Central neuropathic pain
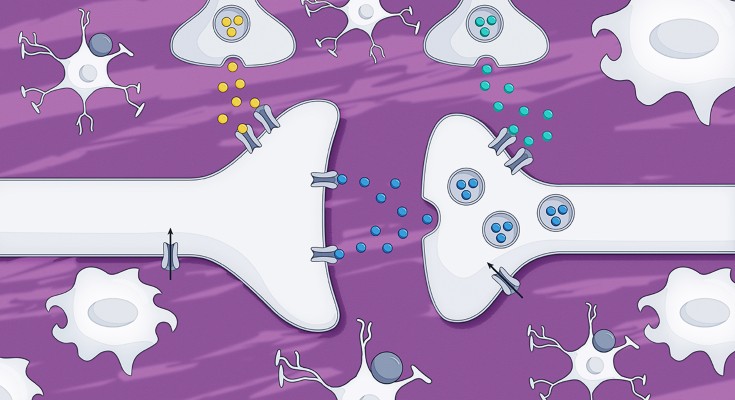
Central neuropathic pain arises from a lesion or disease of the central somatosensory nervous system such as brain injury, spinal cord injury, stroke or multiple sclerosis.

Central neuropathic pain arises from a lesion or disease of the central somatosensory nervous system such as brain injury, spinal cord injury, stroke or multiple sclerosis.
