Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Epigenome editing strategies for the functional annotation of CTCF insulators
Epigenome editing strategies for the functional annotation of CTCF insulators
The role of CTCF-bound insulator elements in enhancer-gene interactions and transcriptional regulation remains poorly understood. Here, the authors investigate multiple epigenome editing strategies for perturbing individual CTCF-bound insulators, and evaluate their effects on genome topology and transcription.
- Daniel R. Tarjan
- , William A. Flavahan
- & Bradley E. Bernstein
-
Article
| Open Access CRISPR-Cas9-based mutagenesis frequently provokes on-target mRNA misregulation
CRISPR-Cas9-based mutagenesis frequently provokes on-target mRNA misregulation
CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing is presumed to knock out gene function by generating a frameshift during NHEJ repair. Here, the authors investigate mRNA and protein expression in edited lines and find genome editing can generate internal ribosome entry sites or alternatively spliced variants.
- Rubina Tuladhar
- , Yunku Yeu
- & Lawrence Lum
-
Article
| Open Access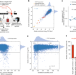 Mitigation of off-target toxicity in CRISPR-Cas9 screens for essential non-coding elements
Mitigation of off-target toxicity in CRISPR-Cas9 screens for essential non-coding elements
Off-target effects in CRISPR screens for essential regulatory elements have not been systematically evaluated. Here the authors find Cas9 nuclease, CRISPRi/a each have distinct off-target effects, and that these can be accurately identified and removed using the GuideScan sgRNA specificity score.
- Josh Tycko
- , Michael Wainberg
- & Michael C. Bassik
-
Article
| Open Access Human genome-edited hematopoietic stem cells phenotypically correct Mucopolysaccharidosis type I
Human genome-edited hematopoietic stem cells phenotypically correct Mucopolysaccharidosis type I
Mucopolysaccharidosis type I (MPSI) is a lysosomal storage disease caused by insufficient iduronidase (IDUA) activity. Here, the authors use an ex vivo genome editing approach to overexpress IDUA in human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells and show it can phenotypically correct MSPI in mouse model.
- Natalia Gomez-Ospina
- , Samantha G. Scharenberg
- & Matthew H. Porteus
-
Matters Arising
| Open Access Reply to ‘Concerns about the feasibility of using “precision guided sterile males” to control insects’
Reply to ‘Concerns about the feasibility of using “precision guided sterile males” to control insects’
- Nikolay P. Kandul
- , Junru Liu
- & Omar S. Akbari
-
Article
| Open Access Engineered CRISPRa enables programmable eukaryote-like gene activation in bacteria
Engineered CRISPRa enables programmable eukaryote-like gene activation in bacteria
CRISPR activation strategies in bacteria are limited due to the reliance on σ70 promoters. Here the authors demonstrate eukaryote-like gene activation with high dynamic ranges using σ54- dependent promoters.
- Yang Liu
- , Xinyi Wan
- & Baojun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access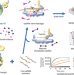 A CRISPR-Cas12a-derived biosensing platform for the highly sensitive detection of diverse small molecules
A CRISPR-Cas12a-derived biosensing platform for the highly sensitive detection of diverse small molecules
Bacterial allosteric transcription factors can sense and respond to a variety of small molecules. Here the authors present CaT-SMelor which uses Cas12a and allosteric transcription factors to detect small molecules in the nanomolar range.
- Mindong Liang
- , Zilong Li
- & Li-Xin Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Expanding C–T base editing toolkit with diversified cytidine deaminases
Expanding C–T base editing toolkit with diversified cytidine deaminases
Cytosine base editors are limited by editing scope and potential off-target effects. Here the authors screen diversified lamprey cytidine deaminases along with different protein fusion architectures and present base editors with improved fidelity.
- Tian-Lin Cheng
- , Shuo Li
- & Zilong Qiu
-
Article
| Open Access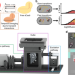 Visualisation of dCas9 target search in vivo using an open-microscopy framework
Visualisation of dCas9 target search in vivo using an open-microscopy framework
Single-particle tracking PALM (sptPALM) provides quantitative information in vivo if the protein of interest remains in a single diffusional state during track acquisition. Here the authors develop a custom-built sptPALM microscope and a Monte-Carlo based diffusion distribution analysis to study dynamic DNA-dCas9 interactions in live bacteria.
- Koen J. A. Martens
- , Sam P. B. van Beljouw
- & Johannes Hohlbein
-
Article
| Open Access Allele specific repair of splicing mutations in cystic fibrosis through AsCas12a genome editing
Allele specific repair of splicing mutations in cystic fibrosis through AsCas12a genome editing
Cystic fibrosis is caused by mutations in the CFTR chloride channel. Here, the authors develop a gene therapy approach using the programmable nuclease AsCas12a to correct a splicing mutation in CFTR, and show efficient repair of the mutation and recovery of CFTR function in patient-derived organoids and airway epithelial cells.
- Giulia Maule
- , Antonio Casini
- & Anna Cereseto
-
Article
| Open Access Functional genetic variants can mediate their regulatory effects through alteration of transcription factor binding
Functional genetic variants can mediate their regulatory effects through alteration of transcription factor binding
Functional variants have been proposed to alter transcription factor binding. Here, the authors provide direct evidence that functional variants within the TBC1D4 gene, encoding an NFκB binding site, can alter transcription factor binding, and use CRISPR-Cas9 to reveal localization of the transcription factor to be the regulator of chromatin accessibility and p65 binding and ultimately TBC1D4 expression.
- Andrew D. Johnston
- , Claudia A. Simões-Pires
- & John M. Greally
-
Article
| Open Access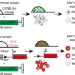 Standard screening methods underreport AAV-mediated transduction and gene editing
Standard screening methods underreport AAV-mediated transduction and gene editing
Conventional methods to detect AAV vector transduction can miss transient or low levels of reporter expression. Here the authors use editing-reporter mice and discover numerous sites of AAV targeting along with better prediction of the gene editing footprint.
- Jonathan F. Lang
- , Sushila A. Toulmin
- & Beverly L. Davidson
-
Article
| Open Access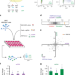 Stimulation of CRISPR-mediated homology-directed repair by an engineered RAD18 variant
Stimulation of CRISPR-mediated homology-directed repair by an engineered RAD18 variant
Manipulating DNA repair pathways can be used to improve the outcomes of CRISPR-based genome editing. Here the authors derive an enhanced RAD18 variant that suppresses 53BP1 recruitment to DNA double-strand breaks to enhance homology-mediated repair.
- Tarun S. Nambiar
- , Pierre Billon
- & Alberto Ciccia
-
Article
| Open Access Satb1 integrates DNA binding site geometry and torsional stress to differentially target nucleosome-dense regions
Satb1 integrates DNA binding site geometry and torsional stress to differentially target nucleosome-dense regions
Satb1 is a master regulator of multiple cellular processes. Here the authors find that Satb1 preferentially targets nucleosome dense regions and combinatorially uses multiple selection criteria including DNA torsion, flanking DNA shape, motif density and periodicity to streamline binding choices.
- Rajarshi P. Ghosh
- , Quanming Shi
- & Jan T. Liphardt
-
Article
| Open Access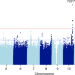 ZRANB3 is an African-specific type 2 diabetes locus associated with beta-cell mass and insulin response
ZRANB3 is an African-specific type 2 diabetes locus associated with beta-cell mass and insulin response
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is prevalent in populations worldwide, however, mostly studied in European and mixed-ancestry populations. Here, the authors perform a genome-wide association study for T2D in over 5,000 sub-Saharan Africans and identify a locus, ZRANB3, that is specific for this population.
- Adebowale A. Adeyemo
- , Norann A. Zaghloul
- & Charles N. Rotimi
-
Article
| Open Access Pooled library screening with multiplexed Cpf1 library
Pooled library screening with multiplexed Cpf1 library
AsCpf1 is an alternative nuclease to Cas9 for CRISPR mediated genome engineering. Here the authors demonstrate functional genomic screens with AsCpf1 that minimize library size with no loss in gene targeting efficiency.
- Jintan Liu
- , Sanjana Srinivasan
- & Giulio Draetta
-
Article
| Open Access Target preference of Type III-A CRISPR-Cas complexes at the transcription bubble
Target preference of Type III-A CRISPR-Cas complexes at the transcription bubble
Type III CRISPR-Cas systems are able to target transcriptionally active DNA sequences in phages and plasmids. Here, the authors reveal the mechanism of the target nucleic acid preference of Type III-A CRISPR-Cas complexes at the transcription bubble by a combination of structural and biochemical approaches.
- Tina Y. Liu
- , Jun-Jie Liu
- & Jennifer A. Doudna
-
Article
| Open Access Modular one-pot assembly of CRISPR arrays enables library generation and reveals factors influencing crRNA biogenesis
Modular one-pot assembly of CRISPR arrays enables library generation and reveals factors influencing crRNA biogenesis
CRISPR array generation is difficult due to reoccurring repeat sequences. Here the authors present CRATES—a modular, one-pot assembly method—and demonstrate the creation of arrays for Cas9, Cas12a and Cas13a for cell-free, bacterial, yeast and mammalian systems.
- Chunyu Liao
- , Fani Ttofali
- & Chase L. Beisel
-
Article
| Open Access Sequential LASER ART and CRISPR Treatments Eliminate HIV-1 in a Subset of Infected Humanized Mice
Sequential LASER ART and CRISPR Treatments Eliminate HIV-1 in a Subset of Infected Humanized Mice
Here, the authors show that sequential treatment with long-acting slow-effective release ART and AAV9- based delivery of CRISPR-Cas9 results in undetectable levels of virus and integrated DNA in a subset of humanized HIV-1 infected mice. This proof-of-concept study suggests that HIV-1 elimination is possible.
- Prasanta K. Dash
- , Rafal Kaminski
- & Howard E. Gendelman
-
Article
| Open Access Generating viable mice with heritable embryonically lethal mutations using the CRISPR-Cas9 system in two-cell embryos
Generating viable mice with heritable embryonically lethal mutations using the CRISPR-Cas9 system in two-cell embryos
Roughly 25% of mouse genes are embryonically lethal when knocked out, preventing the generation of viable mouse models. Here the authors use CRISPR-Cas9 to edit one blastomere of a two-cell embryo to generate viable chimeric mice.
- Yi Wu
- , Jing Zhang
- & Songlin Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient base editing for multiple genes and loci in pigs using base editors
Efficient base editing for multiple genes and loci in pigs using base editors
Base editors can efficiently produce single nucleotide alterations without requiring a double-strand break. Here the authors show base editing at multiple sites simultaneously in pigs.
- Jingke Xie
- , Weikai Ge
- & Liangxue Lai
-
Article
| Open Access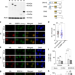 CRISPR-Cas9 fusion to dominant-negative 53BP1 enhances HDR and inhibits NHEJ specifically at Cas9 target sites
CRISPR-Cas9 fusion to dominant-negative 53BP1 enhances HDR and inhibits NHEJ specifically at Cas9 target sites
Global inhibition of NHEJ factors has been one strategy to improve CRISPR-Cas9 mediated HDR. Here the authors fuse a dominant-negative mutant of 53BP1 to Cas9 to enhance HDR frequency, reduce NHEJ specifically at the Cas9 cut sites, and reduce the toxicity associated with global NHEJ inhibition.
- Rajeswari Jayavaradhan
- , Devin M. Pillis
- & Punam Malik
-
Article
| Open Access Inhibition of CRISPR-Cas9 ribonucleoprotein complex assembly by anti-CRISPR AcrIIC2
Inhibition of CRISPR-Cas9 ribonucleoprotein complex assembly by anti-CRISPR AcrIIC2
Anti-CRISPR proteins offer the means of regulating CRISPR-Cas9 activity. Here the authors present the structure and biochemical characterisation of AcrIIC2Nme alone and in complex with Cas9.
- Annoj Thavalingam
- , Zhi Cheng
- & Karen L. Maxwell
-
Article
| Open Access Two HEPN domains dictate CRISPR RNA maturation and target cleavage in Cas13d
Two HEPN domains dictate CRISPR RNA maturation and target cleavage in Cas13d
Cas13d is a class 2 type VI-D CRISPR-Cas RNA-guided RNase. Here the authors present the high-resolution crystal structure of the uncultured Ruminococcus sp. Cas13d (UrCas13d)-crRNA complex and by combining structural, mutational and biochemical studies provide mechanistic insights into the CRISPR-Cas13d system.
- Bo Zhang
- , Yangmiao Ye
- & Songying Ouyang
-
Article
| Open Access Wwp2 maintains cartilage homeostasis through regulation of Adamts5
Wwp2 maintains cartilage homeostasis through regulation of Adamts5
Wwp2 is an HECT-type E3 ubiquitin ligase abundantly expressed in articular cartilage. Here, the authors show that in mice, loss of Wwp2 leads to upregulated Runx2-Adamts5 signaling in articular cartilage and development of osteoarthritis, and that disease severity is reduced by injection of Wwp2 mRNA
- Sho Mokuda
- , Ryo Nakamichi
- & Hiroshi Asahara
-
Article
| Open Access Functional linkage of gene fusions to cancer cell fitness assessed by pharmacological and CRISPR-Cas9 screening
Functional linkage of gene fusions to cancer cell fitness assessed by pharmacological and CRISPR-Cas9 screening
Gene fusions are observed in many cancers but their link to tumour fitness is largely unknown. Here, transcriptomic analysis combined with pharmacological and CRISPR-Cas9 screening of cancer cell lines was used to evaluate the functional linkage between fusions and tumour fitness.
- Gabriele Picco
- , Elisabeth D. Chen
- & Mathew J. Garnett
-
Article
| Open Access Targeted removal of epigenetic barriers during transcriptional reprogramming
Targeted removal of epigenetic barriers during transcriptional reprogramming
Master transcription factors dominantly direct cell fate and barriers ensuring their tissue specific silencing are not clearly defined. Here, the authors demonstrate that inefficient targeted transactivation of Sox1 in neural progenitor cells is surmountable through targeted promoter demethylation using dCas9-Tet1.
- Valentin Baumann
- , Maximilian Wiesbeck
- & Stefan H. Stricker
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling CRISPR-Cas9 with ligand-activated and ligand-deactivated sgRNAs
Controlling CRISPR-Cas9 with ligand-activated and ligand-deactivated sgRNAs
Control of CRISPR-Cas9 activity allows for fine-tuning of editing and gene expression. Here the authors use gRNAs modified with RNA aptamers to enable small molecule control in bacterial systems.
- Kale Kundert
- , James E. Lucas
- & Tanja Kortemme
-
Article
| Open Access Tissue-specific (ts)CRISPR as an efficient strategy for in vivo screening in Drosophila
Tissue-specific (ts)CRISPR as an efficient strategy for in vivo screening in Drosophila
Applicability of CRISPR-Cas9 for in vivo screening has so far been limited. Here the authors characterize tissue specific CRISPR in the Drosophila mushroom body, generating a library of gRNA-harboring plasmids and fly lines for in vivo screening.
- Hagar Meltzer
- , Efrat Marom
- & Oren Schuldiner
-
Article
| Open Access Switching the activity of Cas12a using guide RNA strand displacement circuits
Switching the activity of Cas12a using guide RNA strand displacement circuits
Cas12a is a useful alternative to Cas9 for genome editing and regulation. Here the authors design strand displacement gRNAs that can add functionality to Cas12a by acting as multi-input logic gates.
- Lukas Oesinghaus
- & Friedrich C. Simmel
-
Review Article
| Open Access Humanising the mouse genome piece by piece
Humanising the mouse genome piece by piece
Generation of transgenic mice has become routine in studying gene function and disease mechanisms, but often this is not enough to fully understand human biology. Here, the authors review the current state of the art of targeted genomic humanisation strategies and their advantages over classic approaches.
- Fei Zhu
- , Remya R. Nair
- & Thomas J. Cunningham
-
Article
| Open Access Multifunctional CRISPR-Cas9 with engineered immunosilenced human T cell epitopes
Multifunctional CRISPR-Cas9 with engineered immunosilenced human T cell epitopes
Possible immunogenicity of the Cas9 protein raises concerns about therapeutic applications. Here the authors identify pre-existing CD8+T-cell immunity in healthy individuals and in response modify Cas9 to remove the immunodominant epitopes.
- Shayesteh R. Ferdosi
- , Radwa Ewaisha
- & Karen S. Anderson
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient allelic-drive in Drosophila
Efficient allelic-drive in Drosophila
Gene-drives use CRISPR-Cas9 to be transmitted in a super-Mendelian fashion. Here the authors develop an allelic-drive for selective inheritance of a desired allele.
- Annabel Guichard
- , Tisha Haque
- & Ethan Bier
-
Article
| Open Access Gene correction for SCID-X1 in long-term hematopoietic stem cells
Gene correction for SCID-X1 in long-term hematopoietic stem cells
Gene correction in hematopoietic stem cells could be a powerful way to treat monogenic diseases of the blood and immune system. Here the authors develop a strategy using CRISPR-Cas9 and an aAdeno-Associated vVirus(AAV)-delivered IL2RG cDNA to correct X-linked sSevere Ccombined iImmunodeficiency (SCID-X1) with a high success rate.
- Mara Pavel-Dinu
- , Volker Wiebking
- & Matthew H. Porteus
-
Article
| Open Access Multiplexed Cas9 targeting reveals genomic location effects and gRNA-based staggered breaks influencing mutation efficiency
Multiplexed Cas9 targeting reveals genomic location effects and gRNA-based staggered breaks influencing mutation efficiency
Designing effective genome engineering strategies requires an understanding of the impact that genomic locus has on CRISPR-Cas9 activity. Here the authors use TRIP integrations to profile editing outcomes genome-wide and observe that gRNA sequence influences the structure of the double strand break.
- Santiago Gisler
- , Joana P. Gonçalves
- & Maarten van Lohuizen
-
Article
| Open Access Decoupling tRNA promoter and processing activities enables specific Pol-II Cas9 guide RNA expression
Decoupling tRNA promoter and processing activities enables specific Pol-II Cas9 guide RNA expression
The utility of CRISPR-based technologies could be enhanced with the ability to control the spatial and temporal expression of gRNAs. Here the authors design a tRNA scaffold for highly specific gRNA production from a Pol II promoter.
- David J. H. F. Knapp
- , Yale S. Michaels
- & Tudor A. Fulga
-
Article
| Open Access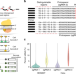 Lineage tracing using a Cas9-deaminase barcoding system targeting endogenous L1 elements
Lineage tracing using a Cas9-deaminase barcoding system targeting endogenous L1 elements
Lineage tracing has provided new insights into cell fate but defining cellular diversity remains a challenge. Here the authors target endogenous repeat regions in mammalian cells with cytidine deaminase fused to nCas9 to create genetic barcodes for fine-resolution mapping.
- Byungjin Hwang
- , Wookjae Lee
- & Duhee Bang
-
Article
| Open Access CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing induces megabase-scale chromosomal truncations
CRISPR-Cas9 genome editing induces megabase-scale chromosomal truncations
CRISPR-Cas9 has been rapidly adopted to generate cell line models of disease. Here the authors show, while attempting to establish a congenital erythropoietic porphyria model, unexpected chromosome truncations generated by a p53-dependent mechanism.
- Grégoire Cullot
- , Julian Boutin
- & Aurélie Bedel
-
Article
| Open Access Precise tuning of gene expression levels in mammalian cells
Precise tuning of gene expression levels in mammalian cells
Analogue regulation of gene expression is important for normal function in mammals but existing genetic technologies are designed to achieve ON/OFF control. Here the authors develop synthetic microRNA silencing-mediated fine-tuners (miSFITs) to precisely control target gene expression levels.
- Yale S. Michaels
- , Mike B. Barnkob
- & Tudor A. Fulga
-
Article
| Open Access Site-specific manipulation of Arabidopsis loci using CRISPR-Cas9 SunTag systems
Site-specific manipulation of Arabidopsis loci using CRISPR-Cas9 SunTag systems
Few approaches for targeted manipulation of the epigenome are available in plants. Here, the authors adapt the dCas9-SunTag system to engineer targeted gene activation and site-specific manipulation of DNA methylation in Arabidopsis.
- Ashot Papikian
- , Wanlu Liu
- & Steven E. Jacobsen
-
Article
| Open Access Engineer chimeric Cas9 to expand PAM recognition based on evolutionary information
Engineer chimeric Cas9 to expand PAM recognition based on evolutionary information
The genomic locations that can be targeted for editing by CRISPR are limited by the presence of the nuclease-specific PAM sequence. Here, the authors show PAM recognition can be expanded by replacing the key region in the PAM interaction domain of SaCas9 with the corresponding region of SaCas9 orthologs.
- Dacheng Ma
- , Zhimeng Xu
- & Zhen Xie
-
Article
| Open Access Loss-of-function mutations in QRICH2 cause male infertility with multiple morphological abnormalities of the sperm flagella
Loss-of-function mutations in QRICH2 cause male infertility with multiple morphological abnormalities of the sperm flagella
Multiple morphological abnormalities of the sperm flagella (MMAF) is a cause of male infertility. Here the authors identify homozygous nonsense mutations of the glutamine rich 2 (QRICH2) gene in two MMAF patients from 2 consanguineous families and show using QRICH2 knockout mice that the protein is required for sperm flagellar formation and motility.
- Ying Shen
- , Feng Zhang
- & Wenming Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Comparative oncogenomics identifies combinations of driver genes and drug targets in BRCA1-mutated breast cancer
Comparative oncogenomics identifies combinations of driver genes and drug targets in BRCA1-mutated breast cancer
It is difficult to identify cancer driver genes in cancers, for instance BRCA1 mutated breast cancer, that are characterised by large scale genomic alterations. Here, the authors develop genetically engineered mouse models of BRCA1-deficient breast cancer that allow highthroughput in vivo perturbation of candidate driver genes, validating drivers Myc, Met, Pten and Rb1, and identifying MCL1 as a collaborating driver whose targeting can impact efficacy of PARP inhibition.
- Stefano Annunziato
- , Julian R. de Ruiter
- & Jos Jonkers
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering of CRISPR-Cas12b for human genome editing
Engineering of CRISPR-Cas12b for human genome editing
The Cas12b family of CRISPR nucleases has been underutilized in mammalian cells due to the high temperature requirement of known members. Here the authors engineer BhCas12b to overcome this limitation for robust and specific genome editing applications in human cells.
- Jonathan Strecker
- , Sara Jones
- & Feng Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access CRISPR analysis suggests that small circular single-stranded DNA smacoviruses infect Archaea instead of humans
CRISPR analysis suggests that small circular single-stranded DNA smacoviruses infect Archaea instead of humans
Smacoviruses are found in the intestinal tract of humans and animals but their precise host remains elusive. Here, the authors identify smacovirus-matching CRISPR spacer sequences in the faecal archaeon Candidatus Methanomassiliicoccus intestinalis, implicating Archaea as a potential host.
- César Díez-Villaseñor
- & Francisco Rodriguez-Valera
-
Article
| Open Access Anti-CRISPR-mediated control of gene editing and synthetic circuits in eukaryotic cells
Anti-CRISPR-mediated control of gene editing and synthetic circuits in eukaryotic cells
Anti-CRISPR proteins derived from phage can abrogate CRISPR activity. The authors repurpose these molecules for demonstrating genomic write-protection and pre-programmed gene expression circuits.
- Muneaki Nakamura
- , Prashanth Srinivasan
- & Lei S. Qi
-
Article
| Open Access Transforming insect population control with precision guided sterile males with demonstration in flies
Transforming insect population control with precision guided sterile males with demonstration in flies
Sterile Insect Technique (SIT) is used to suppress wild populations. Here the authors integrate CRISPR-based technology and SIT to develop a precision guided SIT (pgSIT), and demonstrate its proof-of-principle by generating 100% sterile males.
- Nikolay P. Kandul
- , Junru Liu
- & Omar S. Akbari
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide profiling of adenine base editor specificity by EndoV-seq
Genome-wide profiling of adenine base editor specificity by EndoV-seq
Adenine base editors are an important contribution to the genome editing toolbox. Here the authors present EndoV-seq, an endonuclease-based assay for evaluating genomewide off-target effects of base editing.
- Puping Liang
- , Xiaowei Xie
- & Zhou Songyang
-
Article
| Open Access Genome editing in primary cells and in vivo using viral-derived Nanoblades loaded with Cas9-sgRNA ribonucleoproteins
Genome editing in primary cells and in vivo using viral-derived Nanoblades loaded with Cas9-sgRNA ribonucleoproteins
A current challenge in genome editing is delivering Cas9 and sgRNA into target cells. Here the authors engineer a delivery system based on murine leukemia virus-like particles loaded with Cas9-sgRNA ribonucleoproteins to induce efficient genome editing in both cell culture and in vivo in mouse.
- Philippe E. Mangeot
- , Valérie Risson
- & Emiliano P. Ricci

 Genetic determinants of cellular addiction to DNA polymerase theta
Genetic determinants of cellular addiction to DNA polymerase theta