Research Highlight |
Featured
-
-
Research Highlight |
 Anastrozole superiority to tamoxifen for early breast cancer confirmed
Anastrozole superiority to tamoxifen for early breast cancer confirmed
- Lisa Richards
-
-
Year in Review |
 New therapies and standard of care in oncology
New therapies and standard of care in oncology
2010 was not a year of survival breakthroughs in hematologic malignancies. However, in Hodgkin's disease and multiple myeloma new therapies emerged as the standard of care and nilotinib may be considered the treatment choice for newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia.
- Vincent T. DeVita Jr
- & George P. Canellos
-
Year in Review |
Maximizing survival and minimizing toxicity
Outcomes for patients with oropharyngeal cancer are determined by their tumor characteristics and associated demographics. The role of human papilloma virus-related disease for prognosis and outcomes with chemoradiotherapy is being more clearly defined. EGFR inhibitors are used in conjunction with radiotherapy, and the importance of optimizing radiation quality and minimizing toxicity is the focus of ongoing studies.
- Bruce E. Brockstein
- & Everett E. Vokes
-
Year in Review |
 Novel targets and therapies for a personalized approach
Novel targets and therapies for a personalized approach
2010 has been another prolific year in breast cancer research with a number of original observations bringing us closer to personalized care. Studies with novel targeted agents in defined breast cancer subgroups have revealed exciting developments and highlight the importance of patient selection.
- Michaela J. Higgins
- & José Baselga
-
Year in Review |
 New standards and a predictive biomarker for adjuvant therapy
New standards and a predictive biomarker for adjuvant therapy
Randomized phase III trials have established new standards of care for advanced biliary cancer, HER2-positive advanced gastric or gastro-esophageal junction cancer, and preliminarily, for metastatic pancreatic cancer. There is now a validated predictive biomarker to guide use of adjuvant chemotherapy in patients with stage II colon cancer.
- Manish R. Sharma
- & Richard L. Schilsky
-
Year in Review |
 One size does not fit all
One size does not fit all
Advances in non-small-cell lung cancer over the past decade have resulted in new treatments with minimal toxic effects and dramatic clinical benefits. 2010 saw continued advancement in our understanding of the molecular genetics of lung cancer and of specific targeted inhibitors with remarkable clinical benefit in selected populations.
- Christine M. Lovly
- & David P. Carbone
-
Research Highlight |
 Doxorubicin and sorafenib improves survival in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
Doxorubicin and sorafenib improves survival in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma
- Lisa Hutchinson
-
Review Article |
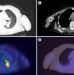 PET–CT for radiotherapy treatment planning and response monitoring in solid tumors
PET–CT for radiotherapy treatment planning and response monitoring in solid tumors
PET–CT is important for the staging of disease, but also in detecting mechanisms of resistance at the molecular level. In combination with tracers, these imaging modalities can delineate the underlying processes of resistance, such as tumor-cell proliferation, hypoxia, and vascular density. The authors of this Review discuss how the use of various tracers makes it possible to predict outcome and monitor response to treatment. By selecting patients on the basis of their mechanism of resistance, it should be possible to avoid the rejection of treatment options by assessing individuals rather than a population as a whole.
- Johan Bussink
- , Johannes H. A. M. Kaanders
- & Wim J. G. Oyen
-
Review Article |
 Emerging therapeutic targets in endometrial cancer
Emerging therapeutic targets in endometrial cancer
Advances in the understanding of the molecular pathology of the two types of endometrial carcinoma have underpinned the first steps in the development and testing of targeted therapies. This Review discusses the therapeutic targets, molecular diversity of tumors, oncogene addiction and synthetic lethality in this hard-to-treat disease.
- Konstantin J. Dedes
- , Daniel Wetterskog
- & Jorge S. Reis-Filho
-
-
-
Review Article |
 Neoadjuvant radiotherapy for locally advanced and high-risk prostate cancer
Neoadjuvant radiotherapy for locally advanced and high-risk prostate cancer
Men with locally advanced or high-risk prostate cancer may benefit from combined modality strategies. This Review discusses the approaches and rational for preoperative and intraoperative radiotherapy and compares them with the utility of postoperative radiotherapy. The urgent need for novel biomarkers for selection purposes is highlighted.
- John Thoms
- , Jayant S. Goda
- & Robert G. Bristow
-
Opinion |
 HER2 and hormone receptor-positive breast cancer—blocking the right target
HER2 and hormone receptor-positive breast cancer—blocking the right target
Chemotherapy and trastuzumab is standard therapy for HER2-positive breast cancer, although aromatase inhibitors combined with anti-HER2 therapies is an option in patients with HER2 and hormone receptor-positive tumors. The activity observed with chemotherapy and anti-HER2 therapies seems to be higher than with aromatase inhibitors and HER-2-based therapies. The authors highlight the data that have led to current treatment strategies and the importance of considering chemotherapy and anti-HER2 therapy for HER2 and hormone receptor-positive tumors.
- Javier Cortés
- , Cristina Saura
- & María Vidal
-
Review Article |
 Targeting cancer stem cells by inhibiting Wnt, Notch, and Hedgehog pathways
Targeting cancer stem cells by inhibiting Wnt, Notch, and Hedgehog pathways
Selectively targeting cancer stem cells with novel therapeutics is gaining importance because disease recurrence after treatment-induced remissions is a major cause of morbidity and mortality. This Review discusses the pathways that are active during development, specifically the Wnt, Notch, and Hedgehog pathways, and the clinical development of therapeutic agents that target these pathways.
- Naoko Takebe
- , Pamela J. Harris
- & S. Percy Ivy
-
Review Article |
 Beyond chemotherapy: new agents for targeted treatment of lymphoma
Beyond chemotherapy: new agents for targeted treatment of lymphoma
A personalized treatment approach for lymphoma has potential to improve treatment responses. In this Review, Anas Younes summarizes the current development status of novel agents for lymphoma and discusses strategies to move the field forward.
- Anas Younes
-
Review Article |
 Preclinical development of molecular-targeted agents for cancer
Preclinical development of molecular-targeted agents for cancer
The high attrition rate for cancer drugs is discussed in this Review of the preclinical models available to cancer researchers and clinicians. The classic methods of drug discovery and analysis are described along with new preclinical strategies, including the genetically engineered mouse models and small-interfering RNA that have identified promising targeted drugs. Better knowledge of oncogenic signaling pathways and the mechanism of action of their inhibitors is probably the most effective way to improve the development of successful anticancer drugs.
- Alberto Ocana
- , Atanasio Pandiella
- & Ian F. Tannock
-
News & Views |
 Failure of bevacizumab in early-stage colon cancer
Failure of bevacizumab in early-stage colon cancer
A randomized phase III trial of patients with stage II and III colon cancer showed no benefit of adding bevacizumab to standard adjuvant oxaliplatin plus fluorouracil and leucovorin. Despite suggestive evidence of a short-term benefit, these data and other similar findings dictate that adjuvant bevacizumab should not be used in colon cancer.
- Daniel J. Sargent
-
-
-
-
-
Research Highlight |
High-dose fulvestrant is a safe and effective therapy for breast cancer
- Rebecca Kirk
-
News & Views |
Maintenance rituximab for relapsed follicular lymphoma
Rituximab has become the mainstay of systemic therapy for patients with follicular lymphoma and is associated with an improved outcome at both diagnosis and relapse, either as induction or maintenance therapy. The challenge lies in maximizing the benefit of this drug in a condition characterized by multiple relapses.
- David Wrench
- & Silvia Montoto
-
News & Views |
Optimizing dose-dense regimens for early-stage breast cancer
Survival of patients with high-risk early-stage breast cancer has been improved by chemotherapy administration at shorter dose intervals: 'dose-dense' therapy. Validation for this approach is provided by the AGO trial, which demonstrated the biggest survival advantage of any study of dose-dense chemotherapy to date.
- Patrick G. Morris
- & Clifford A. Hudis
-
Research Highlight |
 Improved survival in second-line advanced prostate cancer treated with cabazitaxel
Improved survival in second-line advanced prostate cancer treated with cabazitaxel
- Lisa Richards
-
News & Views |
 Chemoradiotherapy for NSCLC—does a 'standard' exist?
Chemoradiotherapy for NSCLC—does a 'standard' exist?
The optimal chemotherapy regimen to be used concurrently with thoracic radiation for locally advanced non-small-cell lung cancer remains uncertain. Studies investigating this question are ongoing.
- Allen M. Chen
- & Primo N. Lara Jr
-
News & Views |
G-CSF counteracts chemotherapy toxicity in neuroblastoma
Incorporating hematopoietic growth factors into chemotherapy regimens is a common method for mitigating toxicity of dose-intensive regimens. A clinical trial has shown that G-CSF can counteract acute toxicities, permitting further dose intensification of induction chemotherapy. However, the effects of these strategies on long-term toxicities and overall survival remain undefined.
- Heidi Russell
- & Jason M. Shohet
-
Review Article |
 Tumor focality in prostate cancer: implications for focal therapy
Tumor focality in prostate cancer: implications for focal therapy
There has been a growing interest in focal treatment for prostate cancer, although this remains a controversial area. Criticism of focal prostate therapy has been based on the fact that prostate cancer is a multifocal disease. The authors of this Review discuss the clinical and biological implications of multifocal prostate cancer in the context of focal therapy patient selection and treatment planning.
- Markos Karavitakis
- , Hashim U. Ahmed
- & Mathias H. Winkler
-
News & Views |
Ultra-targeted APBI using TARGIT—a cautionary note
One of the seven ongoing trials of accelerated partial breast irradiation (APBI) has concluded that single-dose intraoperative radiotherapy should be considered as an alternative to protracted whole-breast irradiation. With a median follow up of 2 years, such conclusions seem premature. Until the risk and pattern of breast recurrence is reported at longer follow up, TARGIT APBI should remain an experimental approach.
- Rajiv Sarin
-
Review Article |
 The role of BRCA mutation testing in determining breast cancer therapy
The role of BRCA mutation testing in determining breast cancer therapy
BRCAmutation carriers have an increased risk of developing breast cancer. Modern technology has made it possible to move genetic screening into the mainstream setting, which is important asBRCA status can influence treatment decisions. The authors of this Review discuss the assessment of familial cancer risk and the criteria for targeting BRCAmutation testing in women with breast cancer. They also examine how this genetic knowledge impacts on optimal patient management.
- Alison H. Trainer
- , Craig R. Lewis
- & Robyn L. Ward
-
Review Article |
 Metastamirs: a stepping stone towards improved cancer management
Metastamirs: a stepping stone towards improved cancer management
MicroRNAs (MiRNAs) can act as oncogenes or tumor-suppressor genes and have differential expression in tumor progression and metastasis. MiRNAs are involved in a number of pathways that contribute to metastasis, including migration, invasion, cell proliferation, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, angiogenesis and apoptosis. This Review provides a summary of the existing data documenting these functions and describes the clinical utility of miRNAs as prognostic and predictive biomarkers and their potential therapeutic applications in advanced cancer.
- Nicole M. A. White
- , Eman Fatoohi
- & George M. Yousef
-
-
Research Highlight |
Reduced-intensity induction therapy for elderly patients with multiple myeloma
- Lisa Richards
-
-
In Brief |
In brief
-
-
News & Views |
Molecular selection for 'smart' study design in lung cancer
The ZODIAC trial reported that the addition of vandetanib to docetaxel in second-line treatment of unselected patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer resulted in a statistically significant improvement in progression-free survival compared with docetaxel alone. Identification of biomarkers to assist in molecular selection of patients for targeted therapy is a tool for 'smart' clinical trial design.
- Amanda Psyrri
- & Barbara Burtness
-
News & Views |
Accelerated radiotherapy for HNSCC in developing countries
The IAEA-ACC study compared accelerated radiotherapy with standard radiotherapy in a multicenter trial conducted in developing countries. Advantages were most notable in patients with early-stage disease, which may limit the utility of this therapy. In countries where resources are limited, however, this strategy may be a cost-effective approach to improving outcomes in patients with head and neck cancer.
- Bruce Brockstein
- & Everett E. Vokes
-
News & Views |
 Effectiveness of adjuvant chemotherapy for resected NSCLC
Effectiveness of adjuvant chemotherapy for resected NSCLC
Two meta-analyses of the Non Small Cell Lung Cancer Meta-analyses Collaborative Group (NSCLC MACG) on the effects of adjuvant chemotherapy on early stage NSCLC after complete or curative resection have demonstrated that adjuvant cisplatin-based regimens are a valid and recommendable option following curative surgery. We discuss these results in the light of current interdisciplinary guidelines and existing meta-analyses of randomized clinical trials.
- Martin Stuschke
- & Christoph Pöttgen
-
News & Views |
Lo and behold, a role for lomustine in acute myeloid leukemia?
Adding lomustine to the standard combination of idarubicin and cytarabine for the treatment of old patients with acute myeloid leukemia improves complete response rates and overall survival. These findings emphasize the importance of dose intensity and raise the question of a unique role for nitrosoureas in the treatment of this disease.
- Frederick R. Appelbaum
-
News & Views |
Tyrosine-kinase inhibitors—new standard for NSCLC therapy
A clinical trial of patients with pharmacogenomically selected non-small-cell lung cancer clearly demonstrated an improvement in progression-free survival after gefitinib treatment compared with standard chemotherapy. This report is the first to suggest that personalized therapy based on pharmacogenomics could be standardized in the treatment of lung cancer.
- Nagahiro Saijo
-
Review Article |
 Translating p53 into the clinic
Translating p53 into the clinic
TheTP53gene is mutated in 50% of reported cancer cases and the p53 pathway is often partially inactivated in the remaining 50%. Clinical trials assessing agents that exploit the p53 system are ongoing. This Review discusses the mechanism of action of these treatments and the future of p53-based therapy.
- Chit Fang Cheok
- , Chandra S. Verma
- & David P. Lane
-
Review Article |
BRCA mutations in the management of breast cancer: the state of the art
Genetic testing for breast cancer susceptibility is widely available in North America and in Europe. The optimum treatment of women with breast (or ovarian) cancer and aBRCA1 or BRCA2 mutation may be different from that of non-carriers. Thus, identifying the BRCAmutation status in patients could assist appropriate decision making for individualized cancer prevention, screening and treatment.
- Steven A. Narod
-
Review Article |
 Molecular mechanisms of metastasis in breast cancer—clinical applications
Molecular mechanisms of metastasis in breast cancer—clinical applications
Circulating tumor cells (CTCs) have a crucial role in the metastatic cascade, tumor dissemination and progression. Furthermore, CTCs are involved in treatment failure, therapy resistance and disease progression. New therapeutic possibilities are offered by the established clinical prognostic and predictive value of CTCs with the additional possibility of using them for the real-time monitoring of systemic-therapy efficacy. This Review discusses the future clinical applications of CTCs in breast cancer including the incorporation of CTCs as end points in clinical trials and the blockade of tumor dissemination and self seeding via the therapeutic targeting of CTCs.
- Michal Mego
- , Sendurai A. Mani
- & Massimo Cristofanilli
-
Opinion |
 Intra-arterial brachytherapy of hepatic malignancies: watch the flow
Intra-arterial brachytherapy of hepatic malignancies: watch the flow
Radio-embolization using radioactive microspheres allows the delivery of high-dose internal radiotherapy to malignant tumors of the liver. The surrogate for measuring flow dynamics for radio-embolization planning does not best represent treatment efficacy. Therefore, Morgan et al. propose that imaging protocols sensitive to changes in vasculature are likely to represent useful predictive markers of malignant lesions that could benefit from radio-embolization.
- Bruno Morgan
- , Andrew S. Kennedy
- & Ricky A. Sharma
-
Research Highlight |
Pulsed treatment in continuation therapy improves disease-free survival in children with hematologic malignancies
- Rebecca Kirk
-
News & Views |
Nilotinib and dasatinib—new 'magic bullets' for CML?
The efficacy of nilotinib and dasatinib as frontline treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia has been documented in small phase II studies. Now, two clinical trials have assessed the effectiveness of second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors in comparison with standard dose imatinib at 1 year. Will these results change our current practice?
- Massimo Breccia
-
News & Views |
Gemcitabine alone or plus cisplatin for biliary tract cancer?
A randomized phase III trial that assessed treatment with cisplatin plus gemcitabine or gemcitabine alone for patients with advanced biliary tract cancer has provided evidence for a new standard treatment option for these patients. The therapeutic outcome (that is, overall survival, disease-free survival, and disease control rate), was significantly better in the combination arm with no increase in toxic effects.
- Werner Scheithauer

 Delays may improve outcomes
Delays may improve outcomes New prognostic factor for brain metastasis from ovarian cancer
New prognostic factor for brain metastasis from ovarian cancer A promising vaccine for glioblastoma multiforme
A promising vaccine for glioblastoma multiforme Panitumumab improves PFS in mCRC with wild-type KRAS
Panitumumab improves PFS in mCRC with wild-type KRAS First prognostic signature for adjuvant lung cancer therapy
First prognostic signature for adjuvant lung cancer therapy New standard of therapy for HER2-positive gastric cancers?
New standard of therapy for HER2-positive gastric cancers? NSCLC treatment—reducing costs and improving outcomes
NSCLC treatment—reducing costs and improving outcomes Alphavirus vector induces immune response in advanced cancers
Alphavirus vector induces immune response in advanced cancers