Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access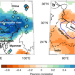 Seven centuries of reconstructed Brahmaputra River discharge demonstrate underestimated high discharge and flood hazard frequency
Seven centuries of reconstructed Brahmaputra River discharge demonstrate underestimated high discharge and flood hazard frequency
This study investigates flood hazards of the Brahmaputra River, Bangladesh. Based on a tree ring reconstruction of seasonal river discharge, climate modelling, and historic documentation of flood events, the authors suggest flood hazard risk is underestimated by ~24–38% in the present day compared to the past 700 years.
- Mukund P. Rao
- , Edward R. Cook
- & Peter J. Webster
-
Article
| Open Access Iceberg melting substantially modifies oceanic heat flux towards a major Greenlandic tidewater glacier
Iceberg melting substantially modifies oceanic heat flux towards a major Greenlandic tidewater glacier
Iceberg melting releases large volumes of freshwater in fjords, yet the impact on oceanic heat delivery to tidewater glaciers is unknown. Here the authors show that iceberg melting invigorates fjord circulation in a large, iceberg-congested fjord, thereby increasing oceanic heat delivery to its tidewater glaciers.
- B. J. Davison
- , T. R. Cowton
- & A. J. Sole
-
Article
| Open Access Global hotspots for the occurrence of compound events
Global hotspots for the occurrence of compound events
Compound climate events such as floods and droughts together can cause severe socio-economic impacts. Here, the authors analyse global hazard pairs from 1980–2014 and find global hotspots for the occurrence of compound events.
- Nina N. Ridder
- , Andy J. Pitman
- & Jakob Zscheischler
-
Article
| Open Access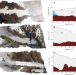 Centennial response of Greenland’s three largest outlet glaciers
Centennial response of Greenland’s three largest outlet glaciers
The Greenland Ice Sheet is the largest land ice contributor to sea level rise and understanding the long-term glacier response to external forcing is key to improved projections. Here the authors show Greenland’s three largest outlet glaciers will likely exceed current worst-case scenario
- Shfaqat A. Khan
- , Anders A. Bjørk
- & Toni Schenk
-
Article
| Open Access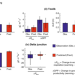 Alaskan carbon-climate feedbacks will be weaker than inferred from short-term experiments
Alaskan carbon-climate feedbacks will be weaker than inferred from short-term experiments
Warming in the high latitudes is expected to stimulate soil organic matter decomposition which leads to enhanced carbon emissions. Here, the authors show that short-term experiments do not capture the complexity of vegetation dynamics in the Arctic and might thus not provide a full picture of long term processes.
- Nicholas J. Bouskill
- , William J. Riley
- & Robert F. Grant
-
Comment
| Open Access A framework for research linking weather, climate and COVID-19
A framework for research linking weather, climate and COVID-19
Early studies of weather, seasonality, and environmental influences on COVID-19 have yielded inconsistent and confusing results. To provide policy-makers and the public with meaningful and actionable environmentally-informed COVID-19 risk estimates, the research community must meet robust methodological and communication standards.
- Benjamin F. Zaitchik
- , Neville Sweijd
- & Xavier Rodó
-
Article
| Open Access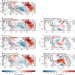 Trans-basin Atlantic-Pacific connections further weakened by common model Pacific mean SST biases
Trans-basin Atlantic-Pacific connections further weakened by common model Pacific mean SST biases
Many climate models failed to reproduce the eastern Pacific cooling that has been linked to slower warming in the early 20th century. Here, the authors present a feedback mechanism between the tropical Pacific and the Atlantic which contributes to this bias as it further dampens the Pacific cooling response in models.
- Chen Li
- , Dietmar Dommenget
- & Shayne McGregor
-
Perspective
| Open Access Redox-informed models of global biogeochemical cycles
Redox-informed models of global biogeochemical cycles
Marine microbial activities fuel biogeochemical cycles that impact the climate, but global models do not account for the myriad physiological processes that microbes perform. Here the authors argue for a model framework that reinterprets the ocean as physics coupled to biologically-driven redox chemistry.
- Emily J. Zakem
- , Martin F. Polz
- & Michael J. Follows
-
Article
| Open Access A circumpolar dust conveyor in the glacial Southern Ocean
A circumpolar dust conveyor in the glacial Southern Ocean
Dust deposition brings iron that fuels ocean productivity, a connection impacting climate over geological time. Here the authors use sediment cores to show that in contrast to dynamics today, during the last glacial maximum westerly winds shuttled dust from Australia and South America around Antarctica and into the South Pacific.
- Torben Struve
- , Katharina Pahnke
- & Gisela Winckler
-
Article
| Open Access A spatial emergent constraint on the sensitivity of soil carbon turnover to global warming
A spatial emergent constraint on the sensitivity of soil carbon turnover to global warming
The fate of the carbon locked away in soil is uncertain, and there are vast differences between models. Here the authors apply observational, spatio-temporal constraints on carbon turnover projections and find that uncertainty in estimations of carbon dynamics are reduced by 50%.
- Rebecca M. Varney
- , Sarah E. Chadburn
- & Peter M. Cox
-
Article
| Open Access Inter-hemispheric synchroneity of Holocene precipitation anomalies controlled by Earth’s latitudinal insolation gradients
Inter-hemispheric synchroneity of Holocene precipitation anomalies controlled by Earth’s latitudinal insolation gradients
Solar insolation is not equally distributed on the Earth’s surface and such imbalances influence the atmospheric circulation. Here, the authors show that latitudinal insolation gradients synchronized the hydroclimate in the Northern mid-latitudes and the African and South American Monsoons throughout the Holocene.
- Michael Deininger
- , Frank McDermott
- & Denis Scholz
-
Article
| Open Access Global warming due to loss of large ice masses and Arctic summer sea ice
Global warming due to loss of large ice masses and Arctic summer sea ice
The disintegration of cryosphere elements such as the Arctic summer sea ice, mountain glaciers, Greenland and West Antarctica is associated with temperature and radiative feedbacks. In this work, the authors quantify these feedbacks and find an additional global warming of 0.43°C.
- Nico Wunderling
- , Matteo Willeit
- & Ricarda Winkelmann
-
Perspective
| Open Access Towards a global-scale soil climate mitigation strategy
Towards a global-scale soil climate mitigation strategy
Reducing soil degradation and improving soil management could make an important contribute to climate change mitigation. Here the authors discuss opportunities and challenges towards implementing a global climate mitigation strategy focused on carbon sequestration in agricultural soils, and propose a framework for guiding region- and soil-specific management options.
- W. Amelung
- , D. Bossio
- & A. Chabbi
-
Article
| Open Access Modulation of late Pleistocene ENSO strength by the tropical Pacific thermocline
Modulation of late Pleistocene ENSO strength by the tropical Pacific thermocline
How the El Niño Southern Oscillation depends on the background conditions is not well known. Here, the authors present individual foraminifera distributions which show that central Pacific variability is related to the warmth and depth of the thermocline across varying climate background conditions over the past ~285,000 years.
- Gerald T. Rustic
- , Pratigya J. Polissar
- & Sarah M. White
-
Article
| Open Access The Iceland-Faroe Slope Jet: a conduit for dense water toward the Faroe Bank Channel overflow
The Iceland-Faroe Slope Jet: a conduit for dense water toward the Faroe Bank Channel overflow
Dense water from the Nordic Seas sustains the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation, yet the upstream pathways are not fully known. Here, the authors provide evidence of a deep current between Iceland and the Faroe Islands, which supplies 50% of the transport through the Faroe Bank Channel overflow.
- Stefanie Semper
- , Robert S. Pickart
- & Bogi Hansen
-
Article
| Open Access Fusing subnational with national climate action is central to decarbonization: the case of the United States
Fusing subnational with national climate action is central to decarbonization: the case of the United States
Climate action from local actors is vital in achieving nationally determined contributions under the Paris Agreement. Here the authors show that existing commitments from U.S. states, cities and business could reduce emissions 25% below 2005 levels by 2030, with expanded subnational action reducing emissions by 37% and federal action by up to 49%.
- Nathan E. Hultman
- , Leon Clarke
- & John O’Neill
-
Article
| Open Access Orbital climate variability on the northeastern Tibetan Plateau across the Eocene–Oligocene transition
Orbital climate variability on the northeastern Tibetan Plateau across the Eocene–Oligocene transition
Marine records indicate a greenhouse to icehouse climate transition at ~34 million years ago, but how the climate changed within continental interiors at this time is less well known. Here, the authors show an orbital climate response shift with aridification on the northeastern Tibetan Plateau during this time.
- Hong Ao
- , Guillaume Dupont-Nivet
- & Zhisheng An
-
Article
| Open Access Recent fall Eurasian cooling linked to North Pacific sea surface temperatures and a strengthening Siberian high
Recent fall Eurasian cooling linked to North Pacific sea surface temperatures and a strengthening Siberian high
In the last years, an extensive winter cooling over central Eurasia has been discussed widely. Here, the authors show that from 2004–2018, the Eurasian cooling in autumn is stronger than that in winter, and that this autumn cooling is likely influenced by the Pacific Decadal Oscillation and the Siberian high.
- Baofu Li
- , Yupeng Li
- & Xun Shi
-
Article
| Open Access Greenhouse gas consequences of the China dual credit policy
Greenhouse gas consequences of the China dual credit policy
China issued the Dual Credit policy to improve vehicle efficiency and accelerate new energy vehicle adoption. Here the authors show that the total Greenhouse gas emissions (GHGs) of the Chinese passenger vehicle fleet are expected to peak in 2032 and a significant reduction in GHG emissions is possible by optimizing the Dual Credit policy.
- Xin He
- , Shiqi Ou
- & Michael Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Vegetation forcing modulates global land monsoon and water resources in a CO2-enriched climate
Vegetation forcing modulates global land monsoon and water resources in a CO2-enriched climate
Monsoon systems have strong impacts on precipitation and food security over large areas of the world. Here, the authors show that plant responses to rising CO2 concentrations in the atmosphere play a key role in modulating seasonal rainfall and water resources over global land monsoon regions.
- Jiangpeng Cui
- , Shilong Piao
- & Gabriel J. Kooperman
-
Article
| Open Access Near-real-time monitoring of global CO2 emissions reveals the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic
Near-real-time monitoring of global CO2 emissions reveals the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic has stopped many human activities, which has had significant impact on emissions of greenhouse gases. Here, the authors present daily estimates of country-level CO2 emissions for different economic sectors and show that there has been a 8.8% decrease in global CO2 emissions in the first half of 2020.
- Zhu Liu
- , Philippe Ciais
- & Hans Joachim Schellnhuber
-
Article
| Open Access Unconventional oil and gas development and ambient particle radioactivity
Unconventional oil and gas development and ambient particle radioactivity
Unconventional oil and gas production has increased drastically in the US, but its environmental impacts are not well known. Here, the authors show that these wells can be associated with elevated levels of airborne particle radioactivity in downwind locations.
- Longxiang Li
- , Annelise J. Blomberg
- & Petros Koutrakis
-
Article
| Open Access Serpentine alteration as source of high dissolved silicon and elevated δ30Si values to the marine Si cycle
Serpentine alteration as source of high dissolved silicon and elevated δ30Si values to the marine Si cycle
The Si cycle is important to ocean productivity and nutrient cycling, however there are uncertainties in global budgets. Here the authors use a multi-isotope approach on seafloor sediments and pore fluids, finding that an unappreciated source of Si to the ocean is the degradation of seafloor serpentinites.
- Sonja Geilert
- , Patricia Grasse
- & Catriona D. Menzies
-
Article
| Open Access Interglacials of the Quaternary defined by northern hemispheric land ice distribution outside of Greenland
Interglacials of the Quaternary defined by northern hemispheric land ice distribution outside of Greenland
This study presents a new definition of interglacials during the Quaternary. The authors find the appearance of interglacials is in general following the 41-kyr cycle of obliquity with various exceptions, suggesting a more complex physical mechanism triggering glacial terminations.
- Peter Köhler
- & Roderik S. W. van de Wal
-
Article
| Open Access Andean drought and glacial retreat tied to Greenland warming during the last glacial period
Andean drought and glacial retreat tied to Greenland warming during the last glacial period
How the abrupt warming events recorded in Greenland ice cores during the last glacial cycle have influenced the tropical climate is not well known. Here the authors present new lake sediment data from the Peruvian Andes that shows that these events resulted in rapid glacier retreat and large reductions in lake level.
- Arielle Woods
- , Donald T. Rodbell
- & Joseph S. Stoner
-
Article
| Open Access Impact of tides and sea-level on deep-sea Arctic methane emissions
Impact of tides and sea-level on deep-sea Arctic methane emissions
This study investigates the effect of changing sea level on deep sea gas emissions in the Arctic. The results show that small decreases in sea-level favors gas release. This implies that sea-level rise may partially counterbalance the effect of warming oceans on gas emissions overall.
- Nabil Sultan
- , Andreia Plaza-Faverola
- & Jochen Knies
-
Article
| Open Access Significant increase of global anomalous moisture uptake feeding landfalling Atmospheric Rivers
Significant increase of global anomalous moisture uptake feeding landfalling Atmospheric Rivers
Increasing atmospheric temperatures are expected to have various impacts on the global water cycle. Here, the authors show that there is an intensification of atmospheric rivers, that causes enhanced evapotranspiration and thus atmospheric moisture uptake in many regions of the world.
- Iago Algarra
- , Raquel Nieto
- & Luis Gimeno
-
Article
| Open Access Reconstructing the electrical structure of dust storms from locally observed electric field data
Reconstructing the electrical structure of dust storms from locally observed electric field data
Electrification is naturally generated in dust storms but its structures remain largely unknown. Here, the authors present an inversion model to reconstruct such structures based on the locally observed electric field data, showing that dust storms exhibit a three-dimensional mosaic charge pattern.
- Huan Zhang
- & You-He Zhou
-
Article
| Open Access High-latitude biomes and rock weathering mediate climate–carbon cycle feedbacks on eccentricity timescales
High-latitude biomes and rock weathering mediate climate–carbon cycle feedbacks on eccentricity timescales
Climate and carbon cycle interactions during major Earth system changes through the Cenozoic remain unclear. Here, the authors present a combined δ13C-δ18O megasplice for the last 35 Ma which allows them to identify three marked intervals of distinct climate–carbon cycle interactions.
- David De Vleeschouwer
- , Anna Joy Drury
- & Heiko Pälike
-
Article
| Open Access Magnesium in subaqueous speleothems as a potential palaeotemperature proxy
Magnesium in subaqueous speleothems as a potential palaeotemperature proxy
Few palaeoclimate archives beyond the polar regions preserve continuous and datable paleotemperature proxy time series over multiple glacial-interglacial cycles. Here, the authors show that Mg concentrations in a subaqueous speleothem from an Italian cave track regional sea-surface temperatures over the last 350,000 years.
- Russell Drysdale
- , Isabelle Couchoud
- & Jon Woodhead
-
Article
| Open Access Temperature variability implies greater economic damages from climate change
Temperature variability implies greater economic damages from climate change
The authors estimate the damages associated with global temperature variability. They find that variability in temperature leads to substantial uncertainty about damages, which imposes costs equivalent to a large fraction of annual consumption today.
- Raphael Calel
- , Sandra C. Chapman
- & Nicholas W. Watkins
-
Article
| Open Access Overestimation of the effect of climatic warming on spring phenology due to misrepresentation of chilling
Overestimation of the effect of climatic warming on spring phenology due to misrepresentation of chilling
Climate warming is advancing spring leaf unfolding, but it is also reducing the cold periods that many trees require to break winter dormancy. Here, the authors show that 7 of 12 current chilling models fail to account for the correct relationship between chilling accumulation and heat requirement, leading to substantial overestimates of the advance of spring phenology under climate change.
- Huanjiong Wang
- , Chaoyang Wu
- & Quansheng Ge
-
Article
| Open Access Local-scale Arctic tundra heterogeneity affects regional-scale carbon dynamics
Local-scale Arctic tundra heterogeneity affects regional-scale carbon dynamics
Carbon stored in the Arctic is threatened by climate change, but models do not capture the local-scale heterogeneity that influences carbon dynamics. Here the authors refine tundra models to account for heterogeneity, finding improved projections and decreased uncertainty in assessing the fate of carbon.
- M. J. Lara
- , A. D. McGuire
- & S. D. Wullschleger
-
Article
| Open Access A biogenic secondary organic aerosol source of cirrus ice nucleating particles
A biogenic secondary organic aerosol source of cirrus ice nucleating particles
Ice nucleating particles impact the global climate by altering cloud formation and properties, but the sources of these emissions are not completely characterized. Here, the authors show that secondary organic aerosols formed from the oxidation of organic gases in the atmosphere can be a source of ice nucleating particles.
- Martin J. Wolf
- , Yue Zhang
- & Daniel J. Cziczo
-
Article
| Open Access Frequent new particle formation over the high Arctic pack ice by enhanced iodine emissions
Frequent new particle formation over the high Arctic pack ice by enhanced iodine emissions
Which vapors are responsible for new particle formation in the Arctic is largely unknown. Here, the authors show that the formation of new particles at the central Arctic Ocean is mainly driven by iodic acid and that particles smaller than 30 nm in diameter can activate as cloud condensation nuclei.
- Andrea Baccarini
- , Linn Karlsson
- & Julia Schmale
-
Article
| Open Access Soil moisture dominates dryness stress on ecosystem production globally
Soil moisture dominates dryness stress on ecosystem production globally
Dryness stresses vegetation and can lead to declines in productivity, increased emission of carbon, and plant mortality, but the drivers of this stress remain unclear. Here the authors show that soil moisture plays a dominant role relative to atmospheric water demand over most global land vegetated areas.
- Laibao Liu
- , Lukas Gudmundsson
- & Sonia I. Seneviratne
-
Article
| Open Access Indian Ocean warming as a driver of the North Atlantic warming hole
Indian Ocean warming as a driver of the North Atlantic warming hole
A significant part of the subpolar North Atlantic has warmed less over the past century than the rest of the global ocean, a feature called the North Atlantic warming hole. Here, the authors show that this anomaly can be explained by remote atmospheric forcing from the rapidly warming Indian Ocean.
- Shineng Hu
- & Alexey V. Fedorov
-
Article
| Open Access Compounding impact of severe weather events fuels marine heatwave in the coastal ocean
Compounding impact of severe weather events fuels marine heatwave in the coastal ocean
Exposure to extreme events is a major concern in coastal regions where human populations and stressed ecosystems are at risk to such phenomena. Here the authors show a marine heatwave on the continental shelf resulted from a novel set of compounding effects due to a tropical storm followed by an atmospheric heatwave.
- B. Dzwonkowski
- , J. Coogan
- & T. Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Summer warming explains widespread but not uniform greening in the Arctic tundra biome
Summer warming explains widespread but not uniform greening in the Arctic tundra biome
Satellites provide clear evidence of greening trends in the Arctic, but high-resolution pan-Arctic quantification of these trends is lacking. Here the authors analyse high-resolution Landsat data to show widespread greening in the Arctic, and find that greening trends are linked to summer warming overall but not always locally.
- Logan T. Berner
- , Richard Massey
- & Scott J. Goetz
-
Article
| Open Access Impacts of solar intermittency on future photovoltaic reliability
Impacts of solar intermittency on future photovoltaic reliability
The intermittency of solar resources is one of the primary challenges for the large-scale integration of the renewable energy. Here Yin et al. used satellite data and climate model outputs to evaluate the geographic patterns of future solar power reliability, highlighting the tradeoff between the maximum potential power and the power reliability.
- Jun Yin
- , Annalisa Molini
- & Amilcare Porporato
-
Article
| Open Access India’s potential for integrating solar and on- and offshore wind power into its energy system
India’s potential for integrating solar and on- and offshore wind power into its energy system
India currently relies heavily on fossil-based sources for its power needs. Here the authors show that renewable energy in India could be cheaper than fossil-based alternatives and could reduce CO2 emissions by 85% by 2040.
- Tianguang Lu
- , Peter Sherman
- & Michael McElroy
-
Article
| Open Access Global temperature modes shed light on the Holocene temperature conundrum
Global temperature modes shed light on the Holocene temperature conundrum
Proxy reconstructions show a decreasing trend from the Middle to Late Holocene, which conflicts with model results showing an increasing trend. Statistical analysis of model output shows that these conflicting results originate from two distinct modes of variability, which dominate at different regions and times.
- Jürgen Bader
- , Johann Jungclaus
- & Martin Claussen
-
Article
| Open Access Cold spells in the Nordic Seas during the early Eocene Greenhouse
Cold spells in the Nordic Seas during the early Eocene Greenhouse
The early Eocene was characterized by exceptionally high global temperatures and no polar ice. Here, clumped isotope paleothermometry of glendonite calcite from the Danish Basin shows that these were formed in waters below 5 °C, indicating that regionalised cool episodes punctuated the background warmth of the early Eocene.
- Madeleine L. Vickers
- , Sabine K. Lengger
- & Christoph Korte
-
Article
| Open Access Potential impacts of mercury released from thawing permafrost
Potential impacts of mercury released from thawing permafrost
Permafrost locks away the largest reservoir of mercury on the planet, but climate warming threatens to thaw these systems. Here the authors use models to show that unconstrained fossil fuel burning will dramatically increase the amount of mercury released into future ecosystems.
- Kevin Schaefer
- , Yasin Elshorbany
- & Elsie M. Sunderland
-
Article
| Open Access Forecasting extreme stratospheric polar vortex events
Forecasting extreme stratospheric polar vortex events
Extreme events high up in the winter stratosphere are known to influence our weather and their predictability has potential to improve seasonal weather forecasts. Here, the authors examine factors that influence their generation and highlight a previously unrecognised sensitivity to the upper equatorial stratosphere.
- L. J. Gray
- , M. J. Brown
- & J. Anstey
-
Article
| Open Access Livestock enclosures in drylands of Sub-Saharan Africa are overlooked hotspots of N2O emissions
Livestock enclosures in drylands of Sub-Saharan Africa are overlooked hotspots of N2O emissions
Africa houses approximately one third of the global cattle, sheep and goat population. Here the authors show that manure accumulation in livestock enclosures can emit significant quantities of the greenhouse gas N2O for decades after abandonment, totaling 5% of continental anthropogenic N2O emissions.
- Klaus Butterbach-Bahl
- , Gretchen Gettel
- & Lutz Merbold
-
Article
| Open Access Low elevation of Svalbard glaciers drives high mass loss variability
Low elevation of Svalbard glaciers drives high mass loss variability
Svalbard glaciers are among the lowest ice masses in the Arctic, with a peak in glacier area below 450 m elevation. Using a high-resolution climate model, here the authors show that a modest warming in the mid-1980s propagated meltwater runoff above the glacier area peak, amplifying Svalbard mass loss from all elevations.
- Brice Noël
- , C. L. Jakobs
- & M. R. van den Broeke
-
Article
| Open Access Using insurance data to quantify the multidimensional impacts of warming temperatures on yield risk
Using insurance data to quantify the multidimensional impacts of warming temperatures on yield risk
The impacts of climate change on agricultural productivity remain debated. Here, the authors present new evidence for the magnitude and causes of U.S. crop insurance losses, using a database of production risk from 1989–2014 across 1733 counties for corn and 1632 counties for soybeans, and find that crop production risk will increase in response to warmer temperatures.
- Edward D. Perry
- , Jisang Yu
- & Jesse Tack
-
Article
| Open Access Methane emissions from natural gas vehicles in China
Methane emissions from natural gas vehicles in China
The methane emissions from natural gas vehicles (NGVs) are unclear. Here the authors report high methane emissions from heavy-duty NGVs, and by using a scenario analysis show that strictly implementing the upcoming China VI standard could reduce GHG emissions by 509 Mt CO2eq for 2020-2030.
- Da Pan
- , Lei Tao
- & Mark A. Zondlo

 Continuous moulting by Antarctic krill drives major pulses of carbon export in the north Scotia Sea, Southern Ocean
Continuous moulting by Antarctic krill drives major pulses of carbon export in the north Scotia Sea, Southern Ocean