Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access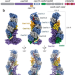 Structural rearrangements allow nucleic acid discrimination by type I-D Cascade
Structural rearrangements allow nucleic acid discrimination by type I-D Cascade
I-D CRISPR-Cascade can target both single-stranded and double-stranded nucleic acids. Here, Schwartz et. al determine these structures and reveal large-scale rearrangements that allow for target discrimination and destruction.
- Evan A. Schwartz
- , Tess M. McBride
- & David W. Taylor
-
Article
| Open Access Multiplex base- and prime-editing with drive-and-process CRISPR arrays
Multiplex base- and prime-editing with drive-and-process CRISPR arrays
Current base- and prime-editing technologies lack efficient strategies to edit multiple genomic loci simultaneously, limiting their applications in complex genomics and polygenic diseases. Here the authors describe drive-and-process CRISPR array architectures for multiplex base-editing and multiplex prime-editing in human cells.
- Qichen Yuan
- & Xue Gao
-
Article
| Open Access Broad-spectrum CRISPR-mediated inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 variants and endemic coronaviruses in vitro
Broad-spectrum CRISPR-mediated inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 variants and endemic coronaviruses in vitro
A major challenge in coronavirus vaccination and treatment is to counteract rapid viral evolution and mutations. Here the authors show that CRISPR-Cas13d can be used as a broad-spectrum antiviral to inhibit human coronaviruses, including new SARS-CoV-2 variants, combined with small molecule drugs for an enhanced antiviral effect in human primary cells.
- Leiping Zeng
- , Yanxia Liu
- & Lei S. Qi
-
Article
| Open Access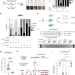 Genome editing in animals with minimal PAM CRISPR-Cas9 enzymes
Genome editing in animals with minimal PAM CRISPR-Cas9 enzymes
PAM requirement is a constraint for genome editing but this has been circumvented by engineered Cas9 nucleases as SpG and SpRY recognizing minimal PAM sequences. Here, the authors validate and optimize SpG and SpRY in vivo expanding the targeting landscape in animals.
- Jeremy Vicencio
- , Carlos Sánchez-Bolaños
- & Miguel A. Moreno-Mateos
-
Article
| Open Access PERSIST platform provides programmable RNA regulation using CRISPR endoRNases
PERSIST platform provides programmable RNA regulation using CRISPR endoRNases
Gene circuits must resist epigenetic silencing for reliable therapeutic applications. Here the authors develop an RNA-level regulation platform using CRISPR endoRNases that is modular, scalable, and more stable than traditional transcriptional versions.
- Breanna DiAndreth
- , Noreen Wauford
- & Ron Weiss
-
Article
| Open Access A genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 knockout screen identifies essential and growth-restricting genes in human trophoblast stem cells
A genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 knockout screen identifies essential and growth-restricting genes in human trophoblast stem cells
Here the authors perform a genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 knockout screen to systematically identify and characterize essential and growth-restricting genes in human trophoblast cells. They identify TEAD1 as a key regulator that plays an important role in the specification, maintenance, and differentiation of the human trophoblast lineage by modulating chromatin architecture and gene expression.
- Chen Dong
- , Shuhua Fu
- & Thorold W. Theunissen
-
Article
| Open Access Double-tap gene drive uses iterative genome targeting to help overcome resistance alleles
Double-tap gene drive uses iterative genome targeting to help overcome resistance alleles
CRISPR gene drives are genetic elements capable of quickly spreading through populations and they offer promising solutions for curbing the spread of vector-borne diseases and controlling crop pest and invasive species populations. Here the authors present a method for overcoming resistance alleles “double-tap,” that encodes additional gRNAs in the gene drive that target the most common generated resistance alleles.
- Alena L. Bishop
- , Víctor López Del Amo
- & Valentino M. Gantz
-
Article
| Open Access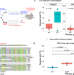 Targeting double-strand break indel byproducts with secondary guide RNAs improves Cas9 HDR-mediated genome editing efficiencies
Targeting double-strand break indel byproducts with secondary guide RNAs improves Cas9 HDR-mediated genome editing efficiencies
Programmable double-strand DNA breaks (DSBs) can be harnessed for precision genome editing through manipulation of the homology-directed repair (HDR) pathway. Here the authors report the development of the double tap - double tap implements secondary gRNAs which target Cas9 to common indel sequences and provides a second chance at HDR.
- Zsolt Bodai
- , Alena L. Bishop
- & Alexis C. Komor
-
Article
| Open Access Comparative optimization of combinatorial CRISPR screens
Comparative optimization of combinatorial CRISPR screens
Combinatorial CRISPR screens can be utilized to identify genetic interactions and functional redundancies of multiple genes. Here, the authors benchmark ten digenic CRISPR technologies and identify novel Cas9 tracrRNA combinations that show superior performance.
- Ruitong Li
- , Olaf Klingbeil
- & William R. Sellers
-
Article
| Open Access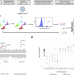 Identification of DAXX as a restriction factor of SARS-CoV-2 through a CRISPR/Cas9 screen
Identification of DAXX as a restriction factor of SARS-CoV-2 through a CRISPR/Cas9 screen
Here, Mac Kain and Maarifi et al. perform a functional CRISPR/Cas9 screen to identify SARS-CoV-2 restriction factors in A549 cells. They identify DAXX, a scaffold protein of nuclear bodies with diverse functions, that has anti-viral activity post SARS-CoV-2 entry, while SARS-CoV-2 has evolved a mechanism to counteract its action via PLpro-mediated proteasomal degradation.
- Alice Mac Kain
- , Ghizlane Maarifi
- & Ferdinand Roesch
-
Article
| Open Access Knockdown of GABAA alpha3 subunits on thalamic reticular neurons enhances deep sleep in mice
Knockdown of GABAA alpha3 subunits on thalamic reticular neurons enhances deep sleep in mice
Uygun et al. show that deletion of GABAA receptors from the thalamic reticular nucleus using CRISPR gene editing in mice boosts the delta waves, indicating a role for GABAA receptors on thalamic reticular nucleus neurons in NREM sleep delta oscillations.
- David S. Uygun
- , Chun Yang
- & Radhika Basheer
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide CRISPR screens identify GATA6 as a proviral host factor for SARS-CoV-2 via modulation of ACE2
Genome-wide CRISPR screens identify GATA6 as a proviral host factor for SARS-CoV-2 via modulation of ACE2
Here, Israeli and Finkel et al. perform genome-wide CRISPR knockout screens to identify host factors required for the infection with SARS-CoV-2 and two additionally variants of concern, Alpha and Beta, unveiling shared and differential host pathways required by the variants, and demonstrate GATA6 is critical for SARS-CoV-2 viral entry through modulation of ACE2 expression.
- Ma’ayan Israeli
- , Yaara Finkel
- & Adi Bercovich-Kinori
-
Article
| Open Access Machine learning-coupled combinatorial mutagenesis enables resource-efficient engineering of CRISPR-Cas9 genome editor activities
Machine learning-coupled combinatorial mutagenesis enables resource-efficient engineering of CRISPR-Cas9 genome editor activities
Screening combinatorial mutants is too massive for wet-lab experiment alone. Here the authors present a machine learning-coupled combinatorial mutagenesis approach to vastly reduce experimental burden for engineering Cas9 genome editing enzymes.
- Dawn G. L. Thean
- , Hoi Yee Chu
- & Alan S. L. Wong
-
Article
| Open Access A loss-of-adhesion CRISPR-Cas9 screening platform to identify cell adhesion-regulatory proteins and signaling pathways
A loss-of-adhesion CRISPR-Cas9 screening platform to identify cell adhesion-regulatory proteins and signaling pathways
Targeting integrin-mediated retention of malignant B cells in their protective microenvironment is an efficacious treatment for lymphoma and leukemia. Here, the authors present an unbiased loss-of-adhesion CRISPR screening method, identifying therapeutic targets for these B-cell malignancies.
- Martin F. M. de Rooij
- , Yvonne J. Thus
- & Marcel Spaargaren
-
Article
| Open Access Inducible and reversible RNA N6-methyladenosine editing
Inducible and reversible RNA N6-methyladenosine editing
RNA modifications, including N6-methyladenosine (m6A), have been reported to regulate fundamental RNA processes and properties, and directly linked to various human diseases. Here, the authors develop a chemically inducible and reversible RNA m6A modification editing platform integrating chemically induced proximity (CIP) and CRISPR methods.
- Huaxia Shi
- , Ying Xu
- & Fu-Sen Liang
-
Article
| Open Access Reprogrammed tracrRNAs enable repurposing of RNAs as crRNAs and sequence-specific RNA biosensors
Reprogrammed tracrRNAs enable repurposing of RNAs as crRNAs and sequence-specific RNA biosensors
In type II CRISPR systems, the guide RNA (gRNA) comprises a CRISPR RNA (crRNA) and a hybridized trans-acting CRISPR RNA (tracrRNA), both being essential in guided DNA targeting functions. Here the authors investigate the programmability of crRNA-tracrRNA hybridization for Cas9 and apply this to biosensing.
- Yang Liu
- , Filipe Pinto
- & Baojun Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Insights into the inhibition of type I-F CRISPR-Cas system by a multifunctional anti-CRISPR protein AcrIF24
Insights into the inhibition of type I-F CRISPR-Cas system by a multifunctional anti-CRISPR protein AcrIF24
Phages use anti-CRISPR proteins (Acrs) to counteract the bacterial CRISPR-Cas systems. Here, the authors characterize AcrIF24, which functions as an Aca (Acr-associated) to repress and regulate its own transcription, dimerizes the Csy complex, blocks the hybridization of target DNA, and tethers non-sequence-specific DNA to the Csy complex.
- Lingguang Yang
- , Laixing Zhang
- & Yue Feng
-
Article
| Open Access Enhancement of prime editing via xrRNA motif-joined pegRNA
Enhancement of prime editing via xrRNA motif-joined pegRNA
The prime editors (PEs) have shown great promise for precise genome modification. Here the authors place a stabilizing viral xrRNA motif to the 3′ of pegRNAs to enhance editing efficiencies.
- Guiquan Zhang
- , Yao Liu
- & Jianghuai Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Lupus enhancer risk variant causes dysregulation of IRF8 through cooperative lncRNA and DNA methylation machinery
Lupus enhancer risk variant causes dysregulation of IRF8 through cooperative lncRNA and DNA methylation machinery
The functional effects of genetic loci associated with autoimmune disease are not well understood. By dissecting an autoimmune disease genetic locus, the authors define an immune cell-type-specific enhancer and the molecular mechanisms underlying the dysregulation of IRF8 expression by lupus risk variants.
- Tian Zhou
- , Xinyi Zhu
- & Nan Shen
-
Article
| Open Access CRISPR-mediated multiplexed live cell imaging of nonrepetitive genomic loci with one guide RNA per locus
CRISPR-mediated multiplexed live cell imaging of nonrepetitive genomic loci with one guide RNA per locus
Three-dimensional (3D) structures of the genome are dynamic, heterogeneous and functionally important. Here the authors present a CRISPR-based approach for labeling the genome at multiple nonrepetitive loci in living cells and to image chromatin loops in the presence and absence of cohesin.
- Patricia A. Clow
- , Menghan Du
- & Albert W. Cheng
-
Article
| Open Access Highly efficient prime editing by introducing same-sense mutations in pegRNA or stabilizing its structure
Highly efficient prime editing by introducing same-sense mutations in pegRNA or stabilizing its structure
Prime editors can mediate all twelve types of base substitutions and small insertions or deletions in living cells but its efficiency remains low. Here the authors introduce same-sense mutations into pegRNAs to increase base-editing efficiency and the pegRNA secondary structure was altered to increase indel-editing efficiency.
- Xiaosa Li
- , Lina Zhou
- & Jia Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Phage peptides mediate precision base editing with focused targeting window
Phage peptides mediate precision base editing with focused targeting window
Base editors are genome engineering tools that can generate nucleotide substitutions without introducing double-stranded breaks. Here the authors show that a phage-derived peptidyl CRISPR inhibitor can be employed to modulate the activity and targeting scope of CRISPR base editor for precision base editing applications.
- Kun Jia
- , Yan-ru Cui
- & Jia Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Guide RNAs containing universal bases enable Cas9/Cas12a recognition of polymorphic sequences
Guide RNAs containing universal bases enable Cas9/Cas12a recognition of polymorphic sequences
Genetic variance poses a major challenge for CRISPR-based human therapeutics and pathogen diagnostics. Here the authors show how to circumvent this issue by using guide RNAs containing universal bases to tailor Cas9/Cas12 specificity.
- Amanda R. Krysler
- , Christopher R. Cromwell
- & Basil P. Hubbard
-
Article
| Open Access Harnessing DSB repair to promote efficient homology-dependent and -independent prime editing
Harnessing DSB repair to promote efficient homology-dependent and -independent prime editing
Prime editing is a next-generation approach for precision genome engineering. Here the authors design a nuclease-based prime editor that leverages DNA repair pathways for targeted genomic insertions.
- Martin Peterka
- , Nina Akrap
- & Marcello Maresca
-
Article
| Open Access Precise tumor immune rewiring via synthetic CRISPRa circuits gated by concurrent gain/loss of transcription factors
Precise tumor immune rewiring via synthetic CRISPRa circuits gated by concurrent gain/loss of transcription factors
“Reinvigoration of antitumor immunity has recently become the central theme for the development of cancer therapies. Here the authors present an adaptable gene circuit to harness the CRISPRa for tumorlocalized immune activation.”
- Yafeng Wang
- , Guiquan Zhang
- & Jianghuai Liu
-
Article
| Open Access FrCas9 is a CRISPR/Cas9 system with high editing efficiency and fidelity
FrCas9 is a CRISPR/Cas9 system with high editing efficiency and fidelity
Gene editing tools have tremendous potential for biomedical and basic research. Here the authors report a Cas9 from Faecalibaculum rodentium (FrCas9) that achieves efficient and specific gene editing in human cells with a NNTA palindrome PAMs for targeting optimal sites at TATA-boxes to enhance CRISPRa/i screening.
- Zifeng Cui
- , Rui Tian
- & Zheng Hu
-
Article
| Open Access A kinetic model predicts SpCas9 activity, improves off-target classification, and reveals the physical basis of targeting fidelity
A kinetic model predicts SpCas9 activity, improves off-target classification, and reveals the physical basis of targeting fidelity
Cas9 off-target sites can be predicted by many bioinformatics tools. Here the authors present low complexity mechanistic model that characterizes SpCas9 kinetics in free-energy terms, allowing quantitative prediction of off-target activity in bulk-biochemistry, single molecule, and whole-genome profiling experiments.
- Behrouz Eslami-Mossallam
- , Misha Klein
- & Martin Depken
-
Article
| Open Access Benchmarking of SpCas9 variants enables deeper base editor screens of BRCA1 and BCL2
Benchmarking of SpCas9 variants enables deeper base editor screens of BRCA1 and BCL2
Numerous rationally-designed and directed-evolution variants of SpCas9 have been reported to expand the utility of CRISPR technology. Here the authors make comparisons of numerous Cas9 variants, nominate options for base editing screens with denser coverage with A>G and C>T base editing screens and identify loss-of-function mutations in BRCA1 and Venetoclax-resistant mutations in BCL2.
- Annabel K. Sangree
- , Audrey L. Griffith
- & John G. Doench
-
Article
| Open Access Cas9 exo-endonuclease eliminates chromosomal translocations during genome editing
Cas9 exo-endonuclease eliminates chromosomal translocations during genome editing
Chromosomal structural variations induced by CRISPR/Cas hinder its application in clinics. Here, the authors fuse Cas9 with optimized TREX2 to generate Cas9TX, which can prevent perfect repair and inhibit repeated cleavage.
- Jianhang Yin
- , Rusen Lu
- & Jiazhi Hu
-
Article
| Open Access Crosstalk between CRISPR-Cas9 and the human transcriptome
Crosstalk between CRISPR-Cas9 and the human transcriptome
The off-target effects of CRISPR-Cas9 are thought to be mediated by its cognate guide RNA. Here the authors show that Cas9 independently interacts with the human transcriptome, correlating with elevated RNA editing even under guide RNA co-expression.
- Aaron A. Smargon
- , Assael A. Madrigal
- & Gene W. Yeo
-
Article
| Open Access Mutation-specific reporter for optimization and enrichment of prime editing
Mutation-specific reporter for optimization and enrichment of prime editing
While prime editing is a promising technique, some genomic sites remain difficult to edit. Here the authors present fluoPEER, fluorescent prime editing and enrichment reporter, to rank the efficiency of pegRNAs and prime editor variants.
- I. F. Schene
- , I. P. Joore
- & S. A. Fuchs
-
Article
| Open Access Investigation of Cas9 antibodies in the human eye
Investigation of Cas9 antibodies in the human eye
Pre-existing antibodies against Cas9 proteins represent a potential issue for gene therapies, including those targeting the eye. Here the authors assess the presence of intraocular antibodies, and show that Cas9 antibodies were prevalent in human serum but not the eye, unless prior bacterial infection occurred.
- Marcus A. Toral
- , Carsten T. Charlesworth
- & Vinit B. Mahajan
-
Article
| Open Access A fast Myosin super enhancer dictates muscle fiber phenotype through competitive interactions with Myosin genes
A fast Myosin super enhancer dictates muscle fiber phenotype through competitive interactions with Myosin genes
The contractile properties of adult myofibers are shaped by their Myosin heavy chain isoform content. Here the authors show that a super enhancer controls the spatiotemporal expression of the genes at the fast myosin heavy chain locus by DNA looping and that this expression profile is recapitulated in a rainbow transgenic mouse model of the locus.
- Matthieu Dos Santos
- , Stéphanie Backer
- & Pascal Maire
-
Article
| Open Access Cell adhesion molecule KIRREL1 is a feedback regulator of Hippo signaling recruiting SAV1 to cell-cell contact sites
Cell adhesion molecule KIRREL1 is a feedback regulator of Hippo signaling recruiting SAV1 to cell-cell contact sites
How cell-cell contact is sensed by Hippo pathway is poorly understood. Here, the authors show that KIRREL1 functions as a feedback regulator of the mammalian Hippo pathway by sensing cell-cell interaction and recruiting SAV1 to cell-cell contacts.
- Atanu Paul
- , Stefano Annunziato
- & Feng Cong
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo CRISPR screens reveal a HIF-1α-mTOR-network regulates T follicular helper versus Th1 cells
In vivo CRISPR screens reveal a HIF-1α-mTOR-network regulates T follicular helper versus Th1 cells
T follicular helper (Tfh) and T help type 1 (Th1) cells both arise from naïve CD4 T cells, but detailed knowledge of their differentiation remains incomplete. Here the authors pursue an in vivo CRISPR screen to identify genes, focusing on druggable targets, regulating Tfh versus Th1 to provide a resource for related studies, while also implicating HIF-1α and VHL in this regulation.
- Bonnie Huang
- , James D. Phelan
- & Pamela L. Schwartzberg
-
Article
| Open Access Prime editing efficiency and fidelity are enhanced in the absence of mismatch repair
Prime editing efficiency and fidelity are enhanced in the absence of mismatch repair
Prime Editing is a versatile genome engineering tool. Here, the authors identify the DNA repair pathway known as mismatch repair as inhibitory for Prime Editing, thus, loss of mismatch repair enhances the efficiency of Prime Editing.
- J. Ferreira da Silva
- , G. P. Oliveira
- & J. I. Loizou
-
Article
| Open Access Genetically stable CRISPR-based kill switches for engineered microbes
Genetically stable CRISPR-based kill switches for engineered microbes
Biocontainment is a key to developing safe genetically-engineered microbes (GEMs). Here the authors demonstrate genetically stable CRISPR-based kill switches that control GEMs’ viability in animal hosts, enabling their safe biomedical applications.
- Austin G. Rottinghaus
- , Aura Ferreiro
- & Tae Seok Moon
-
Article
| Open Access CRISPR-Cas9 induces large structural variants at on-target and off-target sites in vivo that segregate across generations
CRISPR-Cas9 induces large structural variants at on-target and off-target sites in vivo that segregate across generations
CRISPR-Cas9 can introduce unintended off-target effects. Here authors show that unintended mutations produced by in vivo of zebrafish can be inherited by their off-spring.
- Ida Höijer
- , Anastasia Emmanouilidou
- & Adam Ameur
-
Article
| Open Access Inhibition of base editors with anti-deaminases derived from viruses
Inhibition of base editors with anti-deaminases derived from viruses
Anti-deaminases can inhibit APOBEC3, a component of cytosine base editors. Here Zhanjun Li and colleagues repurposed anti-deaminase proteins derived from viruses to inhibit base editors for use in efficient regulation of base editors’ activity in gene modification and therapeutic applications.
- Zhiquan Liu
- , Siyu Chen
- & Zhanjun Li
-
Article
| Open Access Improved gRNA secondary structures allow editing of target sites resistant to CRISPR-Cas9 cleavage
Improved gRNA secondary structures allow editing of target sites resistant to CRISPR-Cas9 cleavage
Some DNA sequences are refractory to CRISPR-Cas9 cleavage, partially due to gRNA misfolding. Here the authors engineer gRNAs to prevent misfolding and further enhanced their stability by chemical modifications allowing robust genome editing regardless of target sequence.
- Stephan Riesenberg
- , Nelly Helmbrecht
- & Svante Pääbo
-
Article
| Open Access Systematic decomposition of sequence determinants governing CRISPR/Cas9 specificity
Systematic decomposition of sequence determinants governing CRISPR/Cas9 specificity
The sequence determinants governing CRISPR/Cas9 specificity are not fully understood. Here, the authors devise a high-throughput dual-target synthetic system to explore the sequence features associated with CRISPR/Cas9 off-target effect, reveal a set of sequence-dependent rules, and develop an off-target prediction model and a strategy for Cas9-based allele-specific editing.
- Rongjie Fu
- , Wei He
- & Han Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide detection of CRISPR editing in vivo using GUIDE-tag
Genome-wide detection of CRISPR editing in vivo using GUIDE-tag
In vivo assessment of nuclease off-target activity has primarily been indirect or through ChIP-based detection of double-strand break DNA repair factors, which can be cumbersome. Here, the authors show that GUIDE-tag, enables one-step off-target genome editing analysis in mouse liver and lung.
- Shun-Qing Liang
- , Pengpeng Liu
- & Wen Xue
-
Article
| Open Access Exploiting a Y chromosome-linked Cas9 for sex selection and gene drive
Exploiting a Y chromosome-linked Cas9 for sex selection and gene drive
CRISPR-based engineering can be used to bias sex ratios. Here the authors develop a transgenic line of Drosophila melanogaster expressing Cas9 from the Y chromosome and functionally characterize the utility of this strain for both sex selection and gene drive.
- Stephanie Gamez
- , Duverney Chaverra-Rodriguez
- & Omar S. Akbari
-
Article
| Open Access Large-scale genome-wide study reveals climate adaptive variability in a cosmopolitan pest
Large-scale genome-wide study reveals climate adaptive variability in a cosmopolitan pest
The diamondback moth is a cosmopolitan pest of significant economic importance. Here the authors analyse globally distributed genomic data to find evidence of climate-associated adaptive variation, and use an ecogenetic index to predict that it will maintain a global pest status under climate change.
- Yanting Chen
- , Zhaoxia Liu
- & Shijun You
-
Article
| Open Access CRISPR-Cas9 effectors facilitate generation of single-sex litters and sex-specific phenotypes
CRISPR-Cas9 effectors facilitate generation of single-sex litters and sex-specific phenotypes
In areas such as animal research and agriculture a single sex is often required in abundance, leading to wasted resources and ethical considerations. Here the authors develop a CRISPR/Cas9 mediated synthetic lethal system that enables the production of single sex offspring that can be repurposed for use in multiple organisms.
- Charlotte Douglas
- , Valdone Maciulyte
- & James M. A. Turner
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering a PAM-flexible SpdCas9 variant as a universal gene repressor
Engineering a PAM-flexible SpdCas9 variant as a universal gene repressor
SpCas9 has a NGG PAM requirement that limits its DNA target range. Here the authors present a PAM-expanded SpdCas9 variant SpdNG-LWQT to target NRN PAMs.
- Jian Wang
- , Yuxi Teng
- & Yajun Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Gene editing enables rapid engineering of complex antibiotic assembly lines
Gene editing enables rapid engineering of complex antibiotic assembly lines
Engineering biosynthetic assembly lines is a powerful path to new natural products but is challenging with current methods. Here the authors use CRISPR-Cas9 to exchange subdomains within NRPS to alter substrate selectivity.
- Wei Li Thong
- , Yingxin Zhang
- & Jason Micklefield
-
Article
| Open Access Cas9-specific immune responses compromise local and systemic AAV CRISPR therapy in multiple dystrophic canine models
Cas9-specific immune responses compromise local and systemic AAV CRISPR therapy in multiple dystrophic canine models
The Cas9-specific T cell response has been speculated to impair CRISPR therapy. Here, the authors show that local and systemic AAV CRISPR therapy induces cytotoxic killing and eliminates rescued dystrophin in canine models of Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
- Chady H. Hakim
- , Sandeep R. P. Kumar
- & Dongsheng Duan
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinformatic and cell-based tools for pooled CRISPR knockout screening in mosquitos
Bioinformatic and cell-based tools for pooled CRISPR knockout screening in mosquitos
Forward genetic approaches such as CRISPR screens are powerful ways to identify essential genes and those that influence host-pathogen interactions. Here the authors design a bioinformatics portal for sgRNA design and a recombination-mediated cassette system for delivery into mosquito cell lines.
- Raghuvir Viswanatha
- , Enzo Mameli
- & Norbert Perrimon

 Engineered Cas12i2 is a versatile high-efficiency platform for therapeutic genome editing
Engineered Cas12i2 is a versatile high-efficiency platform for therapeutic genome editing