Research Highlight |
Featured
-
-
Comment |
Practicing on the edge of oncology: when standard of care feels uncomfortable
The treatments oncologists deliver are generally based on evidence from large randomized controlled trials, consistent with practice guidelines, and congruent with the treatments selected by our peers. In this Comment, we use two scenarios to highlight the discomfort clinicians might feel when they are outliers from the guideline-recommended standard of care.
- Christopher M. Booth
- & Aaron M. Goodman
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Intratumoural administration and tumour tissue targeting of cancer immunotherapies
Intratumoural administration and tumour tissue targeting of cancer immunotherapies
Limited penetration into tumour tissue can restrict the activity of systemically delivered cancer immunotherapies, whereas exposure of various non-malignant tissues to high levels of such agents can lead to problematic toxicities. Intratumoural administration and/or biotechnology strategies for selective targeting of tumour tissues have the potential to circumvent these issues and thereby increase the therapeutic index. Herein, the authors review the historical origins and current landscape of intratumoural and tumour tissue-targeted immunotherapies.
- Ignacio Melero
- , Eduardo Castanon
- & Aurelien Marabelle
-
-
Perspective |
 Applications of liquid biopsy in the Pharmacological Audit Trail for anticancer drug development
Applications of liquid biopsy in the Pharmacological Audit Trail for anticancer drug development
In this Perspective, members of the group that previously proposed the Pharmacological Audit Trail (PhAT) as a tool to improve and accelerate drug development through the use of tissue biomarkers discuss the promise of integrating liquid biopsy approaches into this paradigm. They focus on the potential applications of plasma circulating cell-free tumour DNA and circulating tumour cells as prognostic, predictive, pharmacodynamic, clinical response and resistance biomarkers, while also highlighting key technological considerations, limitations and challenges, and the importance of analytical validation and clinical qualification.
- Abhijit Pal
- , Rajiv Shinde
- & Johann de Bono
-
-
Perspective |
COVID-19 vaccine guidance for patients with cancer participating in oncology clinical trials
Patients with cancer have a high risk of morbidity and mortality from COVID-19. The rapid development of COVID-19 vaccines has provided new hope of mitigating the disease. Herein, the COVID19 and Cancer Clinical Trials Working Group calls for prioritization of patients with cancer, importantly including those participating in oncology clinical trials, for COVID-19 vaccination. The authors also provide operational COVID-19 vaccine guidance for patients participating in oncology clinical trials.
- Aakash Desai
- , Justin F. Gainor
- & Vivek Subbiah
-
News & Views |
Will allogeneic CAR T cells for CD19+ malignancies take autologous CAR T cells ‘off the shelf’?
The question of whether allogeneic chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells could replace autologous CAR T cell therapy has garnered considerable interest, but limited data have been available for comparisons to date. Now, Benjamin et al. have reported their experience with allogeneic anti-CD19 CAR T cells in 21 paediatric and adult patients with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia.
- Amanda M. DiNofia
- & Stephan A. Grupp
-
Review Article |
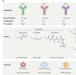 Unlocking the potential of antibody–drug conjugates for cancer therapy
Unlocking the potential of antibody–drug conjugates for cancer therapy
Antibody–drug conjugates (ADCs) constitute a unique class of anticancer agents with demonstrated clinical efficacy against several different cancer types. Herein, the authors discuss the design and mechanisms of action of ADCs and how these properties are reflected in the clinical activity and toxicity profiles of such agents. Potential strategies to overcome the limitations of ADCs and thereby maximize their therapeutic benefit for patients with cancer are also proposed.
- Joshua Z. Drago
- , Shanu Modi
- & Sarat Chandarlapaty
-
Comment |
Oncology approvals in 2020: a year of firsts in the midst of a pandemic
In 2020, despite challenges related to the COVID-19 pandemic, the US FDA approved 30 new drugs and biologic agents, 45 supplemental drug and biologic applications and 1 biosimilar application in oncology.
- Laleh Amiri-Kordestani
- & Richard Pazdur
-
Review Article |
 Advances in the development of personalized neoantigen-based therapeutic cancer vaccines
Advances in the development of personalized neoantigen-based therapeutic cancer vaccines
Personalized neoantigen-based therapeutic vaccines hold promise as cancer immunotherapies. This Review provides an overview of the complex personalized neoantigen vaccine production process, vaccine-induced T cell responses and strategies to enhance these responses. Completed and ongoing clinical studies testing such vaccines are discussed, and considerations for future clinical investigation of this novel, individualized form of immunotherapy are outlined.
- Eryn Blass
- & Patrick A. Ott
-
News & Views |
CDK4/6 inhibitors for HR+HER2− early stage breast cancer — when to escalate treatment?
Opposing results of the monarchE and PALLAS trials investigating the role of adjuvant treatment with the CDK4/6 inhibitors abemaciclib and palbociclib, respectively, in patients with hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative early stage breast cancer have recently been presented. Herein, potential reasons why these two drugs that have similar efficacy in the metastatic setting have produced disparate results in the adjuvant setting are discussed.
- Giuseppe Curigliano
-
Review Article |
 The nuclear export protein XPO1 — from biology to targeted therapy
The nuclear export protein XPO1 — from biology to targeted therapy
Nuclear import and export proteins, such as exportin 1(XPO1), regulate the transport of proteins and other molecules into and out of the nucleus, including several tumour suppressor proteins. The dysregulation of nuclear export can be observed in several types of haematological and solid tumours, providing a rationale for a novel form of targeted therapy. In this Review, the authors describe the development of XPO1 inhibitors, from basic research to clinical approval.
- Asfar S. Azmi
- , Mohammed H. Uddin
- & Ramzi M. Mohammad
-
News & Views |
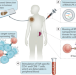 Cancer vaccine induces potent T cell responses — but is it enough?
Cancer vaccine induces potent T cell responses — but is it enough?
Tumour-associated antigens are an attractive therapeutic target in immuno-oncology. Here, the exploratory analyses of T cell responses and preliminary clinical outcomes of the Lipo-MERIT trial of a melanoma vaccine are discussed in the context of prior efforts to harness the immunogenicity of such antigens for antitumour immunity.
- Anjali Rohatgi
- & John M. Kirkwood
-
Comment |
When are results of single-arm studies dramatic?
Single-arm phase II trials can provide compelling results that facilitate the approval of a new therapy. Designing and interpreting single-arm studies based on four principles — instinct, comparative analysis, statistical soundness and like-for-like comparisons — can provide indications as to which drugs are most likely to provide improved therapeutic options for patients.
- Robert H. Glassman
- , Grace Kim
- & Marc J. Kahn
-
Comment |
Simultaneous development of zanubrutinib in the USA and China
Zanubrutinib was recently granted expedited approval by the USA and Chinese drug regulatory authorities for the treatment of mantle cell lymphoma, thus becoming the first investigational new drug discovered in China to achieve simultaneous development in both countries. Here, we provide an overview of the regulatory processes and considerations of the two health authorities and discuss the pathways of concurrent review and approval.
- Guanqiao Li
- , Xiaozhen Liu
- & Xiaoyuan Chen
-
Review Article |
 Histology-agnostic drug development — considering issues beyond the tissue
Histology-agnostic drug development — considering issues beyond the tissue
Therapies are being developed to treat cancers on the basis of specific molecular alterations and markers of immune phenotypes that transcend specific tumour histologies. The authors summarize the development and testing of approved histology-agnostic therapeutic agents, present data on other agents under development and discuss the challenges intrinsic to histology-agnostic drug development in oncology, including biological, regulatory, design and statistical considerations.
- Roberto Carmagnani Pestana
- , Shiraj Sen
- & David S. Hong
-
News & Views |
Olaparib for DNA repair-deficient prostate cancer — one for all, or all for one?
Mature results of the PROfound study demonstrate that the poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor olaparib prolongs progression-free survival compared with second-generation hormonal therapies in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer harbouring BRCA1, BRCA2 or ATM mutations. However, a closer look at the efficacy of olaparib on a gene-by-gene basis suggests that its activity is most pronounced in BRCA2-mutant prostate cancers and might not be equally active in all homologous recombination repair-deficient cancers.
- Emmanuel S. Antonarakis
-
-
Review Article |
 Roles and mechanisms of alternative splicing in cancer — implications for care
Roles and mechanisms of alternative splicing in cancer — implications for care
Alternative splicing enables the regulated generation of multiple mRNA and protein products from a single gene. This Review outlines the splicing process and its alterations in cancer before highlighting related opportunities for the development of innovative therapeutic approaches.
- Sophie C. Bonnal
- , Irene López-Oreja
- & Juan Valcárcel
-
Review Article |
 T cell-engaging therapies — BiTEs and beyond
T cell-engaging therapies — BiTEs and beyond
The use of bispecific antibodies to engage cells of the immune system that are cytotoxic to cancer cells is a major focus of cancer immunotherapy, with approvals for the treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Here, the authors review the clinical results obtained with bispecific antibodies to date. They also discuss the challenges associated with this therapeutic approach and the proposed solutions aimed at preventing or minimizing toxicities, countering immune escape and broadening the indications for these treatments.
- Maria-Elisabeth Goebeler
- & Ralf C. Bargou
-
Review Article |
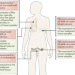 Exploiting the folate receptor α in oncology
Exploiting the folate receptor α in oncology
Cancer cells, like non-malignant cells, are dependent on folate uptake for growth. However, cancer cells are much more reliant on folate receptors (FRs) and particularly FRα for folate uptake than non-malignant cells. In this Review, the authors describe the available data on the role of FRα as a biomarker and as a target of imaging probes, and of targeted therapies in patients with solid tumours.
- Mariana Scaranti
- , Elena Cojocaru
- & Udai Banerji
-
Comment |
Approvals in 2019: international review and a new agnostic molecular entity
In 2019, the FDA Oncology Center of Excellence (OCE) approved 11 new drugs and biologic agents, 30 supplemental drug and biologic applications, and four biosimilar applications in oncology. These included two landmark approvals involving collaboration among international regulators as part of OCE Project Orbis, as well as the approval of three novel antibody–drug conjugates.
- Harpreet Singh
- , Gideon Blumenthal
- & Richard Pazdur
-
Viewpoint |
New drug approvals in oncology
Regulatory approval of new cancer medicines can have important consequence for patients with advanced-stage and/or rare cancers who have exhausted all standard-of-care therapies. However, evidence that new medicines are safe and effective can also take time to accrue, and approval with a lack of evidence may cause unnecessary harm to patients. In this Viewpoint, we asked two leading oncologists involved in clinical drug development, an expert in regulatory science and prescription drug policy, and a prominent patient advocate, to provide their opinions on the current approach to cancer drug approvals.
- Razelle Kurzrock
- , Hagop M. Kantarjian
- & Ellen V. Sigal
-
Review Article |
 Engineering strategies to overcome the current roadblocks in CAR T cell therapy
Engineering strategies to overcome the current roadblocks in CAR T cell therapy
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy, the first approved therapeutic approach with a genetic engineering component, holds substantial promise in the treatment of a range of cancers but is nevertheless limited by various challenges, including toxicities, intrinsic and acquired resistance mechanisms, and manufacturing issues. In this Review, the authors describe the innovative approaches to the engineering of CAR T cell products that are providing solutions to these challenges and therefore have the potential to considerably improve the safety and effectiveness of treatment.
- Sarwish Rafiq
- , Christopher S. Hackett
- & Renier J. Brentjens
-
Perspective |
 A systems approach to clinical oncology uses deep phenotyping to deliver personalized care
A systems approach to clinical oncology uses deep phenotyping to deliver personalized care
A systems biology-based approach incorporating multiscale, longitudinal measurements (from single-cell analyses to whole-body monitoring) would help to decipher the complexity of cancer and would facilitate the development of personalized therapies. The authors of this Perspective discuss how systems biology-based approaches can provide data for early detection of disease transitions, prediction of therapeutic responses and clinical outcomes, and for the design of personalized treatments.
- James T. Yurkovich
- , Qiang Tian
- & Leroy Hood
-
Review Article |
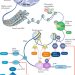 Combining epigenetic drugs with other therapies for solid tumours — past lessons and future promise
Combining epigenetic drugs with other therapies for solid tumours — past lessons and future promise
The use of epigenetic drugs (epi-drugs) as single agents according to a ‘one size fits all’ approach has generally resulted in disappointing therapeutic activity. In this Review, the mechanisms by which epi-drugs can modulate the sensitivity of cancer cells to other diverse forms of anticancer therapy are described, and completed and ongoing clinical trials relating to combination therapies incorporating epi-drugs are discussed. In addition, clinical trial designs and drug development strategies aimed at optimizing the development of such combinations are outlined.
- Daphné Morel
- , Daniel Jeffery
- & Sophie Postel-Vinay
-
Review Article |
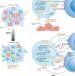 The emerging role of epigenetic therapeutics in immuno-oncology
The emerging role of epigenetic therapeutics in immuno-oncology
Despite promising responses in a minority of patients with cancer, considerable scope remains to improve the efficacy of both immune-checkpoint inhibitors and epigenetic drugs, with one potential strategy involving the combination of these two types of treatment. Here, the authors describe the mechanisms underlying the synergy between immune-checkpoint inhibitors and epigenetic drugs and discuss the ongoing clinical development of such combinations.
- Michael J. Topper
- , Michelle Vaz
- & Stephen B. Baylin
-
Perspective |
 Phase I trials as valid therapeutic options for patients with cancer
Phase I trials as valid therapeutic options for patients with cancer
Oncology phase I trials have been traditionally referred to as ‘toxicity trials’. The distinction of clinical trials into three phases has been challenged in the past few years, leading to the current situation in which response rates are increasingly reported from phase I trials. The authors dissect the ethical dilemmas surrounding the therapeutic intent of phase I trials and provide evidence of contemporary phase I trials as a therapeutic option for patients with cancer.
- Jacob J. Adashek
- , Patricia M. LoRusso
- & Razelle Kurzrock
-
Editorial |
ANNOUNCE prompts questions over the Accelerated Approval process
The negative results of the ANNOUNCE trial, resulting in withdrawal of olaratumab from the market, illustrate the difficulties in balancing access to novel therapies with the need for proven benefit.
-
-
-
-
News & Views |
MAIA under the microscope — bringing trial design into focus
Using the example of the recently reported phase III MAIA trial, we emphasize herein the requirement to dig deeper into trial designs and end points to determine their appropriateness for the questions at hand and to assess whether a benefit in terms of the primary end point — even if statistically significant and seemingly clinically meaningful — is sufficient to warrant a change in clinical practice.
- Prashant Kapoor
- & S. Vincent Rajkumar
-
News & Views |
Anti-CD19 CAR T cell therapy for lymphoma — off to the races!
Recently published data from the ZUMA-1 and JULIET trials suggest that CD19-directed chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell therapy can provide durable remissions, with a low risk of relapse or progression, in 30–40% of patients with relapsed and/or refractory aggressive large B cell lymphoma. Two-year follow-up of the ZUMA-1 clinical trial has not revealed any unexpected toxicities, but further safety monitoring will be needed.
- David G. Maloney
-
Research Highlight |
ARAMIS — is darolutamide set to become the ‘third musketeer’ of nmCRPC?
- David Killock
-
Comment |
Registration studies — when should patients be deemed ineligible for aggressive therapy?
The approval of therapeutic agents that are tested in patients deemed ineligible for intensive or aggressive therapy is increasingly popular. This approach enables comparisons of novel therapies with less-aggressive agents, as well as data from nonrandomized studies to be used for market authorization. Herein, we discuss three mechanisms that could be adopted to avoid the temptation of applying this strategy excessively.
- Rachel J. Cook
- , Jennifer Gill
- & Vinay Prasad
-
Comment |
 Approvals in 2018: a histology-agnostic new molecular entity, novel end points and real-time review
Approvals in 2018: a histology-agnostic new molecular entity, novel end points and real-time review
In 2018, the FDA approved 19 new drug and biologic applications, 38 supplemental drug and biologic applications and 4 biosimilar applications in oncology. These advances in anticancer therapy included a landmark approval of the first histology-agnostic, biomarker-defined new molecular entity and approvals based on real-time data review and novel end points, such as minimal residual disease rate and metastasis-free survival.
- Gideon M. Blumenthal
- & Richard Pazdur
-
-
Consensus Statement
| Open Access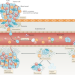 A framework for the development of effective anti-metastatic agents
A framework for the development of effective anti-metastatic agents
Most cancer-related deaths are attributable to metastasis, but few treatments are specifically designed to disrupt this process. In this Position Paper, representatives of the joint Cancer Research UK and Cancer Therapeutics CRC Australia Metastasis Working Group describe the challenges associated with discovering and developing anticancer agents designed specifically to prevent or delay the metastatic outgrowth of cancer and provide guidance on how these challenges might be overcome.
- Robin L. Anderson
- , Theo Balasas
- & James W. A. Ritchie
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Fibroblast growth factor receptors as treatment targets in clinical oncology
Fibroblast growth factor receptors as treatment targets in clinical oncology
FGFR alterations can be detected in a small subset of many different cancer types. Inspired by the successes with other targeted therapies, preliminary attempts to target FGFR-altered cancers have been hampered by low response rates and acquired resistance. In this Review, the author describes the development of FGFR inhibitors thus far, and provides guidance on future research priorities.
- Masaru Katoh
-
Review Article |
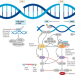 State-of-the-art strategies for targeting the DNA damage response in cancer
State-of-the-art strategies for targeting the DNA damage response in cancer
Inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) is the paradigmatic example of synthetic lethal therapy and is predicated on exploiting DNA repair deficiencies that are a hallmark of cancer. In this Review, the authors review the progress made to date with PARP inhibitors and describe the expanding landscape of novel anticancer therapies targeting the DNA damage response. Potential predictive biomarkers, mechanisms of resistance and combinatorial strategies are discussed.
- Patrick G. Pilié
- , Chad Tang
- & Timothy A. Yap
-
Comment |
Why patients receive treatments that are minimally effective?
The value of medical treatments is an issue that has been actively debated in recent years and is not unique to oncology. In this Comment, we discuss why we pursue treatments which might have limited benefit from the point of view of three parties: the patient, the physician, and the pharmaceutical industry.
- Christopher M. Booth
- & Allan S. Detsky
-
Review Article |
 Making the first move in EGFR-driven or ALK-driven NSCLC: first-generation or next-generation TKI?
Making the first move in EGFR-driven or ALK-driven NSCLC: first-generation or next-generation TKI?
The clinical management of patients with non-small-cell lung carcinoma has greatly evolved owing to the development of tyrosine-kinase inhibitors (TKIs) targeted against the driver mutations of this disease. The authors of this Review describe the existing evidence on the sequential administration of TKIs and the use of next-generation TKIs upfront.
- Gonzalo Recondo
- , Francesco Facchinetti
- & Luc Friboulet
-
Correspondence |
Reply to ‘Economic comments on proposal for a novel cancer drug pricing model’
- Carin A. Uyl-de Groot
- & Bob Löwenberg
-
Correspondence |
Economic comments on proposal for a novel cancer drug pricing model
- Mark J. C. Nuijten
- & Jan Vis

 From the 2021 ASCO Annual Meeting
From the 2021 ASCO Annual Meeting From AACR 2021
From AACR 2021 New window of opportunity with ICIs in melanoma
New window of opportunity with ICIs in melanoma