Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Intranasal mask for protecting the respiratory tract against viral aerosols
Intranasal mask for protecting the respiratory tract against viral aerosols
The spread of many infectious diseases substantially relies on aerosol transmission to the respiratory tract. Here, the authors design an intranasal mask with the ability to intercept viral aerosols, entrap and inactivate virus, thus preventing respiratory tract infection.
- Xiaoming Hu
- , Shuang Wang
- & Wei Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Soft ferroelectret ultrasound receiver for targeted peripheral neuromodulation
Soft ferroelectret ultrasound receiver for targeted peripheral neuromodulation
Neurostimulators are often bulky and uncomfortable. Researchers report a wireless, leadless, and battery-free ultrasound receiver that wraps around the target peripheral nerve and allows precise modulation of organ function, providing a framework for future bioelectronic medicines
- Tong Li
- , Zhidong Wei
- & Zhang-Qi Feng
-
Article
| Open Access Whole-genome sequencing reveals the molecular implications of the stepwise progression of lung adenocarcinoma
Whole-genome sequencing reveals the molecular implications of the stepwise progression of lung adenocarcinoma
Current sequencing technologies can shed light on the stepwise progression of lung adenocarcinoma. Here, the authors characterize tumor progression in lung adenocarcinomas from an early stage using short and long read whole-genome sequencing, bulk and spatial transcriptomics, and epigenomics.
- Yasuhiko Haga
- , Yoshitaka Sakamoto
- & Ayako Suzuki
-
Q&A
| Open Access A conversation about cultivated meat
A conversation about cultivated meat
Summary: Cultivated or cultured meat is promising to revolutionize the food industry in the coming years to decades, helping to resolve concerns related to the environmental impact and ethical implications linked to conventional meat production. We talked to Dr. Sandhya Sriram, the Group CEO and Co-founder of Shiok Meats Pte. Ltd., Singapore; Prof. Shulamit Levenberg, the former Dean of the Biomedical Engineering Department at the Technion, current Director of the Technion Center for 3D Bioprinting and The Rina & Avner Schneur Center for Diabetes Research, as well as the Co-founder and Chief Scientific Adviser of Aleph Farms, Israel; and Dr. Timothy Olsen, Head of Cultured Meat in the Life Science business at Merck KGaA, Germany; about this relatively new and quickly developing sector. They explain what their teams are working on, including the biggest recent accomplishments, speak about the main challenges facing the field and how they can be resolved, and share their visions about the future of cultivated meat, aiming to provide more equitable and sustainable access to nutritious food for the growing world population.
-
Article
| Open Access Induced formation of primordial germ cells from zebrafish blastomeres by germplasm factors
Induced formation of primordial germ cells from zebrafish blastomeres by germplasm factors
Primordial germ cell (PGC) transplantation is an important technology for developmental biology and genetic breeding. Here, Wang et al. develop an approach for PGC induction that enhances the efficiency of PGC transplantation in zebrafish.
- Xiaosi Wang
- , Junwen Zhu
- & Yonghua Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Atherosclerotic plaque development in mice is enhanced by myeloid ZEB1 downregulation
Atherosclerotic plaque development in mice is enhanced by myeloid ZEB1 downregulation
Accumulation of lipid-laden macrophages in the arterial wall is a critical step in atherosclerosis. Here, the authors show that downregulation of Zeb1 in macrophages promotes lipid accumulation and atherosclerotic plaque formation while its restoration with macrophage-targeted nanoparticles reverses these effects.
- M. C. Martinez-Campanario
- , Marlies Cortés
- & Antonio Postigo
-
Article
| Open Access Single-cell spatial metabolomics with cell-type specific protein profiling for tissue systems biology
Single-cell spatial metabolomics with cell-type specific protein profiling for tissue systems biology
The authors developed a framework for joint protein-metabolite profiling at the single-cell level in human tissue combining targeted multiplexed protein imaging and untargeted spatial metabolomics in a single pipeline.
- Thomas Hu
- , Mayar Allam
- & Ahmet F. Coskun
-
Article
| Open Access GNTD: reconstructing spatial transcriptomes with graph-guided neural tensor decomposition informed by spatial and functional relations
GNTD: reconstructing spatial transcriptomes with graph-guided neural tensor decomposition informed by spatial and functional relations
Reconstructing transcriptome-wide spatially-resolved gene expressions requires modelling nonlinear patterns and spatial structures in RNA profiling data. Here, authors introduce a graph-guided neural hierarchical tensor decomposition model that incorporates spatial and functional relations for the task.
- Tianci Song
- , Charles Broadbent
- & Rui Kuang
-
Article
| Open Access Anti-VEGFR2 F(ab′)2 drug conjugate promotes renal accumulation and glomerular repair in diabetic nephropathy
Anti-VEGFR2 F(ab′)2 drug conjugate promotes renal accumulation and glomerular repair in diabetic nephropathy
Poor renal distribution of antibody-based drugs limits the treatment efficiency for diabetic nephropathy and causes side effects. Here, the authors prepare an antibody fragment drug conjugate, antiVEGFR2 F(ab′)2-SS31, improving renal distribution and meriting drug validation in diabetic nephropathy therapy.
- Di Liu
- , Yanling Song
- & Yongzhong Du
-
Article
| Open Access A patterned human primitive heart organoid model generated by pluripotent stem cell self-organization
A patterned human primitive heart organoid model generated by pluripotent stem cell self-organization
Pluripotent stem cell-derived organoids can recapitulate significant hallmarks of human organ development and are becoming critical tools for human research. Here, the authors report significant technical steps for generating sophisticated synthetic human primitive heart organoids.
- Brett Volmert
- , Artem Kiselev
- & Aitor Aguirre
-
Article
| Open Access UniKP: a unified framework for the prediction of enzyme kinetic parameters
UniKP: a unified framework for the prediction of enzyme kinetic parameters
Prediction of enzyme kinetic parameters is essential for designing and optimising enzymes for various biotechnological and industrial applications. Here, authors presented a prediction framework (UniKP), which improves the accuracy of predictions for three enzyme kinetic parameters.
- Han Yu
- , Huaxiang Deng
- & Xiaozhou Luo
-
Article
| Open Access Generation of three-dimensional meat-like tissue from stable pig epiblast stem cells
Generation of three-dimensional meat-like tissue from stable pig epiblast stem cells
Cultured meat technology promises to alleviate protein shortages, but still faces many challenges. Here, the authors achieve serum-free myogenic differentiation of porcine pre-gastrulation epiblast stem cells and generate meat-like tissue via edible plant-based scaffolds without any animal compounds.
- Gaoxiang Zhu
- , Dengfeng Gao
- & Jianyong Han
-
Article
| Open Access Amplified fluorogenic immunoassay for early diagnosis and monitoring of Alzheimer’s disease from tear fluid
Amplified fluorogenic immunoassay for early diagnosis and monitoring of Alzheimer’s disease from tear fluid
Accurate diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease in its earliest stage can prevent the disease and delay the symptoms. Here the authors identify a potential Alzheimer’s biomarker from tear fluid, and develop a nanoparticle-based immunoassay for its detection, demonstrating potential in Alzheimer’s diagnosis.
- Sojeong Lee
- , Eunjung Kim
- & Seungjoo Haam
-
Article
| Open Access STalign: Alignment of spatial transcriptomics data using diffeomorphic metric mapping
STalign: Alignment of spatial transcriptomics data using diffeomorphic metric mapping
Spatial transcriptomics (ST) enables gene expression characterisation within tissue sections, but comparing across sections and technologies remains challenging. Here, authors develop STalign to spatially align ST data and demonstrate applications including aligning to common coordinate frameworks.
- Kalen Clifton
- , Manjari Anant
- & Jean Fan
-
Article
| Open Access Functional and analytical recapitulation of osteoclast biology on demineralized bone paper
Functional and analytical recapitulation of osteoclast biology on demineralized bone paper
Here, authors report demineralized bone paper-based in vitro osteogenic culture and assay platforms that replicate essential bone tissue complexity, osteoclast processes, and drug responses with high fidelity and predictive power.
- Yongkuk Park
- , Tadatoshi Sato
- & Jungwoo Lee
-
Article
| Open Access Saturation genome editing of DDX3X clarifies pathogenicity of germline and somatic variation
Saturation genome editing of DDX3X clarifies pathogenicity of germline and somatic variation
Pathogenic variants of DDX3X are associated with neurodevelopmental disorders (NDD) and cancer. Here, the authors perform saturation genome editing of DDX3X to test the functional impact of 12,776 variants, develop a machine learning classifier to identify variants relevant for NDD, and show that DDX3X predominantly acts as a tumour suppressor in cancer.
- Elizabeth J. Radford
- , Hong-Kee Tan
- & Matthew E. Hurles
-
Article
| Open Access Systemically administered wound-homing peptide accelerates wound healing by modulating syndecan-4 function
Systemically administered wound-homing peptide accelerates wound healing by modulating syndecan-4 function
A systemically administered peptide (CARSKNKDC) that homes to injured tissues, has inherent ability to promote wound healing. Here, the authors show that this peptide binds to syndecan-4 and activates ARF6 to trigger re-epithelialisation and the naturally occurring wound repair pathway.
- Horacio Maldonado
- , Bryan D. Savage
- & Tero A. H. Järvinen
-
Article
| Open Access ANCA: artificial nucleic acid circuit with argonaute protein for one-step isothermal detection of antibiotic-resistant bacteria
ANCA: artificial nucleic acid circuit with argonaute protein for one-step isothermal detection of antibiotic-resistant bacteria
Antibiotic-resistant bacteria pose a growing threat to global health. Here, the authors present an artificial nucleic acid circuit with argonaute protein (ANCA) for one-step, amplification-free, and isothermal detection of carbapenemase-producing Klebsiella pneumoniae.
- Hyowon Jang
- , Jayeon Song
- & Taejoon Kang
-
Article
| Open Access Secretory GFP reconstitution labeling of neighboring cells interrogates cell–cell interactions in metastatic niches
Secretory GFP reconstitution labeling of neighboring cells interrogates cell–cell interactions in metastatic niches
Methodologies to study the mechanisms of cell–cell interactions in metastatic niches remain scarce. Here, the authors develop a secretory GFP reconstitution-based system to tag tissue-resident cells neighboring on cancer cells within the metastatic niche.
- Misa Minegishi
- , Takahiro Kuchimaru
- & Satoshi Nishimura
-
Article
| Open Access Metabolic tagging of extracellular vesicles and development of enhanced extracellular vesicle based cancer vaccines
Metabolic tagging of extracellular vesicles and development of enhanced extracellular vesicle based cancer vaccines
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) have been actively explored for diagnostic and therapeutic applications. Here, the authors report a universal metabolic tagging technology to generate chemically tagged EVs from parent cells, modulate EV-cell interactions, and develop potent EV-based cancer vaccines.
- Rimsha Bhatta
- , Joonsu Han
- & Hua Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Engineering artificial photosynthesis based on rhodopsin for CO2 fixation
Engineering artificial photosynthesis based on rhodopsin for CO2 fixation
Microbial rhodopsins are major contributors to global light harvesting on Earth, but their role in carbon fixation is unclear. Here, the authors construct an artificial photosynthesis system by combining rhodopsin with an extracellular electron uptake mechanism for photoelectrosynthetic CO2 fixation in Ralstonia eutropha.
- Weiming Tu
- , Jiabao Xu
- & Wei E. Huang
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic and static control of the off-target interactions of antisense oligonucleotides using toehold chemistry
Dynamic and static control of the off-target interactions of antisense oligonucleotides using toehold chemistry
Off-target toxicity of antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) poses a challenge for their clinical use. Here, authors develop a toehold-bearing ASO architecture that mitigates a broad spectrum of off-target interactions, significantly enhancing the safety profile of ASO drugs.
- Chisato Terada
- , Kaho Oh
- & Tsuyoshi Yamamoto
-
Article
| Open Access Fully implanted battery-free high power platform for chronic spinal and muscular functional electrical stimulation
Fully implanted battery-free high power platform for chronic spinal and muscular functional electrical stimulation
Electrical stimulation of the neuromuscular system holds promise for therapeutic biomedical applications, but is currently restricted by power. Here, the authors introduce fully implantable resonator-based designs achieving ±20 V compliance and >300 mW output, enabling multichannel, biphasic, current-controlled operation to evoke functional gate patterns for 6-weeks in freely behaving rats.
- Alex Burton
- , Zhong Wang
- & Philipp Gutruf
-
Article
| Open Access Engineered immunogens to elicit antibodies against conserved coronavirus epitopes
Engineered immunogens to elicit antibodies against conserved coronavirus epitopes
A pan-betacoronavirus vaccine will likely require the elicitation of antibodies against spike regions conserved across diverse coronaviruses. Here, authors computationally engineer and experimentally validate immunogens to elicit antibodies against two such spike regions.
- A. Brenda Kapingidza
- , Daniel J. Marston
- & Mihai L. Azoitei
-
Article
| Open Access Xylose and shikimate transporters facilitates microbial consortium as a chassis for benzylisoquinoline alkaloid production
Xylose and shikimate transporters facilitates microbial consortium as a chassis for benzylisoquinoline alkaloid production
It’s challenging to produce natural products using single strains of engineered microbes fed by renewable carbon sources. Here, the authors assemble a microbial consortium consisting of engineered S. stipitis and S. cerevisiae for streamlined production of (S)-norcoclaurine from glucose and xylose simultaneously.
- Meirong Gao
- , Yuxin Zhao
- & Zengyi Shao
-
Article
| Open Access Interrogating ligand-receptor interactions using highly sensitive cellular biosensors
Interrogating ligand-receptor interactions using highly sensitive cellular biosensors
The interaction of membrane-resident proteins plays an essential role in biological processes. Here the authors describe cellular biosensors based on chimeric receptors, as a tool to study the interaction of receptor-ligand pairs such as immune checkpoint molecules or virus attachment proteins and their receptors.
- Maximilian A. Funk
- , Judith Leitner
- & Peter Steinberger
-
Article
| Open Access Local H2 release remodels senescence microenvironment for improved repair of injured bone
Local H2 release remodels senescence microenvironment for improved repair of injured bone
Senescence microenvironment inhibits tissue repair in elderly individuals. Here, the authors demonstrate that local H2 supply has anti-inflammation and anti-senescence effects, and develop a H2-releasing scaffold to enhance aging bone defect repair.
- Shengqiang Chen
- , Yuanman Yu
- & Qianjun He
-
Article
| Open Access Detection of isoforms and genomic alterations by high-throughput full-length single-cell RNA sequencing in ovarian cancer
Detection of isoforms and genomic alterations by high-throughput full-length single-cell RNA sequencing in ovarian cancer
Long-read single-cell RNA sequencing is capable of detecting isoform-level gene expression and genomic alterations such as mutations and gene fusions, thereby providing cell-specific genotype-phenotype information. Here, the authors use long-read scRNA-seq on metastatic ovarian cancer samples and detect cell-type specific isoforms and gene fusions that may otherwise be misclassified in short-read data.
- Arthur Dondi
- , Ulrike Lischetti
- & Niko Beerenwinkel
-
Article
| Open Access A simeprevir-inducible molecular switch for the control of cell and gene therapies
A simeprevir-inducible molecular switch for the control of cell and gene therapies
Chemical inducer of dimerization (CID) modules can be used to effectively control biological processes; however, CID modules have been explored primarily in engineering cells for in vitro applications using inducers that have limited clinical utility. Here, the authors identify a CID module with favorable properties to enable rapid translation from in vitro applications to potential use in humans.
- Stacey E. Chin
- , Christina Schindler
- & Natalie J. Tigue
-
Article
| Open Access Discovery and remodeling of Vibrio natriegens as a microbial platform for efficient formic acid biorefinery
Discovery and remodeling of Vibrio natriegens as a microbial platform for efficient formic acid biorefinery
Formic acid (FA) is a promising CO2-equivalent feedstock for onecarbon biorefinery, but microbial host that can efficiently utilize FA is unavailable. Here, the authors engineer a non-native closed loop in Vibrio natriegens and demonstrate its application in promoting FA utilization.
- Jinzhong Tian
- , Wangshuying Deng
- & Yang Gu
-
Article
| Open Access Ultra-durable cell-free bioactive hydrogel with fast shape memory and on-demand drug release for cartilage regeneration
Ultra-durable cell-free bioactive hydrogel with fast shape memory and on-demand drug release for cartilage regeneration
Achieving successful in vivo cartilage regeneration remains challenging. Here they present a cell-free, multiple hydrogen-bond crosslinked hydrogel loaded with tannic acid and Kartogenin with ultra-durable mechanical properties and stage-dependent drug release behavior to promote cartilage regeneration.
- Yuxuan Yang
- , Xiaodan Zhao
- & Xuesi Chen
-
Article
| Open Access A fully integrated, standalone stretchable device platform with in-sensor adaptive machine learning for rehabilitation
A fully integrated, standalone stretchable device platform with in-sensor adaptive machine learning for rehabilitation
Methods for the wireless, continuous monitoring and analysis of activities directly from the throat skin have not been developed. Here, the authors present a stretchable device platform that provides wireless measurements and machine learning-based analysis of vibrations and muscle electrical activities from the throat.
- Hongcheng Xu
- , Weihao Zheng
- & Libo Gao
-
Article
| Open Access The oxygen-tolerant reductive glycine pathway assimilates methanol, formate and CO2 in the yeast Komagataella phaffii
The oxygen-tolerant reductive glycine pathway assimilates methanol, formate and CO2 in the yeast Komagataella phaffii
One carbon compounds such as CO2, methanol and formate are cost-effective and environmentally friendly microbial feedstocks for biomanufacturing. Here, the authors report the oxygen tolerant reductive glycine pathway in Komagataella phaffii can co-assimilate CO2, methanol and formate.
- Bernd M. Mitic
- , Christina Troyer
- & Diethard Mattanovich
-
Article
| Open Access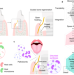 Occlusive membranes for guided regeneration of inflamed tissue defects
Occlusive membranes for guided regeneration of inflamed tissue defects
Symbiosis should be maintained during the oral regeneration period. Herein, authors develop an occlusive membrane that induces symbiosis, thereby improving the performance of guided bone generation therapy.
- Woojin Choi
- , Utkarsh Mangal
- & Jinkee Hong
-
Article
| Open Access In vivo imaging of mitochondrial DNA mutations using an integrated nano Cas12a sensor
In vivo imaging of mitochondrial DNA mutations using an integrated nano Cas12a sensor
Mutations in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) play critical roles in human diseases. Here, the authors describe an integrated Cas12a sensor for sensing mtDNA mutations in vivo, showing potential for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.
- Yanan Li
- , Yonghua Wu
- & Kaixiang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Nanoparticles exhibiting virus-mimic surface topology for enhanced oral delivery
Nanoparticles exhibiting virus-mimic surface topology for enhanced oral delivery
The oral delivery of nano-drug delivery systems (Nano-DDS) remains challenging. Here the authors construct core–shell mesoporous silica nanoparticles with virus-like nanospikes and demonstrate the versatility of these nanoparticles as Nano-DDS to achieve efficient oral drug delivery by mimicking structural feature, chiral recognition, and gene encapsulation of viruses.
- Zhentao Sang
- , Lu Xu
- & Heran Li
-
Article
| Open Access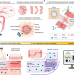 3D bioprinted multilayered cerebrovascular conduits to study cancer extravasation mechanism related with vascular geometry
3D bioprinted multilayered cerebrovascular conduits to study cancer extravasation mechanism related with vascular geometry
Geometrical complexities of blood vessels alter biophysical behaviors of circulating tumor cells, influencing cancer metastasis. Here, the authors develop a 3D bioprinted in vitro brain blood vessel-on-a-chip to investigate continuities between vascular geometry and metastatic cancer development.
- Wonbin Park
- , Jae-Seong Lee
- & Dong-Woo Cho
-
Article
| Open Access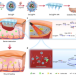 Biofilm microenvironment triggered self-enhancing photodynamic immunomodulatory microneedle for diabetic wound therapy
Biofilm microenvironment triggered self-enhancing photodynamic immunomodulatory microneedle for diabetic wound therapy
The treatment of diabetic wounds tends to be hindered by complex wound environments, and the critical role of the microenvironment in the chronic diabetic wounds has not been explored for therapeutic development. Here, the authors develop a wound microenvironment-responsive microneedle bandage to achieve self-enhanced, catabolic and dynamic therapy of chronic wounds.
- Li Yang
- , Dan Zhang
- & Xiaowei Zeng
-
Article
| Open Access SPACEL: deep learning-based characterization of spatial transcriptome architectures
SPACEL: deep learning-based characterization of spatial transcriptome architectures
Spatial transcriptomics (ST) technologies detect transcript distribution in space. Here, authors present a deep learning based method SPACEL for cell type deconvolution, spatial domain identification and 3D alignment, showcasing it as a valuable toolkit for ST data analysis
- Hao Xu
- , Shuyan Wang
- & Kun Qu
-
Article
| Open Access Four-dimensional hydrogel dressing adaptable to the urethral microenvironment for scarless urethral reconstruction
Four-dimensional hydrogel dressing adaptable to the urethral microenvironment for scarless urethral reconstruction
Urethral repair can be carried out using hydrogels, but the harsh microenvironment hinders the repair. Here, the authors report the development of a 4D hydrogel dressing that can provide an early-vascularised and later-antifibrogenic microenvironment to assist in scarless reconstruction.
- Yujie Hua
- , Kai Wang
- & Kaile Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access A semiconductor 96-microplate platform for electrical-imaging based high-throughput phenotypic screening
A semiconductor 96-microplate platform for electrical-imaging based high-throughput phenotypic screening
Cell-based phenotypic assays link in vitro discovery to disease pathology. Here, the authors report a semiconductor-based microplate platform to perform high-throughput, high-dimensional “electrical imaging” for label-free assessment of live cell morphology and function.
- Shalaka Chitale
- , Wenxuan Wu
- & Jeffrey Abbott
-
Article
| Open Access Cis-trans isomerization of peptoid residues in the collagen triple-helix
Cis-trans isomerization of peptoid residues in the collagen triple-helix
The cis-peptide bond is rare in natural proteins and its impact on protein folding is elusive. Here the authors break the conventional understanding that cis-amide-favoring residues destabilize proteins, elucidate the principles of peptoid cis-trans isomerization in collagen folding, and showcase the use of cis-amide-favoring residues in building programmable and functional peptidomimetics.
- Rongmao Qiu
- , Xiaojing Li
- & Yang Li
-
Article
| Open Access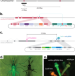 CRISPR-based gene drives generate super-Mendelian inheritance in the disease vector Culex quinquefasciatus
CRISPR-based gene drives generate super-Mendelian inheritance in the disease vector Culex quinquefasciatus
Culex mosquitoes are carriers of major diseases like West Nile virus and are a public health concern. Here the authors present a CRISPR-Cas9 gene drive as a control technology in the Culex quinquefasciatus mosquito species.
- Tim Harvey-Samuel
- , Xuechun Feng
- & Valentino M. Gantz
-
Article
| Open Access Asymmetric CRISPR enabling cascade signal amplification for nucleic acid detection by competitive crRNA
Asymmetric CRISPR enabling cascade signal amplification for nucleic acid detection by competitive crRNA
New strategies are being developed to simplify CRISPR-based nucleic acid detection. By investigating the competitive reaction between a full-sized crRNA and split crRNA for CRISPR-Cas12a, the authors develop an asymmetric CRISPR assay for amplification-free, cascade signal amplification detection of nucleic acids.
- Jeong Moon
- & Changchun Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Diurnal switches in diazotrophic lifestyle increase nitrogen contribution to cereals
Diurnal switches in diazotrophic lifestyle increase nitrogen contribution to cereals
Engineering ammonium excretion diazotrophs suffers from severe penalties to the bacteria. Here, the authors utilize a thermo-sensitive glutamine synthetase-based regulatory switch that permits diurnal changes in diazotrophic lifestyle, coincident with seasonal temperatures for cereal cultivation.
- Yuqian Tang
- , Debin Qin
- & Yi-Ping Wang
-
Article
| Open Access High-sensitive spatially resolved T cell receptor sequencing with SPTCR-seq
High-sensitive spatially resolved T cell receptor sequencing with SPTCR-seq
Understanding T cell behaviour in cancers is vital for improving immunotherapies. Here, the authors present spatially resolved T cell receptor sequencing (SPTCR-seq), a technology that annotates T cell receptors within the tumour ecosystem.
- Jasim Kada Benotmane
- , Jan Kueckelhaus
- & Dieter Henrik Heiland
-
Article
| Open Access Polyethyleneimine-coated MXene quantum dots improve cotton tolerance to Verticillium dahliae by maintaining ROS homeostasis
Polyethyleneimine-coated MXene quantum dots improve cotton tolerance to Verticillium dahliae by maintaining ROS homeostasis
Verticillum wilt is an important cotton disease caused by fungal pathogen Verticillium dahiae. Here, the authors assemble the genomes of defoliating and non-defoliating isolates of the pathogen, identify virulence gene SP3, and develop a disease control strategy using polyethyleneimine-coated MXene quantum dots.
- Ping Qiu
- , Jiayue Li
- & Longfu Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Pan-genome analysis of 13 Malus accessions reveals structural and sequence variations associated with fruit traits
Pan-genome analysis of 13 Malus accessions reveals structural and sequence variations associated with fruit traits
A pan-genome can reduce bias in genetic diversity analysis inherent in using a single reference genome. Here, the authors assemble genomes of 10 diverse apple accessions, conduct pan-genome analysis together with three existing genomes, and reveal the role of mitogen-activated protein kinase homolog MMK2 in fruit coloration.
- Ting Wang
- , Shiyao Duan
- & Ting Wu
-
Article
| Open Access Imaging cellular forces with photonic crystals
Imaging cellular forces with photonic crystals
Current techniques for visualizing cell generated forces suffer from throughput limitations. Here, Gu et al. introduced photonic crystal cellular force microscopy, inspired by chameleons, enabling visualization and quantification of vertically directed cell forces, well-suited for drug screening.
- Qiwei Li
- , Zaozao Chen
- & Zhongze Gu
Browse broader subjects
Browse narrower subjects
- Animal biotechnology
- Applied immunology
- Assay systems
- Biologics
- Biomaterials
- Biomimetics
- Cell delivery
- Environmental biotechnology
- Expression systems
- Functional genomics
- Gene delivery
- Gene therapy
- Genomics
- Industrial microbiology
- Metabolic engineering
- Metabolomics
- Molecular engineering
- Nanobiotechnology
- Nucleic-acid therapeutics
- Oligo delivery
- Peptide delivery
- Plant biotechnology
- Protein delivery
- Proteomics
- Regenerative medicine
- Sequencing
- Stem-cell biotechnology
- Tissue engineering

 Pathway centric analysis for single-cell RNA-seq and spatial transcriptomics data with GSDensity
Pathway centric analysis for single-cell RNA-seq and spatial transcriptomics data with GSDensity