News & Views |
Featured
-
-
Comment |
Rigorous renormalization group
The renormalization group evolved from ad hoc procedures to cope with divergences in perturbative calculations. This Comment summarizes efforts to develop a mathematically rigorous approach to renormalization group calculations.
- Antti Kupiainen
-
Comment |
 Fifty years of Wilsonian renormalization and counting
Fifty years of Wilsonian renormalization and counting
Renormalization began as a tool to eliminate divergences in quantum electrodynamics, but it is now the basis of our understanding of physics at different energy scales. Here, I review its evolution with an eye towards physics beyond the Wilsonian paradigm.
- Philip W. Phillips
-
Article
| Open Access Coupling to octahedral tilts in halide perovskite nanocrystals induces phonon-mediated attractive interactions between excitons
Coupling to octahedral tilts in halide perovskite nanocrystals induces phonon-mediated attractive interactions between excitons
Time-resolved measurements show that coupling between electrons and phonons in lead halide perovskites can mediate attractive interactions between excitons, although the interaction strength depends on the specific material.
- Nuri Yazdani
- , Maryna I. Bodnarchuk
- & Aaron M. Lindenberg
-
Article
| Open Access Modulated Kondo screening along magnetic mirror twin boundaries in monolayer MoS2
Modulated Kondo screening along magnetic mirror twin boundaries in monolayer MoS2
Interactions between a localized magnetic moment and electrons in a metal can produce an emergent resonance that affects the metal’s properties. A realization of this Kondo effect in MoS2 provides an opportunity to study it in microscopic detail.
- Camiel van Efferen
- , Jeison Fischer
- & Wouter Jolie
-
Research Briefing |
 A proximate model material for triangular lattice quantum spin liquids
A proximate model material for triangular lattice quantum spin liquids
Neutron spectroscopy, entanglement analysis, and simulations provide evidence that KYbSe2 closely approximates a 2D quantum spin liquid. Although KYbSe2 displays magnetic ordering at low temperatures, its magnetic dynamics are dominated by fractionalized excitations that exhibit anomalously large quantum entanglement, indicating that on finite timescales KYbSe2 exhibits quantum spin liquid physics.
-
Article |
 Proximate spin liquid and fractionalization in the triangular antiferromagnet KYbSe2
Proximate spin liquid and fractionalization in the triangular antiferromagnet KYbSe2
A detailed analysis of inelastic neutron scattering data, including the evaluation of entanglement witnesses used in quantum information theory, supports the proposal that the triangular-lattice antiferromagnet KYbSe2 is close to a spin-liquid phase.
- A. O. Scheie
- , E. A. Ghioldi
- & D. A. Tennant
-
Article |
 Valley-polarized excitonic Mott insulator in WS2/WSe2 moiré superlattice
Valley-polarized excitonic Mott insulator in WS2/WSe2 moiré superlattice
Interactions between excitons and correlated electrons can lead to the formation of interesting states. Now, evidence suggests that these interactions can give rise to a Mott insulator of excitons.
- Zhen Lian
- , Yuze Meng
- & Su-Fei Shi
-
News & Views |
 Phonon slowdown
Phonon slowdown
A detailed understanding of phonon transport is crucial for engineering the thermal properties of materials. A particular doping strategy is now shown to lead to good thermoelectric performance with low thermal conductivity.
- Zhilun Lu
-
Article |
 Born effective charges and vibrational spectra in superconducting and bad conducting metals
Born effective charges and vibrational spectra in superconducting and bad conducting metals
A computational method capable of capturing the effects of electronic interactions and scattering can help interpret the vibrational reflectance measurements in superconducting and bad metals.
- Guglielmo Marchese
- , Francesco Macheda
- & Francesco Mauri
-
Article |
 Electron charge qubit with 0.1 millisecond coherence time
Electron charge qubit with 0.1 millisecond coherence time
Individual electrons trapped on the surface of solid neon can operate as charge qubits with very long coherence times.
- Xianjing Zhou
- , Xinhao Li
- & Dafei Jin
-
Article |
 Evidence for spinarons in Co adatoms
Evidence for spinarons in Co adatoms
Despite the theoretical prediction of spinaron quasiparticles in artificial nanostructures, experimental evidence has not yet been seen. Now it has been observed in a hybrid system comprising Co atoms on a Cu(111) surface.
- Felix Friedrich
- , Artem Odobesko
- & Matthias Bode
-
News & Views |
 Topological phase transitions have never been faster
Topological phase transitions have never been faster
A nonlinear optical approach has now enabled picosecond control of a complex band structure, driving a non-Hermitian topological phase transition across an exceptional-point singularity.
- Jiangbin Gong
- & Ching Hua Lee
-
News & Views |
 Rotation rearranges electrons
Rotation rearranges electrons
Understanding lattice-geometry-driven electronic structure and orbital character in a titanium-based superconducting kagome metal provides insights into the non-trivial topology and electronic nematicity of correlated quantum matter.
- Bahadur Singh
-
Article |
 Non-affine atomic rearrangement of glasses through stress-induced structural anisotropy
Non-affine atomic rearrangement of glasses through stress-induced structural anisotropy
Resolving the structural changes of a deformed glass on the atomic scale is challenging due to its disordered nature. Now, high-energy diffraction measurements show that non-line-preserving atomic displacements in glasses correlate with structural anisotropy.
- Jie Dong
- , Hailong Peng
- & Haiyang Bai
-
News & Views |
 Spatial correlations of charge noise captured
Spatial correlations of charge noise captured
Measurements of two neighbouring silicon-based qubits show that the charge noise they each experience is correlated, suggesting a common origin. Understanding these correlations is crucial for performing error correction in these systems.
- Łukasz Cywiński
-
Article
| Open Access Resonant enhancement of photo-induced superconductivity in K3C60
Resonant enhancement of photo-induced superconductivity in K3C60
There is evidence that K3C60 can host a photo-induced superconducting state. Now, resonant excitation at low frequencies allows this phenomenon at room temperature and low pumping fluence.
- E. Rowe
- , B. Yuan
- & A. Cavalleri
-
Comment |
 Evolution of superconducting diodes
Evolution of superconducting diodes
Efficient superconducting diodes can be designed according to established physics. However, emerging concepts must be united with known mechanisms in order to unlock functionality in rectification and frequency conversion.
- P. J. W. Moll
- & V. B. Geshkenbein
-
News & Views |
 When Ising met Kibble–Zurek
When Ising met Kibble–Zurek
When a system is driven across a second-order phase transition, defects can form because it cannot respond quickly enough to the new conditions. The Kibble–Zurek mechanism explains this physics, and has now been invoked for Ising-type domains.
- István Kézsmárki
- & Andrés Cano
-
Article |
 Bogoliubov quasiparticle on the gossamer Fermi surface in electron-doped cuprates
Bogoliubov quasiparticle on the gossamer Fermi surface in electron-doped cuprates
Observation of a faint Fermi surface inside the pseudogap of an electron-doped cuprate suggests that Cooper pairing is mediated by antiferromagnetic spin fluctuations.
- Ke-Jun Xu
- , Qinda Guo
- & Zhi-Xun Shen
-
Article |
 A one-third magnetization plateau phase as evidence for the Kitaev interaction in a honeycomb-lattice antiferromagnet
A one-third magnetization plateau phase as evidence for the Kitaev interaction in a honeycomb-lattice antiferromagnet
Na3Ni2BiO6 with a honeycomb lattice is found to host a one-third magnetization plateau phase signifying frustrated interactions and indicates that Kitaev interactions can be realized in high-spin magnets.
- Yanyan Shangguan
- , Song Bao
- & Jinsheng Wen
-
Article |
 Non-trivial band topology and orbital-selective electronic nematicity in a titanium-based kagome superconductor
Non-trivial band topology and orbital-selective electronic nematicity in a titanium-based kagome superconductor
The origin of nematicity in kagome superconductors has been hard to explain due to other entangled phases. Now, the role of orbital hybridization and coupling is revealed to induce electronic nematicity in the kagome superconductor RbTi3Bi5.
- Yong Hu
- , Congcong Le
- & Ming Shi
-
Research Briefing |
 Competing electron solids and electron fluids in the moiré atomic limit
Competing electron solids and electron fluids in the moiré atomic limit
Local thermodynamic measurements of a twisted transition metal dichalcogenide heterostructure reveal competition between unconventional charge order and Hofstadter states. This results from the presence of both flat and dispersive electronic bands, whose energetic ordering can be experimentally tuned.
-
News & Views |
 Three is the optimal number
Three is the optimal number
A trilayer copper oxide superconductor, which exhibits the highest superconducting critical temperature as a function of the number of copper–oxygen planes, is shown to have unusual doped hole distribution and interaction between the planes.
- Atsushi Fujimori
-
Article |
 Hofstadter states and re-entrant charge order in a semiconductor moiré lattice
Hofstadter states and re-entrant charge order in a semiconductor moiré lattice
The interplay between flat and dispersive bands in moiré materials has not yet been examined in detail. Now, the phase diagram of a transition metal dichalcogenide bilayer shows correlated states arising from both types of band.
- Carlos R. Kometter
- , Jiachen Yu
- & Benjamin E. Feldman
-
Article |
 Scaling behaviour and control of nuclear wrinkling
Scaling behaviour and control of nuclear wrinkling
Wrinkling of cell nuclei is associated with disease. During development, the nucleus behaves like a sheet of paper and the wrinkling amplitude can be manipulated without changing its pattern.
- Jonathan A. Jackson
- , Nicolas Romeo
- & Jasmin Imran Alsous
-
News & Views |
 Charges tied with magnetic strings
Charges tied with magnetic strings
Hubbard excitons are elusive quasiparticles that are predicted to form in strongly correlated insulators. Detecting their internal structure and dynamics clarifies the involvement of spin fluctuations in their binding and recombination processes.
- Edoardo Baldini
-
Article |
 Electronic origin of high superconducting critical temperature in trilayer cuprates
Electronic origin of high superconducting critical temperature in trilayer cuprates
Measurements of the electronic structure of a trilayer cuprate superconductor suggest that its high critical temperature is explained by the different doping levels of the layers. The combination of underdoped inner layer and overdoped outer layers supports superconductivity.
- Xiangyu Luo
- , Hao Chen
- & X. J. Zhou
-
Article |
 A Hubbard exciton fluid in a photo-doped antiferromagnetic Mott insulator
A Hubbard exciton fluid in a photo-doped antiferromagnetic Mott insulator
Hole and particle-like quasiparticles of a Mott insulator can pair into excitonic bound states. Now, time-resolved measurements of Sr2IrO4 show signs of an excitonic fluid forming from a photo-excited population of quasiparticles.
- Omar Mehio
- , Xinwei Li
- & David Hsieh
-
Article |
 Fluctuation-enhanced phonon magnetic moments in a polar antiferromagnet
Fluctuation-enhanced phonon magnetic moments in a polar antiferromagnet
Phonons that carry a large magnetic moment may be helpful for creating spintronic devices. Now this phenomenon is observed in an antiferromagnet and is enhanced by the critical fluctuations associated with a phase transition.
- Fangliang Wu
- , Song Bao
- & Qi Zhang
-
-
Editorial |
 Party like it’s LK-99
Party like it’s LK-99
Claims of a room-temperature, ambient-pressure superconductor recently kicked up a storm on social media. As the dust settles, we take stock of what this experience can teach us.
-
Article
| Open Access Evidence of finite-momentum pairing in a centrosymmetric bilayer
Evidence of finite-momentum pairing in a centrosymmetric bilayer
Cooper pairs that form with finite centre-of-mass momentum are rare. Now there is evidence that this can happen below the Pauli limit in a bilayer material.
- Dong Zhao
- , Lukas Debbeler
- & Jurgen Smet
-
Article |
 Observation of the boson peak in a two-dimensional material
Observation of the boson peak in a two-dimensional material
The boson peak refers to an excess in the phonon density of states seen in three-dimensional amorphous materials. Helium-atom scattering experiments have now revealed a boson peak in a two-dimensional material, too, at a frequency similar to that of the bulk material.
- Martin Tømterud
- , Sabrina D. Eder
- & Bodil Holst
-
Article |
 Bond-dependent anisotropy and magnon decay in cobalt-based Kitaev triangular antiferromagnet
Bond-dependent anisotropy and magnon decay in cobalt-based Kitaev triangular antiferromagnet
Geometric frustration and bond-dependent interactions each introduce quantum fluctuations that can create spin liquid phases. Now it is shown that CoI2 is a triangular lattice material that combines both.
- Chaebin Kim
- , Sujin Kim
- & Je-Geun Park
-
Review Article |
 More is different in real-world multilayer networks
More is different in real-world multilayer networks
Describing interdependencies and coupling between complex systems requires tools beyond what the framework of single networks offers. This Review covers recent developments in the study and modelling of multilayer networks.
- Manlio De Domenico
-
News & Views |
 Field guides
Field guides
The guiding of magnetic fields by soft ferromagnetic solids is well known and exploited in magnetic shielding applications. Now, ferroelectric nematic liquids are shown to analogously guide electric fields.
- Alenka Mertelj
-
News & Views |
 Devitrification caught on film
Devitrification caught on film
An experimental approach enables the observation of the microscopic details of the relaxation of a highly equilibrated glass back to the liquid phase in real time. This points to a scenario where devitrification proceeds via localized seeds separated by macroscopic length scales.
- Federico Caporaletti
-
Article |
 Electronic nematicity without charge density waves in titanium-based kagome metal
Electronic nematicity without charge density waves in titanium-based kagome metal
Electronic nematic order as a distinct phase in kagome materials without any entanglement with charge density wave or charge stripe order has not been detected. Now, it is observed in a titanium-based kagome metal.
- Hong Li
- , Siyu Cheng
- & Ilija Zeljkovic
-
Article |
 Strong phonon softening and avoided crossing in aliovalence-doped heavy-band thermoelectrics
Strong phonon softening and avoided crossing in aliovalence-doped heavy-band thermoelectrics
Aliovalent doping affects the electrical properties of semiconductors, but its effect on phonons is unclear. Now, strong softening and deceleration of phonons, causing a significant reduction in lattice thermal conductivity, is reported for Hf-doped NbFeSb.
- Shen Han
- , Shengnan Dai
- & Tiejun Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Unconventional room-temperature carriers in the triangular-lattice Mott insulator TbInO3
Unconventional room-temperature carriers in the triangular-lattice Mott insulator TbInO3
Previous work has suggested that at very low temperatures TbInO3 hosts an unconventional quantum ground state. Terahertz time-domain spectroscopy measurements of its excitations show that related exotic effects can persist to room temperature.
- Taek Sun Jung
- , Xianghan Xu
- & Jae Hoon Kim
-
News & Views |
 Superconducting arrays offer resistance
Superconducting arrays offer resistance
Chains of coupled superconducting islands known as Josephson junction arrays were predicted to be insulating at high impedance, but superconducting behaviour has been observed. A study of the arrays’ transport suggests thermal effects are responsible.
- Dmitri V. Averin
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional neutron far-field tomography of a bulk skyrmion lattice
Three-dimensional neutron far-field tomography of a bulk skyrmion lattice
The three-dimensional spin textures of a skyrmion lattice have now been measured in a bulk material using a tomographic small-angle neutron scattering technique.
- M. E. Henderson
- , B. Heacock
- & D. A. Pushin
-
-
Article
| Open Access Superconductivity from a melted insulator in Josephson junction arrays
Superconductivity from a melted insulator in Josephson junction arrays
Predictions of a quantum superconductor–insulator transition in Josephson junction arrays are not always borne out by experiments. Unexpectedly large thermal effects may explain why.
- S. Mukhopadhyay
- , J. Senior
- & A. P. Higginbotham
-
News & Views |
 A delicate balance of phonons and spins
A delicate balance of phonons and spins
The near-zero thermal expansion of Invar alloy Fe65Ni35 is technologically important but still unexplained. Measurements show that this phenomenon can be explained by the cancellation of magnetic and phonon contributions to the alloy’s entropy.
- Ralf Röhlsberger
-
Article |
 Josephson diode effect derived from short-range coherent coupling
Josephson diode effect derived from short-range coherent coupling
The behaviour of a superconductor can be altered by changing its symmetry properties. Coherently coupling two Josephson junctions breaks time-reversal and inversion symmetries, giving rise to a device with a controllable superconducting diode effect.
- Sadashige Matsuo
- , Takaya Imoto
- & Seigo Tarucha
-
Article
| Open Access Critical slowing down near a magnetic quantum phase transition with fermionic breakdown
Critical slowing down near a magnetic quantum phase transition with fermionic breakdown
YbRh2Si2 has a quantum phase transition between an antiferromagnetic phase and a so-called heavy-Fermi-liquid state. Measurements of critical slowing down suggest that the heavy-fermion quasiparticles break down at the transition.
- Chia-Jung Yang
- , Kristin Kliemt
- & Shovon Pal
-
Article |
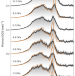 A thermodynamic explanation of the Invar effect
A thermodynamic explanation of the Invar effect
The iron–nickel alloy Invar has an extremely small coefficient of thermal expansion that has been difficult to explain theoretically. A study of Invar under pressure now suggests that there is a cancellation of phonon and spin contributions to expansion.
- S. H. Lohaus
- , M. Heine
- & B. Fultz
-
Article |
 Fluid superscreening and polarization following in confined ferroelectric nematics
Fluid superscreening and polarization following in confined ferroelectric nematics
The ferroelectric uniaxial nematic liquid-crystal phase features a freely reorientable polarization field. When confined in microchannels and subjected to electric fields, this polarization is now found to align with the channels due to a superscreening effect.
- Federico Caimi
- , Giovanni Nava
- & Tommaso Bellini
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Bose–Einstein condensates
- Electronic properties and materials
- Ferroelectrics and multiferroics
- Ferromagnetism
- Magnetic properties and materials
- Molecular electronics
- Phase transitions and critical phenomena
- Quantum fluids and solids
- Quantum Hall
- Semiconductors
- Spintronics
- Structure of solids and liquids
- Superconducting properties and materials
- Surfaces, interfaces and thin films
- Topological matter

 Electron spin finds a fresh excitation
Electron spin finds a fresh excitation Signs of trouble for Fermi surfaces
Signs of trouble for Fermi surfaces Orbitronics in action
Orbitronics in action