Abstract
UV irradiation is an efficient tool for the disinfection of viruses in general and coronavirus specifically. This study explores the disinfection kinetics of SARS-CoV-2 variants wild type (similar to the Wuhan strain) and three variants (Alpha, Delta, and Omicron) by 267 nm UV-LED. All variants showed more than 5 logs average reduction in copy number at 5 mJ/cm2 but inconsistency was evident, especially for the Alpha variant. Increasing the dose to 7 mJ/cm2 did not increase average inactivation but did result in a dramatic decrease in the inactivation inconsistency making this dose the recommended minimum. Sequence analysis suggests that the difference between the variants is likely due to small differences in the frequency of specific UV extra-sensitive nucleotide sequence motifs although this hypothesis requires further experimental testing. In summary, the use of UV-LED with their simple electricity need (can be operated from a battery or photovoltaic panel) and geometrical flexibility could offer many advantages in the prevention of SARS-CoV-2 spread, but minimal UV dose should be carefully considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The efficiency of ultraviolet (UV) irradiation depends on multiple factors such as UV dose, irradiance, irradiation source, microorganism and strain type, matrix, and UV wavelength. UV light-emitting diodes (UV LEDs) emit UV light at specific wavelengths with relatively narrow full width at half maximum (FWHM) bandwidths. For example, UV LED or polychromatic mercury wavelengths in the germicidal range showed lower effectiveness at higher UV wavelengths1,2, while discrepancies of the time–dose reciprocity law were found for UV LED of different wavelengths and UV-damage mechanisms (Ref.3; also see Table 2).
UV irradiation is efficient in the inactivation of viruses in various environments such as aqueous solutions1,4, on surfaces5,6, and in air/bioaerosols7,8. UV irradiation was also found efficient in the inactivation of human coronaviruses (e.g., hOC431) and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV2)9,10. However, the SARS-CoV-2 outbreaks are characterized by the rapid appearance of variants11,12, making comparisons between studies done on different SARS-CoV-2 variants complicated. Our previous study examined the impact of UV LED wavelengths on one strain of human coronavirus (hCV-431). Here we examined the sensitivity of four different variants of the SARS-CoV-2 (wild type, Alpha, Delta, and Omicron) to UV-LED germicidal wavelength with peak emission at 267 nm.
Results and discussion
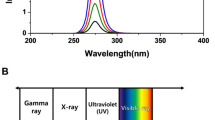
The UV-LED spectra exhibited peak emission at 267 nm with narrow FWHM bandwidth of 12 nm (Fig. 1).
At dose zero (no UV exposure), a variation was found among initial virus copy numbers of the different variants but one-way ANOVA analysis revealed no statistically significant difference (F3,60 = 0.2941, p = 0.83). The irradiation time and dose (fluence) response curve of different SARS-CoV-2 variants to 267 nm UV LED is presented in Fig. 2. First statistically significant inactivation for the w.t., Delta and Omicron variants required exposure to 2 mJ/cm2, while the Alpha variant required 5 mJ/cm2 (Fig. 2b), with higher doses resulting in plateauing up to the maximal dose (10 mJ/cm2). Interestingly, variability in the inactivation efficiency was both UV dose- and variant-dependent, as evident by the error bars size (Fig. 2) and the large coefficient of variance, especially for the Alpha variant (Table 1). This variability at the lower doses should play a role when designing a disinfection system to mitigate coronaviruses and a UV-LED dose of 7 mJ/cm2 is recommended. Additionally, the LED incident irradiance was low in this case—however more powerful LEDs (leading to higher radiant flux at a given exposure time) could mitigate the risk in this variability and should be examined.
To decipher the mechanism underlying the different inactivation efficiency we looked further into the variant's sequences focusing on the sequences stretch YTTC and YCTY ('Y' being C or T), consensus for the highest intensity UV-induced 6-4PP adduct and CPD damage respectively17. Table 2 report the number of appearances of these sequences in the different variant's sequences (see sequence alignment in Supplementary Fig. S1), demonstrating the Alpha variant has the lowest appearance of such sequences, in agreement with its higher tolerance and variance in response to UV at intermediate doses (i.e. 2 mJ/cm2). This hypothesis, if correct, would suggest small changes in the virus genome sequence could result in dramatic changes in its UV resistance, and should be considered when looking for the use of UV irradiation as way to combat pathogenic viruses.
The data presented in Fig. 2b fit nicely with the previously published results, both in suggesting UVC can be effective against SARS-CoV-2 viruses and doses needed for efficient inactivation (Table 3). It is noteworthy that previous published data on the inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 virus in suspension suggested higher doses needed for 3-log reduction (Compare Table 3, lines 1, 4, 6, 7 and 8), probably due to the addition of protein to the suspension8, serving as UV absorbent. Where suspension and aerosols were directly compared8 much lower doses were required for similar activation of the virus in the latter (see line 7 in Table 3), probably due to the much smaller droplet size in the aerosol (in Ref.8 more than 80% of the droplets were smaller than 1 µm while the suspension droplets were probably ~ 1 mm, given they used similar volume to that presented here).
In summary, both our and previous results suggest that the UVC irradiation can be used to combat human coronavirus while mitigating the environmental effects of using disinfectants and allow reuse of respiration masks9,18 lowering plastics wastes originating from such19. Moreover, the use UV as a disinfectant can reduce the use of environmentally problematic chemical disinfecting agent20 and mercury containing UV lamps (in line with the Minamata convention to reduce global mercury pollution). UV-LEDs small format and simple electrical circuitry needed for UVC LEDs could also support their incorporation into air ventilation systems21 although such application is still limited by the UV-LED emission efficiency.
Materials and methods
Four SARS-CoV-2 variants were used in this study: w.t. (w.t-like strain, B.1.1.50, that circulated in Israel 2020); Alpha (B.1.1.7 501Y.V1), containing multiple spike mutations, demonstrated to have 70% higher transmission rate than the w.t. strain13; Delta (B.1.617.2), reported more infectious and causing more severe disease compared to the Alpha variant13; and Omicron (B.1.1.529), containing more than thirty amino acid mutations in the spike protein, and demonstrating mutation rate exceeding that of other variants by 5–11 times as well as enhanced transmissibility and immune evasion14. All the virus variants were isolated at the Mandelbaum lab from leftover respiratory swabs samples (fully anonymized samples) used for routine diagnosis and found positive for SARS-CoV-2. All protocols were conducted under Sheba Medical Center Helsinki Committee approval (number 7875-20-SMC), and under these circumstances’ hospitals don’t require informed consent. Viruses were identified by sequencing (sequences deposited in the NCBI genebank database under accession numbers OQ948263 to OQ948266, respectively. Sequences can also be found in the https://gisaid.org/ under accession numbers EPI_ISL_745046, EPI_ISL_737204, EPI_ISL_2183060 and EPI_ISL_7869197, respectively). Propagation of the viruses was as previously described15.
UV source was a custom-made UV-LEDs device built in collaboration with AquiSense, having a peak emission wavelength at 267 nm (Fig. 1)1,16. Weighted incident irradiance was 0.152 mW/cm2 at the center of the exposure area (measured with a calibrated Ocean Optics USB4000 spectroradiometer equipped with a cosine corrector and integrated for 250–290 nm). UV dose (mJ/cm2) was determined by multiplying the measured irradiation (mW/cm2) by irradiation time (seconds).
Virus irradiation was done as previously described1. Briefly, virus suspension was diluted in Eagle's Minimum Essential Medium without phenol red (UVT > 95%) to a concentration of 10 × 100TCID50 (i.e. 1000-fold the dilution of a virus required to infect 50% of the cells in the cell culture22, here within 5 days of infection). Fifty µl of this virus suspension was placed in each well of a black 24-well plate (giving a layer of ~ 1 mm height in the highest point). All wells were covered with black insulation tape. Each time before irradiation, the tape was removed from a 4-well column or 6-well row for the designated time1,16, resulting in 4 or 6 replicates per plate, accordingly. In each plate tested a column/row of wells was left covered throughout the irradiation to serve as noUV control and as 0 irradiance reference. The process was repeated three times for the shorter irradiation times (1, 2, and 5 mJ/cm2) due to significant variability in results. Zero-irradiation control was kept covered with the tape throughout the irradiation process to allow for other effects.
Virus quantification was done after proliferation, thus quantifying only infective capable viruses. To this end, after irradiation 450 µl Eagle's Minimum Essential Medium supplemented with 2% (v/v) fetal calf serum (MEM- EAGLE) was added to each well (including the “no UV” wells); the content was mixed by pipettation, and 50 µl were transferred to a well of 96-well plate (Applied Biosystems, USA) containing 24-h-old (80–90% confluency) Vero-E6 cells in the same medium, giving final virus concentration of 100TCID50 per well (for pre-irradiated viruses). The plates were incubated for 1 h at 33 °C, unattached viruses washed with media by pippeting, and 200 μL MEM-EAGLE medium containing 2% FCS was added. The cells were then incubated in a humidified incubator with 5% CO2 at 33 °C for five additional days. Total RNA was extracted from the cells using a MagNA Pure 96 Instrument (Roche Life Science) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. Virus copy number in the cells was determined by reverse transcriptase − qPCR (done in CFX-96 thermocycler, Bio-Rad, USA) and compared against a calibration curve constructed from virus solutions of known titers. Oligonucleotides used were E_Sarbeco_F (ACAGGTACGTTAATAGTTAATAGCGT) and E_Sarbeco_R (ATATTGCAGCAGTACGCACACA) and the probe was E_Sarbeco_P1(FAM-ACACTAGCCATCCTTACTGCGCTTCG-BBQ), with conditions as described in Ref.23.
Inactivation and statistical analysis
Log inactivation was calculated for each variant-preparation combination separately as log (N0/N), N and N0 being viral concentrations with and without irradiation respectively, to correct for variability in initial virus numbers (both for different preparation of the same variant and between variants on the same preparation date). To this end, the virus number in each well (Eq. 1, Ndose-variant) was divided by average number of viruses of the corresponding average specific variants noUV wells in the same plate (Eq. 1 N0-variant).
All analyses were done with SPSS statistics for windows v.24 (IBM, Released 2016) with type III sums of squares.
Sequence analysis
Quantification of UV sensitive motifs was done in R (version 4.1.3; 2022-03-10) using custom code (see supplementary information). Sequence comparison was done using the MAFFT algorithm (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/mafft/) and alignment using Clustal Omega (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalo/).
This research was partially funded by Oranim Academic College internal grant and by the Tel Aviv University Center for Combatting Pandemics (TCCP).
Data availability
Sequences of the variants used in this study were deposited in (sequences deposited in the NCBI genebank database under accession numbers OQ948263 (w.t.), OQ948264 (Alpha), OQ948265 (Delta), OQ948266 (Omicron). Sequences can also be found in the https://gisaid.org/ under accession numbers EPI_ISL_745046, EPI_ISL_737204, EPI_ISL_2183060 and EPI_ISL_7869197, respectively) https://gisaid.org/ under accession numbers EPI_ISL_745046 (w.t.), EPI_ISL_737204 (Alpha), EPI_ISL_2183060 (Delta) and EPI_ISL_7869197 (Omicron).
References
Gerchman, Y., Mamane, H., Friedman, N. & Mandelboim, M. UV-LED disinfection of coronavirus: Wavelength effect. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B. Biol. 212, 112044. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2020.112044 (2020).
Ma, B., Gundy, P. M., Gerba, C. P., Sobsey, M. D. & Linden, K. G. UV inactivation of SARS-CoV-2 across the UVC spectrum: KrCl excimer, mercury-vapor, and light-emitting-diode (LED) sources. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.01532-21 (2021).
Pousty, D., Hofmann, R., Gerchman, Y. & Mamane, H. Wavelength-dependent time–dose reciprocity and stress mechanism for UV-LED disinfection of Escherichia coli. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B. Biol. 217, 112129. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2021.112129 (2021).
Boegel, S. J. et al. Robust evaluation of ultraviolet-C sensitivity for SARS-CoV-2 and surrogate coronaviruses. Microbiol. Spectr. 9(2), e00537-21. https://doi.org/10.1128/Spectrum.00537-21 (2021).
Simmons, S. et al. Deactivation of SARS-CoV-2 with pulsed-xenon ultraviolet light: Implications for environmental COVID-19 control. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol 42(2), 127–130. https://doi.org/10.1017/ice.2020.399 (2021).
Gidari, A. et al. SARS-CoV-2 survival on surfaces and the effect of UV-C light. Viruses 13, 408. https://doi.org/10.3390/v13030408 (2021).
Barnewall, R. E. & Bischoff, W. E. Removal of SARS-CoV-2 bioaerosols using ultraviolet air filtration. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 42(8), 1014–1015. https://doi.org/10.1017/ice.2021.103 (2021).
Ueki, H., Ito, M., Furusawa, Y. & Yamayoshi, S. A 265-nanometer high-power deep-UV light-emitting diode rapidly inactivates SARS-CoV-2 aerosols. mSphere 7(2), e0094121. https://doi.org/10.1128/msphere.00941-21 (2022).
Raeiszadeh, M. & Adeli, B. A critical review on ultraviolet disinfection systems against COVID-19 outbreak: Applicability, validation, and safety considerations. ACS Photonics 7(11), 2941–2951. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsphotonics.0c01245(2020) (2020).
Sellera, F. P., Sabino, C. P., Cabral, F. V. & Ribeiro, M. S. A systematic scoping review of ultraviolet C (UVC) light systems for SARS-CoV-2 inactivation. J. Photochem. Photobiol. 8, 100068. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpap.2021.100068 (2021).
CDC. April 26, 2022. SARS-CoV-2 Variant Classifications and Definitions. Retrieved May 22, 2022, from https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/variants/variant-classifications.html.
Markov, P. V., Katzourakis, A. & Stilianakis, N. I. Antigenic evolution will lead to new SARS-CoV-2 variants with unpredictable severity. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 20, 251–252. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-022-00722-z (2022).
Fiolet, T., Kherabi, Y., MacDonald, C.-J., Ghosn, J. & Peiffer-Smadja, N. Comparing COVID-19 vaccines for their characteristics, efficacy and effectiveness against SARS-CoV-2 and variants of concern: A narrative review. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 28(2), 202–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2021.10.005 (2022).
Kannan, S., Shaik Syed Ali, P. & Sheeza, A. Omicron (B.1.1.529)—variant of concern—molecular profile and epidemiology: A mini review. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 25(24), 8019–8022. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202112_27653 (2021).
Nemet, I. et al. Third BNT162b2 vaccination neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 omicron infection. N. Engl. J. Med. 386, 492–494. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMc2119358 (2022).
Betzalel, Y., Gerchman, Y., Cohen-yaniv, V. & Mamane, H. Multiwell plates for obtaining a rapid microbial dose-response curve in UV- LED systems. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2907, 111865 (2020).
Khoe, C. V., Chung, L. H. & Murray, V. The sequence specificity of UV-induced DNA damage in a systematically altered DNA sequence. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 183, 88–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.04.023 (2018).
Hummel, A., Ergai, A., Spiva, L., Toney, S. & Crawford, A. Rapid design and implementation of a UVC decontamination room. Sci. Rep. 12, 835. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-04926-4 (2022).
Delgado-Gallardo, J. et al. Disposable FFP2 and type IIR medical-grade face masks: An exhaustive analysis into the leaching of micro- and nanoparticles and chemical pollutants linked to the COVID-19 pandemic. ES&T Water 2(4), 527–538. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsestwater.1c00319 (2022).
Hora, P. I., Sarah, G., Pati, S. G., McNamara, P. J. & Arnold, W. A. Increased use of quaternary ammonium compounds during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic and beyond: Consideration of environmental implications. Environ. Sci. Technol. Lett. 7(9), 622–631. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.estlett.0c00437 (2020).
Nunayon, S. S., Zhang, H. H. & Lai, A. C. K. Comparison of disinfection performance of UVC-LED and conventional upper-room UVGI systems. Indoor Air 30, 180–191. https://doi.org/10.1111/ina.12619 (2020).
Lei, C., Yang, J., Hu, J. & Sun, X. On the calculation of TCID50 for quantitation of virus infectivity. Virol. Sin. 36(1), 141–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12250-020-00230-5 (2021).
Corman, V. M. et al. Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR. Euro Surveill. 25, 2000045. https://doi.org/10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.3.2000045 (2020).
Acknowledgements
The research was partially funded by the Tel Aviv University Center for Combatting Pandemics https://en-pandemics.tau.ac.il/ (HM) and by Oranim College internal grant (YG).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
N.A. Preformed experiments and collected data, manuscript review. H.M. Secured funding, manuscript review. A.S. Conducted statistical analysis, manuscript review. N.Z. Conducted bioinformatic sequence analysis, manuscript review. M.M. Conceived and designed the analysis, supervised experiments, manuscript review. Y.G. Conceived and designed the analysis, secured funding, wrote first draft, manuscript review.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Atari, N., Mamane, H., Silberbush, A. et al. Disinfection of SARS-CoV-2 by UV-LED 267 nm: comparing different variants. Sci Rep 13, 8229 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-35247-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-35247-9
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.