deep-sea reservoirs on Earth points to rarity of actinide nucleosynthesis
The build-up of short-lived nuclides in the interstellar medium tells us about production frequency and yield of heavy elements by nucleosynthesis. Wallner et al. find a low abundance of live interstellar 244Pu detected from the deep-sea floor, suggesting a rarity for r-process nucleosynthesis sites.
- A. Wallner
- , T. Faestermann
- & P. Steier
-
Article
| Open Access Size dependence of phase transitions in aerosol nanoparticles
Size dependence of phase transitions in aerosol nanoparticles
Although phase transitions are fundamental for understanding aerosol particles, current models are insufficient to explain observations at the nanoscale. Here, the authors present a method for investigating droplets, suggesting particle size is a key determinant in the phase diagram of nanoparticles.
- Yafang Cheng
- , Hang Su
- & Ulrich Pöschl
-
Article |
 Aerosol generation by raindrop impact on soil
Aerosol generation by raindrop impact on soil
Suspended dust and sea salt are currently considered to be two major sources of environmental aerosol particles. Here, Joung and Buie report another mechanism of aerosol generation from rainfall impact on porous soil surfaces, whereby elements can be delivered to the air.
- Young Soo Joung
- & Cullen R. Buie
-
Article |
 Global pattern for the effect of climate and land cover on water yield
Global pattern for the effect of climate and land cover on water yield
The effects of forests on water yield are uncertain, with some studies indicating that increased evapotranspiration reduces water yield and other showing that forests increase it. Here, the authors analyse published data to settle this debate, finding that afforestation has a positive effect on water yield.
- Guoyi Zhou
- , Xiaohua Wei
- & Yongxian Su
-
Article |
 A very long-term transient event preceding the 2011 Tohoku earthquake
A very long-term transient event preceding the 2011 Tohoku earthquake
Slow slip events have been observed in different subduction zones, but their relationship to megathrust earthquakes remains elusive. Here, the authors postulate that a transient event may have led to the 2011 Tohoku earthquake as the hypocentre falls within a zone of positive Coloumb stress change.
- Yusuke Yokota
- & Kazuki Koketsu
-
Article |
 Southern Hemisphere control on Australian monsoon variability during the late deglaciation and Holocene
Southern Hemisphere control on Australian monsoon variability during the late deglaciation and Holocene
The response of the Australian monsoon to deglacial climate change remains largely unknown due to a dearth of high-resolution climate records. Here, the authors reconstruct precipitation variability in four marine sediment cores and show that Australian monsoon variability closely followed Antarctic warming.
- Wolfgang Kuhnt
- , Ann Holbourn
- & Manfred Mudelsee
-
Article |
 Corals concentrate dissolved inorganic carbon to facilitate calcification
Corals concentrate dissolved inorganic carbon to facilitate calcification
Understanding how corals may react to ocean acidification is hampered due to a lack of insight into how corals source the inorganic carbon required to build their skeletons. Here, the authors show that corals are able to concentrate dissolved carbon and that bicarbonate contributes to the carbon pool used to build their skeletons.
- Nicola Allison
- , Itay Cohen
- & Alexander W. Tudhope
-
Article |
 231Pa/230Th evidence for a weakened but persistent Atlantic meridional overturning circulation during Heinrich Stadial 1
231Pa/230Th evidence for a weakened but persistent Atlantic meridional overturning circulation during Heinrich Stadial 1
Marine sedimentary 231Pa/230Th ratios are considered a promising tool for the investigation of past modes of ocean circulation. Here, the authors present a compilation of new and existing Atlantic sedimentary 231Pa/230Th ratios and interpret these data in the context of abrupt cooling during Heinrich Stadial 1.
- Louisa I. Bradtmiller
- , Jerry F. McManus
- & Laura F. Robinson
-
Article
| Open Access Partial melting of deeply subducted eclogite from the Sulu orogen in China
Partial melting of deeply subducted eclogite from the Sulu orogen in China
Natural examples of eclogite-derived migmatite were previously unknown. Here, the authors show evidence of high-pressure melting of eclogite in the Sulu orogen of China, and suggest the melts represent an exhumed example of flow channels in the lower crust, possibly a source of syn-exhumation magmas.
- Lu Wang
- , Timothy M. Kusky
- & Jianmin Fu
-
Article |
 Propagation style controls lava–snow interactions
Propagation style controls lava–snow interactions
How volcanoes and the cryosphere interact is of interest for understanding hazard mitigation at ice-clad volcanoes and for paleoclimate studies. Here, the authors provide quantitative details from an eruption in Kamchatka, demonstrating that two kinds of lava, ′a′a and pahoehoe, produced different snowpack responses.
- B. R. Edwards
- , A. Belousov
- & M. Belousova
-
Article
| Open Access Impact of oceanic-scale interactions on the seasonal modulation of ocean dynamics by the atmosphere
Impact of oceanic-scale interactions on the seasonal modulation of ocean dynamics by the atmosphere
Oceanic mesoscale eddies are thought to derive from internal ocean instability. Here, the authors present a high-resolution simulation of the North Pacific Ocean and show that mesoscale eddies are instead sustained by small-scale mixed-layer instabilities triggered by atmospheric forcing in winter.
- Hideharu Sasaki
- , Patrice Klein
- & Yoshikazu Sasai
-
Article |
 On the conditions of magma mixing and its bearing on andesite production in the crust
On the conditions of magma mixing and its bearing on andesite production in the crust
Andesites are a large part of the continental crust, but their origins remain enigmatic. Here, the authors update older mixing models via high-temperature experiments and thermal calculations, showing that homogeneous mixtures are only possible with high mafic fractions and during high magma flux.
- Mickael Laumonier
- , Bruno Scaillet
- & Laurent Arbaret
-
Article |
 Geochemistry of silicate-rich rocks can curtail spreading of carbon dioxide in subsurface aquifers
Geochemistry of silicate-rich rocks can curtail spreading of carbon dioxide in subsurface aquifers
Carbon sequestration will be vital in mitigating future climate change, and understanding how CO2 behaves in aquifers is important for developing technologies. Here, the authors suggest that silicate-rich rocks inhibit the transport of CO2, which may have consequences for future engineered storage facilities.
- S. S. S. Cardoso
- & J. T. H. Andres
-
Article |
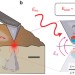 Nanoscale infrared spectroscopy as a non-destructive probe of extraterrestrial samples
Nanoscale infrared spectroscopy as a non-destructive probe of extraterrestrial samples
Infrared spectral mapping offers the non-destructive analyses of samples; however, the spatial resolution is restricted to >10 microns. Here, the authors present a new infrared technique capable of sub-micron scale mineral identification, demonstrated using a chondrule and a cometary dust grain.
- Gerardo Dominguez
- , A. S. Mcleod
- & D. N. Basov
-
Article
| Open Access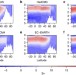 Early warning signals of Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation collapse in a fully coupled climate model
Early warning signals of Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation collapse in a fully coupled climate model
The ability to predict a potential collapse of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation is widely desired, but problematic. Here, using a fully coupled atmosphere-ocean general circulation mode, the authors show that early warning signs can be detected 250 years in advance.
- Chris A. Boulton
- , Lesley C. Allison
- & Timothy M. Lenton
-
Article |
 Isotopic constraints on biogeochemical cycling of copper in the ocean
Isotopic constraints on biogeochemical cycling of copper in the ocean
Trace elements and their isotopes are powerful as tracers in the modern ocean and proxies for oceans of the past, although there are limited data for elements such as copper. Here, the authors present copper isotope data from both seawater and rainwater, providing insight into marine biogeochemical cycling.
- Shotaro Takano
- , Masaharu Tanimizu
- & Yoshiki Sohrin
-
Article |
 A 2,000-year reconstruction of the rain-fed maize agricultural niche in the US Southwest
A 2,000-year reconstruction of the rain-fed maize agricultural niche in the US Southwest
Palaeoclimate research often focuses on continental, hemispheric and global scales, neglecting the local-scale changes of most importance to human adaptation. Here, the authors propose a new tree-ring-based methodology, capable of producing high-frequency, highly local climate-field reconstructions.
- R. Kyle Bocinsky
- & Timothy A. Kohler
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time earthquake monitoring using a search engine method
Real-time earthquake monitoring using a search engine method
Reporting earthquakes, including location and focal mechanism, in real time is a challenge. Here, the authors present an approach similar to a web search engine, estimating earthquake parameters by searching a large database within a second, which will potentially enable early warning systems.
- Jie Zhang
- , Haijiang Zhang
- & Xiong Zhang
-
Article |
 The emergence of modern sea ice cover in the Arctic Ocean
The emergence of modern sea ice cover in the Arctic Ocean
Reconstructing past sea ice coverage in the Arctic is important for future climate predictions. Here, the authors present a new sea ice record from the Eurasian sector of the Arctic Ocean and report that Arctic sea ice reached its modern winter maximum for the first time 2.6 million years ago.
- Jochen Knies
- , Patricia Cabedo-Sanz
- & Antoni Rosell-Melé
-
Article |
 Erosion influences the seismicity of active thrust faults
Erosion influences the seismicity of active thrust faults
Deep tectonic processes are considered to be responsible for stress loading of faults over a seismic cycle. Here, the authors use a mechanical model to demonstrate that erosion also significantly influences the stress loading of faults on this short time scale, potentially leading to fault failure and earthquakes.
- Philippe Steer
- , Martine Simoes
- & J. Bruce H. Shyu
-
Article
| Open Access Permafrost thawing as a possible source of abrupt carbon release at the onset of the Bølling/Allerød
Permafrost thawing as a possible source of abrupt carbon release at the onset of the Bølling/Allerød
Ice core records show evidence for an abrupt, and thus far unexplained, increase in atmospheric CO2 levels ~14,600 years ago. Here, the authors combine ice core data, a precisely dated decline in atmospheric 14C and numerical simulations, and propose thawing permafrost as a possible source of this event.
- Peter Köhler
- , Gregor Knorr
- & Edouard Bard
-
Review Article |
 Global potential of biospheric carbon management for climate mitigation
Global potential of biospheric carbon management for climate mitigation
Carbon mitigation is considered an important and viable pathway towards climate stabilization, but competition for land is high. Here, Canadell and Schulze consider the sustainable implementation of a number of land-based biological carbon mitigation activities and assess the carbon savings achievable by 2050.
- Josep G. Canadell
- & E. Detlef Schulze
-
Article
| Open Access Improving farming practices reduces the carbon footprint of spring wheat production
Improving farming practices reduces the carbon footprint of spring wheat production
Wheat is the world’s second most favoured food source, yet its production has climatic consequences. Here the authors quantify the carbon footprint of wheat production systems and evaluate potential alternative farming practices, with a reduced negative impact on climate.
- Yantai Gan
- , Chang Liang
- & Robert P. Zentner
-
Article |
 Seismic reflection data support episodic and simultaneous growth of the Tibetan Plateau since 25 Myr
Seismic reflection data support episodic and simultaneous growth of the Tibetan Plateau since 25 Myr
How the Tibetan Plateau arrived at its present size and elevation remains a topic of debate. Here, the authors use drill-hole and seismic data from the Tarim basin and conclude that plateau extension was episodic and synchronous along eastern and northern margins, likely occurring via brittle thickening of the upper crust.
- Xiao-Dian Jiang
- & Zheng-Xiang Li
-
Article
| Open Access Extending medium-range predictability of extreme hydrological events in Europe
Extending medium-range predictability of extreme hydrological events in Europe
Extreme winter flooding has caused devastation across Europe in recent years, highlighting the need for improved forecasts. Here, the authors show that the use of water vapour transport, rather than precipitation in weather prediction models, can extend the forecast horizon by as much as 3 days.
- David A. Lavers
- , Florian Pappenberger
- & Ervin Zsoter
-
Article |
 High-pressure radiative conductivity of dense silicate glasses with potential implications for dark magmas
High-pressure radiative conductivity of dense silicate glasses with potential implications for dark magmas
Understanding of the Earth’s interior requires insight into the thermal properties of silicate melts under high pressure. Here, the authors present high-pressure spectroscopic measurements of iron-enriched dense silicate glasses and infer the radiative conductivity of dense melts at the core–mantle boundary.
- Motohiko Murakami
- , Alexander F. Goncharov
- & Craig R. Bina
-
Article
| Open Access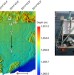 Eruption of a deep-sea mud volcano triggers rapid sediment movement
Eruption of a deep-sea mud volcano triggers rapid sediment movement
Submarine mud volcanoes are difficult to observe from the sea surface and previous recordings at depth have been short term. Here, the authors provide the first long-term monitoring from Håkon Mosby and suggest that mud volcanoes may be more important to the global methane budget than previously thought.
- Tomas Feseker
- , Antje Boetius
- & Dirk de Beer
-
Article |
 Orbital Asian summer monsoon dynamics revealed using an isotope-enabled global climate model
Orbital Asian summer monsoon dynamics revealed using an isotope-enabled global climate model
Asian speleothem δ18O records are widely used as a proxy for summer monsoon intensity, but their validity has been questioned. Here, the authors evaluate their validity using a 150,000-year transient simulation from an isotope-enabled global climate model.
- Thibaut Caley
- , Didier M. Roche
- & Hans Renssen
-
Article |
 Tracing carbonate–silicate interaction during subduction using magnesium and oxygen isotopes
Tracing carbonate–silicate interaction during subduction using magnesium and oxygen isotopes
Carbon fluxes between the Earth’s surface and its interior are ultimately controlled by subduction of carbonated eclogites and carbonates, although the processes are not well understood. Here, the authors demonstrate that coupled Mg and O isotopic studies may help us to trace deep carbon recycling.
- Shui-Jiong Wang
- , Fang-Zhen Teng
- & Shu-Guang Li
-
Article |
 Oxic water column methanogenesis as a major component of aquatic CH4 fluxes
Oxic water column methanogenesis as a major component of aquatic CH4 fluxes
Aquatic methane originates in anoxic sediments and bottom waters, but some studies suggest it may also come from the oxic water column. Here, the authors experimentally confirm this hypothesis, and explore the rates, controls and biochemical pathways of oxic water methanogenesis.
- Matthew J Bogard
- , Paul A del Giorgio
- & Alison M Derry
-
Article |
 Subduction of fracture zones controls mantle melting and geochemical signature above slabs
Subduction of fracture zones controls mantle melting and geochemical signature above slabs
Subduction of fracture zones is predicted to have local geochemical and physical manifestations in volcanic arcs. Here, the authors show boron enrichment near fracture zones in some arcs and infer the processes occurring there using detailed geodynamic modelling.
- Vlad C. Manea
- , William P. Leeman
- & Guizhi Zhu
-
Article |
 Ediacaran 2,500-km-long synchronous deep continental subduction in the West Gondwana Orogen
Ediacaran 2,500-km-long synchronous deep continental subduction in the West Gondwana Orogen
The West Gondwana Orogen is a major continental collision zone exposing numerous eclogites along its strike. Here, the authors present zircon data from eclogites in Mali, Togo and NE Brazil, which indicate that continental subduction occurred simultaneously over at least 2,500 km during the Ediacaran.
- Carlos E. Ganade de Araujo
- , Daniela Rubatto
- & Miguel A. S. Basei
-
Article |
 Evidence for a weakening relationship between interannual temperature variability and northern vegetation activity
Evidence for a weakening relationship between interannual temperature variability and northern vegetation activity
Northern Hemisphere photosynthesis is thought to respond positively to temperature variations, yet the strength of this relationship may change over time. Here, using a combination of satellite data and models, the authors assess the temporal change of this relationship over the past three decades.
- Shilong Piao
- , Huijuan Nan
- & Anping Chen
-
Article
| Open Access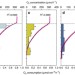 Meiofauna increases bacterial denitrification in marine sediments
Meiofauna increases bacterial denitrification in marine sediments
Excessive nutrient loading is a threat to aquatic ecosystems; however, denitrification may be key in removing large amounts of reactive nitrogen and, therefore, mitigating consequent eutrophication. Here, the authors explore how meiofauna may impact the rate of denitrification in sediments.
- S. Bonaglia
- , F. J. A Nascimento
- & V. Brüchert
-
Article
| Open Access Missing driver in the Sun–Earth connection from energetic electron precipitation impacts mesospheric ozone
Missing driver in the Sun–Earth connection from energetic electron precipitation impacts mesospheric ozone
Energetic electron precipitation (EEP) from the Earth's outer radiation belt can lead to ozone loss in the mesosphere, yet long-term variability has not been quantified. Here, the authors present satellite observations and show that on solar cycle timescales EEP causes ozone to vary by up to 34%.
- M. E. Andersson
- , P. T. Verronen
- & A. Seppälä
-
Article |
 Prediction of extreme floods in the eastern Central Andes based on a complex networks approach
Prediction of extreme floods in the eastern Central Andes based on a complex networks approach
Extreme rainfall events in the eastern Central Andes can result in substantial economic and ecological damage, yet their prediction is difficult. Here, the authors introduce the concept of network divergence and propose a general framework for the prediction of extreme events.
- N. Boers
- , B. Bookhagen
- & J. A. Marengo
-
Article |
 Ultralow viscosity of carbonate melts at high pressures
Ultralow viscosity of carbonate melts at high pressures
Carbonate melt is one of the most important materials involved in the carbon cycle of the Earth’s interior; however, its mobility is poorly understood. Here, the authors suggest that carbonate melts possess much lower viscosities than previously thought, which in turn suggest very high mobility.
- Yoshio Kono
- , Curtis Kenney-Benson
- & Craig E. Manning
-
Article |
 Carbonate-hosted methanotrophy represents an unrecognized methane sink in the deep sea
Carbonate-hosted methanotrophy represents an unrecognized methane sink in the deep sea
Methane is a significant contributor to greenhouse forcing, and determining its fluxes and reservoirs is important in understanding the methane cycle. Here, the authors investigate microbial methane oxidation in carbonates of the deep sea that represent a previously unrecognized biological sink for methane.
- Jeffrey J. Marlow
- , Joshua A. Steele
- & Victoria J. Orphan
-
Article
| Open Access Visualized effect of oxidation on magnetic recording fidelity in pseudo-single-domain magnetite particles
Visualized effect of oxidation on magnetic recording fidelity in pseudo-single-domain magnetite particles
Magnetite provides a valuable record of the Earth's geomagnetic history. Here, Almeida et al. combine electron microscopy and energy-loss spectroscopy to study the effects of in situoxidation on the magnetization fidelity and crystalline phase of pseudo-single domain magnetite grains.
- Trevor P. Almeida
- , Takeshi Kasama
- & Rafal E. Dunin-Borkowski
-
Article |
 Long-term carbon loss in fragmented Neotropical forests
Long-term carbon loss in fragmented Neotropical forests
Tropical forest deforestation is a major source of CO2emissions, yet potential additional emissions through the creation of forest edge areas has been largely overlooked. Here, the authors combine remote sensing and knowledge on spatial processes to estimate carbon loss due to forest fragmentation.
- Sandro Pütz
- , Jürgen Groeneveld
- & Andreas Huth
-
Article |
 Antarctic contribution to meltwater pulse 1A from reduced Southern Ocean overturning
Antarctic contribution to meltwater pulse 1A from reduced Southern Ocean overturning
The Antarctic ice sheets contribution to rising sea levels at the end of the last ice age remains a matter of debate. Here, the authors present a suite of ice-sheet modelling experiments and conclude that the retreating Antarctic ice sheet may have contributed as much as 0.7 m per century to meltwater pulse 1A.
- N. R. Golledge
- , L. Menviel
- & R. H. Levy
-
Article |
 Sensitive response of the Greenland Ice Sheet to surface melt drainage over a soft bed
Sensitive response of the Greenland Ice Sheet to surface melt drainage over a soft bed
The delivery of meltwater to the base of the Greenland Ice Sheet has been shown to regulate ice flow, yet the role of soft basal sediment is unknown. Here, the authors use a three-dimensional ice sheet model to assess the impact of seasonal meltwater delivery on subglacial sediment shear strength and ice flow.
- M. Bougamont
- , P. Christoffersen
- & S. P. Carter
-
Article |
 Sea-level variability over five glacial cycles
Sea-level variability over five glacial cycles
Detailed sea-level records beyond ~150,000 years ago are limited. Here, the authors present a radiometrically constrained sea-level record from the Red Sea, spanning five glacial cycles and examine sea-level rise rates and the effects of past global ice-volume changes on monsoon intensity.
- K. M. Grant
- , E. J. Rohling
- & F. Williams
-
Article |
 How shorter black carbon lifetime alters its climate effect
How shorter black carbon lifetime alters its climate effect
Unlike most aerosols, black carbon absorbs solar radiation, potentially warming the atmosphere, yet its total climate effect remains uncertain. Here, the authors use a chemical transport and global circulation model to investigate the impact of black carbon emissions on global, annual mean radiative forcing.
- Øivind Hodnebrog
- , Gunnar Myhre
- & Bjørn H. Samset
-
Article |
 Real-time QEXAFS spectroscopy measures rapid precipitate formation at the mineral–water interface
Real-time QEXAFS spectroscopy measures rapid precipitate formation at the mineral–water interface
Geochemical reactions at the mineral–water interface are complicated, yet a molecular-scale understanding of their kinetics is critical. Here, Siebecker et al.conduct real-time measurements in a flow-through cell to show the rapid formation of layered double hydroxides at a clay mineral surface.
- Matthew Siebecker
- , Wei Li
- & Donald Sparks
-
Article |
 Subduction of the oceanic Hikurangi Plateau and its impact on the Kermadec arc
Subduction of the oceanic Hikurangi Plateau and its impact on the Kermadec arc
Large igneous province subduction is a rare process with many unknowns. Timm et al.present geochemical and geophysical data providing insights into the Hikurangi Plateau subduction and its impact on arc volcanism, identifying a missing piece of the Ontong Java–Manihiki–Hikurangi super plateau.
- Christian Timm
- , Bryan Davy
- & John A. Gamble
-
Article |
 Persistence of pressure patterns over North America and the North Pacific since AD 1500
Persistence of pressure patterns over North America and the North Pacific since AD 1500
Synoptic-scale atmospheric pressure patterns control moisture delivery and thus drought occurrence across western North America, yet long-term records are lacking. Here, the authors use a novel combination of tree-ring data and self-organizing maps to reconstruct and analyse pressure patterns since AD 1500.
- Erika K. Wise
- & Matthew P. Dannenberg

 Tropical Atlantic temperature seasonality at the end of the last interglacial
Tropical Atlantic temperature seasonality at the end of the last interglacial