Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access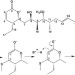 Pironetin reacts covalently with cysteine-316 of α-tubulin to destabilize microtubule
Pironetin reacts covalently with cysteine-316 of α-tubulin to destabilize microtubule
Microtubule assembly and disassembly is the target of many anticancer therapies, with β-tubulin the most-frequent target. Here, the authors used biochemical and biophysical techniques to demonstrate pironetin binds to α-tubulin and thereby inhibits microtubule polymerization providing a basis for the rational design of novel anticancer drugs.
- Jianhong Yang
- , Yuxi Wang
- & Lijuan Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular basis for CPAP-tubulin interaction in controlling centriolar and ciliary length
Molecular basis for CPAP-tubulin interaction in controlling centriolar and ciliary length
Centrioles and cilia are microtubule-based structures of defined architecture, but what regulates this architecture is not clear. Here the authors discover that centrosomal-P4.1-associated-protein (CPAP) binds the α/β-tubulin dimer and licenses it for tubulin delivery contributing to centriolar/ciliary length and architecture control.
- Xiangdong Zheng
- , Anand Ramani
- & Haitao Li
-
Article
| Open Access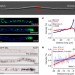 Active diffusion and microtubule-based transport oppose myosin forces to position organelles in cells
Active diffusion and microtubule-based transport oppose myosin forces to position organelles in cells
The mechanisms underlying the positioning of eukaryotic organelles remain elusive. Here Lin et al. use imaging and a mathematical model to show that microtubule-based transport and active diffusion and actin-based polar drift act together to facilitate even distribution of peroxisomes in filamentous fungi.
- Congping Lin
- , Martin Schuster
- & Gero Steinberg
-
Article
| Open Access Aurora-A recruitment and centrosomal maturation are regulated by a Golgi-activated pool of Src during G2
Aurora-A recruitment and centrosomal maturation are regulated by a Golgi-activated pool of Src during G2
The Golgi mitotic checkpoint couples Golgi inheritance with cell cycle transition, and regulates centrosomal recruitment of the mitotic kinase Aurora-A. Here the authors show that upon Golgi ribbon fragmentation in G2, Src phosphorylates Aurora-A at the Golgi, driving its localization to the centrosomes.
- Maria Luisa Barretta
- , Daniela Spano
- & Antonino Colanzi
-
Article
| Open Access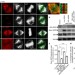 EB1 regulates attachment of Ska1 with microtubules by forming extended structures on the microtubule lattice
EB1 regulates attachment of Ska1 with microtubules by forming extended structures on the microtubule lattice
Ska1 is a kinetochore-localised protein that couples kinetochore movement to microtubule (MT) depolymerisation. Here Thomas et al. show that the MT +TIP binding protein EB1 recruits Ska1 to the MT-kinetochore interface and stabilises the interaction between Ska1 and MTs.
- Geethu E. Thomas
- , K. Bandopadhyay
- & Tapas K. Manna
-
Article
| Open Access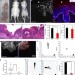 In vivo epidermal migration requires focal adhesion targeting of ACF7
In vivo epidermal migration requires focal adhesion targeting of ACF7
The spectraplakin protein ACF7 binds to actin at focal adhesions and targets microtubule plus ends to focal adhesions, promoting their disassembly. Here the authors reveal that ACF7 is phosphorylated by Src/FAK, and this regulates actin binding and focal adhesion dynamics in vitro and in vivo.
- Jiping Yue
- , Yao Zhang
- & Xiaoyang Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Context-dependent switch in chemo/mechanotransduction via multilevel crosstalk among cytoskeleton-regulated MRTF and TAZ and TGFβ-regulated Smad3
Context-dependent switch in chemo/mechanotransduction via multilevel crosstalk among cytoskeleton-regulated MRTF and TAZ and TGFβ-regulated Smad3
MRTF and TAZ are mechanosensitive transcriptional coactivators, but how they functionally interact is not clear. Here the authors show that MRFT and TAZ exhibit multilevel crosstalk in expression, transport and transcriptional activity; furthermore, TAZ confers sensitivity to TGFβ activation of the smooth muscle actin promoter.
- Pam Speight
- , Michael Kofler
- & András Kapus
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular requirements for the inter-subunit interaction and kinetochore recruitment of SKAP and Astrin
Molecular requirements for the inter-subunit interaction and kinetochore recruitment of SKAP and Astrin
SKAP and Astrin form a heterodimer that localizes to spindle microtubules and to mature microtubule-kinetochore attachments during mitosis. Here, the authors identify molecular requirements for the inter-subunit interaction of SKAP and Astrin and kinetochore recruitment.
- Alexandra Friese
- , Alex C. Faesen
- & Andrea Musacchio
-
Article
| Open Access Microtubule-dependent balanced cell contraction and luminal-matrix modification accelerate epithelial tube fusion
Microtubule-dependent balanced cell contraction and luminal-matrix modification accelerate epithelial tube fusion
During tracheal tube fusion in Drosophila, a pair of tip cells form an adherens junction and then fuse their plasma membranes. Here the authors show that a balanced pulling force mediated by myosin and microtubules, as well as localized deposition of matrix, promotes plasma membrane fusion.
- Kagayaki Kato
- , Bo Dong
- & Shigeo Hayashi
-
Article
| Open Access Fimbrin phosphorylation by metaphase Cdk1 regulates actin cable dynamics in budding yeast
Fimbrin phosphorylation by metaphase Cdk1 regulates actin cable dynamics in budding yeast
Metaphase cells preferentially promote actin cable assembly through cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (Cdk1) activity. Here the authors identify fimbrin as one of the main metaphase Cdk1 targets for cell cycle regulation of actin cable assembly in budding yeast.
- Yansong Miao
- , Xuemei Han
- & David G. Drubin
-
Article
| Open Access PDE6δ-mediated sorting of INPP5E into the cilium is determined by cargo-carrier affinity
PDE6δ-mediated sorting of INPP5E into the cilium is determined by cargo-carrier affinity
PDE6δ regulates the sorting of prenylated cargo proteins. Here Fansa et al. propose that the affinity of the interaction between PDE6δ and its cargo protein determines whether they are released by cytoplasmic or cilia-specific release factors ultimately determining their subcellular localization.
- Eyad Kalawy Fansa
- , Stefanie Kristine Kösling
- & Shehab Ismail
-
Article
| Open Access Engineered kinesin motor proteins amenable to small-molecule inhibition
Engineered kinesin motor proteins amenable to small-molecule inhibition
The use of specific small molecule inhibitors can contribute to the study of kinesins' cellular functions. Here the authors develop a chemical-genetic approach to engineer kinesin motors that can be efficiently inhibited upon addition of cell-permeable molecules.
- Martin F. Engelke
- , Michael Winding
- & Kristen J. Verhey
-
Article
| Open Access Defects in TRPM7 channel function deregulate thrombopoiesis through altered cellular Mg2+ homeostasis and cytoskeletal architecture
Defects in TRPM7 channel function deregulate thrombopoiesis through altered cellular Mg2+ homeostasis and cytoskeletal architecture
Although Mg2+is vital for platelet activation and aggregation, its regulation in these cells is still largely unknown. Here, the authors show that TRPM7, a cation channel and a protein kinase, regulates thrombopoiesis and platelet size by affecting the cytoskeleton of these cells in mice and humans.
- Simon Stritt
- , Paquita Nurden
- & Attila Braun
-
Article
| Open Access Actin nucleation at the centrosome controls lymphocyte polarity
Actin nucleation at the centrosome controls lymphocyte polarity
Cell polarity is marked by re-orientation of the centrosome, but the mechanisms governing centrosome polarization are poorly understood. Here Obino et al. show that in lymphocytes centrosome-associated Arp2/3 nucleates actin that tethers the centrosome to the nucleus; activation depletes Arp2/3 from the centrosome and frees it from the nucleus.
- Dorian Obino
- , Francesca Farina
- & Ana-Maria Lennon-Duménil
-
Article
| Open Access A CEP215–HSET complex links centrosomes with spindle poles and drives centrosome clustering in cancer
A CEP215–HSET complex links centrosomes with spindle poles and drives centrosome clustering in cancer
Centrosome clustering allows survival of cells with amplified centrosomes at the cost of chromosome instability. Here, Chavali et al. show that the centrosome component CEP215 collaborates with the kinesin motor HSET both to maintain spindle poles connections and to cluster centrosomes.
- Pavithra L. Chavali
- , Gayathri Chandrasekaran
- & Fanni Gergely
-
Article
| Open Access Perinuclear Arp2/3-driven actin polymerization enables nuclear deformation to facilitate cell migration through complex environments
Perinuclear Arp2/3-driven actin polymerization enables nuclear deformation to facilitate cell migration through complex environments
Cell migration through micrometric constraints is limited by low deformability of the nucleus. Here the authors show that in dendritic cells a perinuclear actin network nucleated by Arp2/3 increases nuclear deformation and allows the cells to pass through narrow constrictions, likely by rupturing the nuclear lamina.
- Hawa-Racine Thiam
- , Pablo Vargas
- & Matthieu Piel
-
Article
| Open Access The unconventional myosin CRINKLED and its mammalian orthologue MYO7A regulate caspases in their signalling roles
The unconventional myosin CRINKLED and its mammalian orthologue MYO7A regulate caspases in their signalling roles
In addition to their role in apoptosis, caspases are also involved in mediating non-apoptotic events. Here the authors show that the Drosophilamyosin family member CRINKLED and its mammalian counterpart act as substrate adaptor that facilitate caspase-mediated cleavage and localised kinase activity.
- Mariam H. Orme
- , Gianmaria Liccardi
- & Pascal Meier
-
Article
| Open Access Mechanism of intermediate filament recognition by plakin repeat domains revealed by envoplakin targeting of vimentin
Mechanism of intermediate filament recognition by plakin repeat domains revealed by envoplakin targeting of vimentin
Plakin proteins link cell junctions to cytoskeletal frameworks, and their disruption within epithelial and cardiac muscle cells cause skin blistering diseases and cardiomyopathies. Here the authors use structural biology approaches to reveal the mechanism that allows plakins to recognize intermediate filaments within the cytoskeleton.
- Claudia Fogl
- , Fiyaz Mohammed
- & Martyn Chidgey
-
Article
| Open Access Stereocilia-staircase spacing is influenced by myosin III motors and their cargos espin-1 and espin-like
Stereocilia-staircase spacing is influenced by myosin III motors and their cargos espin-1 and espin-like
Stereocilia of the inner ear have graded heights that are thought to be regulated by the myosin-III family members MYO3A and MYO3B. Here the authors identify espin-1 and espin-like (ESPNL) as cargo that differentially influence the functions of both motors to regulate stereocilia length.
- Seham Ebrahim
- , Matthew R. Avenarius
- & Bechara Kachar
-
Article
| Open Access NuSAP governs chromosome oscillation by facilitating the Kid-generated polar ejection force
NuSAP governs chromosome oscillation by facilitating the Kid-generated polar ejection force
During metaphase, alignment of chromosomes is facilitated by oscillations driven by the chromokinesin Kid. Here Li et al. show that the microtubule-associated protein NuSAP is a novel regulator of Kid, regulating the amplitude and velocity of chromosome oscillation.
- Chenyu Li
- , Chenyi Xue
- & Yih-Cherng Liou
-
Article
| Open Access Rapid endothelial cytoskeletal reorganization enables early blood–brain barrier disruption and long-term ischaemic reperfusion brain injury
Rapid endothelial cytoskeletal reorganization enables early blood–brain barrier disruption and long-term ischaemic reperfusion brain injury
Matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) released from infiltrating immune cells are a major contributor to blood-brain barrier (BBB) breakdown following stroke. Here, the authors identify an early, MMP-independent BBB breakdown mechanism caused by rapid cytoskeletal rearrangements in endothelial cells, which could be inhibited by ADF.
- Yejie Shi
- , Lili Zhang
- & Jun Chen
-
Article
| Open Access F-actin-rich contractile endothelial pores prevent vascular leakage during leukocyte diapedesis through local RhoA signalling
F-actin-rich contractile endothelial pores prevent vascular leakage during leukocyte diapedesis through local RhoA signalling
Endothelial cells can support leukocyte extravasation without causing vascular leakage, but the exact mechanism underlying this process has not been fully elucidated. Here the authors show that it is regulated through actomyosin-based endothelial pore confinement, which requires local endothelial RhoA activation.
- Niels Heemskerk
- , Lilian Schimmel
- & Jaap D. van Buul
-
Article
| Open Access Removal of the mechanoprotective influence of the cytoskeleton reveals PIEZO1 is gated by bilayer tension
Removal of the mechanoprotective influence of the cytoskeleton reveals PIEZO1 is gated by bilayer tension
PIEZO1 is a mechanosensitive ion channel, but the mechanism of force transduction is unknown. Here Cox and Bae et al.disrupt the cortical cytoskeleton in HEK293 cells to show that PIEZO1 is gated directly by membrane tension.
- Charles D. Cox
- , Chilman Bae
- & Boris Martinac
-
Article
| Open Access Interplay of active processes modulates tension and drives phase transition in self-renewing, motor-driven cytoskeletal networks
Interplay of active processes modulates tension and drives phase transition in self-renewing, motor-driven cytoskeletal networks
The actin cytoskeleton is a complex network of filaments, cross-linking proteins and motors; although the components are recognised, the behaviour of the network is less understood. Here Mak et al.use a Brownian dynamics model that reveals actin turnover dynamics as a key regulatory mechanism controlling cytoskeletal states.
- Michael Mak
- , Muhammad H. Zaman
- & Taeyoon Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Overlap microtubules link sister k-fibres and balance the forces on bi-oriented kinetochores
Overlap microtubules link sister k-fibres and balance the forces on bi-oriented kinetochores
During metaphase, k-fibre microtubules exert force on kinetochores, but there are also non-kinetochore microtubules close to kinetochores without a known function. Here the authors show that these microtubules, which they call bridging fibres, balance interkinetochore tension by bridging sister k-fibres.
- Janko Kajtez
- , Anastasia Solomatina
- & Iva M. Tolić
-
Article
| Open Access F-actin mechanics control spindle centring in the mouse zygote
F-actin mechanics control spindle centring in the mouse zygote
How the mitotic spindle is positioned in the centre of the cell during the first mitotic division is not clear. Here Chaigne et al.show that the pronucleus coarsely centres using F-actin/Myosin-Vb dynamics, and the metaphase plate is finely centred by an F-actin cage influenced by high cortical tension.
- Agathe Chaigne
- , Clément Campillo
- & Marie-Emilie Terret
-
Article
| Open Access Basal body multipotency and axonemal remodelling are two pathways to a 9+0 flagellum
Basal body multipotency and axonemal remodelling are two pathways to a 9+0 flagellum
Whether basal bodies are pre-committed to form 9+2 motile or 9+0 sensory axonemes and whether interconversion occurs between the two types of axonemes is not clear. Here, the authors used the unicellular eukaryote Leishmania as a model system to demonstrate that 9+0 axonemes can be formed de novoor by restructuring of 9+2 axonemes.
- R. J. Wheeler
- , E. Gluenz
- & K. Gull
-
Article
| Open Access Tank binding kinase 1 is a centrosome-associated kinase necessary for microtubule dynamics and mitosis
Tank binding kinase 1 is a centrosome-associated kinase necessary for microtubule dynamics and mitosis
TANK binding kinase 1 (TBK1) is a non-canonical IκB kinase that regulates immunity via NF-κB. Here Pillai et al. show that TBK1 localizes to centrosomes during mitosis, and regulates microtubule dynamics and spindle formation by phosphorylating the centrosomal protein CEP170 and the mitotic apparatus protein NuMa.
- Smitha Pillai
- , Jonathan Nguyen
- & Srikumar Chellappan
-
Article
| Open Access Arp2/3-mediated F-actin formation controls regulated exocytosis in vivo
Arp2/3-mediated F-actin formation controls regulated exocytosis in vivo
The cytoskeleton plays a crucial role in secretion. Here Tran et al.demonstrate that cortical actin is rearranged at the site of vesicle fusion and recruited to fused secretory granules in Drosophila salivary glands, and show that branched actin nucleators are required for cargo expulsion.
- Duy T. Tran
- , Andrius Masedunskas
- & Kelly G. Ten Hagen
-
Article
| Open Access Kinetochore–microtubule attachment is sufficient to satisfy the human spindle assembly checkpoint
Kinetochore–microtubule attachment is sufficient to satisfy the human spindle assembly checkpoint
The spindle assembly checkpoint protects against premature chromosome segregation during mitosis but it is not known whether microtubule attachment to the kinetochore, or force generated from this interaction, is being monitored. Here the authors uncouple these processes and show that microtubule attachment is sufficient to satisfy the checkpoint.
- Banafsheh Etemad
- , Timo E. F. Kuijt
- & Geert J. P. L. Kops
-
Article
| Open Access Stable kinetochore–microtubule attachment is sufficient to silence the spindle assembly checkpoint in human cells
Stable kinetochore–microtubule attachment is sufficient to silence the spindle assembly checkpoint in human cells
The spindle assembly checkpoint prevents mitotic progression when chromosomes are not properly attached to the mitotic spindle. Here Tauchman et al.show that stable microtubule attachment to the kinetochore, and not tension generated from this interaction, is sufficient to silence the checkpoint.
- Eric C. Tauchman
- , Frederick J. Boehm
- & Jennifer G. DeLuca
-
Article
| Open Access A molecular ruler regulates cytoskeletal remodelling by the Rho kinases
A molecular ruler regulates cytoskeletal remodelling by the Rho kinases
Rho kinases regulate the actin cytoskeleton by controlling stress fibre formation. Truebestein et al.show that the length of its coiled-coil determines ROCK2 function, and propose that the coiled coil acts as a spacer, targeting kinase activity to a discrete distance from the membrane.
- Linda Truebestein
- , Daniel J. Elsner
- & Thomas A. Leonard
-
Article
| Open Access Mitotic cells contract actomyosin cortex and generate pressure to round against or escape epithelial confinement
Mitotic cells contract actomyosin cortex and generate pressure to round against or escape epithelial confinement
In epithelial layers cells must round up prior to division. Here the authors use micropillar arrays to mimic epithelial confinement and show that MDCK cells generate force to create space to divide; if unable to generate sufficient force they escape the micropillars to divide and return to confinement.
- Barbara Sorce
- , Carlos Escobedo
- & Daniel J. Müller
-
Article
| Open Access Single-molecule visualization of a formin-capping protein ‘decision complex’ at the actin filament barbed end
Single-molecule visualization of a formin-capping protein ‘decision complex’ at the actin filament barbed end
Formins promote the polymerization of actin filaments at barbed ends and capping protein prevents polymerization. Here the authors use single molecule imaging to directly visualize a decision complex consisting of the formin mDia1 and capping protein bound simultaneously to the filament barbed end and the dynamic mechanisms by which it forms and dissociates.
- Jeffrey P. Bombardier
- , Julian A. Eskin
- & Jeff Gelles
-
Article
| Open Access Formin and capping protein together embrace the actin filament in a ménage à trois
Formin and capping protein together embrace the actin filament in a ménage à trois
Formins promote actin filament polymerization and capping protein blocks polymerization; both proteins are thought to exclude each other from barbed ends. Here the authors show that both proteins can simultaneously bind barbed ends in a ternary complex while enhancing each other's dissociation from the barbed end.
- Shashank Shekhar
- , Mikael Kerleau
- & Marie-France Carlier
-
Article
| Open Access The molecular architecture of the Dam1 kinetochore complex is defined by cross-linking based structural modelling
The molecular architecture of the Dam1 kinetochore complex is defined by cross-linking based structural modelling
The Dam1 complex binds kinetochores to microtubules during mitosis. Here the authors combine cross-linking/mass spectrometry with structural modelling to derive a structure for the Dam1 complex that changes when bound to microtubules; further, they provide a mechanism for regulation by Aurora B kinase.
- Alex Zelter
- , Massimiliano Bonomi
- & Trisha N. Davis
-
Article
| Open Access The γ-tubulin-specific inhibitor gatastatin reveals temporal requirements of microtubule nucleation during the cell cycle
The γ-tubulin-specific inhibitor gatastatin reveals temporal requirements of microtubule nucleation during the cell cycle
Current microtubule inhibitors target α/β-tubulin, but no specific inhibitor of γ-tubulin has been developed. Here the authors present gatastatin as a γ-tubulin inhibitor and use it to probe the role of γ-tubulin during the cell cycle.
- Takumi Chinen
- , Peng Liu
- & Elmar Schiebel
-
Article
| Open Access Mutations in TRAF3IP1/IFT54 reveal a new role for IFT proteins in microtubule stabilization
Mutations in TRAF3IP1/IFT54 reveal a new role for IFT proteins in microtubule stabilization
Nephrophthisis (NPH) is a common manifestation of ciliopathy diseases. Here the authors identify mutations in intraflagellar transport 54 (IFT54) in patients with NPH and discover an extra-ciliary role for IFT54 in regulating cytoplasmic microtubule dynamics, that contributes to the pathophysiology of this disease.
- Albane A. Bizet
- , Anita Becker-Heck
- & Sophie Saunier
-
Article
| Open Access Phosphoinositide 3-kinase enables phagocytosis of large particles by terminating actin assembly through Rac/Cdc42 GTPase-activating proteins
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase enables phagocytosis of large particles by terminating actin assembly through Rac/Cdc42 GTPase-activating proteins
Phagocytosis of large (but not small) particles requires PI 3-kinase activity. Here, Schlam et al. show that Rho GTPase-activating proteins are recruited to the phagocytic cup by products of PI 3-kinase, resulting in the local inactivation of Rac and Cdc42 and allowing for the completion of internalization of large particles.
- Daniel Schlam
- , Richard D. Bagshaw
- & Sergio Grinstein
-
Article
| Open Access Neuronal uptake and propagation of a rare phosphorylated high-molecular-weight tau derived from Alzheimer’s disease brain
Neuronal uptake and propagation of a rare phosphorylated high-molecular-weight tau derived from Alzheimer’s disease brain
In Alzheimer's disease, tau spreads throughout the brain, however the nature of the tau species propagating from one neuron to another is not known. Here, Takeda et al. identify a rare, high-molecular-weight tau as the primary species taken up and transferred between synaptically connected neurons.
- Shuko Takeda
- , Susanne Wegmann
- & Bradley T. Hyman
-
Article
| Open Access Detyrosinated microtubules modulate mechanotransduction in heart and skeletal muscle
Detyrosinated microtubules modulate mechanotransduction in heart and skeletal muscle
Microtubules are transducers of mechanical energy in muscle cells. Here, the authors show that mechanotransduction is regulated by post-translational detyrosination of microtubules in mouse heart and skeletal muscle, and that reducing detyrosination ameliorates symptoms in a model of Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
- Jaclyn P. Kerr
- , Patrick Robison
- & Christopher W. Ward
-
Article
| Open Access PKA antagonizes CLASP-dependent microtubule stabilization to re-localize Pom1 and buffer cell size upon glucose limitation
PKA antagonizes CLASP-dependent microtubule stabilization to re-localize Pom1 and buffer cell size upon glucose limitation
In fission yeast, cell growth is co-ordinated with division by the cell tip-localized DYRK kinase Pom1, which inhibits the medially placed mitotic activator Cdr2. Here, Kelkar and Martin show that, upon glucose starvation, microtubules are destabilized in a PKA-dependent manner, leading to the deposition of Pom1 at cell sides where it delays mitosis.
- Manasi Kelkar
- & Sophie G. Martin
-
Article
| Open Access Kinesin-5 is a microtubule polymerase
Kinesin-5 is a microtubule polymerase
Kinesin-5 is a tetrameric motor that slides antiparallel microtubules during mitotic spindle assembly. Chen and Hancock show that this motor also promotes microtubule assembly by stabilising protofilaments at growing plus ends, which results in the formation of banana peel-like structures.
- Yalei Chen
- & William O Hancock
-
Article
| Open Access Loss of KLF14 triggers centrosome amplification and tumorigenesis
Loss of KLF14 triggers centrosome amplification and tumorigenesis
Centrosome amplification is common in cancer, but the mechanism is not clear. Here the authors uncover a role for Kruppel-like factor 14 (KLF14) as a transcriptional repressor of polo-like kinase 4 (PLK4); KLF14 depletion correlates with increased PLK4 in human samples and leads to centrosome amplification and tumorigenesis in mice.
- Guangjian Fan
- , Lianhui Sun
- & Chuangui Wang
-
Article
| Open Access A RIAM/lamellipodin–talin–integrin complex forms the tip of sticky fingers that guide cell migration
A RIAM/lamellipodin–talin–integrin complex forms the tip of sticky fingers that guide cell migration
The leading edge of migrating cells contains activated integrins associated with growing actin filaments that form ‘sticky fingers’ to guide cell migration. Here, the authors detect a complex of MRL proteins, talin and activated integrins in lamellipodia and filopodia in living cells, comprising the tips of the ‘sticky fingers’.
- Frederic Lagarrigue
- , Praju Vikas Anekal
- & Mark H. Ginsberg
-
Article
| Open Access A resilient formin-derived cortical actin meshwork in the rear drives actomyosin-based motility in 2D confinement
A resilient formin-derived cortical actin meshwork in the rear drives actomyosin-based motility in 2D confinement
Amoeboid motility is driven by actomyosin-based contraction and exploits differences in the mechanical properties of the cortical cytoskeleton. Here the authors discover that mDia1-like formin A is responsible for generating a subset of actin filaments at the rear of Dictyosteliumthat suppresses lateral protrusions and blebbing during 2D-confined migration.
- Nagendran Ramalingam
- , Christof Franke
- & Jan Faix
-
Article
| Open Access CPI motif interaction is necessary for capping protein function in cells
CPI motif interaction is necessary for capping protein function in cells
Capping protein regulates actin filament dynamics by binding to barbed ends and preventing their growth. Edwards et al. show that capping protein also requires interactions with proteins containing a capping protein interaction motif to promote its proper localization and regulation of actin dynamics.
- Marc Edwards
- , Patrick McConnell
- & John A. Cooper
-
Article
| Open Access PTEN regulates cilia through Dishevelled
PTEN regulates cilia through Dishevelled
The formation of motile cilia is regulated by Dishevelled (DVL), a central component in WNT signalling and planar cell polarity (PCP). Here the authors identify DVL as a novel substrate of the phosphatase PTEN, coupling PTEN to cilia dynamics and PCP.
- Iryna Shnitsar
- , Mikhail Bashkurov
- & Miriam Barrios-Rodiles
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time fluorescence imaging with 20 nm axial resolution
Real-time fluorescence imaging with 20 nm axial resolution
Mapping the nanoscale height and dynamics of structures within the cell is difficult. Here the authors present a two-wavelength total internal reflection fluorescence method to perform real-time imaging with nanometre axial resolution using a conventional microscope.
- Daniel R. Stabley
- , Thomas Oh
- & Khalid Salaita

 Still and rotating myosin clusters determine cytokinetic ring constriction
Still and rotating myosin clusters determine cytokinetic ring constriction