Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access FOXO1 is a master regulator of memory programming in CAR T cells
FOXO1 is a master regulator of memory programming in CAR T cells
The transcription factor FOXO1 has a key role in human T cell memory, and manipulating FOXO1 expression could provide a way to enhance CAR T cell therapies by increasing CAR T cell persistence and antitumour activity.
- Alexander E. Doan
- , Katherine P. Mueller
- & Evan W. Weber
-
Article |
 TRBC1-targeting antibody–drug conjugates for the treatment of T cell cancers
TRBC1-targeting antibody–drug conjugates for the treatment of T cell cancers
Anti-TRBC1 antibody–drug conjugates may offer a more potent T cell cancer therapy by bypassing the fratricide that may be limiting the efficacy of anti-TRBC1 CAR T cells in the clinical trial for patients with T cell cancers.
- Tushar D. Nichakawade
- , Jiaxin Ge
- & Suman Paul
-
Article
| Open Access Targeting of intracellular oncoproteins with peptide-centric CARs
Targeting of intracellular oncoproteins with peptide-centric CARs
Peptide-centric chimeric antigen receptors (PC-CARs) provide a platform to address the challenges involved in targeting intracellular oncoproteins, and PC-CARs based on the neuroblastoma-dependency gene PHOX2B induce elimination of aggressive tumors.
- Mark Yarmarkovich
- , Quinlen F. Marshall
- & John M. Maris
-
Article |
 Latent human herpesvirus 6 is reactivated in CAR T cells
Latent human herpesvirus 6 is reactivated in CAR T cells
Genomics analyses reveal that in vitro culture of CAR T cells can lead to reactivation of a latent herpesvirus, which might be involved in complications in patients receiving associated cell therapies.
- Caleb A. Lareau
- , Yajie Yin
- & Ansuman T. Satpathy
-
Article
| Open Access The PTPN2/PTPN1 inhibitor ABBV-CLS-484 unleashes potent anti-tumour immunity
The PTPN2/PTPN1 inhibitor ABBV-CLS-484 unleashes potent anti-tumour immunity
An orally bioavailable small-molecule active-site inhibitor of the phosphatases PTPN2 and PTPN1, ABBV-CLS-484, demonstrates immunotherapeutic efficacy in mouse models of cancer resistant to PD-1 blockade.
- Christina K. Baumgartner
- , Hakimeh Ebrahimi-Nik
- & Robert T. Manguso
-
Article |
 Reductive carboxylation epigenetically instructs T cell differentiation
Reductive carboxylation epigenetically instructs T cell differentiation
Reductive carboxylation of glutamine by isocitrate dehydrogenase 2 (IDH2) has a role in determining the fate of T cells, and inhibiting this enzyme promotes the differentiation of memory T cells.
- Alison Jaccard
- , Tania Wyss
- & Mathias Wenes
-
Article |
 CD300ld on neutrophils is required for tumour-driven immune suppression
CD300ld on neutrophils is required for tumour-driven immune suppression
A CRISPR–Cas9 screen in a tumour mouse model identifies CD300ld as a tumour receptor on polymorphonuclear myeloid-derived suppressor cells and in vivo experiments indicate that it is a promising target for cancer immunotherapy.
- Chaoxiong Wang
- , Xichen Zheng
- & Min Luo
-
Perspective |
 The complementarity of DDR, nucleic acids and anti-tumour immunity
The complementarity of DDR, nucleic acids and anti-tumour immunity
This Perspective reviews advances in the understanding of the intersection between the DNA damage response and the response to immune checkpoint blockade therapy, and discusses how developments in the field could lead to improved anti-cancer therapies.
- Anand V. R. Kornepati
- , Cody M. Rogers
- & Tyler J. Curiel
-
Article
| Open Access Personalized RNA neoantigen vaccines stimulate T cells in pancreatic cancer
Personalized RNA neoantigen vaccines stimulate T cells in pancreatic cancer
A phase I clinical trial of an adjuvant personalized mRNA neoantigen vaccine, autogene cevumeran, in patients with pancreatic ductal carcinoma demonstrates that the vaccine can induce T cell activity that may correlate with delayed recurrence of disease.
- Luis A. Rojas
- , Zachary Sethna
- & Vinod P. Balachandran
-
Article |
 Co-opting signalling molecules enables logic-gated control of CAR T cells
Co-opting signalling molecules enables logic-gated control of CAR T cells
Logic gating is used to develop a CAR T cell platform that is highly specific and allows the activity of T cells to be restricted to the encounter of two antigens, thus reducing on-target, off-tumour toxicity.
- Aidan M. Tousley
- , Maria Caterina Rotiroti
- & Robbie G. Majzner
-
Perspective |
 CAR immune cells: design principles, resistance and the next generation
CAR immune cells: design principles, resistance and the next generation
This Perspective reviews recent developments in the design and use of chimeric antigen receptors in treatments for cancers and other diseases.
- Louai Labanieh
- & Crystal L. Mackall
-
Article |
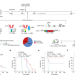 TET2 guards against unchecked BATF3-induced CAR T cell expansion
TET2 guards against unchecked BATF3-induced CAR T cell expansion
Disruption of TET2 increases the antitumour efficacy of CAR T cells, but establishes an epigenetic state that is prone to hyperproliferation and accumulation of secondary mutations.
- Nayan Jain
- , Zeguo Zhao
- & Michel Sadelain
-
Article
| Open Access γδ T cells are effectors of immunotherapy in cancers with HLA class I defects
γδ T cells are effectors of immunotherapy in cancers with HLA class I defects
γδ T cells contribute to the response to immune checkpoint blockade treatment in patients with HLA-class-I-negative DNA mismatch repair-deficient colon cancers. .
- Natasja L. de Vries
- , Joris van de Haar
- & Emile E. Voest
-
Article
| Open Access Neoadjuvant relatlimab and nivolumab in resectable melanoma
Neoadjuvant relatlimab and nivolumab in resectable melanoma
Patients with resectable clinical stage III or oligometastatic stage IV melanoma were given neoadjuvant relatlimab and nivolumab combination immunotherapy, which induced a high pathologic complete response rate, indicating the efficacy and safety of this regimen.
- Rodabe N. Amaria
- , Michael Postow
- & Hussein A. Tawbi
-
Article
| Open Access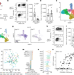 LRRC15+ myofibroblasts dictate the stromal setpoint to suppress tumour immunity
LRRC15+ myofibroblasts dictate the stromal setpoint to suppress tumour immunity
LRRC15-positive cancer-associated fibroblasts constitute a pivotal axis in tumorigenesis and are potential therapeutic targets to improve responses to immune checkpoint blockade.
- Akshay T. Krishnamurty
- , Justin A. Shyer
- & Shannon J. Turley
-
Article
| Open Access PD-1-cis IL-2R agonism yields better effectors from stem-like CD8+ T cells
PD-1-cis IL-2R agonism yields better effectors from stem-like CD8+ T cells
Binding of the PD1-IL2v immunocytokine to PD-1 and IL-2Rβγ on the same cell leads to an alternative differentiation of stem-like CD8+ T cells into better effectors rather than exhausted T cells in models of both chronic infection and cancer.
- Laura Codarri Deak
- , Valeria Nicolini
- & Pablo Umaña
-
Article
| Open Access RASA2 ablation in T cells boosts antigen sensitivity and long-term function
RASA2 ablation in T cells boosts antigen sensitivity and long-term function
Genome-wide CRISPR screens, biochemical studies and animal models show that RASA2 has a key role in regulating T cell function and has potential as a genetic target for enhancing anti-tumour immunity.
- Julia Carnevale
- , Eric Shifrut
- & Alexander Marson
-
Article |
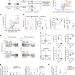 cBAF complex components and MYC cooperate early in CD8+ T cell fate
cBAF complex components and MYC cooperate early in CD8+ T cell fate
cBAF is a negative determinant of memory T cell fate and the manipulation of cBAF early in T cell differentiation can improve cancer immunotherapy.
- Ao Guo
- , Hongling Huang
- & Douglas R. Green
-
Article |
 ADAR1 masks the cancer immunotherapeutic promise of ZBP1-driven necroptosis
ADAR1 masks the cancer immunotherapeutic promise of ZBP1-driven necroptosis
A small molecule can bypass the RNA-editing enzyme ADAR1 to directly activate the Z-form nucleic acid sensor ZBP1, induce necroptosis in tumour fibroblasts and reverse resistance to immune checkpoint blockade in mouse models of melanoma.
- Ting Zhang
- , Chaoran Yin
- & Siddharth Balachandran
-
Article |
 A vaccine targeting resistant tumours by dual T cell plus NK cell attack
A vaccine targeting resistant tumours by dual T cell plus NK cell attack
A vaccine targeting stress proteins expressed by many cancers blocks a tumour escape mechanism, enabling protective immunity mediated by diverse T cell and NK cell populations.
- Soumya Badrinath
- , Maxence O. Dellacherie
- & Kai W. Wucherpfennig
-
Article |
 Androgen receptor activity in T cells limits checkpoint blockade efficacy
Androgen receptor activity in T cells limits checkpoint blockade efficacy
. Androgen-receptor blockade can overcome immunotherapy resistance in prostate cancer by intrinsically enhancing T cell function and IFNγ responses.
- Xiangnan Guan
- , Fanny Polesso
- & Amy E. Moran
-
Article |
 The KEYNOTE-811 trial of dual PD-1 and HER2 blockade in HER2-positive gastric cancer
The KEYNOTE-811 trial of dual PD-1 and HER2 blockade in HER2-positive gastric cancer
Interim analysis of a phase III clinical trial of HER2-positive gastric adenocarinoma shows pembrolizumab plus trastuzumab and chemotherapy improves response rates compared with trastuzumab and chemotherapy alone.
- Yelena Y. Janjigian
- , Akihito Kawazoe
- & Hyun Cheol Chung
-
Article
| Open Access RETRACTED ARTICLE: Cross-HLA targeting of intracellular oncoproteins with peptide-centric CARs
RETRACTED ARTICLE: Cross-HLA targeting of intracellular oncoproteins with peptide-centric CARs
Targeting peptides from unmutated cancer drivers that are expressed in tumours but not in normal tissues using peptide-centric chimeric antigen receptors shows potential as treatment for cancer.
- Mark Yarmarkovich
- , Quinlen F. Marshall
- & John M. Maris
-
Article |
 Epigenetic silencing by SETDB1 suppresses tumour intrinsic immunogenicity
Epigenetic silencing by SETDB1 suppresses tumour intrinsic immunogenicity
A CRISPR–Cas9 screen of chromatin regulators in mouse tumour models treated with immune checkpoint blockade identifies SETDB1 as an epigenetic checkpoint protein that suppresses tumour-intrinsic immunogenicity.
- Gabriel K. Griffin
- , Jingyi Wu
- & Bradley E. Bernstein
-
Article |
 Inhibition of PCSK9 potentiates immune checkpoint therapy for cancer
Inhibition of PCSK9 potentiates immune checkpoint therapy for cancer
Inhibiting the PCSK9 protein, a regulator of cholesterol metabolism, enhances immune checkpoint therapy in mouse models of cancer, in a manner that depends on the regulation of antigen-presenting MHC I molecules.
- Xinjian Liu
- , Xuhui Bao
- & Chuan-Yuan Li
-
Article |
 An RNA vaccine drives immunity in checkpoint-inhibitor-treated melanoma
An RNA vaccine drives immunity in checkpoint-inhibitor-treated melanoma
Results of an exploratory interim analysis from a phase I trial show that an RNA vaccine targeted towards four melanoma-associated antigens produces durable objective responses in patients with melanoma that are accompanied by strong CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell immunity.
- Ugur Sahin
- , Petra Oehm
- & Özlem Türeci
-
Article |
 Mechanisms and therapeutic implications of hypermutation in gliomas
Mechanisms and therapeutic implications of hypermutation in gliomas
Temozolomide therapy seems to lead to mismatch repair deficiency and hypermutation in gliomas, but not to an increase in response to immunotherapy.
- Mehdi Touat
- , Yvonne Y. Li
- & Keith L. Ligon
-
Article |
 Peripheral T cell expansion predicts tumour infiltration and clinical response
Peripheral T cell expansion predicts tumour infiltration and clinical response
Large-scale single-cell sequencing of RNA and T cell receptors in samples from patients with cancer shows clonotypic expansion of effector-like T cells not only in tumour tissue but also in normal adjacent tissues and peripheral blood, which associates with clinical response to cancer immunotherapy.
- Thomas D. Wu
- , Shravan Madireddi
- & Jane L. Grogan
-
Article |
 B cells and tertiary lymphoid structures promote immunotherapy response
B cells and tertiary lymphoid structures promote immunotherapy response
Multiomic profiling of several cohorts of patients treated with immune checkpoint blockade highlights the presence and potential role of B cells and tertiary lymphoid structures in promoting therapy response.
- Beth A. Helmink
- , Sangeetha M. Reddy
- & Jennifer A. Wargo
-
Article |
 B cells are associated with survival and immunotherapy response in sarcoma
B cells are associated with survival and immunotherapy response in sarcoma
Immune profiling of the tumour microenvironment of soft-tissue sarcoma identifies a group of patients with high levels of B-cell infiltration and tertiary lymphoid structures that have improved survival and a high response rate to immune checkpoint blockade therapy.
- Florent Petitprez
- , Aurélien de Reyniès
- & Wolf H. Fridman
-
Article |
 MHC-II neoantigens shape tumour immunity and response to immunotherapy
MHC-II neoantigens shape tumour immunity and response to immunotherapy
In a mouse tumour model, immunotherapy-induced rejection of tumour cells requires presentation of both MHC class I and MHC class II antigens, which activate CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, respectively.
- Elise Alspach
- , Danielle M. Lussier
- & Robert D. Schreiber
-
Review Article |
 Harnessing innate immunity in cancer therapy
Harnessing innate immunity in cancer therapy
The authors review recent developments in our understanding of the antitumour effects of the innate immune system and how this system could be harnessed in the clinic.
- Olivier Demaria
- , Stéphanie Cornen
- & Eric Vivier
-
Letter |
 The Drug Rediscovery protocol facilitates the expanded use of existing anticancer drugs
The Drug Rediscovery protocol facilitates the expanded use of existing anticancer drugs
Clinical benefit was observed in 34% of a cohort of 215 patients with cancer who received treatment with anticancer drugs outside of their approved label, in the Drug Rediscovery protocol trial.
- D. L. van der Velden
- , L. R. Hoes
- & E. E. Voest
-
Letter |
 CD8+ T cells regulate tumour ferroptosis during cancer immunotherapy
CD8+ T cells regulate tumour ferroptosis during cancer immunotherapy
Interferon-γ induces ferroptotic cell death in tumours by suppressing cystine uptake and promoting lipid peroxidation.
- Weimin Wang
- , Michael Green
- & Weiping Zou
-
Letter |
 NR4A transcription factors limit CAR T cell function in solid tumours
NR4A transcription factors limit CAR T cell function in solid tumours
Transfer of NR4A-deficient T cells expressing chimeric antigen receptors is shown to reduce tumour burden and increase survival by shifting T cell transcriptional programs away from exhaustion and towards increased effector function.
- Joyce Chen
- , Isaac F. López-Moyado
- & Anjana Rao
-
Article |
 De novo design of potent and selective mimics of IL-2 and IL-15
De novo design of potent and selective mimics of IL-2 and IL-15
A hyper-stable de novo protein mimic of interleukin-2 computationally designed to not interact with a regulatory T-cell specific receptor subunit has improved therapeutic activity in mouse models of melanoma and colon cancer.
- Daniel-Adriano Silva
- , Shawn Yu
- & David Baker
-
Letter |
 Reprogramming human T cell function and specificity with non-viral genome targeting
Reprogramming human T cell function and specificity with non-viral genome targeting
A non-viral strategy to introduce large DNA sequences into T cells enables the correction of a pathogenic mutation that causes autoimmunity, and the replacement of an endogenous T-cell receptor with an engineered receptor that can recognize cancer antigens.
- Theodore L. Roth
- , Cristina Puig-Saus
- & Alexander Marson
-
Letter |
 A neoantigen fitness model predicts tumour response to checkpoint blockade immunotherapy
A neoantigen fitness model predicts tumour response to checkpoint blockade immunotherapy
An immune fitness model for tumours under checkpoint blockade immunotherapy is proposed, through which the authors show that the presentation and recognition properties of dominant neoantigens distributed over tumour subclones are predictive of response in melanoma and lung cancer cohorts.
- Marta Łuksza
- , Nadeem Riaz
- & Benjamin D. Greenbaum
-
Letter |
 Personalized RNA mutanome vaccines mobilize poly-specific therapeutic immunity against cancer
Personalized RNA mutanome vaccines mobilize poly-specific therapeutic immunity against cancer
The authors report the first-in-human application of personalized neo-antigen RNA vaccines in patients with melanoma.
- Ugur Sahin
- , Evelyna Derhovanessian
- & Özlem Türeci
-
Letter |
 Targeting a CAR to the TRAC locus with CRISPR/Cas9 enhances tumour rejection
Targeting a CAR to the TRAC locus with CRISPR/Cas9 enhances tumour rejection
Introducing chimeric antigen receptors into the endogenous T-cell receptor locus reduces tonic signalling, averts accelerated T-cell differentiation and delays T-cell exhaustion, leading to enhanced function and anti-tumour efficacy compared to random integrations.
- Justin Eyquem
- , Jorge Mansilla-Soto
- & Michel Sadelain
-
Letter |
 Systemic RNA delivery to dendritic cells exploits antiviral defence for cancer immunotherapy
Systemic RNA delivery to dendritic cells exploits antiviral defence for cancer immunotherapy
The development of a nanoparticle RNA vaccine is reported that preferentially targets dendritic cells after systemic administration, and is shown to provide durable interferon-α-dependent antigen-specific immunity in mouse tumour models; initial results in advanced melanoma patients indicate potential efficacy in humans.
- Lena M. Kranz
- , Mustafa Diken
- & Ugur Sahin
-
Letter |
 Mutant MHC class II epitopes drive therapeutic immune responses to cancer
Mutant MHC class II epitopes drive therapeutic immune responses to cancer
The authors show that a large fraction of tumour mutations is immunogenic and predominantly recognized by CD4+ T cells; they use these data to design synthetic messenger-RNA-based vaccines specific against tumour mutations, and show that these can reject tumours in mice.
- Sebastian Kreiter
- , Mathias Vormehr
- & Ugur Sahin
-
-
Outlook |
 Calling cells to arms
Calling cells to arms
Increased understanding of immune- and tumour-cell biology has led to an explosion of research into potential ways to harness the immune system to kill cancer. By Emily Elert.
- Emily Elert
-
Outlook |
 Bacteriology: A caring culture
Bacteriology: A caring culture
William Coley found a way to prompt the immune system to fight cancer over a century ago. After years of neglect, scientists are now seeking to replicate his success.
- Sarah DeWeerdt
-
Outlook |
 Cancer vaccines: Material breach
Cancer vaccines: Material breach
An experimental vaccine implanted beneath the skin could usher in biomaterial-based immunotherapies for cancer.
- Elie Dolgin
-
Outlook |
 Q&A: Evidence presenter
Q&A: Evidence presenter
Immunologist Karolina Palucka, at the Baylor Institute for Immunology Research in Dallas, Texas, helped treat Nobel prizewinner Ralph Steinman's pancreatic cancer with dendritic cells — the cells he co-discovered. Here she explains the use of dendritic cells in cancer immunotherapy.
- Karolina Palucka
-
Outlook |
 Medical imaging: Removing the blindfold
Medical imaging: Removing the blindfold
Using a variety of creative imaging techniques, researchers are tracking the dynamic interactions of immune and cancer cells. Their results will guide drug development.
- Katherine Bourzac
-
Outlook |
 Adoptive cell therapy: Honing that killer instinct
Adoptive cell therapy: Honing that killer instinct
Genetically altered immune cells are helping to push life-threatening cancers into remission and generating a buzz.
- Courtney Humphries

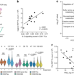 PGE2 inhibits TIL expansion by disrupting IL-2 signalling and mitochondrial function
PGE2 inhibits TIL expansion by disrupting IL-2 signalling and mitochondrial function Cancer immunotherapy
Cancer immunotherapy