News & Views |
Featured
-
-
News & Views |
A new standard combination for recurrent ovarian cancer?
Ovarian cancer that recurs more than 6 months following primary chemotherapy can respond to many different drugs, but retreatment with a combination of carboplatin and paclitaxel has become a standard of care. A combination of pegylated liposomal doxorubicin and carboplatin may provide a slightly, but significantly, greater therapeutic index than carboplatin and paclitaxel.
- Robert C. Bast Jr
- & Maurie Markman
-
Research Highlight |
 PARP inhibitor olaparib is safe and effective in patients with BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations
PARP inhibitor olaparib is safe and effective in patients with BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations
- Lisa Hutchinson
-
Review Article |
 Drug resistance in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer
Drug resistance in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer
This article reviews resistance to chemotherapy in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC), which is a result of mechanisms of resistance specific to prostate cancer and to general mechanisms common to different cancer types. New therapies targeting these mechanisms are outlined and their potential impact in future and ongoing clinical trials is discussed. Knowledge of the mechanisms of drug resistance offers great hope for future effective therapy; however, drug resistance in metastatic CRPC is multifactorial and complex and the development of new medical therapies remains challenging.
- Bostjan Seruga
- , Alberto Ocana
- & Ian F. Tannock
-
Research Highlight |
Patients with high-risk APL benefit from risk-adapted consolidation therapy
- Lisa Hutchinson
-
-
Correspondence |
Lenalidomide for bortezomib-resistant multiple myeloma
- Chiara Briani
- , Tamara Berno
- & Renato Zambello
-
Correspondence |
Author reply: Lenalidomide for bortezomib-resistant multiple myeloma
- Heinz Ludwig
- & Niklas Zojer
-
Correspondence |
Lenalidomide efficacy in bortezomib-resistant myeloma
- Alessandro Gozzetti
- , Rosaria Crupi
- & Monica Bocchia
-
Case Study |
 Complete molecular response in CML after p210 BCR–ABL1-derived peptide vaccination
Complete molecular response in CML after p210 BCR–ABL1-derived peptide vaccination
A 63-year-old woman with chronic myeloid leukemia who achieved a complete cytogenic response after 6 years of interferon-alpha went on to lose molecular response 2 years after treatment cessation. In this Case Study, Monica Bocchia and colleagues demonstrate the positive outcome in this patient following treatment with a therapeutic vaccine that consists of the p210 BCR–ABL1-derived peptide. The patient has maintained a complete molecular response for over 39 months.
- Monica Bocchia
- , Marzia Defina
- & Francesco Lauria
-
Review Article |
Rechallenging with anthracyclines and taxanes in metastatic breast cancer
Adjuvant treatment with anthracycline–taxane combination therapy in high-risk early-stage breast cancer has raised the important question of how to manage patients who relapse. In the metastatic setting, one option is rechallenging with the same agent, or class of agent, that has been used in the adjuvant setting. This Review comprehensively examines the evidence from clinical trials for rechallenging with both anthracyclines and taxanes, and highlights issues to be examined in the context of future clinical trials.
- Carlo Palmieri
- , Jonathan Krell
- & David Miles
-
Review Article |
 Future directions of bone-targeted therapy for metastatic breast cancer
Future directions of bone-targeted therapy for metastatic breast cancer
Bone is the most common site of breast cancer metastasis, resulting in substantial morbidity and mortality. A number of therapies are being developed, including bisphosphonates, which target factors that promote tumor growth in bone. The authors of this Review outline the underlying mechanisms that drive this pathological process, and highlight potential molecular targets that will improve therapeutic interventions for metastatic breast cancer. Tools that assess response in individual patients and guide appropriate treatment are also discussed.
- Tomifumi Onishi
- , Naoki Hayashi
- & Naoto T. Ueno
-
Opinion |
 A changing perspective: improving access to fertility preservation
A changing perspective: improving access to fertility preservation
Cancer treatment in young women can lead to reduced fertility—a serious issue for patients who wish to have children. In this Perspectives, Letourneau and coauthors highlight the importance of making sure that oncologists and fertility teams are aware of this issue and work together to educate patients of the risks involved. Furthermore, options for fertility preservation are discussed.
- Joseph M. Letourneau
- , Michelle E. Melisko
- & Mitchell P. Rosen
-
Review Article |
 Treating prostate cancer with radiotherapy
Treating prostate cancer with radiotherapy
This Review focuses on the adverse effects of radical radiotherapy for localized prostate cancer. The authors discuss the methodological issues that make comparison between the different treatment modalities problematic, and describe the pattern of adverse effects that occur over time after radiotherapy. Recent technical advances, such as intensity modulation and image guidance, will hopefully further improve the toxicity profile of prostate radiotherapy.
- Anna Wilkins
- & Chris Parker
-
Review Article |
 Making the best of PARP inhibitors in ovarian cancer
Making the best of PARP inhibitors in ovarian cancer
Inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase (PARP) have shown promise as therapeutic agents for the treatment of ovarian cancers with mutations inBRCA1 or BRCA2. By exploiting the synthetic lethal interaction that exists between PARP inhibition and BRCA mutations, these agents specifically kill cancer cells by targeting their DNA repair system. The authors of this Review describe the importance of BRCAmutations for the efficacy of PARP inhibitors. They also discuss the preclinical and clinical trial results of PARP inhibitors, the challenges related to the use of these agents, and future directions.
- Susana Banerjee
- , Stan B. Kaye
- & Alan Ashworth
-
Opinion |
 Off-tumor target—beneficial site for antiangiogenic cancer therapy?
Off-tumor target—beneficial site for antiangiogenic cancer therapy?
Antiangiogenic therapy inhibits tumor growth by targeting the blood vessels of the tumor. Antiangiogenic therapy often correlates with longer survival in patients without affecting tumor growth. This positive response may be due to the off-tumor target effects of antiangiogenic drugs. In this article, Yihai Cao describes the potential mechanisms underlying the benefits of targeting off-tumor sites, and how these events improve outcomes in patients with cancer-associated systemic syndromes.
- Yihai Cao
-
Review Article |
Weekly paclitaxel in the treatment of recurrent ovarian cancer
This Review discusses the advantages and disadvantages of weekly paclitaxel for the treatment of relapsed ovarian cancer. When compared with the 3 weekly schedule, weekly paclitaxel is better tolerated, with a reduced frequency of toxic effects; however, response duration can be short. Importantly, patients with tumors that are resistant to 3-weekly paclitaxel have responded to treatment with weekly paclitaxel. Current research focuses to increase response duration include the combination of weekly paclitaxel with molecular-targeted agents and the use of molecular profiling to better select patients for treatment.
- Richard D. Baird
- , David S. P. Tan
- & Stan B. Kaye
-
Research Highlight |
 Activated PI3K/AKT confers resistance to trastuzumab but not lapatinib
Activated PI3K/AKT confers resistance to trastuzumab but not lapatinib
- Lisa Hutchinson
-
-
-
-
News & Views |
Optimizing chemotherapy and radiotherapy for anaplastic glioma
The optimum approach for the treatment of rare anaplastic gliomas following surgical resection is uncertain. A recent study has now provided a greater understanding of the heterogeneous tumor biology of these tumors and has emphasized the prognostic importance of chromosome 1p19q deletion, IDH mutation and MGMT promoter methylation. The importance of radiotherapy and chemotherapy for treating these heterogeneous tumors is being elucidated for subgroups of patients.
- Patrick G. Morris
- & Andrew B. Lassman
-
News & Views |
 Denileukin diftitox—a step towards a 'magic bullet' for CTCL
Denileukin diftitox—a step towards a 'magic bullet' for CTCL
Investigators found that denileukin diftitox, which targets the interleukin-2 receptor, achieves objective response rates in 44% of patients with cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, with a median duration of response of 7.8 months and 2% incidence of severe vascular leak syndrome. The inclusion of a placebo arm in the study revealed several additional interesting observations.
- Marshall E. Kadin
- & Eric C. Vonderheid
-
Correspondence |
 Flows and flaws in primary central nervous system lymphoma
Flows and flaws in primary central nervous system lymphoma
- Andrés J. M. Ferreri
- , Gerald Illerhaus
- & Franco Cavalli
-
News & Views |
Biomarkers in NSCLC for selecting cetuximab therapy
A phase III trial investigated the efficacy of carboplatin and a taxane with and without cetuximab, a monoclonal antibody against EGFR, in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. This trial did not reveal an improvement in the primary end point of progression-free survival (according to an independent radiological review committee) with the addition of cetuximab to the carboplatin and taxane regimen. A retrospective investigation of potential biomarkers did not reveal any significant association between these biomarkers and cetuximab efficacy.
- Thomas E. Stinchcombe
- & Mark A. Socinski
-
Review Article |
Whole-brain radiation therapy in breast cancer patients with brain metastases
Brain metastases are a frequent complication in patients with advanced breast cancer. Whole-brain radiation therapy (WBRT) is the standard treatment for these patients, but it can cause neurocognitive damage, and results are suboptimal. Therapies that reduce toxic effects, improve local control, and prevent recurrences are needed. The authors of this Review outline the current strategies and novel developments in WBRT, and discuss new irradiation modalities that are improving outcomes in breast cancer patients with brain metastases.
- Cyrus Chargari
- , François Campana
- & Youlia M. Kirova
-
Review Article |
 Chemoimmunotherapy of chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Chemoimmunotherapy of chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia has long been regarded as an incurable disease of the elderly. Consolidation strategies using non-cross resistant agents have improved the success rates of patients with residual disease at the end of induction treatment. This Review discusses chemoimmunotherapy regimens that contain purine analogs and rituximab and considers new developments in induction and consolidation strategies that are leading the path towards cure.
- Constantine S. Tam
- & Michael J. Keating
-
-
-
Research Highlight |
Lapatinib is effective in patients with p95HER2-positive tumors
- Lisa Hutchinson
-
News & Views |
 Neoadjuvant trial design: time for a brave new world?
Neoadjuvant trial design: time for a brave new world?
In the NOAH clinical trial, trastuzumab treatment for locally advanced breast cancer was associated with increased complete and overall response rate and improved event-free survival. The ability to identify this advantage in a relatively smaller number of patients (compared with adjuvant therapy trials) suggests that the neoadjuvant setting might serve to inform the design of adjuvant trials and indicate appropriate off-study adjuvant therapy.
- Heather L. McArthur
- & Clifford A. Hudis
-
News & Views |
 Pazopanib: carving a niche in a crowded therapeutic landscape
Pazopanib: carving a niche in a crowded therapeutic landscape
Encouraging data have been reported from a randomized, double-blind, phase III trial comparing pazopanib therapy to placebo in treatment-naive and cytokine-refractory patients with advanced renal-cell carcinoma. The challenge that lies ahead is determining where pazopanib fits into the crowded therapeutic algorithms for this disease.
- Sumanta Kumar Pal
- & Robert A. Figlin
-
News & Views |
Importance of patient selection for EGFR TKIs in lung cancer
Platinum-based chemotherapy has been the standard first-line treatment for patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer for decades. However, a recent study has shown the superiority of gefitinib treatment in comparison with chemotherapy in a molecularly selected cohort of patients harboring sensitizing EGFR mutations. These results demonstrate the importance of incorporating molecular selection into the design of lung cancer trials that use EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
- Ariel Lopez-Chavez
- & Giuseppe Giaccone
-
Review Article |
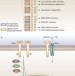 Understanding resistance to EGFR inhibitors—impact on future treatment strategies
Understanding resistance to EGFR inhibitors—impact on future treatment strategies
EGFR is one of the most studied targets in oncology, and several inhibitors have shown promising results in selected patient populations. However, intrinsic and acquired resistance to these targeted therapies is increasingly recognized. The authors of this Review describe the successful translation of EGFR inhibitors to the clinic, and highlight the mechanisms of resistance to these agents that limit their long-term efficacy. Understanding these processes will allow researchers to develop therapies that overcome resistance and ultimately lead to more successful outcomes.
- Deric L. Wheeler
- , Emily F. Dunn
- & Paul M. Harari
-
Review Article |
 Molecular circuits of solid tumors: prognostic and predictive tools for bedside use
Molecular circuits of solid tumors: prognostic and predictive tools for bedside use
The rapid pace of research in cancer biology, and the advent of molecular targeted therapies has made personalized medicine a reality. This knowledge has generated a vast panel of molecular biomarkers. This Review presents the molecular, prognostic and predictive factors for the six solid tumors associated with the highest mortality. The authors discuss the key biomarkers for each disease site according to its associated clinicopathological presentation and specific associated molecular interactions.
- Charles Ferté
- , Fabrice André
- & Jean-Charles Soria
-
Review Article |
 Targeted therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer—is it becoming a reality?
Targeted therapy in non-small-cell lung cancer—is it becoming a reality?
Survival outcomes for advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer remain poor; however, molecular targeted agents offer new opportunities provided that patients are selected for treatment according to their tumor profile. This Review highlights the promising activity shown with novel targeted therapies that interfere with the IGF-1R pathway and agents that inhibit the EML4-ALK fusion protein. Aberrations in other key signaling pathways that have been identified as crucial targets, especially in resistant patients, are also discussed.
- Filip Janku
- , David J. Stewart
- & Razelle Kurzrock
-
Review Article |
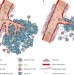 Metronomic chemotherapy: new rationale for new directions
Metronomic chemotherapy: new rationale for new directions
Metronomic chemotherapy is the chronic administration of chemotherapeutic agents at relatively low, minimally toxic doses, and with no prolonged drug-free breaks. This type of chemotherapy inhibits tumor growth primarily through anti-angiogenic mechanisms. The latest clinical trials of metronomic chemotherapy in adult and pediatric cancer patients are discussed and the authors highlight the research efforts that need to be made to facilitate the optimal development of metronomic chemotherapy in the clinic.
- Eddy Pasquier
- , Maria Kavallaris
- & Nicolas André
-
-
Research Highlight |
Significant overall survival advantage for RCC patients treated with autologous tumor lysate vaccine
- Lisa Hutchinson
-
-
-
-
-
Correspondence |
Radioembolization for colorectal liver metastases
- Maarten A. D. Vente
- , Maurice A. A. J. van den Bosch
- & Johannes F. W. Nijsen
-
News & Views |
 Hypofractionation for breast cancer—clinical implications
Hypofractionation for breast cancer—clinical implications
A recent landmark study reported the long-term results that compared a standard course of whole-breast irradiation (25 treatments over 5 weeks) with a hypofractionated course of radiation (16 treatments over 3.5 weeks) in patients with early-stage, node-negative breast cancer. The trial demonstrated equivalence of results with respect to overall survival, local control, toxicity and cosmetic outcomes.
- Bruce G. Haffty
-
News & Views |
 Alternatives to surgery after failure of instillation therapy
Alternatives to surgery after failure of instillation therapy
Management of high-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer represents a difficult challenge in clinical practice. The dilemma is to decide between an organ-sparing approach or radical cystectomy with the risk of undertreatment or overtreatment for this group of patients. This issue is especially important for patients who have failed previous intravesical therapy.
- Christian Weiss
- & Claus Rödel
-
Case Study |
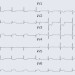 A case of variant angina in a patient under chronic treatment with sorafenib
A case of variant angina in a patient under chronic treatment with sorafenib
A 63-year-old male patient under chronic treatment with sorafenib for an unresectable multifocal hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) presented with suspected variant angina. Spontaneous spasm occurred during cardiac catheterization and was revealed during coronary angiogram with the unusual feature of a retrograde transient filling of a contralateral branch. Italo Porto and colleagues contend that the effects of sorafenib treatment were primarily responsible for the major cardiovascular event observed in this case, and suggest that clinicians should be aware of this possible severe complication of sorafenib therapy.
- Italo Porto
- , Andrea Leo
- & Filippo Crea
-
Review Article |
 Treatment of localized prostate cancer: when is active surveillance appropriate?
Treatment of localized prostate cancer: when is active surveillance appropriate?
Many men diagnosed with prostate cancer as a consequence of PSA testing have clinically insignificant disease. In this Review, Peter Albertsen discusses risk assessment in prostate cancer and strategies to identify these patients at low-risk of disease progression. The benefits of active surveillance are considered as an option for these men, as opposed to either surgery or radiation that are recommended for men who have a significant risk of disease progression.
- Peter C. Albertsen
-
Review Article |
Molecular markers to individualize adjuvant therapy for colon cancer
Prognostic and predictive markers in colon cancer might help define which patients with stage II disease are likely to benefit from adjuvant therapy. In this Review, Tara Gangadhar and Richard Schilsky discuss the recent clinical development of such markers, including microsatellite instability and 18q loss of heterozygosity. Further validation of these markers could potentially lead to the individualization of adjuvant therapy in colon cancer.
- Tara Gangadhar
- & Richard L. Schilsky
-

 Intermediate-risk endometrial cancer—adjuvant treatment
Intermediate-risk endometrial cancer—adjuvant treatment Allo SCT offers hope as second-line therapy for CML
Allo SCT offers hope as second-line therapy for CML Conventional chemotherapy boosts the effect of cancer vaccines
Conventional chemotherapy boosts the effect of cancer vaccines