Article
|
Open Access
Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Training an Ising machine with equilibrium propagation
Training an Ising machine with equilibrium propagation
Ising machines have been usually applied to predefined combinatorial problems due to their distinct physical properties. The authors introduce an approach that utilizes equilibrium propagation for the training of Ising machines and achieves high accuracy performance on classification tasks.
- Jérémie Laydevant
- , Danijela Marković
- & Julie Grollier
-
Article
| Open Access Frequency tunable magnetostatic wave filters with zero static power magnetic biasing circuitry
Frequency tunable magnetostatic wave filters with zero static power magnetic biasing circuitry
Magnetostatic wave filters have a wide working frequency range, small size and high Q-factor, however, they are hampered by the need for a large external electromagnet to provide a bias magnetic field. Here, Du et al demonstrate an extremely small and low power external magnetic bias assembly with zero static power consumption, removing the need for bulky and energy intensive electromagnets.
- Xingyu Du
- , Mohamad Hossein Idjadi
- & Roy H. Olsson III
-
Article
| Open Access Dynamic acoustic optimization of pulse tube refrigerators for rapid cooldown
Dynamic acoustic optimization of pulse tube refrigerators for rapid cooldown
Pulse tube refrigerators are a critical enabling technology for many disciplines that require low temperatures, including quantum computing. Here, the authors show that dynamically optimizing the acoustic parameters of the refrigerator can improve conventional cooldown speeds up to 3.5 times.
- Ryan Snodgrass
- , Vincent Kotsubo
- & Joel Ullom
-
Article
| Open Access Programmable photoacoustic patterning of microparticles in air
Programmable photoacoustic patterning of microparticles in air
Here the authors integrate optical and acoustic manipulation techniques to generate localized Lamb fields that emulate arbitrary laser patterns and demonstrate programmable nanoparticle patterning over a centimeter-scale area.
- Ruoqin Zhang
- , Xichuan Zhao
- & Feng Li
-
Article
| Open Access Enhancements of electric field and afterglow of non-equilibrium plasma by Pb(ZrxTi1−x)O3 ferroelectric electrode
Enhancements of electric field and afterglow of non-equilibrium plasma by Pb(ZrxTi1−x)O3 ferroelectric electrode
The physics of how ferroelectric materials enhance plasma properties and discharge is unclear. Here, the authors enhance surface charge, electric field and afterglow of nonequilibrium plasma by ferroelectric barrier discharge with evidence from laser diagnostics.
- Yijie Xu
- , Ning Liu
- & Yiguang Ju
-
Article
| Open Access Wide field-of-hearing metalens for aberration-free sound capture
Wide field-of-hearing metalens for aberration-free sound capture
Achieving a wide angular response in single layer acoustic metalenses is challenging. By leveraging perfect acoustic symmetry conversion, the authors realize an aberration free metalens with a wide field-of-hearing, up to 140 degrees.
- Dongwoo Lee
- , Beomseok Oh
- & Junsuk Rho
-
Article
| Open Access Thermodiffusive desalination
Thermodiffusive desalination
Current desalination technologies are energy intensive and suffer from membrane degradation and fouling. Here, authors propose and explore the potential of thermodiffusion as a means of membrane-free, single-phase thermal desalination. A pathway towards a feasible thermodiffusive desalination is provided.
- Shuqi Xu
- , Alice J. Hutchinson
- & Juan F. Torres
-
Article
| Open Access Compact meta-differentiator for achieving isotropically high-contrast ultrasonic imaging
Compact meta-differentiator for achieving isotropically high-contrast ultrasonic imaging
High-contrast ultrasonic imaging holds significant importance in biomedical and engineering applications. Here, the authors present a compact spatial differentiator tailored for underwater isotropic edge-enhanced imaging, facilitating the realization of high-contrast ultrasonic imaging.
- Yurou Jia
- , Suying Zhang
- & Xiaojun Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Passive frequency comb generation at radiofrequency for ranging applications
Passive frequency comb generation at radiofrequency for ranging applications
In contrast to the commonly studied optical frequency combs, here, the authors demonstrate a radio frequency system able to wirelessly and passively generate frequency combs as a battery-free solution for far-field ranging of unmanned vehicles in GPS-denied settings.
- Hussein M. E. Hussein
- , Seunghwi Kim
- & Cristian Cassella
-
Article
| Open Access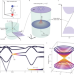 Observation of vortex-string chiral modes in metamaterials
Observation of vortex-string chiral modes in metamaterials
Vortex string, hypothetical topological defects in cosmology, are predicted to support massless chiral modes. The authors successfully mimicked vortex-string physics in a metamaterial system and experimentally observed the chiral modes within it.
- Jingwen Ma
- , Ding Jia
- & Xiang Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional flat Landau levels in an inhomogeneous acoustic crystal
Three-dimensional flat Landau levels in an inhomogeneous acoustic crystal
Artificial magnetic fields have been meticulously engineered in a 3D acoustic crystal, facilitating the creation of 3D flat bands through Landau quantization of quasiparticles arising from nodal-ring band degeneracies.
- Zheyu Cheng
- , Yi-Jun Guan
- & Baile Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Spatially selective delivery of living magnetic microrobots through torque-focusing
Spatially selective delivery of living magnetic microrobots through torque-focusing
The delivery of therapeutic payloads and living vectors to tumors remains a clinical challenge. Here the authors explore a spatially targeted control strategy applying torque density to magnetotactic bacteria, demonstrating feasibility in vitro and in vivo.
- Nima Mirkhani
- , Michael G. Christiansen
- & Simone Schuerle
-
Article
| Open Access Robust temporal adiabatic passage with perfect frequency conversion between detuned acoustic cavities
Robust temporal adiabatic passage with perfect frequency conversion between detuned acoustic cavities
Phase matching is pivotal for realizing complete energy transfer for classical waves. Here, authors propose temporal quasi-phase matching method and realize robust and complete energy transfer between arbitrarily detuned acoustic cavities by combing the concept of stimulated Raman adiabatic passage.
- Zhao-Xian Chen
- , Yu-Gui Peng
- & Yan-Qing Lu
-
Article
| Open Access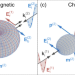 Optical Tellegen metamaterial with spontaneous magnetization
Optical Tellegen metamaterial with spontaneous magnetization
Here the authors propose an isotropic three-dimensional metamaterial with nonreciprocal magnetoelectric resonant responses at visible and mid-infrared frequencies. The proposed metamaterials do not require external magnetization.
- Shadi Safaei Jazi
- , Ihar Faniayeu
- & Viktar Asadchy
-
Article
| Open Access Perfect circular polarization of elastic waves in solid media
Perfect circular polarization of elastic waves in solid media
The authors introduce a method for non-destructive testing based on circularly polarized ultrasound in solids, enabled by metamaterials, allows for detecting internal defects regardless of their orientation. This innovation will redefine ultrasonic non-destructive examination.
- Jeseung Lee
- , Minwoo “Joshua” Kweun
- & Yoon Young Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Optimizing multi-user indoor sound communications with acoustic reconfigurable metasurfaces
Optimizing multi-user indoor sound communications with acoustic reconfigurable metasurfaces
Indoor sound fields are disordered due to reflections and multiple scattering, which scrambles acoustic communication. Here, based on tunable metasurfaces and communication theories, the authors demonstrate multi-channel, multi-spectral, cross-talk-free acoustic communication in a room.
- Hongkuan Zhang
- , Qiyuan Wang
- & Guancong Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Acoustic spin rotation in heavy-metal-ferromagnet bilayers
Acoustic spin rotation in heavy-metal-ferromagnet bilayers
Controlling spin direction is the key for spintronic devices as it induces efficient and field-free switching. Herein, the authors propose using lattice vibrations in acoustic devices to replace the charge motion in conventional spintronic devices to realize the rotation of spin direction, that is, acoustic spin rotation. Acoustic spin rotation offers higher efficiency than spin rotation in conventional charge-current based spintronic devices.
- Yang Cao
- , Hao Ding
- & Dezheng Yang
-
Article
| Open Access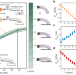 A retrofit sensing strategy for soft fluidic robots
A retrofit sensing strategy for soft fluidic robots
In existing soft robotic sensing strategies, additional components and design changes are often required to sense the environment. Zou et al. introduce a retrofit self-sensing strategy for soft pneumatic actuators, utilizing internal pressure variations arising from interactions.
- Shibo Zou
- , Sergio Picella
- & Johannes T. B. Overvelde
-
Article
| Open Access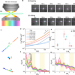 Unconventionally fast transport through sliding dynamics of rodlike particles in macromolecular networks
Unconventionally fast transport through sliding dynamics of rodlike particles in macromolecular networks
Transport of rodlike particles in macromolecular networks is relevant to various biological processes and technological applications, where thin rods have been mainly in focus. Here the authors investigate diffusion dynamics of thick rods in confinement media of macromolecular networks, and uncover dependence of translational diffusion upon rod length.
- Xuanyu Zhang
- , Xiaobin Dai
- & Li-Tang Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Flow-induced periodic chiral structures in an achiral nematic liquid crystal
Flow-induced periodic chiral structures in an achiral nematic liquid crystal
Under strong surface or geometric constraints, achiral nematic liquid crystals can form chiral structures. Using pressure driven flow, Zhang et al. show a pathway to mirror symmetry breaking that does not require such constraints and that occurs in nematic lyotropic chromonic liquid crystals.
- Qing Zhang
- , Weiqiang Wang
- & Irmgard Bischofberger
-
Article
| Open Access Phase transitions in 2D multistable mechanical metamaterials via collisions of soliton-like pulses
Phase transitions in 2D multistable mechanical metamaterials via collisions of soliton-like pulses
In high-dimensional multistable mechanical metamaterials, phase transitions can be remotely nucleated and controlled via collisions of nonlinear pulses, potentially bringing new insights for the design of reconfigurable structures.
- Weijian Jiao
- , Hang Shu
- & Jordan R. Raney
-
Article
| Open Access Orbital topological edge states and phase transitions in one-dimensional acoustic resonator chains
Orbital topological edge states and phase transitions in one-dimensional acoustic resonator chains
The researchers demonstrate orbital-dependent sound-matter interactions in acoustic systems. They unveil duality symmetry and topological phase transitions beyond the conventional SSH model expanding the fundamental understanding of sound-matter interaction.
- Feng Gao
- , Xiao Xiang
- & Andrea Alù
-
Article
| Open Access Pressure-induced reversal of Peierls-like distortions elicits the polyamorphic transition in GeTe and GeSe
Pressure-induced reversal of Peierls-like distortions elicits the polyamorphic transition in GeTe and GeSe
The subtle distortion in atomic structure underlies the drastic changes in the properties of amorphous phase-change materials. Here authors show that that pressure can reverse the Peierls-like distortions introduced by temperature, eliciting a polyamorphic transition in GeTe and GeSe.
- Tomoki Fujita
- , Yuhan Chen
- & Shuai Wei
-
Article
| Open Access Continuous and efficient elastocaloric air cooling by coil-bending
Continuous and efficient elastocaloric air cooling by coil-bending
In this work, authors demonstrate a low-force and energy-efficient elastocaloric air cooling approach based on coil-bending of NiTi ribbons/wires. The device achieves continuous cold outlet airflow with a temperature drop of 10.6 K and a specific cooling power of 2.5 W g−1 at a low specific driving force of 26 N g−1.
- Xueshi Li
- , Peng Hua
- & Qingping Sun
-
Article
| Open Access Higher-order singularities in phase-tracked electromechanical oscillators
Higher-order singularities in phase-tracked electromechanical oscillators
The authors report a controllable third-order cusp singularity in the phase-tracked closed-loop oscillation of two coupled mechanical modes. This finding addresses the challenge of constructing and controlling higher-order singularities.
- Xin Zhou
- , Xingjing Ren
- & Hui Jing
-
Article
| Open Access Ultrasonic barrier-through imaging by Fabry-Perot resonance-tailoring panel
Ultrasonic barrier-through imaging by Fabry-Perot resonance-tailoring panel
Breakthrough ultrasonic imaging captures objects behind barriers. Leveraging Fabry-Perot resonance with a unique resonance-tailoring panel, our method allows imaging through high-impedance barriers helping to revolutionise underwater and brain imaging.
- Chung Il Park
- , Seungah Choe
- & Yoon Young Kim
-
Article
| Open Access Emulator-based Bayesian inference on non-proportional scintillation models by compton-edge probing
Emulator-based Bayesian inference on non-proportional scintillation models by compton-edge probing
Scintillators are widely used for radiation detection and require proper calibration in such applications. Here the authors discuss a Bayesian inference and machine learning method in combination with the Compton-edge probing that can describe the non-proportional scintillation response of inorganic scintillators.
- David Breitenmoser
- , Francesco Cerutti
- & Sabine Mayer
-
Article
| Open Access Superwavelength self-healing of spoof surface sonic Airy-Talbot waves
Superwavelength self-healing of spoof surface sonic Airy-Talbot waves
The Airy-Talbot effect is experimentally demonstrated for spoof surface acoustic waves in a structured metasurface. Owing to its self-imaging and self-healing properties, the authors achieve robust multipath transmission of nonperiodic signals.
- Hao-xiang Li
- , Jing-jing Liu
- & Johan Christensen
-
Article
| Open Access Potential drivers of the recent large Antarctic ozone holes
Potential drivers of the recent large Antarctic ozone holes
The record-breaking ozone holes of recent years contribute to a steady decline of mid-spring ozone in the Antarctic, contrary to signs of early-spring recovery. Changes in descending air at the core of the ozone hole might be the driver.
- Hannah E. Kessenich
- , Annika Seppälä
- & Craig J. Rodger
-
Article
| Open Access Realistic prediction and engineering of high-Q modes to implement stable Fano resonances in acoustic devices
Realistic prediction and engineering of high-Q modes to implement stable Fano resonances in acoustic devices
The authors demonstrate that laser Doppler vibrometer measurements are a powerful tool for predicting the maximum pressure enhancement of high-Q modes. The results presented enable future applications of acoustic BICs by filling the missing data gap on field enhancement.
- Felix Kronowetter
- , Marcus Maeder
- & Steffen Marburg
-
Article
| Open Access Three-dimensional ultrasound matrix imaging
Three-dimensional ultrasound matrix imaging
Ultrasound is a flexible and powerful medical tool. Yet, brain imaging has remained elusive so far for ultrasound due to the blurring induced by the skull. Here, a 3D non-invasive approach is proposed to make the skull digitally transparent and image brain tissues at unprecedented resolution.
- Flavien Bureau
- , Justine Robin
- & Alexandre Aubry
-
Article
| Open Access A reprogrammable mechanical metamaterial with origami functional-group transformation and ring reconfiguration
A reprogrammable mechanical metamaterial with origami functional-group transformation and ring reconfiguration
Programmability is a key property for multifunctional metamaterials, but it is limited by homo-element. Here, the authors show a mechanical metamaterials with heterogeneous elements, achieving various mechanical behaviours by functional group transformation and ring configuration.
- Xinyu Hu
- , Ting Tan
- & Zhimiao Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Realization and topological properties of third-order exceptional lines embedded in exceptional surfaces
Realization and topological properties of third-order exceptional lines embedded in exceptional surfaces
The authors report an experimental realization of order-3 exceptional lines (EL3) in a stack of three coupled acoustic cavities. The EL3 are embedded in an order-2 exceptional surface. The authors use the winding number of resultants of the Hamiltonian matrix to diagnose the topology of EL3.
- Weiyuan Tang
- , Kun Ding
- & Guancong Ma
-
Article
| Open Access Strain topological metamaterials and revealing hidden topology in higher-order coordinates
Strain topological metamaterials and revealing hidden topology in higher-order coordinates
Some systems can exhibit topologically non-trivial characteristics only when specific coordinate transformations are applied. Here, the authors report on a family of metamaterials whose topological properties are unveiled in higher order coordinates (such as strain) and predicts that topological edge states can exist for diverse boundary conditions.
- Florian Allein
- , Adamantios Anastasiadis
- & Georgios Theocharis
-
Article
| Open Access Noise resilient exceptional-point voltmeters enabled by oscillation quenching phenomena
Noise resilient exceptional-point voltmeters enabled by oscillation quenching phenomena
Here the authors demonstrate a nonlinear exceptional-point sensing platform. They harness oscillation quenching phenomena to overcome the noise-sensitivity of techniques based on exceptional point degeneracies.
- Arunn Suntharalingam
- , Lucas Fernández-Alcázar
- & Tsampikos Kottos
-
Comment
| Open Access Guidelines for measuring and reporting particle removal efficiency in fibrous media
Guidelines for measuring and reporting particle removal efficiency in fibrous media
Adopting standardized and reliable methodologies to accurately measure particle removal efficiency when developing fibrous materials for controlling airborne contamination is crucial. Here, the authors recommend best practices for experimental assessments and reporting to ensure a reliable evaluation of new airborne particle filtration media and technologies.
- Paolo Tronville
- , Vincenzo Gentile
- & Jesus Marval
-
Article
| Open Access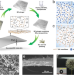 Decorated bacteria-cellulose ultrasonic metasurface
Decorated bacteria-cellulose ultrasonic metasurface
The researchers report a class of silica-nanoparticle-decorated bacteria-cellulose ultrasonic metasurfaces that feature excellent stability in water and mechanical processability. They demonstrate it as holographic meta-lens and 3D imaging meta-lens.
- Zong-Lin Li
- , Kun Chen
- & Xue-Feng Zhu
-
Article
| Open Access Dexterous electrical-driven soft robots with reconfigurable chiral-lattice foot design
Dexterous electrical-driven soft robots with reconfigurable chiral-lattice foot design
Animals use dexterous locomotion to hunt for food or flee from danger. Inspired by this strategy, Wang et al. design a soft robot, containing dielectric elastomer artificial muscles and reconfigurable chiral feet, which enables spontaneous change in movement direction in a controlled and reversible way.
- Dong Wang
- , Baowen Zhao
- & Guoying Gu
-
Article
| Open Access Vacancy-mediated anomalous phononic and electronic transport in defective half-Heusler ZrNiBi
Vacancy-mediated anomalous phononic and electronic transport in defective half-Heusler ZrNiBi
Vacancy has only played a stereotyped role as a scattering center in thermoelectrics, and the boundaries of its versatility have not been tested. Here, authors reveal the multifunctionality of vacancy in tailoring the phononic and electronic transport in a defective half-Heusler ZrNiBi.
- Wuyang Ren
- , Wenhua Xue
- & Zhifeng Ren
-
Article
| Open Access Acoustic microbubble propulsion, train-like assembly and cargo transport
Acoustic microbubble propulsion, train-like assembly and cargo transport
Experiments show how confined microbubbles in a viscous gel can be controllably moved by means of an acoustic field. Ensembles of such microbubbles can be made to self-assemble into a train-like arrangement, which can trap, transport and release microparticles.
- Jakub Janiak
- , Yuyang Li
- & Daniel Ahmed
-
Article
| Open Access Observation of geometry-dependent skin effect in non-Hermitian phononic crystals with exceptional points
Observation of geometry-dependent skin effect in non-Hermitian phononic crystals with exceptional points
Recent theoretical works reveal that the topologically nontrivial exceptional points can guarantee the geometry-dependent skin effect, but it remains to be confirmed by experiments. Here the authors realize a reciprocal non-Hermitian phononic crystal with exceptional points, and observe the geometry-dependent skin effect.
- Qiuyan Zhou
- , Jien Wu
- & Zhengyou Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Stiefel-Whitney topological charges in a three-dimensional acoustic nodal-line crystal
Stiefel-Whitney topological charges in a three-dimensional acoustic nodal-line crystal
Symmetry plays a crucial role in defining the band topology. Here, the authors experimentally demonstrate that spacetime inversion symmetry can lead to Stiefel-Whitney topological charges and protect hinge states in an acoustic nodal-line semimetal.
- Haoran Xue
- , Z. Y. Chen
- & Baile Zhang
-
Article
| Open Access Implant-to-implant wireless networking with metamaterial textiles
Implant-to-implant wireless networking with metamaterial textiles
Implanted bioelectronic devices have proven useful for health sensing and therapy, while the interconnection of distributed implants remains challenging. Here, the authors demonstrate direct implant-to-implant wireless networking at the scale of the human body using metamaterial textiles.
- Xi Tian
- , Qihang Zeng
- & John S. Ho
-
Article
| Open Access Self-bridging metamaterials surpassing the theoretical limit of Poisson’s ratios
Self-bridging metamaterials surpassing the theoretical limit of Poisson’s ratios
Natural and engineered Poisson’s ratios obey fundamental bounds determined by stability, linearity, and thermodynamics. Here, the authors design and realize self-bridging metamaterials with Poisson’s ratios surpassing the theoretical bounds.
- Jinhao Zhang
- , Mi Xiao
- & Fengwen Wang
-
Article
| Open Access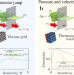 Frozen sound: An ultra-low frequency and ultra-broadband non-reciprocal acoustic absorber
Frozen sound: An ultra-low frequency and ultra-broadband non-reciprocal acoustic absorber
The control of sound is a common engineering problem and requires the development of new processes to bypass conventional limits. Here, the authors report an efficient, low-frequency, and nonreciprocal absorber based on thermoacoustic effect.
- Anis Maddi
- , Come Olivier
- & Yves Aurégan
-
Article
| Open Access Tesla valves and capillary structures-activated thermal regulator
Tesla valves and capillary structures-activated thermal regulator
Unwanted vapor backflow and chaotic two-phase flow patterns can hinder thermal transport performance in their respective systems. Here, the authors revisit the classic Tesla valve design and demonstrate a Tesla valve-based thermal regulator with capillary structures that can suppress vapor backflow and achieve directional two-phase flow.
- Wenming Li
- , Siyan Yang
- & Zuankai Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Pen-drawn Marangoni swimmer
Pen-drawn Marangoni swimmer
Marangoni swimmers have high relative speed, considering the body length and absence of a mechanical system but the fabricating is complex. Song et al. transform simple pen strokes into dynamic, programmable robots that can ‘swim’ with striking versatility.
- Seo Woo Song
- , Sumin Lee
- & Jiyun Kim
-
Article
| Open Access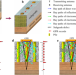 Quality evaluation of ground improvement by deep cement mixing piles via ground-penetrating radar
Quality evaluation of ground improvement by deep cement mixing piles via ground-penetrating radar
Subgrade settlement is a serious distress which poses a huge threat to the service life and operation safety of roads. Here, authors propose the application of ground-penetrating radar as technical solution for the quality evaluation of ground improvement in soft soil subgrade reinforcement engineering.
- Hongyan Shen
- , Xinsheng Li
- & Yueying Yan
-
Article
| Open Access Non-Hermitian control between absorption and transparency in perfect zero-reflection magnonics
Non-Hermitian control between absorption and transparency in perfect zero-reflection magnonics
Absorption, transmission and reflection are three processes characterizing optical devices. Absorption allows for signal conversion and transmission is important for signal transfer, however, reflection is frequently detrimental to device performance. Here, Qian et al demonstrate a magnonic device with controllable absorption and transmission while maintain zero reflection.
- Jie Qian
- , C. H. Meng
- & C. -M. Hu

 Revealing the spatial nature of sublattice symmetry
Revealing the spatial nature of sublattice symmetry