Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access A chemical proteomics approach for global mapping of functional lysines on cell surface of living cell
A chemical proteomics approach for global mapping of functional lysines on cell surface of living cell
Ligand discovery against membrane proteins has been a major challenge, mainly due to the peculiar nature of their natural habitat. Here, the authors designed a new chemical proteomic probe that targets the lysines exposed on the cell surface and developed a chemical proteomic strategy for global analysis of surface functionality in living cells.
- Ting Wang
- , Shiyun Ma
- & Haojie Lu
-
Article
| Open Access Toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domain-containing proteins have NAD-RNA decapping activity
Toll/interleukin-1 receptor (TIR) domain-containing proteins have NAD-RNA decapping activity
Toll/interleukin-1 receptor domain-containing proteins can catabolize NAD+. Here, Wang et al show that these proteins can also function as NAD-RNA decapping enzymes by releasing the NAM moiety from the NAD-RNA, resulting in the regulation of gene expression.
- Xufeng Wang
- , Dongli Yu
- & Xuemei Chen
-
Article
| Open Access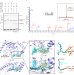 Structure-guided engineering enables E3 ligase-free and versatile protein ubiquitination via UBE2E1
Structure-guided engineering enables E3 ligase-free and versatile protein ubiquitination via UBE2E1
Ubiquitin E3 ligases are key to accessing ubiquitinated proteins, but only a few substrates have defined E3 ligases. Here, the authors reveal the mechanism of naturally occurring E3-independent ubiquitination and develop an E3-free enzymatic strategy for the versatile generation of ubiquitinated proteins.
- Xiangwei Wu
- , Yunxiang Du
- & Lei Liu
-
Article
| Open Access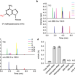 C2-methyladenosine in tRNA promotes protein translation by facilitating the decoding of tandem m2A-tRNA-dependent codons
C2-methyladenosine in tRNA promotes protein translation by facilitating the decoding of tandem m2A-tRNA-dependent codons
Duan et al. demonstrate that the m2A modification is ubiquitous in plants and tRNA m2A37 promotes a relaxed conformation of tRNA, enhancing translation efficiency by facilitating decoding of tandem m2A-tRNA-dependent codons.
- Hong-Chao Duan
- , Chi Zhang
- & Guifang Jia
-
Article
| Open Access Asymmetric nucleosome PARylation at DNA breaks mediates directional nucleosome sliding by ALC1
Asymmetric nucleosome PARylation at DNA breaks mediates directional nucleosome sliding by ALC1
Bacic et al. demonstrate that PARP1/HPF1 preferentially modify histone tails closest to the DNA break, directing ALC1-catalyzed nucleosome sliding. These findings suggest a mechanism for rendering DNA breaks more accessible to repair factors.
- Luka Bacic
- , Guillaume Gaullier
- & Sebastian Deindl
-
Article
| Open Access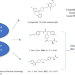 Discovery of a peripheral 5HT2A antagonist as a clinical candidate for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis
Discovery of a peripheral 5HT2A antagonist as a clinical candidate for metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis
Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH), an advanced form of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD), can progress to liver fibrosis. Here, the authors develop a peripheral 5HT2A antagonist for the treatment of MASLD and MASH.
- Haushabhau S. Pagire
- , Suvarna H. Pagire
- & Jin Hee Ahn
-
Article
| Open Access Multiple redox switches of the SARS-CoV-2 main protease in vitro provide opportunities for drug design
Multiple redox switches of the SARS-CoV-2 main protease in vitro provide opportunities for drug design
Here the authors demonstrate that the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro) is subject to redox regulation in vitro, reversibly switching between the enzymatically active dimer and the functionally dormant monomer through redox modifications of cysteine residues.
- Lisa-Marie Funk
- , Gereon Poschmann
- & Kai Tittmann
-
Article
| Open Access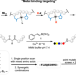 Copper assisted sequence-specific chemical protein conjugation at a single backbone amide
Copper assisted sequence-specific chemical protein conjugation at a single backbone amide
Direct, site-specific methods of protein functionalization are of interest, but challenging due to difficulty in chemically differentiating a single site within a large protein. Here, the authors develop a Copper Assisted Sequence-specific conjugation Tag (CAST) method to achieve rapid, site-specific protein backbone chemical modification with pinpoint accuracy, and prepare various on-demand modified recombinant proteins using CAST.
- Mengzhun Guo
- , Kai Zhao
- & Bobo Dang
-
Article
| Open Access A simple method for developing lysine targeted covalent protein reagents
A simple method for developing lysine targeted covalent protein reagents
The combination of a covalent electrophile with a peptide or protein-based scaffold enables the targeting of shallow protein surfaces, but the approaches to convert native peptide sequences into covalent binders are missing. Here, the authors report the design of protein-based thiomethacrylate ester electrophiles that can be installed on unprotected peptides and proteins via cysteine side chains and react efficiently and selectively with cysteine and lysine side chains on the target.
- Ronen Gabizon
- , Barr Tivon
- & Nir London
-
Article
| Open Access C-terminal modification and functionalization of proteins via a self-cleavage tag triggered by a small molecule
C-terminal modification and functionalization of proteins via a self-cleavage tag triggered by a small molecule
Specific modification or functionalization of proteins at the C-terminus is of interest but remains challenging. Here, the authors report an approach for the efficient modification of C-terminus by fusion of the cysteine protease domain (CPD) on the C-terminus of the protein of interest, and subsequent functionalization with amine-containing molecules triggered by InsP6-mediated CPD self-cleavage.
- Yue Zeng
- , Wei Shi
- & Feng Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Structure-based design of a phosphotyrosine-masked covalent ligand targeting the E3 ligase SOCS2
Structure-based design of a phosphotyrosine-masked covalent ligand targeting the E3 ligase SOCS2
SH2 domains are challenging to target using small molecules. Here, the authors develop phosphotyrosine-based covalent ligands of the E3 ligase SOCS2 using structure-based design. A pro-drug approach yields cell active inhibitors that block SOCS2 substrate recruitment.
- Sarath Ramachandran
- , Nikolai Makukhin
- & Alessio Ciulli
-
Article
| Open Access A chemical catalyst enabling histone acylation with endogenous acyl-CoA
A chemical catalyst enabling histone acylation with endogenous acyl-CoA
Chemical catalysts that can promote physiologically important post-translational modifications acting as enzyme surrogates have not been reported. Here, the authors develop mBnA, a chemical catalyst that promotes histone lysine acylation in live cells by activating endogenous acyl-CoAs as the only acyl donors.
- Misuzu Habazaki
- , Shinsuke Mizumoto
- & Motomu Kanai
-
Article
| Open Access Genetically encoded discovery of perfluoroaryl macrocycles that bind to albumin and exhibit extended circulation in vivo
Genetically encoded discovery of perfluoroaryl macrocycles that bind to albumin and exhibit extended circulation in vivo
Peptide-based therapeutics are promising therapeutic modalities, however, their prevalent drawback is poor circulation half-life in vivo. Here, the authors report the selection of albumin-binding macrocyclic peptides from genetically encoded libraries of peptides modified by perfluoroaryl-cysteine chemistry, with decafluoro-diphenylsulfone.
- Jeffrey Y. K. Wong
- , Arunika I. Ekanayake
- & Ratmir Derda
-
Article
| Open Access Click-electrochemistry for the rapid labeling of virus, bacteria and cell surfaces
Click-electrochemistry for the rapid labeling of virus, bacteria and cell surfaces
Methods for direct covalent ligation of microorganism surfaces are scarce. Here, the authors developed a rapid electrochemical process for the direct covalent ligation and labelling of the surfaces of virus, bacteria and cells using N-methylluminol, a fully tyrosine-selective protein anchoring group.
- Sébastien Depienne
- , Mohammed Bouzelha
- & Sébastien G. Gouin
-
Article
| Open Access Lenalidomide derivatives and proteolysis-targeting chimeras for controlling neosubstrate degradation
Lenalidomide derivatives and proteolysis-targeting chimeras for controlling neosubstrate degradation
Lenalidomide is effective for treating several hematological cancers but has teratogenic effect on the fetus. Here, the authors identify modifications that make lenalidomide more selective and effective when used as a stand-alone molecular glue or integrated in PROTACs.
- Satoshi Yamanaka
- , Hirotake Furihata
- & Tatsuya Sawasaki
-
Article
| Open Access Epigenetic mechanisms to propagate histone acetylation by p300/CBP
Epigenetic mechanisms to propagate histone acetylation by p300/CBP
Histone acetylation activates gene transcription but its direct read/write mechanism is unknown. Here the authors show by cryo-electron microscopy that p300/CBP reads acetylation at histone H4 and writes it to other histones in the nucleosome.
- Masaki Kikuchi
- , Satoshi Morita
- & Takashi Umehara
-
Article
| Open Access Affinity and cooperativity modulate ternary complex formation to drive targeted protein degradation
Affinity and cooperativity modulate ternary complex formation to drive targeted protein degradation
Targeted protein degradation using proteolysis targeting chimeras (PROTACs) represents an emergent therapeutic modality, however, the design of PROTACs is challenging due to multiple steps involved in PROTAC-induced degradation. Here, the authors establish a predictive framework to guide the design of potent degraders.
- Ryan P. Wurz
- , Huan Rui
- & Amit Vaish
-
Article
| Open Access Bioinspired one-pot furan-thiol-amine multicomponent reaction for making heterocycles and its applications
Bioinspired one-pot furan-thiol-amine multicomponent reaction for making heterocycles and its applications
Homogeneous engineering of proteins is promising to study biological functions and for the development of therapeutic conjugates. Here, the authors report a one-pot multicomponent Furan-Thiol-Amine reaction for diverse applications, including labelling of peptides, synthesis of macrocyclic and stapled peptides, selective modification of different proteins with varying payloads, and labelling of lysine and cysteine in a complex human proteome.
- Yuwen Wang
- , Patrick Czabala
- & Monika Raj
-
Article
| Open Access Modular synthesis of clickable peptides via late-stage maleimidation on C(7)-H tryptophan
Modular synthesis of clickable peptides via late-stage maleimidation on C(7)-H tryptophan
Cyclic peptides are of interest due to their application in pharmaceutical industry, but currently there are limited methodologies for their synthesis. Here, the authors report an efficient and direct peptide cyclization via rhodium(III)-catalysed C(7)-H maleimidation.
- Peng Wang
- , Jiang Liu
- & Yuguo Zheng
-
Article
| Open Access Amide-to-ester substitution as a stable alternative to N-methylation for increasing membrane permeability in cyclic peptides
Amide-to-ester substitution as a stable alternative to N-methylation for increasing membrane permeability in cyclic peptides
Naturally occurring peptides with high membrane permeability often have backbone ester bonds. Here, the authors investigated the effect of an amide-to-ester substitution on membrane permeability of peptides and found the substitution is useful for improving membrane permeability of cyclic peptides.
- Yuki Hosono
- , Satoshi Uchida
- & Shinsuke Sando
-
Article
| Open Access Noncanonical amino acids as doubly bio-orthogonal handles for one-pot preparation of protein multiconjugates
Noncanonical amino acids as doubly bio-orthogonal handles for one-pot preparation of protein multiconjugates
Site-specific protein multi-conjugates are important for both scientific and translational research. Here, the authors genetically encode unnatural amino acids which contain both tetrazine and azide, and use the doubly bio-orthogonal handles to generate bi- and tri-conjugate proteins in high yields.
- Yong Wang
- , Jingming Zhang
- & Tao Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Iron-sulfur clusters are involved in post-translational arginylation
Iron-sulfur clusters are involved in post-translational arginylation
The enzyme ATE1 catalyzes eukaryotic post-translation arginylation, a key protein modification necessary for cellular homeostasis. Here, the authors show that ATE1s are previously unrealized iron-sulfur proteins that use this oxygen-sensitive inorganic cofactor to control cellular arginylation
- Verna Van
- , Janae B. Brown
- & Aaron T. Smith
-
Article
| Open Access A natural biological adhesive from snail mucus for wound repair
A natural biological adhesive from snail mucus for wound repair
Natural adhesives have received a lot of attention recently. Here, the authors develop a natural biological adhesive from snail mucus that can adhere to wet tissue and be used to accelerate healing of skin wounds.
- Tuo Deng
- , Dongxiu Gao
- & Mingyi Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Chemical reaction-mediated covalent localization of bacteria
Chemical reaction-mediated covalent localization of bacteria
Transplantation of helpful bacteria has been used to treat disease through modulating host microbiota. Here, the authors report a strategy to control bacteria localization in the jejunum, via an in vivo in-situ thiol-disulfide exchange reaction between surface-reactive bacteria and mucous.
- Huilong Luo
- , Yanmei Chen
- & Jinyao Liu
-
Article
| Open Access YiaC and CobB regulate lysine lactylation in Escherichia coli
YiaC and CobB regulate lysine lactylation in Escherichia coli
The characterization of lysine lactylation (Kla) in prokaryotes remains unclear. Here, the authors identify the regulatory enzymes (YiaC as a lactylase and CobB as a delactylase) and functional network of Kla and reveal a Kla-mediated molecular mechanism for glycolysis regulation in Escherichia coli.
- Hanyang Dong
- , Jianji Zhang
- & Kai Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Traceless cysteine-linchpin enables precision engineering of lysine in native proteins
Traceless cysteine-linchpin enables precision engineering of lysine in native proteins
Controlling the selectivity of the chemical modification of a genetic-manipulation-free protein is currently problematic. Here the authors report a method using cysteine-based chemoselective Linchpin Directed site-selective Modification of the lysine residue in a protein.
- Neelesh C. Reddy
- , Rajib Molla
- & Vishal Rai
-
Article
| Open Access Elucidation of divergent desaturation pathways in the formation of vinyl isonitrile and isocyanoacrylate
Elucidation of divergent desaturation pathways in the formation of vinyl isonitrile and isocyanoacrylate
While canonical oxygen-rebound pathway has been utilized by several Fe/2OG enzymes, insights into the desaturation process remain to be elucidated. Here, the authors suggest that a carbocation might be deployed to enable chemically divergent desaturations through decarboxylation and deprotonation.
- Wantae Kim
- , Tzu-Yu Chen
- & Wei-chen Chang
-
Article
| Open Access Halogenation of tyrosine perturbs large-scale protein self-organization
Halogenation of tyrosine perturbs large-scale protein self-organization
Sun et al. has studied the genetically encodable halotyrosines in proteins of the prokaryotic cell division machinery to elucidate the general role of halogenation in cellular lifespan and oxidative damage-induced diseases such as aging and cancer.
- Huan Sun
- , Haiyang Jia
- & Nediljko Budisa
-
Article
| Open Access Development of NanoLuc-targeting protein degraders and a universal reporter system to benchmark tag-targeted degradation platforms
Development of NanoLuc-targeting protein degraders and a universal reporter system to benchmark tag-targeted degradation platforms
t ag-T argetedP roteinD egrader (tTPD) systems are powerful tools for preclinical target validation. Here the authors extend the tTPD platform by developing NanoTACs that degrade NanoLuc tagged substrates and benchmark each tTPD system using an interchangeable tag reporter system.- Christoph Grohmann
- , Charlene M. Magtoto
- & Rebecca Feltham
-
Article
| Open Access Guide RNAs containing universal bases enable Cas9/Cas12a recognition of polymorphic sequences
Guide RNAs containing universal bases enable Cas9/Cas12a recognition of polymorphic sequences
Genetic variance poses a major challenge for CRISPR-based human therapeutics and pathogen diagnostics. Here the authors show how to circumvent this issue by using guide RNAs containing universal bases to tailor Cas9/Cas12 specificity.
- Amanda R. Krysler
- , Christopher R. Cromwell
- & Basil P. Hubbard
-
Article
| Open Access Unprotected peptide macrocyclization and stapling via a fluorine-thiol displacement reaction
Unprotected peptide macrocyclization and stapling via a fluorine-thiol displacement reaction
Strategies capable of stapling unprotected peptides in a straightforward, chemoselective, and clean manner, as well as promoting cellular uptake are of great interest. Here the authors report a peptide macrocyclization and stapling strategy which satisfies those criteria, based on a fluorine thiol displacement reaction.
- Md Shafiqul Islam
- , Samuel L. Junod
- & Rongsheng E. Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Altered succinylation of mitochondrial proteins, APP and tau in Alzheimer’s disease
Altered succinylation of mitochondrial proteins, APP and tau in Alzheimer’s disease
Succinylation is a metabolism-associated post-translational protein modification. Here the authors describe changes to the succinylation of proteins in the brain of individuals with Alzheimer’s disease.
- Yun Yang
- , Victor Tapias
- & Gary E. Gibson
-
Article
| Open Access Hydrogen peroxide signaling via its transformation to a stereospecific alkyl hydroperoxide that escapes reductive inactivation
Hydrogen peroxide signaling via its transformation to a stereospecific alkyl hydroperoxide that escapes reductive inactivation
A major question in redox signaling is how H2O2 oxidizes target protein thiols in the presence of glutathione peroxidases and peroxiredoxins. We reveal signaling by H2O2 via its enzymatic conversion to an alkyl hydroperoxide that stereo-specifically escapes peroxidases and oxidizes target proteins.
- Raphael F. Queiroz
- , Christopher P. Stanley
- & Roland Stocker
-
Article
| Open Access Structural basis of the regulation of the normal and oncogenic methylation of nucleosomal histone H3 Lys36 by NSD2
Structural basis of the regulation of the normal and oncogenic methylation of nucleosomal histone H3 Lys36 by NSD2
An upregulation of NSD2, a histone H3 lysine 36 (H3K36) methyltransferase is linked to multiple myeloma and other types of cancer. Here, the authors provide insights into the regulatory mechanism of NSD2 by determining the 2.8 Å cryo-EM structure of the NSD2 bound nucleosome complex, and based on MD simulations they discuss how two oncogenic mutations enhance NSD2 activity.
- Ko Sato
- , Amarjeet Kumar
- & Toru Sengoku
-
Article
| Open Access Gene editing with CRISPR-Cas12a guides possessing ribose-modified pseudoknot handles
Gene editing with CRISPR-Cas12a guides possessing ribose-modified pseudoknot handles
Development of Cas12a for human therapeutics and diagnostics may significantly benefit from, or even require, chemical modification of its guide RNA. Here the authors show that the noncanonical 5′ pseudoknot structure of the AsCas12a crRNA guide can be heavily modified and still retain very high editing activity in cells and trans cleavage activity in vitro.
- Eman A. Ageely
- , Ramadevi Chilamkurthy
- & Keith T. Gagnon
-
Article
| Open Access Engineered osteoclasts as living treatment materials for heterotopic ossification therapy
Engineered osteoclasts as living treatment materials for heterotopic ossification therapy
Heterotopic ossification (HO) is the formation of pathological mature bone within extraskeletal soft tissues, and there are currently no reliable methods for removing these calcified plaques. Here, the authors demonstrate that chemically engineered osteoclasts coated with tetracycline can improve their targeting capacity to ectopic calcifications, which extends their bone resorption functions for the treatment of HO.
- Wenjing Jin
- , Xianfeng Lin
- & Ruikang Tang
-
Article
| Open Access Wdr1 and cofilin are necessary mediators of immune-cell-specific apoptosis triggered by Tecfidera
Wdr1 and cofilin are necessary mediators of immune-cell-specific apoptosis triggered by Tecfidera
The mechanism-of-action of many electrohilic drugs remains poorly understood. Here, the authors use a redox-targeting approach to elucidate the basis for the innate immune cell toxicity of dimethyl fumarate, showing that it modifies Keap1 to trigger mitochondrial-targeted neutrophil/macrophage apoptosis.
- Jesse R. Poganik
- , Kuan-Ting Huang
- & Yimon Aye
-
Article
| Open Access Spontaneous hydrolysis and spurious metabolic properties of α-ketoglutarate esters
Spontaneous hydrolysis and spurious metabolic properties of α-ketoglutarate esters
Analogues of α-ketoglutarate are used in many cellular studies but assumptions are made about cellular uptake. Here, the authors show that esterified analogues rapidly hydrolyse in aqueous medium resulting in an analogue which can be quickly taken up by many cell lines, contrary to prevailing assumptions.
- Seth J. Parker
- , Joel Encarnación-Rosado
- & Alec C. Kimmelman
-
Article
| Open Access Nuclear ADP-ribosylation drives IFNγ-dependent STAT1α enhancer formation in macrophages
Nuclear ADP-ribosylation drives IFNγ-dependent STAT1α enhancer formation in macrophages
STAT1a is required for pro-inflammatory responses in macrophages. Here the authors reveal that post-translational modification of STAT1a, ADPribosylation, plays a critical role in enhancer formation and activation, thus modulating IFNγ-stimulated inflammatory responses in macrophages.
- Rebecca Gupte
- , Tulip Nandu
- & W. Lee Kraus
-
Article
| Open Access Synergistic sequence contributions bias glycation outcomes
Synergistic sequence contributions bias glycation outcomes
Advanced glycation end-products (AGEs), such as methylglyoxal-derived hydroimidazolone isomer (MGH-1), are associated with disease and age-related disorders, and occur spontaneously, so it is unclear why specific protein sites become modified with specific AGEs. Here, the authors use a combinatorial peptide library to determine the chemical features that favour MGH-1 formation for short peptides and demonstrate a key role of tyrosine in this process.
- Joseph M. McEwen
- , Sasha Fraser
- & Rebecca A. Scheck
-
Article
| Open Access Modification of N-terminal α-amine of proteins via biomimetic ortho-quinone-mediated oxidation
Modification of N-terminal α-amine of proteins via biomimetic ortho-quinone-mediated oxidation
Methods for selective modification of the N-terminus of proteins are of high interest, but mostly require specific amino acid residues. Here, the authors report a selective and fast method for N-terminal modification of proteins based on quinone-mediated oxidation of the alpha-amine to aldehyde or ketone, and apply it to diverse proteins.
- Siyao Wang
- , Qingqing Zhou
- & Ping Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Biochemical and structural characterization of the BioZ enzyme engaged in bacterial biotin synthesis pathway
Biochemical and structural characterization of the BioZ enzyme engaged in bacterial biotin synthesis pathway
Biotin is an essential enzyme cofactor and two pathways for the generation of the biotin precursor pimeloyl-ACP are known. Here, the authors identify and characterize a third pathway for biotin precursor synthesis involving BioZ and they also present the Agrobacterium tumefaciens BioZ crystal structure.
- Sitao Zhang
- , Yongchang Xu
- & Youjun Feng
-
Article
| Open Access Cellular macromolecules-tethered DNA walking indexing to explore nanoenvironments of chromatin modifications
Cellular macromolecules-tethered DNA walking indexing to explore nanoenvironments of chromatin modifications
Investigation of spatial organization and relationships of biomolecules in cellular nanoenvironments is necessary to understand essential biological processes, but methodologically challenging. Here, the authors report cellular macromolecules-tethered DNA walking indexing (Cell-TALKING) to probe the nanoenvironments of DNA modifications around histone post-translational modifications, and explore the nanoenvironments in different cancer cell lines and clinical specimens.
- Feng Chen
- , Min Bai
- & Yongxi Zhao
-
Article
| Open Access Ligand-directed two-step labeling to quantify neuronal glutamate receptor trafficking
Ligand-directed two-step labeling to quantify neuronal glutamate receptor trafficking
The analysis of AMPA-type glutamate receptor (AMPAR) trafficking is essential for understanding molecular mechanisms of learning and memory, but the analytical tools are currently limited. Here, the authors report a method that combines affinity-based receptor labeling and bioorthogonal click chemistry to quantify AMPAR distribution and trafficking under physiological conditions.
- Kento Ojima
- , Kazuki Shiraiwa
- & Shigeki Kiyonaka
-
Article
| Open Access NeissLock provides an inducible protein anhydride for covalent targeting of endogenous proteins
NeissLock provides an inducible protein anhydride for covalent targeting of endogenous proteins
Covalent conjugation of endogenous protein complexes offers many opportunities for fundamental and clinical research. Based on a bacterial protein domain that forms a reactive anhydride in the presence of Ca2+, the authors here develop a system that enables the covalent capture of endogenous binding partners.
- Arne H. A. Scheu
- , Sheryl Y. T. Lim
- & Mark Howarth
-
Article
| Open Access Analysing the mechanism of mitochondrial oxidation-induced cell death using a multifunctional iridium(III) photosensitiser
Analysing the mechanism of mitochondrial oxidation-induced cell death using a multifunctional iridium(III) photosensitiser
Mitochondrial oxidation-induced cell death is an important physiological process activated by cancer therapeutics, but its investigation is challenging. Here, the authors report a multifunctional iridium(III) photosensitiser, Ir-OA, able to induce mitochondrial oxidative stress and monitor the corresponding changes in mitochondrial properties.
- Chaiheon Lee
- , Jung Seung Nam
- & Tae-Hyuk Kwon
-
Article
| Open Access A substrate binding model for the KEOPS tRNA modifying complex
A substrate binding model for the KEOPS tRNA modifying complex
KEOPS is an evolutionary conserved complex with a core of four core subunits—Pcc1, Kae1, Bud32 and Cgi121—that catalyzes the universal and essential tRNA modification N6-threonylcarbamoyl adenosine (t6A). Here the authors describe a Cgi121-tRNA crystal structure and new composite model of the KEOPS holo-enzyme-substrate complex that shed light on the t6A catalytic cycle and its regulation.
- Jonah Beenstock
- , Samara Mishelle Ona
- & Frank Sicheri
-
Article
| Open Access Cryo-electron microscopy structures of pyrene-labeled ADP-Pi- and ADP-actin filaments
Cryo-electron microscopy structures of pyrene-labeled ADP-Pi- and ADP-actin filaments
For almost forty years, N-(1-pyrene) iodoacetamide has been used to label actin at C374, but the mechanisms of the fluorescence changes are still unknown due to the lack of structural information. Here authors provide cryo-EM structures of actin filaments with N-1-pyrene conjugated to cysteine 374 and either ADP or ADP-phosphate in the active site.
- Steven Z. Chou
- & Thomas D. Pollard
-
Article
| Open Access Biomimetic α-selective ribosylation enables two-step modular synthesis of biologically important ADP-ribosylated peptides
Biomimetic α-selective ribosylation enables two-step modular synthesis of biologically important ADP-ribosylated peptides
ADP-ribosylated peptides are important molecular tools, however, the lack of effective synthetic methods hinders the access to their complex structures. Here, the authors present a biomimetic α-selective ribosylation reaction coupled with click chemistry ultimately providing a two-step modular synthesis of α-ADP-ribosylated peptides.
- Anlian Zhu
- , Xin Li
- & Lingjun Li

 HBO1 catalyzes lysine lactylation and mediates histone H3K9la to regulate gene transcription
HBO1 catalyzes lysine lactylation and mediates histone H3K9la to regulate gene transcription