Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Evolution of masting in plants is linked to investment in low tissue mortality
Evolution of masting in plants is linked to investment in low tissue mortality
Factors behind interspecific variation in masting are unclear. Here, the authors show that, in 517 species of terrestrial perennial plants, masting is more frequent in species that have high stem tissue density, suggesting that stronger stress resistance may buffer against missed reproductive opportunities.
- Valentin Journé
- , Andrew Hacket-Pain
- & Michał Bogdziewicz
-
Article
| Open Access Synthesizing evidence for the external cycling of NOx in high- to low-NOx atmospheres
Synthesizing evidence for the external cycling of NOx in high- to low-NOx atmospheres
External cycling regenerates nitrogen oxides from the NOx oxidative reservoir, NOz. Aircraft observations reveal NOx external cycling compensates for NOx aging, sustaining NOx distribution and production of OH radicals far from NOx emission sources
- Chunxiang Ye
- , Xianliang Zhou
- & Shaojie Song
-
Article
| Open Access Changes in orogenic style and surface environment recorded in Paleoproterozoic foreland successions
Changes in orogenic style and surface environment recorded in Paleoproterozoic foreland successions
Two different styles of orogenesis during the Neoarchean and Paleoproterozoic are recorded in the depositional-to-deformational evolution of the orogenic foreland of the North China Craton, and would have differently changed the surface environment.
- Bo Huang
- , Man Liu
- & Qunye Qian
-
Article
| Open Access Energy transfer of imbalanced Alfvénic turbulence in the heliosphere
Energy transfer of imbalanced Alfvénic turbulence in the heliosphere
How and via which mechanism the energy transfers between scales in imbalanced Alfvénic turbulence is an open question. Here, the authors show that the energy transfer of imbalanced Alfvénic turbulence is completed by coherent interactions between Alfvén waves and co-propagating anomalous fluctuations.
- Liping Yang
- , Jiansen He
- & Ziqi Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Higher Antarctic ice sheet accumulation and surface melt rates revealed at 2 km resolution
Higher Antarctic ice sheet accumulation and surface melt rates revealed at 2 km resolution
High-resolution 2-km Antarctic maps reveal higher snowfall and surface melt than low-resolution products, reconciling satellite-observed ice sheet mass change. Projected higher surface melt near grounding lines threatens future ice shelf stability.
- Brice Noël
- , J. Melchior van Wessem
- & Michiel R. van den Broeke
-
Article
| Open Access Vertical tearing of subducting plates controlled by geometry and rheology of oceanic plates
Vertical tearing of subducting plates controlled by geometry and rheology of oceanic plates
Vertical tearing promotes continuous segmentation of subducting plates, but its dynamics and physical controls remain debated. This work indicates that trench geometry and plate rheology control the self-sustained process of vertical tearing.
- Yaguang Chen
- , Hanlin Chen
- & Taras Gerya
-
Article
| Open Access A fungal plant pathogen discovered in the Devonian Rhynie Chert
A fungal plant pathogen discovered in the Devonian Rhynie Chert
Here, the authors describe a pathogenic fungus from a 400-million-year-old fossil plant from the Devonian Rhynie Chert in Scotland. They use advanced imaging methods to determine that the fungus belongs to the sac fungi, the most diverse group of Fungi today.
- Christine Strullu-Derrien
- , Tomasz Goral
- & David L. Hawksworth
-
Article
| Open Access Volcaniclastic density currents explain widespread and diverse seafloor impacts of the 2022 Hunga Volcano eruption
Volcaniclastic density currents explain widespread and diverse seafloor impacts of the 2022 Hunga Volcano eruption
During the 2022 Hunga Volcano eruption, 10 km3 of seafloor material was removed, fueling long-run out seafloor density currents. These powerful currents damaged seafloor cables over a length of >100 km, reshaped the seafloor, and caused mass-mortality of seafloor life.
- Sarah Seabrook
- , Kevin Mackay
- & Michael J. M. Williams
-
Article
| Open Access Warming-induced vapor pressure deficit suppression of vegetation growth diminished in northern peatlands
Warming-induced vapor pressure deficit suppression of vegetation growth diminished in northern peatlands
Growing vapor pressure deficit inhibits vegetation growth. Here, Chen et al. combine satellite and eddy covariance data with field experiments showing that plant growth in northern peatlands is not constrained by water even in the presence of a warming-induced water pressure deficit.
- Ning Chen
- , Yifei Zhang
- & Xianwei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Demographics and risk of isolation due to sea level rise in the United States
Demographics and risk of isolation due to sea level rise in the United States
Risk of isolation is expected to disproportionately affect racial minority populations in the U.S. as sea level rise increases. Communities with more renters, older adults, and lower-income populations will also be impacted.
- Kelsea Best
- , Qian He
- & Tom Logan
-
Article
| Open Access Marine toxin domoic acid alters nitrogen cycling in sediments
Marine toxin domoic acid alters nitrogen cycling in sediments
Domoic acid, a red tide algal toxin, enhances nitrification, dissimilates nitrate reduction to ammonification in sediments, while concurrently inhibiting denitrification, anammox, and nitrogen fixation.
- Zelong Li
- , Jing Wang
- & Jingfeng Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Long-range atmospheric transport of microplastics across the southern hemisphere
Long-range atmospheric transport of microplastics across the southern hemisphere
Airborne microplastics (MPs) are observed over the Southern Ocean and Antarctica. MPs morphology is the primary factor influencing the hemispheric transport to these remote areas that may suffer increased pollution from urbanized, land-based sources.
- Qiqing Chen
- , Guitao Shi
- & Denise M. Mitrano
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying global colonization pressures of alien vertebrates from wildlife trade
Quantifying global colonization pressures of alien vertebrates from wildlife trade
This study compiled a comprehensive global database on live terrestrial vertebrate trade and used it to investigate traded alien species. The authors identify 7,780 species involved in trade globally and show that countries with greater trading power, higher incomes and larger human populations import more alien species, which emerge as hotspots for establishment richness of aliens.
- Yiming Li
- , Tim M. Blackburn
- & Siqi Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Feasible supply of steel and cement within a carbon budget is likely to fall short of expected global demand
Feasible supply of steel and cement within a carbon budget is likely to fall short of expected global demand
A new study explores the global feasible supply of steel and cement within Paris-compliant carbon budgets, explicitly considering uncertainties in the deployment of infrastructure and it shows that feasible supply may fall short of expected global demand.
- Takuma Watari
- , André Cabrera Serrenho
- & Julian Allwood
-
Article
| Open Access Diurnal temperature range as a key predictor of plants’ elevation ranges globally
Diurnal temperature range as a key predictor of plants’ elevation ranges globally
This study relates 88,000 elevation range sizes of vascular plants in 44 mountains to short-term and long-term temperature variation. The authors finding of decreasing elevation range sizes with greater diurnal temperature range supports a novel biodiversity hypothesis and indicates increased extinction risk of continental species.
- Arnaud Gallou
- , Alistair S. Jump
- & John-Arvid Grytnes
-
Article
| Open Access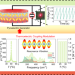 Thermoelectric coupling effect in BNT-BZT-xGaN pyroelectric ceramics for low-grade temperature-driven energy harvesting
Thermoelectric coupling effect in BNT-BZT-xGaN pyroelectric ceramics for low-grade temperature-driven energy harvesting
Pyroelectric energy harvesting has received increasing attention due to its ability to convert low-grade waste heat into electricity. Here, authors report an enhanced thermoelectric coupling BNT-BZT-xGaN pyroelectric energy harvester by facilitating resonance vibration between Ga and Ti, O atoms.
- Meng Shen
- , Kun Liu
- & Kui Yao
-
Article
| Open Access Utilizing river and wastewater as a SARS-CoV-2 surveillance tool in settings with limited formal sewage systems
Utilizing river and wastewater as a SARS-CoV-2 surveillance tool in settings with limited formal sewage systems
COVID-19 has impacted health systems unequally and widespread SARS-CoV-2 testing for community surveillance has been limited globally. This work in Malawi highlights how river and wastewater can be used to detect emerging SARS-CoV-2 waves, identify variants of concern, and provide an early warning system.
- Kayla G. Barnes
- , Joshua I. Levy
- & Nicholas Feasey
-
Article
| Open Access A physiological approach for assessing human survivability and liveability to heat in a changing climate
A physiological approach for assessing human survivability and liveability to heat in a changing climate
Research examining the ability to survive or safely live under extreme heat often oversimplifies human exposure and responses. Here, the authors apply a physiology-based approach for young and older adults to improve survivability estimates and introduce liveability in current and future climates.
- Jennifer Vanos
- , Gisel Guzman-Echavarria
- & Ollie Jay
-
Article
| Open Access A polymer tethering strategy to achieve high metal loading on catalysts for Fenton reactions
A polymer tethering strategy to achieve high metal loading on catalysts for Fenton reactions
This work reports a self-polymerization confinement strategy to develop and synthesize carbon-supported metal catalysts with high metal loading. Efficient Fenton reactivity is observed for samples containing well dispersed iron sites.
- Lixin Wang
- , Longjun Rao
- & Mingyang Xing
-
Article
| Open Access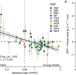 Increased photosynthesis during spring drought in energy-limited ecosystems
Increased photosynthesis during spring drought in energy-limited ecosystems
Ecosystem productivity generally declines under drought. Here, the authors show that spring droughts are linked to increases in gross primary productivity in energy-limited ecosystems in the Northern Hemisphere, and that terrestrial biosphere models tend not to capture this.
- David L. Miller
- , Sebastian Wolf
- & Trevor F. Keenan
-
Article
| Open Access Ocean warming drives rapid dynamic activation of marine-terminating glacier on the west Antarctic Peninsula
Ocean warming drives rapid dynamic activation of marine-terminating glacier on the west Antarctic Peninsula
Warm ocean waters and favourable bathymetry caused Cadman Glacier on the Antarctic Peninsula to increase speed by 94% from 2018 to 2019. This led to increased ice discharge, glacier retreat of 8 kilometres, and glacier thinning by 20 meters per year.
- Benjamin J. Wallis
- , Anna E. Hogg
- & Carlos Moffat
-
Article
| Open Access Compensating transport trends in the Drake Passage frontal regions yield no acceleration in net transport
Compensating transport trends in the Drake Passage frontal regions yield no acceleration in net transport
Time series of high spatial resolution ocean temperature, salinity and velocity across Drake Passage show that compensating trends across the frontal regions yield no acceleration in net transport over the last 15 years despite increased wind stress.
- Manuel O. Gutierrez-Villanueva
- , Teresa K. Chereskin
- & Janet Sprintall
-
Article
| Open Access Months-long seismicity transients preceding the 2023 MW 7.8 Kahramanmaraş earthquake, Türkiye
Months-long seismicity transients preceding the 2023 MW 7.8 Kahramanmaraş earthquake, Türkiye
Unique seismic transients since 2014 were detected during 8 months before the 2023 MW 7.8 Kahramanmaraş earthquake on the East Anatolian Fault. They are consistent with experiments and models of heterogeneous rupture affecting multiple fault segments.
- G. Kwiatek
- , P. Martínez-Garzón
- & M. Bohnhoff
-
Article
| Open Access Ocean fronts as decadal thermostats modulating continental warming hiatus
Ocean fronts as decadal thermostats modulating continental warming hiatus
This paper shows the inherent coupling of winter cold extremes over land and marine heatwaves in the past decade. These events are projected to recur with increased frequency, especially when ocean fronts undergo anomalous decadal warming.
- Mi-Kyung Sung
- , Soon-Il An
- & Minhee Chang
-
Article
| Open Access Thermal sensitivity of field metabolic rate predicts differential futures for bluefin tuna juveniles across the Atlantic Ocean
Thermal sensitivity of field metabolic rate predicts differential futures for bluefin tuna juveniles across the Atlantic Ocean
In this study, the authors use a dataset of stable isotope compositions of otoliths from Atlantic bluefin tuna to infer the thermal sensitivity of metabolic performance in their first year of life. They then assess the likely trajectories of tuna production until end century under differing emission scenarios in their two main spawning grounds, the western Atlantic and Mediterranean Sea.
- Clive N. Trueman
- , Iraide Artetxe-Arrate
- & Igaratza Fraile
-
Article
| Open Access Metagenomic profiles of archaea and bacteria within thermal and geochemical gradients of the Guaymas Basin deep subsurface
Metagenomic profiles of archaea and bacteria within thermal and geochemical gradients of the Guaymas Basin deep subsurface
The authors study microbial communities in hydrothermally heated, subseafloor sediment layers. They find that microbial abundance and diversity decrease with sediment depth and temperature, and provide evidence for the existence of a specialized deep, hot biosphere.
- Paraskevi Mara
- , David Geller-McGrath
- & Andreas Teske
-
Article
| Open Access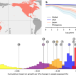 The social costs of tropical cyclones
The social costs of tropical cyclones
The estimates of the societal costs of carbon currently used for policy evaluations may be too low due to an insufficient representation of tropical cyclone damage. Accounting for them substantially increases the estimated benefits of climate change mitigation measures.
- Hazem Krichene
- , Thomas Vogt
- & Christian Otto
-
Article
| Open Access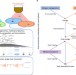 Hi-C metagenome sequencing reveals soil phage–host interactions
Hi-C metagenome sequencing reveals soil phage–host interactions
This study uses high-throughput chromosome conformation capture (Hi-C) to identify phage–host relationships in soil. By coupling Hi-C with DNA and RNA sequencing, the authors demonstrate the impact of soil drying on phage–host interactions and the downstream effects on abundances and interspecies interactions within bacterial communities.
- Ruonan Wu
- , Michelle R. Davison
- & Kirsten S. Hofmockel
-
Article
| Open Access Middle east warming in spring enhances summer rainfall over Pakistan
Middle east warming in spring enhances summer rainfall over Pakistan
In recent decades, land warming over the Middle East and a northward shift of the low-level jet in the atmosphere have led to unprecedented summer monsoon rainfall increase over Pakistan and northwestern India, areas that used to be arid to semi-arid.
- Baosheng Li
- , Lei Zhou
- & Raghu Murtugudde
-
Article
| Open Access Risk to rely on soil carbon sequestration to offset global ruminant emissions
Risk to rely on soil carbon sequestration to offset global ruminant emissions
While accounting for intrinsic differences between short- and long-lived greenhouse gases, solely relying on soil carbon sequestration in grasslands to offset warming effect of emissions from current ruminant systems is not feasible
- Yue Wang
- , Imke J. M. de Boer
- & Corina E. van Middelaar
-
Article
| Open Access Bony-fish-like scales in a Silurian maxillate placoderm
Bony-fish-like scales in a Silurian maxillate placoderm
The origin and early evolution of large scales in bony fishes and small scales in cartilaginous fishes are unclear. Here, the authors report a 425-million-year-old fish, Entelognathus, with a mosaic of scale and fin spine characters.
- Xindong Cui
- , Matt Friedman
- & Min Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Diversification of flowering plants in space and time
Diversification of flowering plants in space and time
Global spatiotemporal patterns of plant diversification are unclear. Here, the authors use a genus-level phylogeny and global distribution data for 14,244 flowering plant genera, finding a negative correlation between spatial patterns of diversification and genus diversity.
- Dimitar Dimitrov
- , Xiaoting Xu
- & Zhiheng Wang
-
Comment
| Open AccessOne Health approach at the heart of the French Committee for monitoring and anticipating health risks
Following the COVID-19 pandemic, the French government established a committee for monitoring and anticipating health risks. In this Comment, the authors describe the One Health approach taken by the committee, and outline its aims, composition, and initial actions.
- Thierry Lefrançois
- , Bruno Lina
- & Brigitte Autran
-
Article
| Open Access Surrounding greenness is associated with lower risk and burden of low birth weight in Iran
Surrounding greenness is associated with lower risk and burden of low birth weight in Iran
Quantifying well-being effects of greenness is of great importance for achieving the Global Nutrition Targets 2025 for low birth weight. Here, the authors show underlying health benefits of improved green space in lowering low birth weight risk and burden in Iran.
- Siqi Luo
- , Yaqi Wang
- & Yunquan Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Experimental mining plumes and ocean warming trigger stress in a deep pelagic jellyfish
Experimental mining plumes and ocean warming trigger stress in a deep pelagic jellyfish
The deep ocean is increasingly subjected to human-induced environmental change, but little is known about species-specific responses to stressors, including those from deep sea mining. This study shows that elevated temperatures and simulated sediment plumes cause physiological stress in a cosmopolitan deep-sea jellyfish, confirming the detrimental impact of seabed mining.
- Vanessa I. Stenvers
- , Helena Hauss
- & Henk-Jan T. Hoving
-
Article
| Open Access Potential drivers of the recent large Antarctic ozone holes
Potential drivers of the recent large Antarctic ozone holes
The record-breaking ozone holes of recent years contribute to a steady decline of mid-spring ozone in the Antarctic, contrary to signs of early-spring recovery. Changes in descending air at the core of the ozone hole might be the driver.
- Hannah E. Kessenich
- , Annika Seppälä
- & Craig J. Rodger
-
Article
| Open Access Isolation may select for earlier and higher peak viral load but shorter duration in SARS-CoV-2 evolution
Isolation may select for earlier and higher peak viral load but shorter duration in SARS-CoV-2 evolution
The COVID-19 pandemic has seen the emergence of different variants. Analyzing the evolution from the Wuhan strain to the Delta variant, clinical data reveals a fivefold increase in peak viral load and a 1.5-fold faster time to peak.
- Junya Sunagawa
- , Hyeongki Park
- & Ryo Yamaguchi
-
Article
| Open Access Double superionicity in icy compounds at planetary interior conditions
Double superionicity in icy compounds at planetary interior conditions
At high pressures, water and ammonia are known to exhibit superionic states. Here it is shown that many planetary ices (H-C-N-O compounds) exhibit a superionic state, and in some cases, a doubly superionic state, in which multiple elements diffuse simultaneously.
- Kyla de Villa
- , Felipe González-Cataldo
- & Burkhard Militzer
-
Article
| Open Access Climate warming and elevated CO2 alter peatland soil carbon sources and stability
Climate warming and elevated CO2 alter peatland soil carbon sources and stability
No inherently stable peat soil carbon. Researchers found that all molecular components of peatland soil organic carbon responded to warming and eCO2, including the components presumed to be slow cycling and stable.
- Nicholas O. E. Ofiti
- , Michael W. I. Schmidt
- & Avni Malhotra
-
Article
| Open Access Wind-driven device for cooling permafrost
Wind-driven device for cooling permafrost
This work demonstrates a wind-powered device for cooling permafrost in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau region. Composed of a windmill, mechanical clutch, and a heat exchanger with a phase change material, pilot experiments show soil temperature reduction with superior efficiency compared to traditional thermosyphons.
- Yinghong Qin
- , Tianyu Wang
- & Weixin Yuan
-
Article
| Open Access Flood insurance is a driver of population growth in European floodplains
Flood insurance is a driver of population growth in European floodplains
This study finds that flood insurance policy design affects economic development in floodplains and, consequently, flood risk in Europe. Therefore, the authors advocate for flood insurance design to be integrated in climate change adaptation policy.
- Max Tesselaar
- , W. J. Wouter Botzen
- & Jeroen C. J. H. Aerts
-
Article
| Open Access Economic valuation of temperature-related mortality attributed to urban heat islands in European cities
Economic valuation of temperature-related mortality attributed to urban heat islands in European cities
Urban heat islands have the greatest acute impacts on human mortality risk during extreme heat. However, protracted cold seasons result in greater annually integrated protective effects in most European cities under the current climate.
- Wan Ting Katty Huang
- , Pierre Masselot
- & Gabriele Manoli
-
Article
| Open Access Deep-sea origin and depth colonization associated with phenotypic innovations in scleractinian corals
Deep-sea origin and depth colonization associated with phenotypic innovations in scleractinian corals
Scleractinian corals are important in both shallow and deep ecosystems. Here, the authors use global spatial distribution data with a phylogenetic approach to examine directionality and speed of colonization during depth diversification, finding an offshore-onshore pattern of evolution and that depth dispersion is associated with phenotypic innovations.
- Ana N. Campoy
- , Marcelo M. Rivadeneira
- & Chris Venditti
-
Article
| Open Access Tree mortality during long-term droughts is lower in structurally complex forest stands
Tree mortality during long-term droughts is lower in structurally complex forest stands
Tree height and forest structure may both determine forest responses to drought. Here, the authors analyse highresolution airborne LIDAR data on <1 million trees during the 2012-2016 California drought and find that presence of both tall trees and structurally complex stands reduces tree mortality under drought.
- Qin Ma
- , Yanjun Su
- & Qinghua Guo
-
Article
| Open Access Fostering temporal crop diversification to reduce pesticide use
Fostering temporal crop diversification to reduce pesticide use
The potential of crop diversification to reduce pesticide use has not been quantified at large scales. Here, the authors use a national network of 1334 cropping system to identify the effect of increasing temporal crop diversity on pesticide use for 16 common crops.
- Maé Guinet
- , Guillaume Adeux
- & Nicolas Munier-Jolain
-
Article
| Open Access A neotropical perspective on the uniqueness of the Holocene among interglacials
A neotropical perspective on the uniqueness of the Holocene among interglacials
A 670,000-year vegetation and climate history from Lake Junín, Peru, showed that the last interglacial was the warmest while the current interglacial had uniquely high fire frequencies that were caused by humans; fundamentally altering the ecosystem.
- J. Schiferl
- , M. Kingston
- & M. B. Bush
-
Article
| Open Access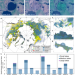 Tracking lake drainage events and drained lake basin vegetation dynamics across the Arctic
Tracking lake drainage events and drained lake basin vegetation dynamics across the Arctic
The Arctic is dotted with lakes, including thermokarst lakes highly threatened by climate change. Here, the authors investigate 35 years of lake drainage events and related vegetation trends across the Arctic, finding differences between thermokarst and non-thermokarst lake drainage events.
- Yating Chen
- , Xiao Cheng
- & Chengxin Wang
-
Article
| Open Access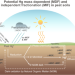 Mercury deposition and redox transformation processes in peatland constrained by mercury stable isotopes
Mercury deposition and redox transformation processes in peatland constrained by mercury stable isotopes
Mercury isotope signatures in groundwater, soil gas, solid peat, and atmosphere suggest that dark abiotic reduction of peat soil HgII to volatile Hg0 does not play a significant role in mobilizing Hg during peat mass loss
- Chuxian Li
- , Martin Jiskra
- & Kevin Bishop
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence of an upper ionospheric electric field perturbation correlated with a gamma ray burst
Evidence of an upper ionospheric electric field perturbation correlated with a gamma ray burst
Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are known to have impact on Earth’s lower ionosphere, but GRB impacts on the upper ionosphere was not observed before. Here, the authors show strong electric field variation at 500 km in the ionosphere caused by GRB221009A.
- Mirko Piersanti
- , Pietro Ubertini
- & Paolo Zuccon

 Unveiling patterns in human dominated landscapes through mapping the mass of US built structures
Unveiling patterns in human dominated landscapes through mapping the mass of US built structures