Featured
-
-
Viewpoint |
New drug approvals in oncology
Regulatory approval of new cancer medicines can have important consequence for patients with advanced-stage and/or rare cancers who have exhausted all standard-of-care therapies. However, evidence that new medicines are safe and effective can also take time to accrue, and approval with a lack of evidence may cause unnecessary harm to patients. In this Viewpoint, we asked two leading oncologists involved in clinical drug development, an expert in regulatory science and prescription drug policy, and a prominent patient advocate, to provide their opinions on the current approach to cancer drug approvals.
- Razelle Kurzrock
- , Hagop M. Kantarjian
- & Ellen V. Sigal
-
News & Views |
A balancing act: dual immune-checkpoint inhibition for oesophagogastric cancer
A minority of patients with gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma derive benefit from immune-checkpoint inhibition (ICI). In a large-cohort phase III study, the nivolumab (1 mg/kg) plus ipilimumab (3 mg/kg) arm (which was based on promising preliminary data from CheckMate 032) was closed owing to unacceptably high levels of mortality and morbidity. Our quest for better biomarkers than programmed cell death 1 ligand 1 (PD-L1) and safer dual ICI strategies must continue.
- Kazuto Harada
- , Ahmed A. F. Abdelhakeem
- & Jaffer A. Ajani
-
News & Views |
Does adjuvant ipilimumab have little adverse effect on quality of life?
Adjuvant ipilimumab is associated with an 11% improvement in 5-year overall survival in patients with high-risk melanoma, but at the cost of considerable toxicity, with half of patients discontinuing treatment owing to adverse events. An analysis of quality-of-life (QoL) outcomes, however, showed little impact of adverse effects of this treatment on QoL, which is puzzling.
- Paul Lorigan
- & Adele C. Green
-
Consensus Statement
| Open Access Clinical development of new drug–radiotherapy combinations
Clinical development of new drug–radiotherapy combinations
The National Cancer Research Institute Clinical and Translational Radiotherapy Research Working Group (CTRad) includes academia, industry, patient groups and regulatory bodies representatives. In this Consensus Statement, recommendations are provided with the aim of increasing the number of novel drugs being successfully registered in combination with radiotherapy in clinical trials for patients with cancer.
- Ricky A. Sharma
- , Ruth Plummer
- & Stephen R. Wedge
-
Review Article |
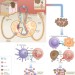 Safety profiles of anti-CTLA-4 and anti-PD-1 antibodies alone and in combination
Safety profiles of anti-CTLA-4 and anti-PD-1 antibodies alone and in combination
Immune checkpoint inhibition is a novel approach to cancer treatment with enormous potential to improve the outcomes of patients with a range of malignancies. However, owing to this novel approach, a range of adverse events have emerged with different aetiologies to those of more conventional cancer treatments. In this Review, the authors describe the occurrence, and optimal management of adverse events resulting from use of immune checkpoint inhibitors.
- Celine Boutros
- , Ahmad Tarhini
- & Caroline Robert
-
News & Views |
 Strategies to optimize expedited investigational new drug safety reports
Strategies to optimize expedited investigational new drug safety reports
Accurate and efficient expedited investigational new drug (IND) reporting is a crucial component of clinical research. The FDA, pharmaceutical companies, institutional review boards, and clinical investigators should develop dynamic standardized electronic forms with preferred, predetermined terms to harmonize their practices and to help optimize the quality of clinical research and maximize patient safety.
- Apostolia M. Tsimberidou
-
Review Article |
 Systems biology approaches to adverse drug effects: the example of cardio-oncology
Systems biology approaches to adverse drug effects: the example of cardio-oncology
Cardiotoxic effects of chemotherapy can occur in various different ways depending upon the type of chemotherapy used and various patient characteristics. In this Review, the authors describe the established cardiotoxic effects of anthracyclines and HER2 inhibitors, and describe a systems medicine approach that might enable the optimal management of acute and chronic cardiotoxcities in patients who are receiving, or have received, these therapies.
- Sherry-Ann Brown
- , Nicole Sandhu
- & Joerg Herrmann
-

 You can have your cake and eat it!
You can have your cake and eat it!