News & Views |
Featured
-
-
Research Highlights |
Diet makes gut change speed
-
Article |
 Single cell activity reveals direct electron transfer in methanotrophic consortia
Single cell activity reveals direct electron transfer in methanotrophic consortia
The anaerobic oxidation of methane in marine sediments is performed by consortia of methane-oxidizing archaea and sulfate-reducing bacteria; an examination of the role of interspecies spatial positioning on single cell activity reveals that interspecies electron transfer may overcome the requirement for close spatial proximity, a proposition supported by large multi-haem cytochromes in ANME-2 genomes as well as redox-active electron microscopy staining.
- Shawn E. McGlynn
- , Grayson L. Chadwick
- & Victoria J. Orphan
-
Letter |
 Cyanate as an energy source for nitrifiers
Cyanate as an energy source for nitrifiers
The ammonia-oxidizing archaeon Nitrososphaera gargensis can utilize cyanate as the only source of energy for growth due to the presence of a cyanase enzyme, and cyanase-encoding nitrite-oxidizing bacteria can work together with cyanase-negative ammonia oxidizers to collectively grow on cyanate via reciprocal feeding; cyanases are widespread in the environment according to metagenomic data sets, pointing to the potential importance of cyanate in the nitrogen cycle.
- Marton Palatinszky
- , Craig Herbold
- & Michael Wagner
-
Research Highlights |
 Ocean survey finds huge diversity
Ocean survey finds huge diversity
-
Letter |
 Interaction and signalling between a cosmopolitan phytoplankton and associated bacteria
Interaction and signalling between a cosmopolitan phytoplankton and associated bacteria
Molecular characterization of interactions between a globally distributed marine diatom and its bacterial consortium.
- S. A. Amin
- , L. R. Hmelo
- & E. V. Armbrust
-
Outlook |
 Microbiome: The puzzle in a bee's gut
Microbiome: The puzzle in a bee's gut
By analysing bacteria that live in the digestive tracts of bees, researchers hope to learn about the role of microbes in insect health.
- Alla Katsnelson
-
Letter |
 Counteraction of antibiotic production and degradation stabilizes microbial communities
Counteraction of antibiotic production and degradation stabilizes microbial communities
Mathematical modelling and simulations reveal that including antibiotic degraders in ecological models of microbial species interaction allows the system to robustly move towards an intermixed stable state, more representative of real-world observations.
- Eric D. Kelsic
- , Jeffrey Zhao
- & Roy Kishony
-
News |
 Panda guts not suited to digesting bamboo
Panda guts not suited to digesting bamboo
Bear’s microbiome shows poor evolutionary adaptation to the fibrous food.
- Allie Wilkinson
-
Outlook |
 Microbiome: Microbial mystery
Microbiome: Microbial mystery
Gut bacteria have an important but elusive role in the formation of colorectal cancer.
- Sarah DeWeerdt
-
News |
 Microbiomes raise privacy concerns
Microbiomes raise privacy concerns
DNA from microbes living on the human body can be used to identify individuals.
- Ewen Callaway
-
News |
 Bacteria bonanza found in remote Amazon village
Bacteria bonanza found in remote Amazon village
Genes for antibiotic resistance among those found in most-diverse human microbiome.
- Boer Deng
-
Innovations In |
 Why Microbiome Treatments Could Pay Off Soon
Why Microbiome Treatments Could Pay Off Soon
Effective interventions may come before all the research is in
- Rob Knight
-
Innovations In |
 The Gene–Microbe Link
The Gene–Microbe Link
Evidence that genes shape the microbiome may point to new treatments for common diseases
- Ruth E. Ley
-
Innovations In |
 Your Microbes at Work: Fiber Fermenters Keep Us Healthy
Your Microbes at Work: Fiber Fermenters Keep Us Healthy
-
-
Innovations In |
 Microbiome Engineering
Microbiome Engineering
Synthetic biology may lead to the creation of smart microbes that can detect and treat disease
- Justin L. Sonnenburg
-
Innovations In |
 Thinking from the Gut
Thinking from the Gut
The microbiome may yield a new class of psychobiotics for the treatment of anxiety, depression and other mood disorders
- Charles Schmidt
-
Innovations In |
 The Diverse Microbiome of the Hunter-Gatherer
The Diverse Microbiome of the Hunter-Gatherer
The Hadza of Tanzania offer a snapshot of the co-adaptive capacity of the gut ecosystem
- Stephanie L. Schnorr
-
Innovations In |
 The Peacekeepers
The Peacekeepers
Amid the trillions of microbes that live in the intestines, scientists have found a few species that seem to play a key role in keeping us healthy
- Moises Velasquez-Manoff
-
News |
 Food preservatives linked to obesity and gut disease
Food preservatives linked to obesity and gut disease
Mouse study suggests that emulsifiers alter gut bacteria, leading to the inflammatory bowel condition colitis.
- Sara Reardon
-
Letter |
 Dietary emulsifiers impact the mouse gut microbiota promoting colitis and metabolic syndrome
Dietary emulsifiers impact the mouse gut microbiota promoting colitis and metabolic syndrome
Emulsifying agents, which are common food additives in the human diet, induce low-grade inflammation and obesity/metabolic syndrome in mice, suggesting that further investigation into the potential impact of dietary emulsifiers on the gut microbiota and human heath are warranted.
- Benoit Chassaing
- , Omry Koren
- & Andrew T. Gewirtz
-
Article |
 Biogeography and individuality shape function in the human skin metagenome
Biogeography and individuality shape function in the human skin metagenome
Previous work has shown that human skin is home to a rich and varied microbiota; here a metagenomic approach for samples from physiologically diverse body sites illuminates that the skin microbiota, including bacterial, fungal and viral members, is shaped by the local biogeography and yet marked by strong individuality.
- Julia Oh
- , Allyson L. Byrd
- & Julia A. Segre
-
Letter |
 Members of the human gut microbiota involved in recovery from Vibrio cholerae infection
Members of the human gut microbiota involved in recovery from Vibrio cholerae infection
Recovery from cholera is characterized by a pattern of accumulation of bacterial taxa that shows similarities to the pattern of maturation of the gut microbiota in healthy children, raising the possibility that some of these taxa may be useful for ‘repair’ of the gut microbiota in individuals whose gut communities have been ‘wounded’ through a variety of insults.
- Ansel Hsiao
- , A. M. Shamsir Ahmed
- & Jeffrey I. Gordon
-
Article |
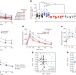 Artificial sweeteners induce glucose intolerance by altering the gut microbiota
Artificial sweeteners induce glucose intolerance by altering the gut microbiota
Non-caloric artificial sweeteners (NAS), widely used food additives considered to be safe and beneficial alternatives to sugars, are shown here to lead to the development of glucose intolerance through compositional and functional changes in the gut microbiota of mice, and the deleterious metabolic effects are transferred to germ-free mice by faecal transplant; NAS-induced dysbiosis and glucose intolerance are also demonstrated in healthy human subjects.
- Jotham Suez
- , Tal Korem
- & Eran Elinav
-
Letter |
 Persistent gut microbiota immaturity in malnourished Bangladeshi children
Persistent gut microbiota immaturity in malnourished Bangladeshi children
Bacterial species whose representation defines healthy postnatal assembly of the gut microbiota in Bangladeshi children during their first 2 years are identified, and a model is constructed to compare healthy children to those with severe acute malnutrition (SAM); results show that SAM is associated with microbiota immaturity that is only partially ameliorated by existing nutritional interventions.
- Sathish Subramanian
- , Sayeeda Huq
- & Jeffrey I. Gordon
-
-
Outlook |
 Microbiome: A complicated relationship status
Microbiome: A complicated relationship status
Nothing is simple about the links between the bacteria living in our guts and obesity.
- Sarah Deweerdt
-
Letter |
 Dynamics and associations of microbial community types across the human body
Dynamics and associations of microbial community types across the human body
The microbiome composition of 300 individuals sampled over 12–18 months was partitioned into microbial community types, which could be associated with the type found at other body sites, as well as with whether individuals were breastfed as an infant, their gender and their level of education.
- Tao Ding
- & Patrick D. Schloss
-
Letter |
 Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome
Diet rapidly and reproducibly alters the human gut microbiome
Consuming diets rich in plant versus animal products changes the microbes found in the human gut within days, with important implications for our health and evolution.
- Lawrence A. David
- , Corinne F. Maurice
- & Peter J. Turnbaugh
-
Letter |
 Histone deacetylase 3 coordinates commensal-bacteria-dependent intestinal homeostasis
Histone deacetylase 3 coordinates commensal-bacteria-dependent intestinal homeostasis
This work identifies a role for intestinal epithelial cell (IEC)-intrinsic expression of histone deacetylase 3 in regulating commensal-bacteria-dependent gene expression and intestinal homeostasis; IEC-specific HDAC3 deficiency gives rise to Paneth cell abnormalities, impaired intestinal barrier function, and increased DSS-induced intestinal inflammation in commensal-bacteria-containing, but not germ-free, mice.
- Theresa Alenghat
- , Lisa C. Osborne
- & David Artis
-
Letter |
 Microbiota-liberated host sugars facilitate post-antibiotic expansion of enteric pathogens
Microbiota-liberated host sugars facilitate post-antibiotic expansion of enteric pathogens
Antibiotic treatment disturbs the commensal microbiota and is often followed by infection with enteric pathogens such as Salmonella typhimurium and Clostridium difficile; pathogen expansion is fuelled by antibiotic-driven accumulation of commensal-liberated host mucosal carbohydrates.
- Katharine M. Ng
- , Jessica A. Ferreyra
- & Justin L. Sonnenburg
-
Letter |
 Diverse type VI secretion phospholipases are functionally plastic antibacterial effectors
Diverse type VI secretion phospholipases are functionally plastic antibacterial effectors
A functionally diverse superfamily of bacterial phospholipase enzymes that mediate antagonisitc interactions as effectors of the type VI secretion system is uncovered; these enzymes degrade the bacterial membrane, representing a novel mechanism of bacterial competition.
- Alistair B. Russell
- , Michele LeRoux
- & Joseph D. Mougous
-
Outlook |
 Microbiome: The surface brigade
Microbiome: The surface brigade
Our skin is home to thousands of species of bacteria — and when these microscopic societies are disrupted, skin infections can arise.
- Bijal Trivedi
-
Outlook |
 Microbiome: Cultural differences
Microbiome: Cultural differences
Studies of gut bacteria are beginning to untangle how diet affects health in old age — but determining cause and effect is tricky.
- Virginia Hughes
-
Article |
 Genomic variation landscape of the human gut microbiome
Genomic variation landscape of the human gut microbiome
A framework for metagenomic variation analysis to explore variation in the human microbiome is developed; the study describes SNPs, short indels and structural variants in 252 faecal metagenomes of 207 individuals from Europe and North America.
- Siegfried Schloissnig
- , Manimozhiyan Arumugam
- & Peer Bork
-
News & Views |
 Algae's complex origins
Algae's complex origins
The nuclear genomes of two of nature's most complex cells have been sequenced. The data will help to determine the evolutionary path from symbioses between species to a multi-compartmental unicellular organism. See Article p.59
- Sven B. Gould
-
Research Highlights |
Ancient origin for gut microbiome
-
News |
 Fungus that controls zombie-ants has own fungal stalker
Fungus that controls zombie-ants has own fungal stalker
A specialized parasite fungus can control ants' behavior. But that fungus also faces its own deadly, specialized parasites.
- Katherine Harmon
-
Research Highlights |
Cheating yeast finish last
-
Letter |
 Resurrection of endogenous retroviruses in antibody-deficient mice
Resurrection of endogenous retroviruses in antibody-deficient mice
Novel pathogenic infectious retroviruses, generated by recombination between replication-defective endogenous retroviruses in the absence of a functional antibody response, are identified; these recombinant retroviruses establish infection of mouse colonies and ultimately cause cancer.
- George R. Young
- , Urszula Eksmond
- & George Kassiotis
-
News & Views |
 Resident risks
Resident risks
An innovative method for probing the genomes of the vast community of microorganisms that inhabit the human gut provides an alternative approach to identifying risk factors for type 2 diabetes. See Letter p.55
- Julia Oh
- & Julia A. Segre
-
Research Highlights |
Ecosystems compete
-
Review Article |
 Functional interactions between the gut microbiota and host metabolism
Functional interactions between the gut microbiota and host metabolism
- Valentina Tremaroli
- & Fredrik Bäckhed
-
-
Article |
 Antibiotics in early life alter the murine colonic microbiome and adiposity
Antibiotics in early life alter the murine colonic microbiome and adiposity
Treatment of young mice with low levels of antibiotics results in increases in adiposity and causes both a change in the composition of the intestinal microbial community and an alteration in the activity of microbial metabolic pathways, leading to increased short-chain fatty acid production.
- Ilseung Cho
- , Shingo Yamanishi
- & Martin J. Blaser
-
News |
 E. coli strain linked to cancer in mice
E. coli strain linked to cancer in mice
DNA-damaging bacterium flourishes in the guts of mice with inflammatory bowel disease.
- Ewen Callaway
-
News |
 Pregnancy alters resident gut microbes
Pregnancy alters resident gut microbes
Third-trimester microbiota resembles that of people at risk of diabetes.
- Monya Baker
-
Letter |
 Revealing structure and assembly cues for Arabidopsis root-inhabiting bacterial microbiota
Revealing structure and assembly cues for Arabidopsis root-inhabiting bacterial microbiota
Roots of land plants are populated by a specific microbiota capable of modulating plant growth and development; here large-scale sequencing analysis shows that the bacterial community inhabiting Arabidopsis roots is influenced by soil type and plant genotype, and that plant cell-wall features serve as colonization cue for a subcommunity of the root microbiota.
- Davide Bulgarelli
- , Matthias Rott
- & Paul Schulze-Lefert
-
Letter |
 Defining the core Arabidopsis thaliana root microbiome
Defining the core Arabidopsis thaliana root microbiome
Sequencing of the Arabidopsis thaliana root microbiome shows that its composition is strongly influenced by location, inside or outside the root, and by soil type.
- Derek S. Lundberg
- , Sarah L. Lebeis
- & Jeffery L. Dangl

 A bacterial nudge to T-cell function
A bacterial nudge to T-cell function The Microbes Within
The Microbes Within Obesity
Obesity Genomic approaches to studying the human microbiota
Genomic approaches to studying the human microbiota