Volume 6
-
No. 12 December 2022
Context-aware graph deep learning for prognostic histopathologyThis issue highlights the development of machine-learning models for the detection of signs of disease in external photographs of the eyes, for the optimization of the trade-off between prediction performance and feature cost in healthcare applications, for the expert-level detection of pathologies from unannotated chest X-ray images, for transforming the style of tissue images, for the fast search and retrieval of whole-slide images, for the derivation of prognostic contextual histopathological features from whole-slide images of tumours, and for the characterization of tumour microenvironments from spatial protein profiles.
The cover illustrates that graph deep learning applied to gigapixel whole-slide images of tumours can leverage information in the tumour microenvironment to derive interpretable histopathological features with prognostic value.
See Lee et al.
-
No. 11 November 2022
Monitoring metabolites and nutrients in sweatThis issue highlights a low-cost device to screen for hearing loss, microneedle arrays for the wireless monitoring of multiple biomarkers in interstitial fluid, a wearable biosensor for the detection of metabolites and nutrients in sweat, a human intestine-on-a-chip for the recapitulation of essential features of environmental enteric dysfunction, a humanized minipig model for the toxicological testing of therapeutic antibodies, engineered adeno-associated viruses with enhanced transduction of cells of the central nervous system or with size-optimized genomes encoding compact adenine base editors, the generation of potent allogeneic chimaeric antigen receptor T cells devoid of alloreactive potential, and the mapping and activation of pancreatic nerves for the study of how they regulate glucose metabolism.
The cover illustrates a wearable electrochemical biosensor for the continuous detection of trace levels of metabolites and nutrients in sweat.
See Wang et al.
-
No. 10 October 2022
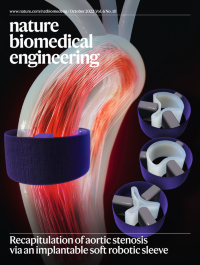
Recapitulation of aortic stenosis via an implantable soft robotic sleeveThis issue highlights an inexpensive catheter-like device for sensing gastrointestinal motility, collagen-binding peptides that home to osteoarthritic tissue, and implantable biomaterials for a number of biomedical applications — in particular, strain-programmed patches for diabetic-wound healing, a soft robotic sleeve for the modelling of aortic stenosis, injectable depots for brachytherapy, adhesive drug depots for tendon healing, and antibiotic-loaded bone-cement matrices for the treatment of bone infections.
The cover illustrates an implantable soft robotic sleeve that recapitulates the haemodynamics and biomechanics of aortic stenosis.
See Rosalia et al.
-
No. 9 September 2022
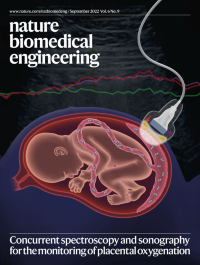
Concurrent spectroscopy and sonography for the monitoring of placental oxygenationThis issue highlights optical, optoacoustic, ultrasound and magnetic-resonance imaging technologies applied to the monitoring of oxygen haemodynamics in the placenta, to the longitudinal assessment of amyloid-β deposits in mice, to measuring autophagic flux in the hearts of live mice, to uncovering nanostructures in iteratively expanded ex vivo brain tissue, and to detect inflammation-associated mRNA in live mice.
The cover illustrates the integration of optical spectroscopy and ultrasound imaging to non-invasively monitor placental oxygen haemodynamics in pregnant women.
See Wang et al.
-
No. 8 August 2022
Automated Cas13-based detection of SARS-CoV-2 in salivaThis issue highlights point-of-care assays and sequencing technology for the detection of infectious agents and for the study of host responses to infectious diseases.
The cover illustrates a microfluidic cartridge for the automated amplification and detection of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in saliva via the Cas13-mediated cleavage of a quenched fluorophore.
See Chandrasekaran et al.
-
No. 7 July 2022
An inhalable virus-like-particle vaccine against COVID-19This issue highlights an inhalable virus-like-particle vaccine against COVID-19, a method for the rapid cloning of antigen-specific T cell receptors, a protease-sensitive mask for interleukin-12 to lower its toxicity, CAR T cells expressing a bacterial virulence factor, libraries of immune cells displaying a diverse repertoire of chimeric antigen receptors, a barcoded library of CD19-specific chimeric antigen receptors, the encapsulation of antibiotics in glucosylated polymeric nanoparticles for oral delivery, enucleated human mesenchymal stromal cells for drug delivery, tumour vaccines produced in the gut by ingested engineered bacteria, and an engineered biotherapeutic for the prevention of antibiotic-induced dysbiosis.
The cover illustrates an inhalable virus-like-particle vaccine made of exosomes derived from lung cells and decorated with a recombinant SARS-CoV-2 receptor-binding domain.
See Wang et al.
-
No. 6 June 2022
Wireless endovascular stimulation of peripheral nervesThis issue highlights the restoration of glucose homeostasis via ultrasound-mediated stimulation of hepatoportal nerves, an endovascular implant for peripheral-nerve stimulation, an analysis of the performance of compression and amplification algorithms for hearing aids, a cutaneous mechanoneural interface for eliciting tactile feedback through electrical stimulation, an organic implant for wireless peripheral-nerve stimulation, deep brain stimulation by near-infrared light via injected photothermal transducers, and modular hardware and software for the remote operation of wireless networks for the study of rodent behaviour.
The cover illustrates a wireless and battery-free millimetric endovascular implant for the stimulation of peripheral nerves that are difficult to reach by surgery.
See Chen et al.
-
No. 5 May 2022
Finding tumours via Cerenkov luminescence imagingThis issue highlights performance and functionality enhancements in hardware and software for a range of imaging modalities, including Cerenkov luminescence imaging, light-sheet microscopy, photoacoustic computed tomography, ultrasound localization microscopy, chemical exchange saturation transfer magnetic resonance imaging, magnetic resonance fingerprinting, and a number of optical-imaging techniques.
The cover illustrates that a clinical fibrescope for Cerenkov luminescence imaging can be used to detect tumour location in patients with cancer who had undergone routine molecular imaging.
See Pratt et al.
-
No. 4 April 2022
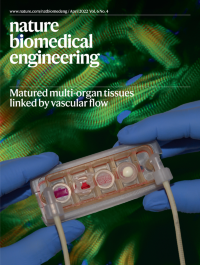
Matured multi-organ tissues linked by vascular flowThis issue highlights that forced mitophagy can reduce mtDNA heteroplasmy in mitochondrial replacement therapy, a multi-organ chip with matured tissues, the maturation of human cardiac microtissues on a chip, methods for the expansion of human atrial myocytes, for the reprogramming of fibroblasts into cardiovascular progenitor cells and for the conversion of quiescent cardiomyocytes into pacemaker cells, and organoids recapitulating neural-tube morphogenesis, programmatically patterned from the orthogonal differentiation of pluripotent stem cells, derived from pluripotent stem cells with genetically ablated cilia, or used for the screening of modulators of gut epithelia.
The cover illustrates tissue chips with matured human heart, liver, bone and skin tissue niches linked by recirculating vascular flow.
See Ronaldson-Bouchard et al.
-
No. 3 March 2022
Spectral fingerprinting of ovarian cancer in serum samplesThis issue highlights the performance of paper-based cell-free diagnostics for the detection of the Zika and chikungunya viruses in serum samples, a method for the tracking of thousands of mutations with fewer reads per locus than conventional hybrid-capture duplex sequencing, that ovarian cancer can be predicted via a fingerprint obtained via machine learning from the emissions of carbon-nanotube sensors in serum samples, fast and sensitive electromechanical and biochemical methods for the detection of biomolecules, cell-free diagnostics via multi-arm junction RNAs that execute molecular logic, and the urinary detection of early responses to checkpoint blockade via protease-cleaved antibody-conjugated sensors.
The cover illustrates that the analysis, via machine learning, of near-infrared-fluorescence emissions of carbon-nanotube sensors placed in serum samples can be used to predict ovarian cancer.
See Kim et al.
-
No. 2 February 2022
Prime editing of pathogenic mutations in mouse eyes and liversThis issue highlights microfluidic sorting for the recovery of potent tumour-infiltrating lymphocytes, the generation of potent CAR T cells in one day, systemic anticancer immunity via intratumourally injected alum-tethered cytokines, synergistic checkpoint blockade and radiotherapy–radiodynamic therapy via nanoscale metal–organic frameworks, in vivo genome editing via disruption of Cas9 activity in the liver, a brain-wide Cas9-mediated therapy for familial Alzheimer’s disease, prime editing for the correction of mutations in adult mice, the restoration of dystrophin expression by suppressing a nonsense mutation via unnatural amino acids, and the reversal of RNA toxicity in myotonic dystrophy via a decoy RNA-binding protein.
The cover illustrates that prime editing can precisely correct disease-causing mutations in adult mice with hereditary tyrosinaemia and Leber congenital amaurosis.
See Jang et al.
-
No. 1 January 2022
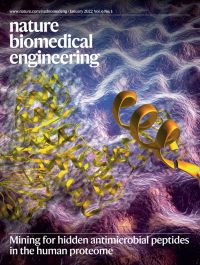
Mining for hidden antimicrobial peptides in the human proteomeThis issue highlights biomaterial vaccines that protect mice and pigs against septic shock from bacterial infections, cancer vaccines from cryogenically silicified tumour cells, the biomaterial-mediated modulation of oral microbiota in synergy with checkpoint blockade, systemic anticancer responses by flagellated bacteria coated with antigen-adsorbing polymer nanoparticles, mesenchymal stromal cells coated with a gel incorporating chemomechanical cues for the inhibition of aberrant tissue remodelling, the mining of the human proteome for peptides with antibacterial activity, mitophagy inducers that improve the pathology of Alzheimer’s disease, and genetically programmed biosensors for enhancing the tropism of bacteria.
The cover illustrates that the human proteome can be algorithmically mined to identify thousands of encrypted peptides with antibacterial activity.
See Torres et al.