Featured
-
-
Article
| Open Access Probiotic-derived ferrichrome inhibits colon cancer progression via JNK-mediated apoptosis
Probiotic-derived ferrichrome inhibits colon cancer progression via JNK-mediated apoptosis
Probiotics have tumour-suppressive effects in cancer cell lines and in animal models. In this study, the authors demonstrate that ferrichrome produced by Lactobacillus caseiATCC334 can suppress colon cancer growth inducing apoptosis via the JNK pathway.
- Hiroaki Konishi
- , Mikihiro Fujiya
- & Yutaka Kohgo
-
Article
| Open Access Rational design of a protein that binds integrin αvβ3 outside the ligand binding site
Rational design of a protein that binds integrin αvβ3 outside the ligand binding site
Integrins are transmembrane proteins that have important roles in cell adhesion and signalling. Here the authors design a therapeutic protein that binds integrin αvβ3, has anti-angiogenic activity, and reduces tumour growth in xenograft models, while being seemingly well tolerated.
- Ravi Chakra Turaga
- , Lu Yin
- & Zhi-Ren Liu
-
Article
| Open Access Identification of an activation site in Bak and mitochondrial Bax triggered by antibodies
Identification of an activation site in Bak and mitochondrial Bax triggered by antibodies
During apoptosis, Bak and Bax are activated by BH3-only proteins binding to a specific hydrophobic groove. Here, the authors show that antibodies can also activate Bak and mitochondrial Bax by binding to the α1-α2 loop, thus identifying a potential clinical target.
- Sweta Iyer
- , Khatira Anwari
- & Ruth M. Kluck
-
Article
| Open Access miR-216b regulation of c-Jun mediates GADD153/CHOP-dependent apoptosis
miR-216b regulation of c-Jun mediates GADD153/CHOP-dependent apoptosis
The transcription factor CHOP/GADD153 regulates apoptosis in response to the unfolded protein response. Here the authors show that CHOP/GADD153 regulates the expression of miR-216b, which targets c-Jun and sensitizes cells to ER stress-dependent apoptosis.
- Zhenhua Xu
- , Yiwen Bu
- & J. Alan Diehl
-
Article
| Open Access Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies discovers multiple loci for chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies discovers multiple loci for chronic lymphocytic leukemia
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia is a highly inheritable cancer. Here the authors conduct a metaanalysis of four genome-wide association studies and identify three novel loci located near EOMES, SERPINB6 and LPPassociated with risk of this disease.
- Sonja I. Berndt
- , Nicola J. Camp
- & Susan L. Slager
-
Article
| Open Access EAF2 mediates germinal centre B-cell apoptosis to suppress excessive immune responses and prevent autoimmunity
EAF2 mediates germinal centre B-cell apoptosis to suppress excessive immune responses and prevent autoimmunity
EAF2 has been previously known as a transcriptional elongation factor and a proapoptotic gene lost in prostate cancer. Here the authors show that EAF2 is required for apoptosis of germinal centre B cells, and that EAF2-deficient mice develop excessive antibody responses and autoimmunity.
- Yingqian Li
- , Yoshimasa Takahashi
- & Ji-Yang Wang
-
Article
| Open Access Mito-priming as a method to engineer Bcl-2 addiction
Mito-priming as a method to engineer Bcl-2 addiction
Apoptosis often requires mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization, a process targeted by Bcl-2-binding BH3 mimetics. Here the authors describe and apply 'mito-priming', a method that allows triggering mitochondrial apoptosis in a synchronous manner, facilitating the investigation of mitochondrial apoptosis and its regulation by Bcl-2 proteins.
- Jonathan Lopez
- , Margaux Bessou
- & Stephen W. G. Tait
-
Article
| Open Access Endoplasmic reticulum stress drives proteinuria-induced kidney lesions via Lipocalin 2
Endoplasmic reticulum stress drives proteinuria-induced kidney lesions via Lipocalin 2
Proteinuria promotes chronic kidney disease progression. Karoui et al. show that proteinuria stimulates overexpression of iron transporting protein lipocalin-2 via Ca2+release-induced ER stress, which leads to tubular apoptosis, and that inhibition of this pathway by PBA delays renal deterioration in proteinuric mice.
- Khalil El Karoui
- , Amandine Viau
- & Fabiola Terzi
-
Article
| Open Access TIA1 oxidation inhibits stress granule assembly and sensitizes cells to stress-induced apoptosis
TIA1 oxidation inhibits stress granule assembly and sensitizes cells to stress-induced apoptosis
Cytoplasmic stress granules (SG) are intracellular aggregates that suppress translation and sequester apoptosis regulatory factors. Here the authors show that reactive oxygen species oxidise the SG-nucleating protein TIA1, preventing SG formation and promoting apoptosis in the presence of additional stress.
- Kyoko Arimoto-Matsuzaki
- , Haruo Saito
- & Mutsuhiro Takekawa
-
Article
| Open Access The KDM3A–KLF2–IRF4 axis maintains myeloma cell survival
The KDM3A–KLF2–IRF4 axis maintains myeloma cell survival
Several histone modifiers have been implicated in the survival of multiple myeloma cells. Here, the authors reveal a role for the histone demethylase KDM3A in the survival of this haematologic cancer, and show that mechanistically KDM3A removes H3K9 methylation from the promoters of KLF2 and IRF4, genes essential for myeloma cell survival.
- Hiroto Ohguchi
- , Teru Hideshima
- & Kenneth C. Anderson
-
Article |
 Active JNK-dependent secretion of Drosophila Tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase by loser cells recruits haemocytes during cell competition
Active JNK-dependent secretion of Drosophila Tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase by loser cells recruits haemocytes during cell competition
Slow-dividing ‘loser’ cells are outcompeted by more robust ‘winner’ cells and eliminated by macrophage-like haemocytes in the fruit fly larva. Here the authors show that the dying loser cells secrete the enzyme Tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase that upon Mmp2-mediated cleavage acts as a haemocyte chemoattractant.
- Sergio Casas-Tintó
- , Fidel-Nicolás Lolo
- & Eduardo Moreno
-
Article
| Open Access Engulfment pathways promote programmed cell death by enhancing the unequal segregation of apoptotic potential
Engulfment pathways promote programmed cell death by enhancing the unequal segregation of apoptotic potential
Programed cell death occurs in a stereotypic fashion duringC. elegansdevelopment, and it is thought that engulfment promotes programmed cell death. Here the authors present evidence that a signaling function of the conserved engulfment pathways, not the process of engulfment itself, promotes apoptotic cell death.
- Sayantan Chakraborty
- , Eric J. Lambie
- & Barbara Conradt
-
Article
| Open Access Bax monomers form dimer units in the membrane that further self-assemble into multiple oligomeric species
Bax monomers form dimer units in the membrane that further self-assemble into multiple oligomeric species
The proapoptotic protein Bax triggers cell death by forming pores in the outer mitochondrial membrane. Using single-particle TIRF imaging, the authors show that Bax binds the membrane in a monomeric state before forming dimers and multimers of dimers, which are disassembled by the survival protein Bcl-xL.
- Yamunadevi Subburaj
- , Katia Cosentino
- & Ana J. García-Sáez
-
Article
| Open Access PARP14 promotes the Warburg effect in hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting JNK1-dependent PKM2 phosphorylation and activation
PARP14 promotes the Warburg effect in hepatocellular carcinoma by inhibiting JNK1-dependent PKM2 phosphorylation and activation
Tumour cells can survive by evading cell death pathways and altering their metabolism to adapt to their local environment. In this study, Iansanteet al. show that the anti-apoptotic protein PARP14 maintains low PKM2 activity, leading to enhanced glycolysis, demonstrating a link between suppression of apoptosis and altered metabolism.
- Valeria Iansante
- , Pui Man Choy
- & Salvatore Papa
-
Article
| Open Access RTN1 mediates progression of kidney disease by inducing ER stress
RTN1 mediates progression of kidney disease by inducing ER stress
ER stress is associated with the pathogenesis of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and new CKD therapies are needed. Here the authors show that expression of Rtn1 can control severity of renal disease and that inhibition of its expression can attenuate ER stress and CKD.
- Ying Fan
- , Wenzhen Xiao
- & John C. He
-
Article
| Open Access Netrin-1 regulates somatic cell reprogramming and pluripotency maintenance
Netrin-1 regulates somatic cell reprogramming and pluripotency maintenance
Reprogramming holds great promise for regenerative medicine but the molecular mechanisms governing the generation of induced pluripotent stem cells remain unclear. Here, the authors reveal functions for the axonal guidance cue Netrin-1 in constraining apoptosis at the early stage of reprogramming and in established pluripotent cells.
- Duygu Ozmadenci
- , Olivier Féraud
- & Fabrice Lavial
-
Article
| Open Access Aneuploidy generates proteotoxic stress and DNA damage concurrently with p53-mediated post-mitotic apoptosis in SAC-impaired cells
Aneuploidy generates proteotoxic stress and DNA damage concurrently with p53-mediated post-mitotic apoptosis in SAC-impaired cells
CENP-E regulates chromosome alignment during mitosis to distribute chromosomes equally into daughter cells. Here, the authors show that CENP-E inhibition causes p53-mediated post-mitotic apoptosis in tumours where the spindle assembly checkpoint is compromised, suggesting that CENP-E is a therapeutic target for these cancers.
- Akihiro Ohashi
- , Momoko Ohori
- & Kentaro Iwata
-
Article
| Open Access KDEL receptor 1 regulates T-cell homeostasis via PP1 that is a key phosphatase for ISR
KDEL receptor 1 regulates T-cell homeostasis via PP1 that is a key phosphatase for ISR
KDEL receptors are known to be involved in retrotransporting chaperones to the endoplasmic reticulum from the Golgi complex. Here the authors unravel a role of KDEL receptor 1 in regulating integrated stress responses in naïve T cells through its association with protein phosphatase 1.
- Daisuke Kamimura
- , Kokichi Katsunuma
- & Masaaki Murakami
-
Article |
 The ZNF304-integrin axis protects against anoikis in cancer
The ZNF304-integrin axis protects against anoikis in cancer
Ovarian cancer is often accompanied by metastases at the time of diagnosis and has a poor survival rate. In this study, Aslan et al.identify a role for ZNF304 in ovarian cancer metastasis and show that the protein transcriptionally regulates β1 integrin, resulting in a reduction in programmed cell death.
- Burcu Aslan
- , Paloma Monroig
- & Gabriel Lopez-Berestein
-
Article
| Open Access Programmed cell death 5 mediates HDAC3 decay to promote genotoxic stress response
Programmed cell death 5 mediates HDAC3 decay to promote genotoxic stress response
The tumour suppressor p53 is known to be inhibited by histone deacetylase 3 but the molecular mechanism is poorly understood. Here Choi et al. show regulation by programmed cell death 5 and an essential role in activating p53 following DNA damage.
- Hyo-Kyoung Choi
- , Youngsok Choi
- & Ho-Geun Yoon
-
Article
| Open Access A novel mechanism of generating extracellular vesicles during apoptosis via a beads-on-a-string membrane structure
A novel mechanism of generating extracellular vesicles during apoptosis via a beads-on-a-string membrane structure
During apoptosis, cells break up into smaller fragments to facilitate removal. Here the authors characterize a beads-on-a-string structure formed by monocytes undergoing apoptosis in vitro, which shears into apoptotic bodies lacking nuclear contents, and is blocked by the antidepressant sertraline.
- Georgia K. Atkin-Smith
- , Rochelle Tixeira
- & Ivan K.H. Poon
-
Article |
 Tie-mediated signal from apoptotic cells protects stem cells in Drosophila melanogaster
Tie-mediated signal from apoptotic cells protects stem cells in Drosophila melanogaster
Some normal and cancer stem cells are resistant to killing by genotoxins, but the mechanism for this resistance is poorly understood. Here the authors show that adult stem cells inDrosophila melanogastergermline and midgut are resistant to genotoxic stimuli and find that this is mediated by signalling via the receptor tyrosine kinase Tie released from apoptotic cells.
- Yalan Xing
- , Tin Tin Su
- & Hannele Ruohola-Baker
-
Article
| Open Access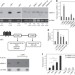 Expression of the vault RNA protects cells from undergoing apoptosis
Expression of the vault RNA protects cells from undergoing apoptosis
Cellular functions of the vault complex, a large ribonucleoprotein assembly remain elusive. Here, the authors show that Epstein–Barr virus infection enhances the expression of the vault complex-associated RNAs, which leads to improved survival of infected cells due to the inhibition of cell apoptosis.
- Melanie Amort
- , Birgit Nachbauer
- & Norbert Polacek
-
Article
| Open Access The NOXA–MCL1–BIM axis defines lifespan on extended mitotic arrest
The NOXA–MCL1–BIM axis defines lifespan on extended mitotic arrest
Cells experiencing extended mitotic arrest often undergo cell death as a result of steadily declining levels of the apoptotic inhibitor MCL1, but the mechanism controlling this process is poorly understood. Here, Haschka et al.show that the BH3-only protein NOXA promotes the degradation of MCL1, enabling BIM-dependent cell death.
- Manuel D. Haschka
- , Claudia Soratroi
- & Luca L. Fava
-
Article |
 Amplification of oxidative stress by a dual stimuli-responsive hybrid drug enhances cancer cell death
Amplification of oxidative stress by a dual stimuli-responsive hybrid drug enhances cancer cell death
Cancer cells have elevated levels of reactive oxygen species. Here the authors show that cancer cells can be selectively killed in vitro and in vivoby an oxidative stress-activated drug, which amplifies the generation of reactive oxygen species while blocking the cells’ antioxidant defense.
- Joungyoun Noh
- , Byeongsu Kwon
- & Dongwon Lee
-
Article |
 Dissociation of Bak α1 helix from the core and latch domains is required for apoptosis
Dissociation of Bak α1 helix from the core and latch domains is required for apoptosis
During apoptosis, Bak undergoes major conformational changes that lead to mitochondrial permeabilization. Here, the authors characterize changes that occur within the Bak N-terminus using a series of antibodies and a novel tethering approach, demonstrating that dissociation of the α1 helix is a key early step in the unfolding of Bak.
- Amber E. Alsop
- , Stephanie C. Fennell
- & Ruth M. Kluck
-
Article |
 Attenuation of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay facilitates the response to chemotherapeutics
Attenuation of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay facilitates the response to chemotherapeutics
Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD) is a pathway that controls endogenous transcript levels and limits the production of aberrant mRNAs. Here the authors show that NMD is attenuated in cells treated with chemotherapeutic compounds through caspase-mediated proteolytic cleavage of UPF1, a key NMD effector.
- Maximilian W. Popp
- & Lynne E. Maquat
-
Article |
 Alendronate inhalation ameliorates elastase-induced pulmonary emphysema in mice by induction of apoptosis of alveolar macrophages
Alendronate inhalation ameliorates elastase-induced pulmonary emphysema in mice by induction of apoptosis of alveolar macrophages
Macrophages have a role in the pathogenesis of pulmonary emphysema. Here the authors show that inhalation—but not oral delivery—of the anti-osteoporosis drug alendronate attenuates lung damage in a mouse model of emphysema by inducing apoptosis of alveolar macrophages.
- Manabu Ueno
- , Toshitaka Maeno
- & Masahiko Kurabayashi
-
Article
| Open Access Highly specific in vivo gene delivery for p53-mediated apoptosis and genetic photodynamic therapies of tumour
Highly specific in vivo gene delivery for p53-mediated apoptosis and genetic photodynamic therapies of tumour
Alterations of p53 are associated with more than half of all human cancers. Here the authors present a new pH-sensitive nanoparticle that is delivered via systemic circulation and combines gene delivery to restore p53 with expression of Killerred protein to induce photosensitization.
- S.-Ja Tseng
- , Zi-Xian Liao
- & Ivan M. Kempson
-
Article |
 A lysine-rich motif in the phosphatidylserine receptor PSR-1 mediates recognition and removal of apoptotic cells
A lysine-rich motif in the phosphatidylserine receptor PSR-1 mediates recognition and removal of apoptotic cells
The phosphatidylserine receptor PSR-1 has been proposed to mediate recognition of apoptotic cells by phagocytes; however, this function has been contested. Yang et al. identify a lysine-rich motif in C. elegansPSR-1 that binds phosphatidylserine, and show that this motif is required for its phagocytic function.
- Hengwen Yang
- , Yu-Zen Chen
- & Ding Xue
-
Article |
 Modification of DBC1 by SUMO2/3 is crucial for p53-mediated apoptosis in response to DNA damage
Modification of DBC1 by SUMO2/3 is crucial for p53-mediated apoptosis in response to DNA damage
SIRT1 is a deacetylase that is negatively regulated by binding to DBC1. Here Park et al.show that DNA damage-induced SUMO2/3 conjugation of DBC1 promotes the SIRT1–DBC1 interaction, leading to an increase in acetylated p53 and induction of apoptosis.
- Jong Ho Park
- , Seong Won Lee
- & Chin Ha Chung
-
Article |
 PARP13 regulates cellular mRNA post-transcriptionally and functions as a pro-apoptotic factor by destabilizing TRAILR4 transcript
PARP13 regulates cellular mRNA post-transcriptionally and functions as a pro-apoptotic factor by destabilizing TRAILR4 transcript
The poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase PARP13 targets RNA viruses by binding to viral RNA and promoting its degradation by cellular decay factors such as the exosome. Todorova et al. find that PARP13 also plays a much broader role as a regulator of host mRNA stability, and promotes apoptosis by degrading TRAILR4transcripts.
- Tanya Todorova
- , Florian J. Bock
- & Paul Chang
-
Article |
 SNX13 reduction mediates heart failure through degradative sorting of apoptosis repressor with caspase recruitment domain
SNX13 reduction mediates heart failure through degradative sorting of apoptosis repressor with caspase recruitment domain
Identification of pathways that drive proper cardiac function is key to prevention and treatment of heart disease. Here the authors describe a novel pathway that regulates cardiomyocyte survival, which involves a sorting protein, SNX13, and its binding partner, ARC, a multifunctional inhibitor of apoptosis.
- Jun Li
- , Changming Li
- & Yi-Han Chen
-
Article |
 WT1 controls antagonistic FGF and BMP-pSMAD pathways in early renal progenitors
WT1 controls antagonistic FGF and BMP-pSMAD pathways in early renal progenitors
The transcription factor Wilms’ tumour 1 (WT1) regulates kidney development, and Wt1 mutations are associated with renal cancer. Here the authors identify WT1 target genes in renal progenitors during early kidney development in mouse embryos and show that loss of Wt1suppresses FGF and induces BMP signalling.
- Fariba Jian Motamedi
- , Danielle A. Badro
- & Andreas Schedl
-
Article |
 Skp2 suppresses apoptosis in Rb1-deficient tumours by limiting E2F1 activity
Skp2 suppresses apoptosis in Rb1-deficient tumours by limiting E2F1 activity
The pRb target E2F1 possesses contradictory activities in promoting proliferation and apoptosis. Here, the authors define a pRb-Skp2-p27-cyclin A-E2F1 survival pathway that can be disrupted to prevent Rb1-deficient tumorigenesis in the pituitary intermediate lobe.
- Zhonglei Lu
- , Frederick Bauzon
- & Liang Zhu
-
Article |
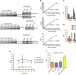 Differential affinity of FLIP and procaspase 8 for FADD’s DED binding surfaces regulates DISC assembly
Differential affinity of FLIP and procaspase 8 for FADD’s DED binding surfaces regulates DISC assembly
In response to activation of death receptors, a multimeric signalling complex assembles in which FADD binds caspase 8 and FLIP through structurally similar binding surfaces. Majkut et al.show that each surface preferentially binds to one of the two proteins, resulting in the formation of a trimeric intermediate.
- J. Majkut
- , M. Sgobba
- & D. B. Longley
-
Article |
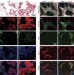 MafB promotes atherosclerosis by inhibiting foam-cell apoptosis
MafB promotes atherosclerosis by inhibiting foam-cell apoptosis
In the early stages of atherosclerosis, macrophages in the vessel wall convert into foam cells, which promote the rise of atherosclerotic plaques. Here Hamada et al. show that the macrophage transcription factor MafB inhibits foam-cell apoptosis, and that its absence promotes atherosclerosis development in mice.
- Michito Hamada
- , Megumi Nakamura
- & Satoru Takahashi
-
Article |
 UTX coordinates steroid hormone-mediated autophagy and cell death
UTX coordinates steroid hormone-mediated autophagy and cell death
Cells in Drosophila salivary glands undergo hormone-dependent apoptosis when larvae pupate. Here, the authors show that the histone methylase dUTX regulates activation of key cell death and autophagy genes leading to the removal of salivary glands during the Drosophilalarval–pupal transition.
- Donna Denton
- , May T. Aung-Htut
- & Sharad Kumar
-
Article |
 Caspase-mediated activation of Caenorhabditis elegans CED-8 promotes apoptosis and phosphatidylserine externalization
Caspase-mediated activation of Caenorhabditis elegans CED-8 promotes apoptosis and phosphatidylserine externalization
As they die, apoptotic cells present phosphatidylserine on the outer leaflet of the plasma membrane, which serves as an ‘eat-me’ signal for nearby phagocytes. Chen et al. identify the caspase substrate CED-8 as a key regulator of phosphatidylserine externalization during apoptosis in C. elegans.
- Yu-Zen Chen
- , James Mapes
- & Ding Xue
-
Article |
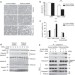 Pellino3 targets RIP1 and regulates the pro-apoptotic effects of TNF-α
Pellino3 targets RIP1 and regulates the pro-apoptotic effects of TNF-α
Pellino family proteins are ubiquitin ligases known to regulate immune signalling. Here Yang et al. show that Pellino3 regulates apoptotic TNF signalling by modulating the composition of the death-induced signalling complex, and that absence of Pellino3 sensitizes mice to TNF.
- Shuo Yang
- , Bingwei Wang
- & Paul N. Moynagh
-
Article |
 Smad6 inhibits non-canonical TGF-β1 signalling by recruiting the deubiquitinase A20 to TRAF6
Smad6 inhibits non-canonical TGF-β1 signalling by recruiting the deubiquitinase A20 to TRAF6
The cytokine TGF-β signals through canonical, Smad-dependent, and non-canonical, Smad-independent pathways. Jung et al. show that Smad6, an inhibitor of canonical TGF-β signalling, also inhibits a non-canonical pathway by recruiting a deubiquitinase to TRAF6.
- Su Myung Jung
- , Ji-Hyung Lee
- & Seok Hee Park
-
Article |
 Visualization of caspase-3-like activity in cells using a genetically encoded fluorescent biosensor activated by protein cleavage
Visualization of caspase-3-like activity in cells using a genetically encoded fluorescent biosensor activated by protein cleavage
Proteases of the caspase family are important regulators of apoptosis. Here, Zhang et al. present a genetically encoded protein biosensor that fluoresces if cleaved by caspase-3-like proteases, allowing real-time measurements of apoptosis in cells.
- Jiao Zhang
- , Xin Wang
- & Binghui Li
-
Article |
 Distinct pathways mediate axon degeneration during apoptosis and axon-specific pruning
Distinct pathways mediate axon degeneration during apoptosis and axon-specific pruning
Recent studies suggest that there is an overlap between neuronal apoptosis and axon-specific degeneration. Cusack and colleagues show that the caspase-dependent pathways mediating axon degeneration during apoptosis are distinct from those mediating localized axon pruning.
- Corey L. Cusack
- , Vijay Swahari
- & Mohanish Deshmukh
-
Article |
 FOXO3 signalling links ATM to the p53 apoptotic pathway following DNA damage
FOXO3 signalling links ATM to the p53 apoptotic pathway following DNA damage
The protein ataxia-telangiectasia mutated (ATM) detects DNA damage and can trigger cellular apoptosis, but how this process is regulated at the molecular level is unclear. Here, Chunget al. show that the transcription factor FOXO3 controls the formation of ATM-containing signalling complexes at sites of DNA damage that trigger apoptosis.
- Young Min Chung
- , See-Hyoung Park
- & Mickey C.-T. Hu
-
Article |
 Ubiquitination and degradation of the FADD adaptor protein regulate death receptor-mediated apoptosis and necroptosis
Ubiquitination and degradation of the FADD adaptor protein regulate death receptor-mediated apoptosis and necroptosis
Fas-associated protein with death domain (FADD) is part of a signalling complex that controls some forms of programmed cell death. Lee and colleagues demonstrate that FADD ubiquitination by the E3 ubiquitin ligase MKRN1 regulates FADD protein stability and thereby cell death.
- Eun-Woo Lee
- , Jung-Hoon Kim
- & Jaewhan Song
-
Article |
 miR-484 regulates mitochondrial network through targeting Fis1
miR-484 regulates mitochondrial network through targeting Fis1
Abnormal mitochondrial fission leads to apoptosis and disease. Li and colleagues reveal the mechanism with which the transcription factor Foxo3a suppresses Fis1-mediated mitochondrial fission and apoptosis in cardiomyocytes and adrenocortical cancer cells, which involves miR-484 inhibition of Fis1 translation.
- Kun Wang
- , Bo Long
- & Pei-Feng Li
-
Article |
 A mitochondria-targeted inhibitor of cytochrome c peroxidase mitigates radiation-induced death
A mitochondria-targeted inhibitor of cytochrome c peroxidase mitigates radiation-induced death
Radiomitigating compounds could be used to protect against ionizing radiation. In this study, mitochondria-targeted oleic and stearic acid derivatives are shown to inhibit pro-apoptotic oxidative events, prevent cell death, and protect mice against lethal doses of radiation.
- Jeffrey Atkinson
- , Alexandr A. Kapralov
- & Valerian E. Kagan
-
Article
| Open Access Synthetic human cell fate regulation by protein-driven RNA switches
Synthetic human cell fate regulation by protein-driven RNA switches
The control of cell fate and apoptosis is a continuing challenge in synthetic biology. In this study, systems are developed in which an intracellularly expressed genome-encoded protein simultaneously achieves up- and downregulation of two distinct apoptosis pathways.
- Hirohide Saito
- , Yoshihiko Fujita
- & Tan Inoue

 Male-killing symbiont damages host’s dosage-compensated sex chromosome to induce embryonic apoptosis
Male-killing symbiont damages host’s dosage-compensated sex chromosome to induce embryonic apoptosis