Abstract
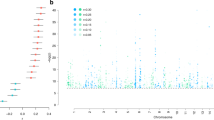
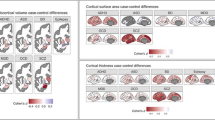
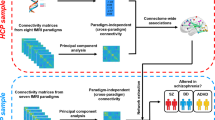
Psychiatric disorders are complex, heritable and highly polygenic. Supported by findings of abnormalities in functional magnetic resonance imaging-based measures of brain connectivity, current theoretical and empirical accounts have conceptualized them as disorders of brain connectivity and dysfunctional integration of brain signaling. However, the extent to which these findings reflect common genetic factors remains unclear. Here we performed a multivariate genome-wide association analysis of functional magnetic resonance imaging-based functional brain connectivity in a sample of 30,701 individuals from the UK Biobank and investigated the shared genetic determinants with eight major psychiatric disorders. The analysis revealed significant genetic overlap between functional brain connectivity and schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, autism spectrum disorder, anxiety and major depression, adding further genetic support for the dysconnectivity hypothesis of psychiatric disorders and identifying potential genetic and functional targets for future studies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$59.00 per year
only $4.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data used in this study are part of the publicly available UK Biobank initiative (https://www.ukbiobank.ac.uk/). Summary statistics for the disorders are publicly available through their respective consortia (Supplementary Table 1). The summary statistics for the multivariate analyses are available on GitHub (https://www.github.com/norment/open-science).
Code availability
Code is publicly available on GitHub (https://www.github.com/norment/open-science).
References
Anttila, V. et al. Analysis of shared heritability in common disorders of the brain. Science 360, eaap8757 (2018).
Fullerton, J. M. & Nurnberger, J. I. Polygenic risk scores in psychiatry: will they be useful for clinicians? F1000Research 8, PMC6676506 (2019).
Smoller, J. W. et al. Psychiatric genetics and the structure of psychopathology. Mol. Psychiatry 24, 409–420 (2019).
Sullivan, P. F. & Geschwind, D. H. Defining the genetic, genomic, cellular, and diagnostic architectures of psychiatric disorders. Cell 177, 162–183 (2019).
Vos, T. et al. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 396, 1204–1222 (2020).
Paulus, M. P. & Thompson, W. K. The challenges and opportunities of small effects: the new normal in academic psychiatry. JAMA Psychiatry 76, 353–354 (2019).
Pettersson-Yeo, W., Allen, P., Benetti, S., McGuire, P. & Mechelli, A. Dysconnectivity in schizophrenia: where are we now? Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 35, 1110–1124 (2011).
Syan, S. K. et al. Resting-state functional connectivity in individuals with bipolar disorder during clinical remission: a systematic review. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. JPN 43, 298–316 (2018).
Hong, S.-J. et al. Atypical functional connectome hierarchy in autism. Nat. Commun. 10, 1022 (2019).
Gao, Y. et al. Impairments of large-scale functional networks in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder: a meta-analysis of resting-state functional connectivity. Psychol. Med. 49, 2475–2485 (2019).
Brakowski, J. et al. Resting state brain network function in major depression—depression symptomatology, antidepressant treatment effects, future research. J. Psychiatr. Res. 92, 147–159 (2017).
Akiki, T. J., Averill, C. L. & Abdallah, C. G. A network-based neurobiological model of PTSD: evidence from structural and functional neuroimaging studies. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 19, 81 (2017).
Xu, J. et al. Anxious brain networks: a coordinate-based activation likelihood estimation meta-analysis of resting-state functional connectivity studies in anxiety. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 96, 21–30 (2019).
Fuglset, T. S., Landrø, N. I., Reas, D. L. & Rø, Ø. Functional brain alterations in anorexia nervosa: a scoping review. J. Eat. Disord. 4, 32 (2016).
Wen, Z. et al. Synaptic dysregulation in a human iPS cell model of mental disorders. Nature 515, 414–418 (2014).
Devor, A. et al. Genetic evidence for role of integration of fast and slow neurotransmission in schizophrenia. Mol. Psychiatry 22, 792–801 (2017).
Howard, D. M. et al. Genome-wide association study of depression phenotypes in UK Biobank identifies variants in excitatory synaptic pathways. Nat. Commun. 9, 1470 (2018).
Trubetskoy, V., Pardiñas, A.F., Qi, T. et al. Mapping genomic loci implicates genes and synaptic biology in schizophrenia. Nature 604, 502–508 (2022).
Lopez de Lara, C. et al. Implication of synapse-related genes in bipolar disorder by linkage and gene expression analyses. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 13, 1397–1410 (2010).
Arnatkeviciute, A., Fulcher, B., Bellgrove, M. & Fornito, A. Where the genome meets the connectome: Understanding how genes shape human brain connectivity. NeuroImage 244, 118570 (2021).
Barabási, D. L. & Barabási, A.-L. A genetic model of the connectome. Neuron 105, 435–445.e5 (2020).
Fornito, A. et al. Genetic influences on cost-efficient organization of human cortical functional networks. J. Neurosci. 31, 3261–3270 (2011).
Smith, S. M. et al. An expanded set of genome-wide association studies of brain imaging phenotypes in UK Biobank. Nat. Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41593-021-00826-4 (2021).
Yang, Z. et al. Genetic and environmental contributions to functional connectivity architecture of the human brain. Cereb. Cortex 26, 2341–2352 (2016).
Cao, H., Zhou, H. & Cannon, T. D. Functional connectome-wide associations of schizophrenia polygenic risk. Mol. Psychiatry https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-020-0699-3 (2020).
Miller, D. R. et al. Posttraumatic stress disorder symptom severity is associated with reduced default mode network connectivity in individuals with elevated genetic risk for psychopathology. Depress. Anxiety 34, 632–640 (2017).
Hibar, D. P. et al. Cortical abnormalities in bipolar disorder: an MRI analysis of 6503 individuals from the ENIGMA Bipolar Disorder Working Group. Mol. Psychiatry 23, 932–942 (2018).
Walton, E. et al. Exploration of shared genetic architecture between subcortical brain volumes and anorexia nervosa. Mol. Neurobiol. 56, 5146–5156 (2019).
Zhao, B. et al. Large-scale GWAS reveals genetic architecture of brain white matter microstructure and genetic overlap with cognitive and mental health traits (n = 17,706). Mol. Psychiatry https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-019-0569-z (2019).
van der Meer, D. et al. Understanding the genetic determinants of the brain with MOSTest. Nat. Commun. 11, 3512 (2020).
Smith, S. M. et al. Network modelling methods for FMRI. NeuroImage 54, 875–891 (2011).
Smitha, K. A. et al. Resting state fMRI: a review on methods in resting state connectivity analysis and resting state networks. Neuroradiol. J. 30, 305–317 (2017).
Kaufmann, T. et al. Disintegration of sensorimotor brain networks in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Bull. 41, 1326–1335 (2015).
Shi, H., Mancuso, N., Spendlove, S. & Pasaniuc, B. Local genetic correlation gives insights into the shared genetic architecture of complex traits. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 101, 737–751 (2017).
Smeland, O. B. et al. Discovery of shared genomic loci using the conditional false discovery rate approach. Hum. Genet. 139, 85–94 (2020).
Demontis, D. et al. Discovery of the first genome-wide significant risk loci for attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Nat. Genet. 51, 63–75 (2019).
Duncan, L. et al. Significant locus and metabolic genetic correlations revealed in genome-wide association study of anorexia nervosa. Am. J. Psychiatry 174, 850–858 (2017).
Otowa, T. et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies of anxiety disorders. Mol. Psychiatry 21, 1391–1399 (2016).
Grove, J. et al. Identification of common genetic risk variants for autism spectrum disorder. Nat. Genet. 51, 431–444 (2019).
Mullins, N. et al. Genome-wide association study of more than 40,000 bipolar disorder cases provides new insights into the underlying biology. Nat. Genet. 53, 817–829 (2021).
Wray, N. R. et al. Genome-wide association analyses identify 44 risk variants and refine the genetic architecture of major depression. Nat. Genet. 50, 668–681 (2018).
Duncan, L. E. et al. Largest GWAS of PTSD (N = 20 070) yields genetic overlap with schizophrenia and sex differences in heritability. Mol. Psychiatry 23, 666–673 (2018).
Pardiñas, A. F. et al. Common schizophrenia alleles are enriched in mutation-intolerant genes and in regions under strong background selection. Nat. Genet. 50, 381–389 (2018).
Watanabe, K. et al. A global overview of pleiotropy and genetic architecture in complex traits. Nat. Genet. 51, 1339–1348 (2019).
Jiang, X. et al. Genome-wide association study in 79,366 European-ancestry individuals informs the genetic architecture of 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels. Nat. Commun. 9, 260 (2018).
Watanabe, K., Taskesen, E., van Bochoven, A. & Posthuma, D. Functional mapping and annotation of genetic associations with FUMA. Nat. Commun. 8, 1826 (2017).
Koopmans, F. et al. SynGO: an evidence-based, expert-curated knowledge base for the synapse. Neuron 103, 217–234.e4 (2019).
Dean, C. et al. Synaptotagmin-IV modulates synaptic function and long-term potentiation by regulating BDNF release. Nat. Neurosci. 12, 767–776 (2009).
Dean, C. et al. Neurexin mediates the assembly of presynaptic terminals. Nat. Neurosci. 6, 708–716 (2003).
Jassal, B. et al. The reactome pathway knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 48, D498–D503 (2020).
Friston, K., Brown, H. R., Siemerkus, J. & Stephan, K. E. The dysconnection hypothesis. Schizophr. Res. 176, 83–94 (2016).
van den Heuvel, M. P. & Sporns, O. A cross-disorder connectome landscape of brain dysconnectivity. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 20, 435–446 (2019).
Kaufmann, T. et al. Task modulations and clinical manifestations in the brain functional connectome in 1615 fMRI datasets. NeuroImage 147, 243–252 (2017).
Frei, O. et al. Bivariate causal mixture model quantifies polygenic overlap between complex traits beyond genetic correlation. Nat. Commun. 10, 2417–2417 (2019).
Werme, J., van der Sluis, S., Posthuma, D. & de Leeuw, C. A. An integrated framework for local genetic correlation analysis. Nat. Gen. 54, 274–282 (2022).
Finn, E. S. et al. Functional connectome fingerprinting: identifying individuals using patterns of brain connectivity. Nat. Neurosci. 18, 1664–1671 (2015).
Kaufmann, T. et al. Delayed stabilization and individualization in connectome development are related to psychiatric disorders. Nat. Neurosci. 20, 513–515 (2017).
Lynall, M.-E. et al. Functional connectivity and brain networks in schizophrenia. J. Neurosci. 30, 9477–9487 (2010).
Rolls, E. T., Cheng, W. & Feng, J. Brain dynamics: the temporal variability of connectivity, and differences in schizophrenia and ADHD. Transl. Psychiatry 11, 70 (2021).
Shadrin, A. A. et al. Vertex-wise multivariate genome-wide association study identifies 780 unique genetic loci associated with cortical morphology. NeuroImage. 244, 118603 (2021).
Shadrin, A. A. et al. Vertex-wise multivariate genome-wide association study identifies 780 unique genetic loci associated with cortical morphology. NeuroImage 244, 118603 (2021).
Shadrin, A. A. et al. Novel loci associated with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder are revealed by leveraging polygenic overlap with educational attainment. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 57, 86–95 (2018).
Bycroft, C. et al. The UK Biobank resource with deep phenotyping and genomic data. Nature 562, 203–209 (2018).
Alfaro-Almagro, F. et al. Image processing and quality control for the first 10,000 brain imaging datasets from UK Biobank. NeuroImage 166, 400–424 (2018).
Jenkinson, M., Beckmann, C. F., Behrens, T. E. J., Woolrich, M. W. & Smith, S. M. FSL. NeuroImage 62, 782–790 (2012).
Smith, S. M. et al. Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. NeuroImage 23, S208–S219 (2004).
Jenkinson, M., Bannister, P., Brady, M. & Smith, S. Improved optimization for the robust and accurate linear registration and motion correction of brain images. NeuroImage 17, 825–841 (2002).
Griffanti, L. et al. ICA-based artefact removal and accelerated fMRI acquisition for improved resting state network imaging. NeuroImage 95, 232–247 (2014).
Salimi-Khorshidi, G. et al. Automatic denoising of functional MRI data: combining independent component analysis and hierarchical fusion of classifiers. NeuroImage 90, 449–468 (2014).
Beckmann, C. F. & Smith, S. M. Probabilistic independent component analysis for functional magnetic resonance imaging. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 23, 137–152 (2004).
rfMRI_ICA_d25. FMRIB Software Library https://www.fmrib.ox.ac.uk/ukbiobank/group_means/rfMRI_ICA_d25.html.
Smith, S. M. et al. Functional connectomics from resting-state fMRI. Spec. Issue Connect. 17, 666–682 (2013).
Woolrich, M. W., Behrens, T. E. J., Beckmann, C. F., Jenkinson, M. & Smith, S. M. Multilevel linear modelling for FMRI group analysis using Bayesian inference. NeuroImage 21, 1732–1747 (2004).
Yeo, B. T. T. et al. The organization of the human cerebral cortex estimated by intrinsic functional connectivity. J. Neurophysiol. 106, 1125–1165 (2011).
Chang, C. C. et al. Second-generation PLINK: rising to the challenge of larger and richer datasets. Gigascience 4, 7 (2015).
Andreassen, O. A. et al. Improved detection of common variants associated with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder using pleiotropy-informed conditional false discovery rate. PLoS Genet. 9, e1003455 (2013).
Finucane, H. K. et al. Partitioning heritability by functional annotation using genome-wide association summary statistics. Nat. Genet. 47, 1228–1235 (2015).
Bulik-Sullivan, B. K. et al. LD Score regression distinguishes confounding from polygenicity in genome-wide association studies. Nat. Genet. 47, 291–295 (2015).
Bulik-Sullivan, B. et al. An atlas of genetic correlations across human diseases and traits. Nat. Genet. 47, 1236–1241 (2015).
Lee, J. J., McGue, M., Iacono, W. G. & Chow, C. C. The accuracy of LD Score regression as an estimator of confounding and genetic correlations in genome-wide association studies. Genet. Epidemiol. 42, 783–795 (2018).
Loughnan, R. J. et al. Generalization of cortical MOSTest genome-wide associations within and across samples. NeuroImage 263, 119632 (2022).
Acknowledgements
The authors were funded by the Research Council of Norway (#276082 LifespanHealth, #323961 BRAINGAP, #223273 NORMENT, #283798 ERA-NET Neuron SYNSCHIZ, #249795, #298646 and #300767), the South-East Norway Regional Health Authority (2019101, 2019107 and 2020086) and the European Research Council under the European Union’s Horizon2020 Research and Innovation program (ERC Starting Grant #802998), as well as the Horizon2020 Research and Innovation Action Grant CoMorMent (#847776). This research has been conducted using the UK Biobank Resource (access code 27412, https://www.ukbiobank.ac.uk/). This work was performed on the TSD (Tjenester for Sensitive Data) facilities, owned by the University of Oslo, operated and developed by the TSD service group at the University of Oslo, IT-Department (USIT). Computations were also performed on resources provided by UNINETT Sigma2—the National Infrastructure for High Performance Computing and Data Storage in Norway.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
D.R. and T.K. conceived the study; D.R. analyzed the data with contributions from T.K.; D.R., D.v.d.M., D.A., O.F., A.A.S., R.L., C.C.F., A.M.D., O.A.A., L.T.W. and T.K. contributed with conceptual input on methods and/or interpretation of results; D.R. and T.K. wrote the first draft of the paper, and D.R., D.v.d.M., D.A., O.F., A.A.S., R.L., C.C.F., A.M.D., O.A.A., L.T.W. and T.K. contributed to the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
D.R., D.v.d.M., D.A., O.F., A.A.S., R.L., C.C.F., L.T.W. and T.K. declare no conflicts of interest. O.A.A. is a consultant to HealthLytix and received speakers honorarium from Lundbeck. A.M.D. is a Founder of and holds equity in CorTechs Labs, Inc., and serves on its Scientific Advisory Board. The terms of this arrangement have been reviewed and approved by UCSD in accordance with its conflict of interest policies.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Mental Health thanks Andrew Grotzinger and the other, anonymous, reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figs. 1–9 and Tables 1–8.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Roelfs, D., van der Meer, D., Alnæs, D. et al. Genetic overlap between multivariate measures of human functional brain connectivity and psychiatric disorders. Nat. Mental Health 2, 189–199 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s44220-023-00190-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44220-023-00190-1
This article is cited by
-
Abundant pleiotropy across neuroimaging modalities identified through a multivariate genome-wide association study
Nature Communications (2024)