Volume 7
-
No. 12 December 2023
Optoacoustically detected skin angiopathy correlates with diabetes stageThis issue highlights strategies towards the simplification of the operation of diagnostic assays for point-of-care use. It also describes plasmonically active fluorescent gold nanorods as antibody-conjugated labels for enhancing the sensitivity of lateral-flow assays, the fluorescence lifetime of injected indocyanine green as a universal marker of solid tumours in patients, that the growth of aortic aneurysms can be predicted via a physiomarker describing a transition from stable blood flow to unstable aortic fluttering, that RNAs derived from transposable elements are enriched in the cell-free transcriptome of patients with cancer, and that dermal features derived from optoacoustic tomograms can be used to correlate microangiopathy phenotypes with diabetes stage.
The cover illustrates that explainable morphophysiological features extracted via machine learning from raster-scan optoacoustic mesoscopy images of the skin can be used to correlate skin-microangiopathy phenotypes with diabetes stage.
See Karlas et al.
-
No. 11 November 2023
Functionally distinct T cells in viscoelastically dissimilar matricesThis issue highlights that interstitial-fluid shear stresses lower blood pressure in individuals with hypertension, that functionally distinct T cell populations can be generated from extracellular matrices with different viscoelasticity, a method for rapid single-cell physical phenotyping, a Cas12a-based assay for the detection of cellular traction forces, that elevated tissue-scale forces can drive foreign-body responses to implants, that advanced glycation end-products can mediate the crosslinking of liver extracellular matrix in cirrhosis, that bone-matrix mineralization induces a quiescent phenotype in breast cancer cells, an intravital method for measuring solid stresses in tumours, electro-metabolic coupling in vascularized cardiac organoids, and that microtopography can influence chromatin conformation and osteogenic differentiation in human mesenchymal stromal cells.
The cover illustrates that the viscoelasticity of extracellular matrices can be altered to generate functionally distinct T cell populations from T cells that received the same stimulation.
See Adu-Berchie et al.
-
No. 10 October 2023
In-ear monitoring of brain states and of lactate in sweatThis issue highlights advances in the application of wearable, ingestible or implantable bioelectronic devices for the monitoring of health status, disease progression or the effectiveness of treatment. It also includes electronic scaffolds for tracking the migration of brain cells after injury, and implants that facilitate closed-loop neuromodulation in small animals.
The cover illustrates the integration, on an earbud, of sensors for brain activity (via electroencephalography, electrooculography and electrodermal activity) and of lactate levels (electrochemically, in sweat).
See Xu et al.
-
No. 9 September 2023
Antigen-agnostic tumour tagging for CAR T cell therapyThis issue highlights the generation of T cells expressing a tumour-directed receptor constitutively and an inducible transgene, the suppression of tumour growth via the cooperative phagocytic activity of macrophages, a nanoparticle targeting myeloid-cell-rich haematopoietic organs for resolving immunoparalysis, the amphiphilic tagging of cancer cells for the universal redirection of CAR T cells against tumours, an interleukin-6-adsorbing hydrogel for the suppression of cytokine release syndrome, glycosylated antigens for the suppression of established immune responses, a fusion protein of an immunosuppressive enzyme for treating local inflammation, the transcriptomic profiling of the fate of human CAR T cells in vivo, and the microfluidic isolation of tumour-reactive lymphocytes from peripheral blood.
The cover illustrates that the tagging of tumour cells with an amphiphilic ligand for a chimaeric antigen receptor on T cells allows for the universal redirection of the cells against solid tumours.
See Zhang et al.
-
No. 8 August 2023
Imaging two PET tracers simultaneouslyThis issue highlights polarimetric endoscopy for the detection of laryngeal lesions, the imaging of posterior scleral birefringence to predict the onset of myopia, the magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging of the metabolism of glucose and neurotransmitters in the human brain, the quantification of intratumoural heterogeneity via PET–MRI and machine learning, the simultaneous imaging of two PET tracers, and lens-free holography and deep learning for the quantification of viral plaque.
The cover illustrates a reconstruction method for the simultaneous imaging of two radiotracers for PET.
See Pratt et al.
-
No. 7 July 2023
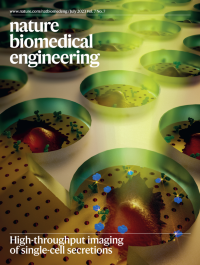
High-throughput imaging of single-cell secretionsThis issue highlights a caller of genomic variants that leverages machine learning to reduce read-mapping costs, a method for the in vivo screening of hydrogels for antifibrotic properties, collagen-replacement therapy via mRNA-encapsulating extracellular vesicles delivered intradermally via microneedles, the high-throughput in vivo screening of libraries of nanoparticle formulations for the delivery of mRNA to the liver, an investigation of the effects of the spatial distribution and placement of antigens in nanoparticle-based cancer vaccines, a subcutaneous Zika vaccine consisting of a hydrogel electrostatically entrapping the live virus, and a microwell array for the image-based spatiotemporal profiling of single-cell secretions.
The cover illustrates a plasmonic microwell array for the spatiotemporal monitoring of secreted proteins from hundreds of single cells.
See Ansaryan et al.
-
No. 6 June 2023
A vision transformer for decoding surgical activityThis issue highlights representation-learning strategies for processing multimodal inputs and for improving the robustness and training efficiency of machine-learning models, a vision transformer for decoding surgical activity, a machine-learning pipeline for mining the entire space of polypeptide-chain sequences to identify potent antimicrobial peptides, ensembles of machine-learning models for explaining the molecular basis of synergetic drug combinations, and a machine-learning model that links genome sequence and non-coding RNA expression at the cell-type level.
The cover illustrates a machine-learning system for the decoding of intraoperative surgical activity from videos commonly collected during robotic surgeries.
See Kiyasseh et al.
-
No. 5 May 2023
Peptide-boosted uptake of CRISPR enzymesThis issue highlights that prime editing can efficiently correct the sickle-cell allele in patient haematopoietic stem cells, a Cas9-based gene therapy for Huntington’s disease tested in pigs, the efficient peptide-mediated delivery of CRISPR enzymes, a method for the knock-in and stable expression of large payloads in primary human cells, that adding cytosine stretches to the 5′ end of single-guide RNAs constrains the activity of Cas9, and a library of cytosine base editors for the precise ablation of every mtDNA protein-coding gene in the mouse mitochondrial genome.
The cover illustrates that a peptide identified via screening aids the delivery of CRISPR ribonucleoprotein into cells, increasing the yield of edited primary human lymphocytes.
See Foss et al.
-
No. 4 April 2023
Bioresorbable optoelectronic neural interfacesThis issue includes a focus on neurotechnologies for the treatment of conditions of the central and peripheral nervous systems, with emphasis on neural interfaces and on motor and visual neural prostheses.
The cover illustrates a bioresorbable silicon-based optoelectronic thin film for the selective excitation or inhibition of neural activities in peripheral and central nervous tissues.
See Huang et al.
-
No. 3 March 2023
Hepatocyte-targeting nanoparticles for enhanced hepatobiliary MRIThis issue highlights that hepatobiliary MRI can be enhanced by an ultrasmall nanoparticle targeting hepatocytes, that transmembrane water-efflux rate is a sensitive biomarker of the expression of aquaporin-4, a hydrogel-based metamaterial for profiling extracellular vesicles in patient samples, a near-infrared fluorophore for the imaging of aggregates of amyloid-β and tau through the skull of mice, nanoparticles producing ultrasound-induced afterglow luminescence, a library of renally cleared fluorescence probes for the tracking of tumour-infiltrating leukocytes, liposomal nanoparticles for spatially mapping light in deep tissue via MRI, and a tomographic method for the location of photon pairs produced from high-energy X-rays.
The cover illustrates an ultrasmall nanoparticle with a manganese ferrite core and with surface ligands with high specificity for hepatocytes, for use as a contrast agent for imaging the liver and the biliary tree.
See Zhang et al.
-
No. 2 February 2023
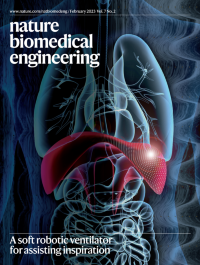
A soft robotic ventilator for assisting inspirationThis issue highlights an intravascular infused biomaterial for treating inflammation, an implantable soft robotic ventilator, the intraoperative histology of bone tissue via photoacoustic microscopy and deep learning, neural organoids for spinal-cord regeneration, piezoelectric nanoparticles for deep brain stimulation, receptor agonists with enhanced pharmacokinetics, and alterations in chromatin organization in diseased tenocytes.
The cover illustrates that a contractile soft robotic actuator implanted above the diaphragm can augment its respiratory performance (as indicated by the right half of the image).
See Hu et al.
-
No. 1 January 2023
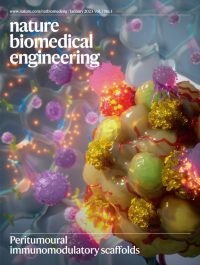
Peritumoural immunomodulatory scaffoldsThis issue highlights an anti-CD98 antibody with pH-dependent binding for antitumour therapy, cytotoxic CAR T cells derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells with enhanced proliferation and persistency in solid tumours, intragastrically delivered polymeric micelles releasing butyrate for the restoration of barrier-protective responses in mouse models of gut inflammation, peritumourally implanted immunomodulatory macroporous scaffolds providing systemic antitumour immunity, and pathogen-mimicking polymer nanoparticles inducing T-helper-17-cell-mediated antitumour immunity
The cover illustrates that a scaffold releasing specific small molecules and antibodies can suppress regulatory T cells and attract and stimulate effector T cells when implanted peritumourally in mice.
See Majedi et al.