Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access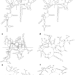 R2DT is a framework for predicting and visualising RNA secondary structure using templates
R2DT is a framework for predicting and visualising RNA secondary structure using templates
Non-coding RNA function is poorly understood, partly due to the challenge of determining RNA secondary (2D) structure. Here, the authors present a framework for the reproducible prediction and visualization of the 2D structure of a wide array of RNAs, which enables linking RNA sequence to function.
- Blake A. Sweeney
- , David Hoksza
- & Anton I. Petrov
-
Article
| Open Access Large variation in anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody prevalence among essential workers in Geneva, Switzerland
Large variation in anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody prevalence among essential workers in Geneva, Switzerland
Many job sectors classified as ‘essential’ have continued operating with limited restrictions during the COVID-19 pandemic, potentially placing workers at higher risk of infection. Here, the authors show that seropositivity rates in workers vary widely across and between job sectors in Geneva, Switzerland.
- Silvia Stringhini
- , María-Eugenia Zaballa
- & Idris Guessous
-
Article
| Open Access Optimizing vaccine allocation for COVID-19 vaccines shows the potential role of single-dose vaccination
Optimizing vaccine allocation for COVID-19 vaccines shows the potential role of single-dose vaccination
Most COVID-19 vaccines require two doses but a single dose provides partial protection, so it is unclear how best to prioritize vaccine distribution in the context of limited supply. Here, the authors show that campaigns in which some age groups receive one dose while others receive both doses may be optimal.
- Laura Matrajt
- , Julia Eaton
- & Holly Janes
-
Article
| Open Access Replicate sequencing libraries are important for quantification of allelic imbalance
Replicate sequencing libraries are important for quantification of allelic imbalance
Allele-specific expression in diploid organisms can be quantified by RNA-seq and it is common practice to rely on a single library. Here, the authors show that the standard approach has variable error rate and present Qllelic as a tool to improve reproducibility of allele-specific RNA-seq analysis.
- Asia Mendelevich
- , Svetlana Vinogradova
- & Alexander A. Gimelbrant
-
Article
| Open Access Generative modeling of single-cell time series with PRESCIENT enables prediction of cell trajectories with interventions
Generative modeling of single-cell time series with PRESCIENT enables prediction of cell trajectories with interventions
Single-cell RNA-Seq allows us to observe snapshots of how biological systems change over time at cellular resolution. Here, the authors develop a generative framework that uses time-resolved single-cell data to model how cells change in physical time, including in response to perturbations.
- Grace Hui Ting Yeo
- , Sachit D. Saksena
- & David K. Gifford
-
Article
| Open Access Impact of DNA methylation on 3D genome structure
Impact of DNA methylation on 3D genome structure
Multi-layered epigenetic regulation in higher eukaryotes makes it challenging to disentangle the individual effects of modifications on chromatin structure and function. Here, the authors expressed mammalian DNA methyltransferases in yeast, which have no DNA methylation, to show that methylation has intrinsic effects on chromatin structure.
- Diana Buitrago
- , Mireia Labrador
- & Modesto Orozco
-
Article
| Open Access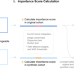 Identification of putative causal loci in whole-genome sequencing data via knockoff statistics
Identification of putative causal loci in whole-genome sequencing data via knockoff statistics
Association analyses that capture rare and noncoding variants in whole genome sequencing data are limited by factors like statistical power. Here, the authors present KnockoffScreen, a statistical method using the knockoff framework to detect, localise and prioritise rare and common risk variants at genome-wide scale.
- Zihuai He
- , Linxi Liu
- & Iuliana Ionita-Laza
-
Article
| Open Access Synthetic neural-like computing in microbial consortia for pattern recognition
Synthetic neural-like computing in microbial consortia for pattern recognition
Complex biological systems have individual cells acting collectively to solve complex tasks. Here the authors implement neural network-like computing in a bacterial consortia to recognise patterns.
- Ximing Li
- , Luna Rizik
- & Ramez Daniel
-
Article
| Open Access Controlling COVID-19 via test-trace-quarantine
Controlling COVID-19 via test-trace-quarantine
Initial COVID-19 containment in the United States focused on limiting mobility, including school and workplace closures, with enormous societal and economic costs. Here, the authors demonstrate the feasibility of a test-trace-quarantine strategy using an agent-based model and detailed data on the Seattle region.
- Cliff C. Kerr
- , Dina Mistry
- & Daniel J. Klein
-
Article
| Open Access Pairing a high-resolution statistical potential with a nucleobase-centric sampling algorithm for improving RNA model refinement
Pairing a high-resolution statistical potential with a nucleobase-centric sampling algorithm for improving RNA model refinement
Predicting RNA structure from sequence is challenging due to the relative sparsity of experimentally-determined RNA 3D structures for model training. Here, the authors propose a way to incorporate knowledge on interactions at the atomic and base–base level to refine the prediction of RNA structures.
- Peng Xiong
- , Ruibo Wu
- & Yaoqi Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access Distinct axial and lateral interactions within homologous filaments dictate the signaling specificity and order of the AIM2-ASC inflammasome
Distinct axial and lateral interactions within homologous filaments dictate the signaling specificity and order of the AIM2-ASC inflammasome
AIM2-ASC inflammasomes are filamentous signalling platforms that play a central role in host innate defence. Here, the authors present the filament cryo-EM structure of the inflammasome receptor AIM2, which is very similar to the adaptor ASC filament structure. By employing Rosetta and Molecular Dynamics simulations the authors provide further insights into the directionality and recognition mechanisms of the individual AIM2 and ASC filaments, which is further validated with biochemical and cellular experiments.
- Mariusz Matyszewski
- , Weili Zheng
- & Jungsan Sohn
-
Article
| Open Access The epidemicity index of recurrent SARS-CoV-2 infections
The epidemicity index of recurrent SARS-CoV-2 infections
Several prognostic indices are available to predict the long-term fate of emerging infectious diseases and the effect of their containment measures, including a variety of reproduction numbers. Here, the authors introduce the epidemicity index, a complementary index to evaluate the potential for transient increases of SARS-Cov-2 epidemics.
- Lorenzo Mari
- , Renato Casagrandi
- & Marino Gatto
-
Article
| Open Access Deep generative model embedding of single-cell RNA-Seq profiles on hyperspheres and hyperbolic spaces
Deep generative model embedding of single-cell RNA-Seq profiles on hyperspheres and hyperbolic spaces
Single-cell RNA-seq allows the study of tissues at cellular resolution. Here, the authors demonstrate how deep learning can be used to gain biological insight from such data by accounting for biological and technical variability. Data exploration is improved by accurately visualizing cells on an interactive 3D surface.
- Jiarui Ding
- & Aviv Regev
-
Article
| Open Access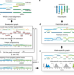 Integrative reconstruction of cancer genome karyotypes using InfoGenomeR
Integrative reconstruction of cancer genome karyotypes using InfoGenomeR
Karyotyping of cancer genomes at the base-level is technically challenging. Here, the authors introduce InfoGenomeR, an algorithm that can infer cancer genome karyotypes from whole-genome sequencing data, and test their model on breast, ovarian and brain cancer samples; and identify private and shared mutations between primary and metastatic cancer samples.
- Yeonghun Lee
- & Hyunju Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Protein design and variant prediction using autoregressive generative models
Protein design and variant prediction using autoregressive generative models
The ability to design functional sequences is central to protein engineering and biotherapeutics. Here the authors introduce a deep generative alignment-free model for sequence design applied to highly variable regions and design and test a diverse nanobody library with improved properties for selection experiments.
- Jung-Eun Shin
- , Adam J. Riesselman
- & Debora S. Marks
-
Article
| Open Access Leveraging community mortality indicators to infer COVID-19 mortality and transmission dynamics in Damascus, Syria
Leveraging community mortality indicators to infer COVID-19 mortality and transmission dynamics in Damascus, Syria
Reported COVID-19 mortality rates have been relatively low in Syria, but there has been concern about overwhelmed health systems. Here, the authors use community mortality indicators and estimate that <3% of COVID-19 deaths in Damascus were reported as of 2 September 2020.
- Oliver J. Watson
- , Mervat Alhaffar
- & Patrick Walker
-
Article
| Open Access Conserved long-range base pairings are associated with pre-mRNA processing of human genes
Conserved long-range base pairings are associated with pre-mRNA processing of human genes
Functional RNA secondary structure is important for the pre-mRNA processing including splicing, cleavage and polyadenylation, and RNA editing. Here the authors present a catalog of conserved long-range RNA structures in the human transcriptome by defining pairs of conserved complementary regions (PCCR) in pre-aligned evolutionarily conserved regions.
- Svetlana Kalmykova
- , Marina Kalinina
- & Dmitri Pervouchine
-
Article
| Open Access RA3 is a reference-guided approach for epigenetic characterization of single cells
RA3 is a reference-guided approach for epigenetic characterization of single cells
Methods for profiling differences between individual cells are constantly expanding. Here, the authors present a computational framework for the analysis of chromatin accessibility data at the single-cell level that takes into account previous knowledge and data-specific characteristics.
- Shengquan Chen
- , Guanao Yan
- & Zhixiang Lin
-
Article
| Open Access Learning cis-regulatory principles of ADAR-based RNA editing from CRISPR-mediated mutagenesis
Learning cis-regulatory principles of ADAR-based RNA editing from CRISPR-mediated mutagenesis
The RNA sequence and secondary structure regulate RNA editing by ADAR. Here the authors employ a CRISPR/Cas9-mediated saturation mutagenesis and machine learning to predict RNA editing efficiency of specific substrates.
- Xin Liu
- , Tao Sun
- & Jin Billy Li
-
Article
| Open Access Harnessing machine learning to guide phylogenetic-tree search algorithms
Harnessing machine learning to guide phylogenetic-tree search algorithms
Likelihood optimization in phylogenetic tree reconstruction is computationally intensive, especially as the number of sequences and taxa included increase. Here, Azouri et al. show how an artificial intelligence approach can reduce computational time without losing accuracy of tree inference.
- Dana Azouri
- , Shiran Abadi
- & Tal Pupko
-
Article
| Open Access The SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein is dynamic, disordered, and phase separates with RNA
The SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein is dynamic, disordered, and phase separates with RNA
SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid (N) protein is responsible for viral genome packaging. Here the authors employ single-molecule spectroscopy with all-atom simulations to provide the molecular details of N protein and show that it undergoes phase separation with RNA.
- Jasmine Cubuk
- , Jhullian J. Alston
- & Alex S. Holehouse
-
Article
| Open Access Implications of the school-household network structure on SARS-CoV-2 transmission under school reopening strategies in England
Implications of the school-household network structure on SARS-CoV-2 transmission under school reopening strategies in England
Many countries have closed schools as part of their COVID-19 response. Here, the authors model SARS-CoV-2 transmission on a network of schools and households in England, and find that risk of transmission between schools is lower if primary schools are open than if secondary schools are open.
- James D. Munday
- , Katharine Sherratt
- & Sebastian Funk
-
Article
| Open Access Hospital load and increased COVID-19 related mortality in Israel
Hospital load and increased COVID-19 related mortality in Israel
COVID-19 has caused many healthcare systems to become overwhelmed, potentially impacting patient care. Here, the authors show that COVID-19-related in-hospital mortality rates in Israel increased in periods of moderate or high hospital load, independent of patient characteristics.
- Hagai Rossman
- , Tomer Meir
- & Malka Gorfine
-
Article
| Open Access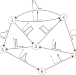 Controlling network ensembles
Controlling network ensembles
Application of the control usually requires complete knowledge of the system, which is rare for biological networks characterized by uncertainty. Klickstein et al. propose an optimal control for uncertain systems represented by network ensembles where only weight distributions for edges are known.
- Isaac Klickstein
- & Francesco Sorrentino
-
Article
| Open Access scGNN is a novel graph neural network framework for single-cell RNA-Seq analyses
scGNN is a novel graph neural network framework for single-cell RNA-Seq analyses
Single-cell RNA-Seq suffers from heterogeneity in sequencing sparsity and complex differential patterns in gene expression. Here, the authors introduce a graph neural network based on a hypothesis-free deep learning framework as an effective representation of gene expression and cell–cell relationships.
- Juexin Wang
- , Anjun Ma
- & Dong Xu
-
Article
| Open Access Reconstructing unseen transmission events to infer dengue dynamics from viral sequences
Reconstructing unseen transmission events to infer dengue dynamics from viral sequences
Phylogeographic analyses can provide broad descriptions of the spread of pathogens between populations, but are limited by incomplete sampling. Here, the authors develop an inference framework that reconstructs sequential transmission events and use it to characterise dynamics of dengue in Thailand.
- Henrik Salje
- , Amy Wesolowski
- & Derek A. T. Cummings
-
Article
| Open Access A computer-guided design tool to increase the efficiency of cellular conversions
A computer-guided design tool to increase the efficiency of cellular conversions
Transcription factor over-expression-based cellular conversion methods often endure low conversion efficiency. Here the authors show how to increase conversion efficiency by combining a computational method for prioritizing more efficient TF combinations with a transposon-based genomic integration system for delivery.
- Sascha Jung
- , Evan Appleton
- & Antonio del Sol
-
Article
| Open Access Model-based evaluation of school- and non-school-related measures to control the COVID-19 pandemic
Model-based evaluation of school- and non-school-related measures to control the COVID-19 pandemic
The role of school-based contacts in the epidemiology of SARS-CoV-2 is incompletely understood. Here, the authors use an age-structured transmission model fitted to age-specific seroprevalence and hospital admission data to assess the effects of school-based measures during the COVID-19 pandemic in the Netherlands.
- Ganna Rozhnova
- , Christiaan H. van Dorp
- & Mirjam E. Kretzschmar
-
Article
| Open Access Evaluating the impact of curfews and other measures on SARS-CoV-2 transmission in French Guiana
Evaluating the impact of curfews and other measures on SARS-CoV-2 transmission in French Guiana
Identifying effective combinations of control measures in different populations is important for SARS-CoV-2 control. Here, the authors show that in French Guiana, which has a relatively young population, curfews and localised lockdowns appeared to contribute to reducing transmission.
- Alessio Andronico
- , Cécile Tran Kiem
- & Simon Cauchemez
-
Article
| Open Access DeepTCR is a deep learning framework for revealing sequence concepts within T-cell repertoires
DeepTCR is a deep learning framework for revealing sequence concepts within T-cell repertoires
The advent of high-throughput T-cell receptor sequencing has allowed for the rapid and thorough characterization of the adaptive immune response. Here the authors show how deep learning can reveal both descriptive and predictive sequence concepts within the immune repertoire.
- John-William Sidhom
- , H. Benjamin Larman
- & Alexander S. Baras
-
Article
| Open Access Predicting the public health impact of a malaria transmission-blocking vaccine
Predicting the public health impact of a malaria transmission-blocking vaccine
Malaria transmission-blocking vaccines are in development, but roll-out strategies have not been assessed. Here, the authors show that transmission-blocking activity is likely to be higher in the field than in laboratory conditions, and that school-aged children are an important group to target.
- Joseph D. Challenger
- , Daniela Olivera Mesa
- & Thomas S. Churcher
-
Article
| Open Access Real-time tracking and prediction of COVID-19 infection using digital proxies of population mobility and mixing
Real-time tracking and prediction of COVID-19 infection using digital proxies of population mobility and mixing
Digital proxies of human mobility can be used to monitor social distancing, and therefore have potential to infer COVID-19 dynamics. Here, the authors integrate travel card data from Hong Kong into a transmission model and show that it can be used to track transmissibility in near real-time.
- Kathy Leung
- , Joseph T. Wu
- & Gabriel M. Leung
-
Article
| Open Access Improving gene function predictions using independent transcriptional components
Improving gene function predictions using independent transcriptional components
Our understanding of the function of many transcripts is still incomplete, limiting the interpretability of transcriptomic data. Here the authors use consensus-independent component analysis, together with a guilt-by-association approach, to improve the prediction of gene function.
- Carlos G. Urzúa-Traslaviña
- , Vincent C. Leeuwenburgh
- & Rudolf S. N. Fehrmann
-
Article
| Open Access Cells recognize osmotic stress through liquid–liquid phase separation lubricated with poly(ADP-ribose)
Cells recognize osmotic stress through liquid–liquid phase separation lubricated with poly(ADP-ribose)
Cells experience various osmotic perturbation, but cellular osmosensing mechanisms remain obscure. Here, the authors report that cells recognize osmotic stress from the inside through macromolecular crowding-driven and poly(ADP-ribose)-conditioned liquid–liquid phase separation.
- Kengo Watanabe
- , Kazuhiro Morishita
- & Hidenori Ichijo
-
Article
| Open Access Ecology-guided prediction of cross-feeding interactions in the human gut microbiome
Ecology-guided prediction of cross-feeding interactions in the human gut microbiome
Understanding a complex microbial ecosystem such as the human gut microbiome requires information about both microbial species and the metabolites they produce and secrete. Here, the authors propose an ecology-based computational method to predict hundreds of new experimentally untested cross-feeding interactions in the human gut microbiome.
- Akshit Goyal
- , Tong Wang
- & Sergei Maslov
-
Article
| Open Access A game theoretic approach reveals that discretizing clinical information can reduce antibiotic misuse
A game theoretic approach reveals that discretizing clinical information can reduce antibiotic misuse
Antibiotic resistance is a major public health concern, exacerbated by antibiotic over-prescription. Here we show, using game theory, that reduction of over-prescription can be achieved by discretizing the clinical information given to physician, e.g., by decision support systems.
- Maya Diamant
- , Shoham Baruch
- & Uri Obolski
-
Article
| Open Access Optimal marker gene selection for cell type discrimination in single cell analyses
Optimal marker gene selection for cell type discrimination in single cell analyses
The selection of a small set of cellular labels to distinguish a subpopulation of cells from a complex mixture is an important task in cell biology. Here the authors propose a method for supervised genetic marker selection using linear programming and provides a Python package scGeneFit that implements this approach.
- Bianca Dumitrascu
- , Soledad Villar
- & Barbara E. Engelhardt
-
Article
| Open Access Robust inference of kinase activity using functional networks
Robust inference of kinase activity using functional networks
Kinases drive fundamental changes in cell state, but predicting kinase activity based on substrate-level changes can be challenging. Here the authors introduce a computational framework that utilizes similarities between substrates to robustly infer kinase activity.
- Serhan Yılmaz
- , Marzieh Ayati
- & Mehmet Koyutürk
-
Article
| Open Access Reduction in mobility and COVID-19 transmission
Reduction in mobility and COVID-19 transmission
Social distancing policies aiming to reduce COVID-19 transmission have been reflected in reductions in human mobility. Here, the authors show that reduced mobility is correlated with decreased transmission, but that this relationship weakened over time as social distancing measures were relaxed.
- Pierre Nouvellet
- , Sangeeta Bhatia
- & Christl A. Donnelly
-
Article
| Open Access Modelling safe protocols for reopening schools during the COVID-19 pandemic in France
Modelling safe protocols for reopening schools during the COVID-19 pandemic in France
The role of children in the spread of COVID-19 is not fully understood, and the circumstances under which schools should be opened are therefore debated. Here, the authors demonstrate protocols by which schools in France can be safely opened without overwhelming the healthcare system.
- Laura Di Domenico
- , Giulia Pullano
- & Vittoria Colizza
-
Article
| Open Access Rare genetic variants affecting urine metabolite levels link population variation to inborn errors of metabolism
Rare genetic variants affecting urine metabolite levels link population variation to inborn errors of metabolism
Metabolites are indicators of health and disease; genetic studies can reveal variants influencing their levels. Here, the authors investigate the contribution of rare, exonic variants on the levels of urine metabolites and generate predictions on metabolic consequences underlying metabolic disease.
- Yurong Cheng
- , Pascal Schlosser
- & Anna Köttgen
-
Article
| Open Access Quantifying population contact patterns in the United States during the COVID-19 pandemic
Quantifying population contact patterns in the United States during the COVID-19 pandemic
Physical distancing measures have been widely adopted to reduce the spread of COVID-19. This study quantifies changes in interpersonal contact patterns in the US and finds an 82% reduction in contacts during early lockdowns in March and steady increases thereafter.
- Dennis M. Feehan
- & Ayesha S. Mahmud
-
Article
| Open Access Forecasting influenza activity using machine-learned mobility map
Forecasting influenza activity using machine-learned mobility map
Human mobility plays a central role in the spread of infectious diseases and can help in forecasting incidence. Here the authors show a comparison of multiple mobility benchmarks in forecasting influenza, and demonstrate the value of a machine-learned mobility map with global coverage at multiple spatial scales.
- Srinivasan Venkatramanan
- , Adam Sadilek
- & Madhav Marathe
-
Article
| Open Access Assessing the influence of climate on wintertime SARS-CoV-2 outbreaks
Assessing the influence of climate on wintertime SARS-CoV-2 outbreaks
Spread of SARS-CoV-2 in the early phase of the pandemic has been driven by high population susceptibility, but virus sensitivity to climate may play a role in future outbreaks. Here, the authors simulate SARS-CoV-2 dynamics in winter assuming climate dependence is similar to an endemic coronavirus strain.
- Rachel E. Baker
- , Wenchang Yang
- & Bryan T. Grenfell
-
Article
| Open Access Genome-wide fine-mapping identifies pleiotropic and functional variants that predict many traits across global cattle populations
Genome-wide fine-mapping identifies pleiotropic and functional variants that predict many traits across global cattle populations
Genomic prediction of phenotype may be improved by using DNA mutations with functional, evolutionary, and pleiotropic consequences. Here the authors describe a method for genome-wide fine-mapping of QTLs and develop a genotyping array for improved prediction of genetic values for cattle traits.
- Ruidong Xiang
- , Iona M. MacLeod
- & Michael E. Goddard
-
Article
| Open Access Detection of aberrant splicing events in RNA-seq data using FRASER
Detection of aberrant splicing events in RNA-seq data using FRASER
Aberrant splicing is a major contributor to rare disease, but detection accuracy using current methods is limited. Here, the authors develop an algorithm that detects aberrant splicing and intron retention events from RNA-seq data and apply it to diagnosis in mitochondrial disease.
- Christian Mertes
- , Ines F. Scheller
- & Julien Gagneur
-
Article
| Open Access Modelling the global burden of drug-resistant tuberculosis avertable by a post-exposure vaccine
Modelling the global burden of drug-resistant tuberculosis avertable by a post-exposure vaccine
Vaccines preventing tuberculosis disease progression have shown promising results in recent trials. Here, the authors use mathematical modelling to estimate that this type of vaccine could avert 10% of cases of rifampicin-resistant tuberculosis and 7% of deaths from 2020-2035.
- Han Fu
- , Joseph A. Lewnard
- & Nimalan Arinaminpathy
-
Article
| Open Access Mathematical model of COVID-19 intervention scenarios for São Paulo—Brazil
Mathematical model of COVID-19 intervention scenarios for São Paulo—Brazil
Incidence of COVID-19 has been high in parts of South America including Brazil, and information on effective intervention strategies is needed. Here, the authors use mathematical modelling to show that reductions in social distancing should be made gradually to avoid a severe second peak of cases.
- Osmar Pinto Neto
- , Deanna M. Kennedy
- & Renato Amaro Zângaro
-
Article
| Open Access Inferring high-resolution human mixing patterns for disease modeling
Inferring high-resolution human mixing patterns for disease modeling
The growing need for realism in addressing complex public health questions calls for accurate models of the human contact patterns that govern disease transmission. Here, the authors generate effective population-level contact matrices by using highly detailed macro (census) and micro (survey) data on key socio-demographic features.
- Dina Mistry
- , Maria Litvinova
- & Alessandro Vespignani

 Hybrid AI-assistive diagnostic model permits rapid TBS classification of cervical liquid-based thin-layer cell smears
Hybrid AI-assistive diagnostic model permits rapid TBS classification of cervical liquid-based thin-layer cell smears