Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access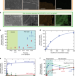 Electrochemically-mediated selective capture of heavy metal chromium and arsenic oxyanions from water
Electrochemically-mediated selective capture of heavy metal chromium and arsenic oxyanions from water
Chromium and arsenic are prevalent water pollutants, but their removal is currently limited by low selectivity. Here, the authors use redox-active metallopolymer electrodes based on poly(vinyl)ferrocene to selectively remove the two heavy metal oxyanions at concentrations as low as 100 ppb.
- Xiao Su
- , Akihiro Kushima
- & T. Alan Hatton
-
Article
| Open Access Breaking the scaling relationship via thermally stable Pt/Cu single atom alloys for catalytic dehydrogenation
Breaking the scaling relationship via thermally stable Pt/Cu single atom alloys for catalytic dehydrogenation
Enhancing the catalytic activity of noble-metal alloys is frequently accompanied by side reactions. Here, the authors describe an approach to break the scaling relationship for propane dehydrogenation, by assembling single atom alloys, to achieve simultaneous enhancement of propylene selectivity and propane conversion.
- Guodong Sun
- , Zhi-Jian Zhao
- & Jinlong Gong
-
Article
| Open Access Measuring macromolecular size distributions and interactions at high concentrations by sedimentation velocity
Measuring macromolecular size distributions and interactions at high concentrations by sedimentation velocity
Many aspects of concentrated macromolecular solutions, such as encountered in cytosol or in pharmaceutical formulations, are dependent on particle size distributions and weak intermolecular interactions. Here, the authors exploit hydrodynamic separation in the centrifugal field to measure both.
- Sumit K. Chaturvedi
- , Jia Ma
- & P. Schuck
-
Article
| Open Access Energy level tuned indium arsenide colloidal quantum dot films for efficient photovoltaics
Energy level tuned indium arsenide colloidal quantum dot films for efficient photovoltaics
Existing n-type colloidal quantum dot materials easily lose their doping polarity in air. Here Song et al. passivate the reactive covalent surface of indium arsenide quantum dots to gain the energy-level tunability and show p–n junction type solar cells with 7.92% certified efficiency.
- Jung Hoon Song
- , Hyekyoung Choi
- & Sohee Jeong
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of active sites on supported metal catalysts with carbon nanotube hydrogen highways
Identification of active sites on supported metal catalysts with carbon nanotube hydrogen highways
Understanding the location and nature of the catalytic active site is critical for controlling a catalyst’s activity and selectivity. Here, the authors separate the metal from the support by a controlled distance while maintaining the ability to promote defects via the use of carbon nanotube hydrogen highways.
- Nicholas M. Briggs
- , Lawrence Barrett
- & Steven P. Crossley
-
Article
| Open Access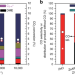 Selective conversion of CO2 and H2 into aromatics
Selective conversion of CO2 and H2 into aromatics
Selective conversion of CO2 and H2 into aromatics remains challenging due to the high unsaturation degree and complex structure of aromatics. Here the authors report a composite catalyst of ZnAlOx and H-ZSM-5 which promotes the formation of aromatics with high selectivity while inhibiting CO and CH4 formation in CO2 hydrogenation reactions.
- Youming Ni
- , Zhiyang Chen
- & Zhongmin Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Long-term deep-supercooling of large-volume water and red cell suspensions via surface sealing with immiscible liquids
Long-term deep-supercooling of large-volume water and red cell suspensions via surface sealing with immiscible liquids
Supercooled water is susceptible to spontaneous freezing, and preventing this process is a challenge. Here, the authors use surface sealing with immiscible liquids to eliminate primary ice nucleation at the water/air interface, enabling deep supercooling of large volumes of water and red cell suspensions for long time periods.
- Haishui Huang
- , Martin L. Yarmush
- & O. Berk Usta
-
Article
| Open Access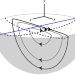 Persistent structures in a three-dimensional dynamical system with flowing and non-flowing regions
Persistent structures in a three-dimensional dynamical system with flowing and non-flowing regions
Understanding mixing in yield stress materials, such as paint and sand, is complicated due to the coexistence of solid-like and fluid-like regimes. Zaman et al. examine mixing in a granular material in three dimensions and find persistent complex non-mixing structures within the chaotic flowing regime.
- Zafir Zaman
- , Mengqi Yu
- & Paul B. Umbanhowar
-
Article
| Open Access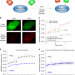 Monitoring the action of redox-directed cancer therapeutics using a human peroxiredoxin-2-based probe
Monitoring the action of redox-directed cancer therapeutics using a human peroxiredoxin-2-based probe
Current sensors for intracellular H2O2 are not sensitive enough to detect all biologically relevant H2O2 fluctuations. Here the authors develop a peroxiredoxin-2-based FRET probe that is sensitive enough to measure changes in H2O2 concentration in response to the cancer therapeutic piperlongumine.
- Troy F. Langford
- , Beijing K. Huang
- & Hadley D. Sikes
-
Article
| Open Access Energy-efficient CO2 hydrogenation with fast response using photoexcitation of CO2 adsorbed on metal catalysts
Energy-efficient CO2 hydrogenation with fast response using photoexcitation of CO2 adsorbed on metal catalysts
While many heterogeneous chemical transformations require high temperatures, such conditions are costly and corrosive to the catalysts. Here, authors enhance CO2 hydrogenation over metal nanoparticles by light irradiation via an unusual mechanism and reduce the reaction’s energetic demands.
- Chanyeon Kim
- , Seokwon Hyeon
- & Hyunjoo Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Bottle-grade polyethylene furanoate from ring-opening polymerisation of cyclic oligomers
Bottle-grade polyethylene furanoate from ring-opening polymerisation of cyclic oligomers
The synthesis of polyethylene furanoate, a promising renewable resource-based bioplastic, still has challenges. Here the authors show that bottle-grade polyethylene furanoate can be obtained within minutes from ring-opening polymerisation of its cyclic oligomers, thereby avoiding degradation and discolouration.
- Jan-Georg Rosenboom
- , Diana Kay Hohl
- & Massimo Morbidelli
-
Article
| Open Access Catalyst-TiO(OH)2 could drastically reduce the energy consumption of CO2 capture
Catalyst-TiO(OH)2 could drastically reduce the energy consumption of CO2 capture
The notoriously slow kinetics in CO2 desorption hinders the development of efficient CO2 capture technologies. Here, the authors discover that nanostructured TiO(OH)2 as a catalyst is capable of dramatically increasing the rates of CO2 desorption from spent monoethanolamine.
- Qinghua Lai
- , Sam Toan
- & Maohong Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Efficient solar hydrogen generation in microgravity environment
Efficient solar hydrogen generation in microgravity environment
While renewable energy production is a terrestrial concern, far less attention is devoted to solar-to-fuel conversion for long-term space missions. Here, the authors explore photoelectrochemical hydrogen generation in microgravity and overcome microgravity’s limitations by electrode nanostructuring.
- Katharina Brinkert
- , Matthias H. Richter
- & Hans-Joachim Lewerenz
-
Article
| Open Access Single-layer graphene membranes by crack-free transfer for gas mixture separation
Single-layer graphene membranes by crack-free transfer for gas mixture separation
Graphene shows great promise for gas separation applications, but obtaining large membranes that are free of cracks and tears remains highly challenging. Here, the authors realize monolayer, crack-free, millimeter-scale graphene membranes that exhibit selective gas permeation solely thanks to their intrinsic defects
- Shiqi Huang
- , Mostapha Dakhchoune
- & Kumar Varoon Agrawal
-
Article
| Open Access Vapor sublimation and deposition to build porous particles and composites
Vapor sublimation and deposition to build porous particles and composites
Fabrication of porous nanoparticles is often hampered by low efficiency production methods, challenging isolation of the material and poor control over the fabrication process. Here the authors demonstrate a facile ice-template vapor-phase synthesis which allows for production of porous poly-para-xylylene particles on a large scale.
- Hsing-Ying Tung
- , Zhen-Yu Guan
- & Hsien-Yeh Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Stable complete methane oxidation over palladium based zeolite catalysts
Stable complete methane oxidation over palladium based zeolite catalysts
Palladium supported on zeolite is a highly active catalyst for complete methane oxidation, but its stability needs to be improved. Here, the authors design a highly active catalyst resistant to steam-induced sintering under reaction conditions by alleviating the high mobility of palladium nanoparticles and zeolite degradation.
- Andrey W. Petrov
- , Davide Ferri
- & Oliver Kröcher
-
Article
| Open Access Optimization of the structural characteristics of CaO and its effective stabilization yield high-capacity CO2 sorbents
Optimization of the structural characteristics of CaO and its effective stabilization yield high-capacity CO2 sorbents
The economic operation of a carbon dioxide capture technique of calcium looping necessitates highly effective CaO-based CO2 sorbents. Here, the authors report a facile one-pot synthesis approach to yield highly effective, MgO-stabilized, CaO-based CO2 sorbents featuring highly porous multishelled morphologies.
- Muhammad Awais Naeem
- , Andac Armutlulu
- & Christoph R. Müller
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoparticle-templated nanofiltration membranes for ultrahigh performance desalination
Nanoparticle-templated nanofiltration membranes for ultrahigh performance desalination
Nanofiltration membranes are important for water desalination technologies, but designing membranes that achieve both high permeance and high salt rejection remains challenging. Here, the authors use sacrificial nanoparticles in the membrane fabrication process, leading to crumpled structures with ultrahigh permeance.
- Zhenyi Wang
- , Zhangxin Wang
- & Jian Jin
-
Article
| Open Access Reconfigurable engineered motile semiconductor microparticles
Reconfigurable engineered motile semiconductor microparticles
Active particles that demonstrate life-like behavior may find use in bio-inspired technologies, but achieving on-demand reconfiguration remains challenging. Here, the authors demonstrate controllable, collective behavior in silicon microparticles, which are fabricated via conventional semiconductor methods.
- Ugonna Ohiri
- , C. Wyatt Shields IV
- & Nan Jokerst
-
Article
| Open Access Topologically guided tuning of Zr-MOF pore structures for highly selective separation of C6 alkane isomers
Topologically guided tuning of Zr-MOF pore structures for highly selective separation of C6 alkane isomers
The separation of C6 alkane isomers is crucial to the petroleum refining industry, but the distillation methods in place are energy intensive. Here, the authors design a series of topologically-guided zirconium-based metal-organic frameworks with optimized pore structures for efficient C6 alkane isomer separations.
- Hao Wang
- , Xinglong Dong
- & Jing Li
-
Article
| Open Access Pharmaceutical concentration using organic solvent forward osmosis for solvent recovery
Pharmaceutical concentration using organic solvent forward osmosis for solvent recovery
Solvent recovery is an important process in the pharmaceutical industry, but organic solvent nanofiltration membranes operate under high pressures. Here the authors demonstrate organic solvent forward osmosis — an alternative process that does not require application of external pressure and may prove to be economically favorable.
- Yue Cui
- & Tai-Shung Chung
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding the adsorption process in ZIF-8 using high pressure crystallography and computational modelling
Understanding the adsorption process in ZIF-8 using high pressure crystallography and computational modelling
Understanding host–guest interactions and structural changes within porous materials is crucial for enhancing gas storage properties. Here, the authors combine cryogenic loading of gases with high pressure crystallography and computational techniques to obtain atomistic detail of adsorption-induced structural and energetic changes in ZIF-8.
- Claire L. Hobday
- , Christopher H. Woodall
- & Stephen A. Moggach
-
Article
| Open Access Combining CO2 reduction with propane oxidative dehydrogenation over bimetallic catalysts
Combining CO2 reduction with propane oxidative dehydrogenation over bimetallic catalysts
The oxidative dehydrogenation of propane by CO2 (CO2-ODHP) can potentially fill the gap of propylene production while consuming a greenhouse gas. Here, the authors identify non-precious FeNi and precious NiPt catalysts supported on CeO2 as promising catalysts for CO2-ODHP and dry reforming, respectively, in flow reactor studies.
- Elaine Gomez
- , Shyam Kattel
- & Jingguang G. Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Computer-aided discovery of a metal–organic framework with superior oxygen uptake
Computer-aided discovery of a metal–organic framework with superior oxygen uptake
The emergence of thousands of metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) has created the challenge of finding promising structures for particular applications. Here, the authors present a tool for computer-aided material discovery where a large number of MOFs are screened, with the top-ranked structure synthesized for oxygen storage applications.
- Peyman Z. Moghadam
- , Timur Islamoglu
- & David Fairen-Jimenez
-
Article
| Open Access Adsorption-based atmospheric water harvesting device for arid climates
Adsorption-based atmospheric water harvesting device for arid climates
Harvesting water from the atmosphere is an important solution to water scarcity, but doing so in arid climates is highly challenging. Here, the authors develop a metal-organic framework-based water harvesting device that can deliver over 0.25 L of water per kg of adsorbent over a single cycle at relative humidities of 10–40% and at subzero dew points.
- Hyunho Kim
- , Sameer R. Rao
- & Evelyn N. Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-thin enzymatic liquid membrane for CO2 separation and capture
Ultra-thin enzymatic liquid membrane for CO2 separation and capture
Porous membranes show great promise for CO2 separation and capture, but are currently limited by a trade-off between permeance and selectivity. Here, the authors fabricate a bio-inspired, ultra-thin enzymatic liquid membrane that displays exceptional CO2 permeability and selectivity under ambient conditions.
- Yaqin Fu
- , Ying-Bing Jiang
- & C. Jeffrey Brinker
-
Article
| Open Access Bio-inspired counter-current multiplier for enrichment of solutes
Bio-inspired counter-current multiplier for enrichment of solutes
Improving the efficiency of gas separation technology is needed, since existing methods represent a significant portion of the world’s energy consumption. Here, the authors report an enhancement in the release rate of carbon dioxide and oxygen using a counter-current amplification method inspired by fish.
- Kyle Brubaker
- , Armand Garewal
- & Aaron P. Esser-Kahn
-
Article
| Open Access Anti-fouling graphene-based membranes for effective water desalination
Anti-fouling graphene-based membranes for effective water desalination
Intrinsic limitations of nanoporous graphene limit its applications in water treatment. Here the authors produce post-treatment-free, low-cost graphene-based membranes from renewable biomass and demonstrate their high water permeance and antifouling properties using real seawater.
- Dong Han Seo
- , Shafique Pineda
- & Kostya (Ken) Ostrikov
-
Article
| Open Access MXene molecular sieving membranes for highly efficient gas separation
MXene molecular sieving membranes for highly efficient gas separation
Two-dimensional materials show great potential for membrane technologies, but their disordered channels hinder their molecular sieving performance. Here, Wang, Gogotsi and colleagues design a MXene membrane with ordered nanochannels that exhibits an excellent H2/CO2 gas separation performance.
- Li Ding
- , Yanying Wei
- & Yury Gogotsi
-
Article
| Open Access Development of an oral once-weekly drug delivery system for HIV antiretroviral therapy
Development of an oral once-weekly drug delivery system for HIV antiretroviral therapy
Poor adherence to daily antiretrovirals can significantly affect treatment efficacy, but oral long-acting antiretrovirals are currently lacking. Here, the authors develop a once-weekly oral dosage form for anti-HIV drugs, assess its pharmacokinetics in pigs, and model its impact on viral resistance and disease epidemics.
- Ameya R. Kirtane
- , Omar Abouzid
- & Giovanni Traverso
-
Article
| Open Access Creating nanoscale emulsions using condensation
Creating nanoscale emulsions using condensation
Emulsions—stabilized mixtures of immiscible liquids—are found in many products, ranging from pharmaceuticals to food. Here Guha et al. propose a simple emulsification method where water vapor is condensed onto oil with surfactant, producing a water-in-oil emulsion with droplets as small as 100 nm.
- Ingrid F. Guha
- , Sushant Anand
- & Kripa K. Varanasi
-
Article
| Open Access Sequence and entropy-based control of complex coacervates
Sequence and entropy-based control of complex coacervates
Monomer sequence is an emerging tool to precisely encode information (and thus structure and function) into polymer systems. Here the authors use sequence-control in complex coacervates to understand how monomer sequence translates to physical material properties.
- Li-Wei Chang
- , Tyler K. Lytle
- & Sarah L. Perry
-
Article
| Open Access Multifunctional nanocomposite hollow fiber membranes by solvent transfer induced phase separation
Multifunctional nanocomposite hollow fiber membranes by solvent transfer induced phase separation
Coating porous membranes with nanoparticles can enhance their separation and antifouling properties, but methods to do so remain complex. Here, Lee and colleagues use solvent transfer-induced phase separation to prepare nanoparticle-functionalized hollow fiber membranes from bicontinuous interfacially jammed emulsion gels.
- Martin F. Haase
- , Harim Jeon
- & Daeyeon Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Molecular rheotaxis directs DNA migration and concentration against a pressure-driven flow
Molecular rheotaxis directs DNA migration and concentration against a pressure-driven flow
Implementing a nucleic acid preconcentration method can improve the sensitivity of microfluidic analysis systems. Here Friedrich et al. concentrate DNA by many orders of magnitude using pressure-driven flow, which could lead to a simple and practical microanalysis platform.
- Sarah M. Friedrich
- , Jeffrey M. Burke
- & Tza-Huei Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Large-scale water collection of bioinspired cavity-microfibers
Large-scale water collection of bioinspired cavity-microfibers
Spider-silk-mimicking microfibers often suffer from low efficiency and durability in water collection. Here, the authors fabricate robust microfibers with spindle cavity-knots and different topological fiber-networks with improved water-collecting performance
- Ye Tian
- , Pingan Zhu
- & Liqiu Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Strict molecular sieving over electrodeposited 2D-interspacing-narrowed graphene oxide membranes
Strict molecular sieving over electrodeposited 2D-interspacing-narrowed graphene oxide membranes
Producing graphene oxide membranes with narrow channels is desirable for small molecule separations, but methods to narrow the 2D spacing typically result in membrane damage. Here the authors exploit electrophoresis-deposition to prepare GO membranes that are reduced in situ, leading to narrow and uniform 2D channels.
- Benyu Qi
- , Xiaofan He
- & Yuhan Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Understanding activity trends in electrochemical water oxidation to form hydrogen peroxide
Understanding activity trends in electrochemical water oxidation to form hydrogen peroxide
Producing hydrogen peroxide via electrochemical oxidation of water is an attractive route to this valuable product. Here the authors theoretically and experimentally investigate hydrogen peroxide production activity trends for a range of metal oxides and identify the optimal bias ranges for high Faraday efficiencies.
- Xinjian Shi
- , Samira Siahrostami
- & Jens K. Nørskov
-
Article
| Open Access Heterogeneous multi-compartmental hydrogel particles as synthetic cells for incompatible tandem reactions
Heterogeneous multi-compartmental hydrogel particles as synthetic cells for incompatible tandem reactions
Cells contain isolated compartments where cascade enzymatic biochemical reactions occur to form essential biological products with high efficiency. Here the authors produce functional hydrogel particles with multiple compartments via microfluidics that contain spatially immobilized natural enzymes in distinct domains for one-pot, tandem reactions.
- Hongliang Tan
- , Song Guo
- & Chia-Hung Chen
-
Article
| Open Access Reactivation of dead sulfide species in lithium polysulfide flow battery for grid scale energy storage
Reactivation of dead sulfide species in lithium polysulfide flow battery for grid scale energy storage
Lithium polysulfide batteries suffer from the precipitation of insoluble and irreversible sulfide species on the surface of carbon and lithium. Here the authors show a reactivation strategy by a reaction with cheap sulfur powder under stirring and heating to recover the cell capacity.
- Yang Jin
- , Guangmin Zhou
- & Yi Cui
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrathin metal–organic framework membrane production by gel–vapour deposition
Ultrathin metal–organic framework membrane production by gel–vapour deposition
MOF-based membranes have shown great promise in separation applications, but producing thin membranes that allow for high fluxes remains challenging. Here, the authors use a gel–vapour deposition strategy to fabricate composite membranes with less than 20 nm thicknesses and high gas permeances and selectivities.
- Wanbin Li
- , Pengcheng Su
- & Eddy Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access Effect of water activity on rates of serpentinization of olivine
Effect of water activity on rates of serpentinization of olivine
Serpentinization of mantle rocks occurs in a variety of tectonic settings, but the controls on the rates of serpentinization are poorly constrained. Here, the authors developed anin situexperimental method to show that the rate of serpentinization is strongly controlled by the salinity of the reacting fluid.
- Hector M. Lamadrid
- , J. Donald Rimstidt
- & Robert J. Bodnar
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic-template-directed multiscale assembly for large-area coating of highly-aligned conjugated polymer thin films
Dynamic-template-directed multiscale assembly for large-area coating of highly-aligned conjugated polymer thin films
Controlling macromolecular assembly across length scales during solution coating of semiconducting polymers is still a challenge. Here the authors show a biomineralization inspired dynamic templating method that expedites polymer nucleation and assembly which allows for surface reconfiguration.
- Erfan Mohammadi
- , Chuankai Zhao
- & Ying Diao
-
Article
| Open Access Hierarchical porous carbons with layer-by-layer motif architectures from confined soft-template self-assembly in layered materials
Hierarchical porous carbons with layer-by-layer motif architectures from confined soft-template self-assembly in layered materials
2D nanomaterials are promising capacitive energy storage materials, but their tendency to restack hinders electrolyte transport. Here, Yamauchi and colleagues introduce 2D ordered mesoporous carbons in between MXene layers, and metal removal affords all-carbon porous 2D–2D heterostructures in which restacking is prevented.
- Jie Wang
- , Jing Tang
- & Yusuke Yamauchi
-
Article
| Open Access Temperature-regulated guest admission and release in microporous materials
Temperature-regulated guest admission and release in microporous materials
Regulating guest access and release in porous materials remains an important goal. Here, May and colleagues elucidate the mechanism by which guest admission can be temperature-regulated in typical microporous materials, and experimentally exploit this process to achieve appreciable and reversible hydrogen storage.
- Gang (Kevin) Li
- , Jin Shang
- & Eric F. May
-
Article
| Open Access Membraneless water filtration using CO2
Membraneless water filtration using CO2
Water treatment processes mostly rely on the use of membranes and filters, which have high pumping costs and require periodic replacement. Here, the authors describe an efficient membraneless method that induces directed motion of suspended colloidal particles by exposing the suspension to CO2.
- Sangwoo Shin
- , Orest Shardt
- & Howard A. Stone
-
Article
| Open Access Directly converting CO2 into a gasoline fuel
Directly converting CO2 into a gasoline fuel
Direct hydrogenation of CO2 into liquid fuels can mitigate CO2 emissions and reduce the rapid depletion of fossil fuels. Here, the authors show an iron-based multifunctional catalyst that converts CO2to gasoline with high selectivity due to synergistic cooperation of multiple catalytic active sites.
- Jian Wei
- , Qingjie Ge
- & Jian Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Electrochemical generation of sulfur vacancies in the basal plane of MoS2 for hydrogen evolution
Electrochemical generation of sulfur vacancies in the basal plane of MoS2 for hydrogen evolution
In order to fully utilize sulfur vacancies in MoS2 catalysts for industrial applications, a facile and general route for making sulfur vacancies in MoS2 is needed. Here, the authors introduce a scalable route towards generating sulfur vacancies on the MoS2basal plane using electrochemical desulfurization.
- Charlie Tsai
- , Hong Li
- & Frank Abild-Pedersen
-
Article
| Open Access Mechano-regulated surface for manipulating liquid droplets
Mechano-regulated surface for manipulating liquid droplets
Droplet manipulation is an essential task for designing microfluidic platforms such as lab-on-chip devices. Here Tanget al. develop a non-wettable mesh with reversible liquid adhesion controlled by mechanically inserting wettable pillars which allows for effective and rapid droplet manoeuvring.
- Xin Tang
- , Pingan Zhu
- & Liqiu Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Stable and solubilized active Au atom clusters for selective epoxidation of cis-cyclooctene with molecular oxygen
Stable and solubilized active Au atom clusters for selective epoxidation of cis-cyclooctene with molecular oxygen
Gold catalysts have previously been reported for the epoxidation of alkenes with molecular oxygen. Here the authors show that, rather than the gold nanoparticles, the active species for this reaction are actually small, soluble gold species stabilized by the oxidised organic products.
- Linping Qian
- , Zhen Wang
- & Harold H. Kung

 Porous supraparticle assembly through self-lubricating evaporating colloidal ouzo drops
Porous supraparticle assembly through self-lubricating evaporating colloidal ouzo drops