Abstract
This study aimed to investigate the effects of cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) on anxiety and depression in cancer survivors. The PubMed, Embase, PsycINFO, and Cochrane Library databases were searched. Randomized controlled trials that evaluated the effects of CBT in cancer survivors were included. The standardized mean difference (SMD) was used as an effect size indicator. Fifteen studies were included. For the depression score, the pooled results of the random effects model were as follows: pre-treatment versus post-treatment, SMD (95% confidence interval [CI]) = 0.88 (0.46, 1.29), P < 0.001; pre-treatment versus 3-month follow-up, 0.83 (0.09, 1.76), P = 0.08; pre-treatment versus 6-month follow-up, 0.92 (0.27, 1.58), P = 0.006; and pre-treatment versus 12-month follow-up, 0.21 (− 0.28, 0.70), P = 0.40. For the anxiety score, the pooled results of the random effects model were as follows: pre-treatment versus post-treatment, 0.97 (0.58, 1.36), P < 0.001; pre-treatment versus 3-month follow-up, 1.45 (− 0.82, 3.72), P = 0.21; and pre-treatment versus 6-month follow-up, 1.00 (0.17, 1.83), P = 0.02). The pooled result of the fixed effects model for the comparison between pre-treatment and the 12-month follow-up was 0.10 (− 0.16, 0.35; P = 0.45). The subgroup analysis revealed that the geographical location, treatment time and treatment form were not sources of significant heterogeneity. CBT significantly improved the depression and anxiety scores of the cancer survivors; such improvement was maintained until the 6-month follow-up. These findings support recommendations for the use of CBT in survivors of cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
The concept of cancer survivors was first proposed by Fitzhugh Mullan, a physician diagnosed with cancer1. According to the National Coalition for Cancer Survivorship, “an individual is considered to be a cancer survivor from the time of diagnosis through the balance of his or her life.” This definition includes family members, caregivers, and friends because survivorship experience also affects them2. With the promotion of cancer screening and improvements in treatment, the survival rate of patients with cancer continues to improve. This leads to a dramatic increase in the number of survivors over the past few decades3,4. As reported by the National Cancer Center based on data from 17 cancer registries in China, the 5-year survival rates for 26 types of cancer increased from 30.9 to 40.5% between 2003 and 20155. In the United States, the number of cancer survivors increased from approximately 3 million in 1971 to nearly 15.5 million in 20166,7,8. This number is expected to reach more than 26 million by 20406,7. Owing to the prolonged survival period after treatment, efforts need to be made to improve the quality of life and survival status of cancer survivors.
Cancer survivors often face physical, psychological, and psychosocial challenges that extend into long-term survivorship9,10. It has been reported that they are prone to experiencing fatigue, sleep disorders, chronic pain, fear of recurrence, anxiety, and depression, which not only disrupt the quality of life and return to usual activities but can also be barriers to engaging in survivorship care11,12,13. Among these psychosocial challenges, psychological problems, such as depression and anxiety require early identification, because they are often under-diagnosed and under-treated14. Some cohort studies have shown that cancer survivors report higher rates of anxiety and depression than individuals without a history of cancer15,16. Depression is reported in approximately 8–33% of patients with cancer and anxiety in approximately 17–23%17,18. Depression is associated with poor adherence to cancer treatment and poor survival19,20. Additionally, it is detrimental to quality of life and is correlated with a two-fold increase in the risk of all-cause death among cancer survivors21. Psychological anxiety makes patients irritable, unable to concentrate, negative, and very pessimistic, all of which can decrease their quality of life22. For cancer survivors, these psychological disorders not only interfere with quality of life but can also become barriers to engaging in survivorship care. This is especially for women, adolescents, and young individuals, because they are particularly at risk for mood disturbances23. Seriously, these disorders are difficult to alleviate with drugs, leaving the needs of cancer survivors for improved quality of life, especially their psychosocial needs, far unmet. Health-related quality of life is a multidimensional construct that encompasses physical functioning as well as psychosocial aspects of emotional and social functioning. There has been a paradigm shift in health service delivery to a more holistic approach, which considers quality of life and overall functioning24.
Several studies have reported that psychosocial interventions can effectively treat these distressing emotions, with cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) being the most frequently used approach25. The term CBT describes a group of psychotherapeutic techniques that treat psychological distress and maladaptive behaviors by changing cognitions and behaviors26. CBT describes a hybrid of strategies to facilitate cognitive, behavioral, emotional and social change. The interventions include the teaching of social skills through role playing, problem solving techniques, coping skills, examining alternative ways of perception, and engagement in verbally mediated self-control27. According to CBT, the emotions and behaviors of individuals are determinants of their cognitive processes. Once cognitive defects are corrected, negative emotions and behaviors improve. As a result, CBT aims to modify cancer survivors’ wrong cognition into a more rational manner of thinking, helping them gain a sense of control over the disease and increasing their confidence in fighting it28. Furthermore, CBT has been traditionally used for patients with mental health disorders, such as depression and anxiety29. Many randomized controlled trials (RCTs) have examined the effects of CBT on anxiety and depression among cancer survivors. However, the results are inconsistent and not comprehensive because of the wide variations in sample sizes, ethnicities, and outcome assessment methods used.
In this study, a meta-analysis of RCTs was conducted to comprehensively evaluate the effect of CBT on anxiety and depression in cancer survivors through a dynamic follow-up from 3 to 12 months.
Methods
The meta-analysis procedure was performed in accordance with the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analysis (PRISMA) statement guidelines30. As this study analyzed data from previously published studies, ethical ratification was not required. Considering that this study is a meta-analysis study using the existing peer-reviewed literature,and no human/animal patients were directly involved in the study, receiving their con-sent to participate or consent to publish was not considered as necessary.
Search strategy
According to the predefined search strategy, we identified appropriate literature using the following electronic databases: PubMed, PsycINFO, Embase, and Cochrane Library. The search keywords included “cognitive behavioral therapy,” “cognitive behavior therapy,” “neoplasms,” “cancer,” “anxiety,” and “depression.” Keywords in the same category were combined with “OR” and those in different categories with “AND.” Subject terms and free words were searched in combination, and the retrieval method was adjusted according to database characteristics. The retrieval steps for the PubMed database are presented in Supplementary table 1. We focused on articles published up to May 23, 2022, without language restrictions. Additionally, the references of relevant reviews and the included literature were searched for eligible studies.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria for study selection
The inclusion criteria for the studies were as follows: (1) participant: cancer survivors (patients with cancer who had completed treatment, except for targeted treatments or hormonal treatments); (2) variable compared: differences in the effects of CBT and treatment as usual (TAU) on depression and anxiety in patients with cancer; and (3) study type: RCT.
The exclusion criteria were as follows: (1) non-literary research, such as review and meeting abstracts; (2) third-generation CBT, such as mindfulness-based cognitive therapy and acceptance and commitment therapy; (3) patients receiving or preparing to receive standard treatments, such as surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or immunotherapy; and (4) repeated publications or multiple articles with the same data (only the article with the most complete research information was retained).
Data extraction and quality assessment
Two reviewers independently completed literature screening. After obtainment of the included literature, information on the first author, publication year, country, basic participant characteristics (sample size, sex, and age), cancer type and stage, follow-up time, intervention period, and study outcome was independently extracted according to the pre-designed table. After the data extraction, the two reviewers exchanged the tables, and disagreements were resolved via discussion. The quality of the RCTs was assessed using the Cochrane Collaboration’s tool31.
Statistical analysis
The standardized mean difference (SMD) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were used as the effect size indicators to evaluate the differences in the anxiety and depression scores between post-treatment and the 3/6/12-month follow-up. Cochran’s Q test and I2 test were used for heterogeneity testing32. P < 0.05 or I2 > 50% indicated significant heterogeneity, and the random effects model was used for the data analysis. Random-effects model attempted to generalize findings beyond the included studies by assuming that the selected studies are random samples from a larger population33. P ≥ 0.05 or I2 ≤ 50% indicated non-significant heterogeneity, and the fixed effects model was applied for the meta-analysis. Fixed-effect models assume that the population effect sizes are the same for all studies33. Subgroup analysis was performed according to the geographical location and treatment time. The effect of a single study on the meta-analysis was evaluated using a one-by-one exclusion method34. Publication bias was evaluated using the Egger test35. When significant publication bias existed, the stability of the combined results was assessed using the trim-and-fill method36. All statistical analyses were performed using the Stata 12.0 and RevMan 5.3 software.
Results
Literature search
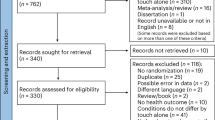
The literature retrieval results and screening processes are presented in Fig. 1. A total of 2992 articles were retrieved from the electronic databases (1019 from PubMed, 1024 from Embase, 511 from the Cochrane Library, and 438 from PsycINFO) in this meta-analysis. After duplicate elimination, 2059 articles remained. Thereafter, 2012 articles were further removed by browsing the titles and abstracts. Finally, 15 articles were included after full-text reading, including 13 quantitative analyses37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,48,49 and 2 qualitative analyses.
Study characteristics and quality assessment
The publication dates of the 15 articles ranged from 2003 to 2022. These studies were conducted in China, the United Kingdom, South Korea, Iran, the United States, and Canada. The sample size ranged from 29 to 294, with 1979 cases. Of the included articles, seven reported on patients with breast cancer37,38,42,43,44,50,51, one on patients with melanoma47, five on patients with mixed cancers39,46,48,52,53, one on patients with laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma49 and one on patients with head and neck cancer54. The average age of the participants ranged from 37.45 to 59.7 years. The CBT intervention period was 2–12 weeks, and the follow-up period was within 12 months after the intervention. The rating scales used for anxiety and depression are listed in Table 1.
The methodological quality assessment results of the included articles are shown in Supplementary Fig. 1A and B. Bias mainly included performance and detection biases. The bias level of the included studies was uncertain, and the methodological quality was moderate.
Meta-analysis
For the depression score, the change values between CBT and TAU in the four outcome indicators (A, pre-treatment vs. post-treatment; B, pre-treatment vs. 3-month follow-up; C, pre-treatment vs. 6-month follow-up; D, pre-treatment vs. 12-month follow-up) showed significant heterogeneity among the included articles (I2 > 50%, P < 0.05). The pooled results of the random effects model were as follows: pre-treatment versus post-treatment, SMD (95% CI) 0.88 (0.46, 1.29), P < 0.001 (Fig. 2A); pre-treatment versus 3-month follow-up, 0.83 (0.09, 1.76), P = 0.08 (Fig. 2B); pre-treatment versus 6-month follow-up, 0.92 (0.27, 1.58), P = 0.006 (Fig. 2C); and pre-treatment versus 12-month follow-up, 0.21 (− 0.28, 0.70), P = 0.40 (Fig. 2D). The pooled results suggested that CBT significantly improved the depression scores of the cancer survivors after the intervention and at the 6-month follow-up. However, there was no obvious improvement in the depression scores at the 12-month follow-up.
Forest plot of the random effects model meta-analysis of the comparison of the change values of the depression scores between CBT and TAU: (A) pre-treatment versus post-treatment, (B) pre-treatment versus 3-month follow-up, (C) pre-treatment versus 6-month follow-up, and (D) pre-treatment versus 12-month follow-up. CBT cognitive behavioral therapy, TAU treatment as usual.
For the anxiety score, the change values between CBT and TAU in the comparisons of pre-treatment with post-treatment, pre-treatment with the 3-month follow-up, and pre-treatment with the 6-month follow-up showed significant heterogeneity among the included articles (I2 > 50%, P < 0.05). The pooled results of the random effect models were as follows: pre-treatment versus post-treatment, SMD (95% CI) = 0.97 (0.58, 1.36), P < 0.0001 (Fig. 3A); pre-treatment versus 3-month follow-up, 1.45 (− 0.82, 3.72), P = 0.21 (Fig. 3B); and pre-treatment versus 6-month follow-up, 1.00 (0.17, 1.83), P = 0.02 (Fig. 3C). The included articles comparing pre-treatment with the 12-month follow-up showed no significant heterogeneity, and the pooled result of the fixed effects model was SMD (95% CI) = 0.10 (− 0.16, 0.35), P = 0.45 (Fig. 3D). The pooled results suggested that CBT also significantly improved the anxiety scores of the patients with cancer after intervention and at the 6-month follow-up. Similarly, there was no significant improvement in the anxiety scores at the 12-month follow-up.
Forest plot of the random effects model meta-analysis of the comparison of the change values of the anxiety scores between CBT and TAU: (A) pre-treatment versus post-treatment, (B) pre-treatment versus 3-month follow-up, and (C) pre-treatment versus 6-month follow-up, and the fixed effects model meta-analysis of the comparison of the change values obtained (D) pre-treatment and at the 12-month follow-up. CBT cognitive behavioral therapy, TAU treatment as usual.
Subgroup analysis
Since the number of included studies that conducted 3-, 6-, and 12-month follow-ups was fewer than five, this meta-analysis only performed subgroup analysis on the changes post-treatment (Table 2). For the depression scores in the subgroup analysis according to the geographical location, the pooled results of the European subgroup were not significant (SMD [95% CI] = 0.13 [− 0.06, 0.32], P = 0.19), whereas the combined effect values of the other subgroups were significant (American: SMD [95% CI] = 0.53 [0.12, 0.95], P = 0.01; Asian: 1.47 [0.85, 2.09], P < 0.00001; Oceanian: 1.10 [0.71, 1.50], P < 0.00001) (Supplementary Fig. 2A). In the subgroup analysis according to the treatment time, the pooled results of the less than or equal to 6 weeks subgroup were not significant (SMD [95% CI] = 0.61 [− 0.53, 1.74], P = 0.29), while the combined effect values of the more than 6 weeks subgroup were significant (SMD [95% CI] = 0.95 [0.47, 1.43], P = 0.0001) (Supplementary Fig. 2B). For the subgroup analysis of treatment form, the pooled results of group therapy and individual therapy were statistically significant (P < 0.05, Supplementary Fig. 2C).
Similarly, for the anxiety scores in the subgroup analysis according to the geographical location, the pooled results of the American subgroups had no significant difference (P > 0.05), while those of the other subgroups had a significant difference (European: SMD [95% CI] = 0.50 [0.25, 0.74], P < 0.00001; Asian: 1.19 [0.50, 1.88], P = 0.0007; Oceanian: 1.21 [0.81, 1.61], P < 0.00001) (Supplementary Fig. 3A). In the subgroup analysis according to the treatment time, the pooled results of both the less than or equal to 6 weeks subgroup (SMD [95% CI] = 1.04 [0.16, 1.93], P = 0.02) and more than 6 weeks subgroup (0.95 [0.48, 1.42], P < 0.0001) were significantly different (Supplementary Fig. 3B). The pooled results of group therapy and individual therapy were statistically significant (P < 0.05, Supplementary Fig. 3). In addition, the subgroup analysis showed that the geographical location, treatment time and treatment form were not sources of significant heterogeneity.
Sensitivity analysis and publication bias test
Only two studies reported the anxiety scores at the 3-month follow-up and depression and anxiety scores at the 12-month follow-up, making them unsuitable for the sensitivity analysis or publication bias test. The analysis results for the depression and anxiety scores at the other time points are summarized in Table 3. The sensitivity analysis revealed that the intervention effect of CBT was stable at post-treatment, the 3-month follow-up, and the 6-month follow-up. For post-treatment, the SMD (95% CI) of the pooled results changed from 0.73 (0.36, 1.09) to 0.97 (0.54, 1.41); for the 3-month follow-up, from 0.31 (− 0.08, 0.69) to 1.00 (− 0.71, 2.71); and for the 6-month follow-up, from 0.58 (0.28, 0.87) to 1.13 (0.09, 2.18). The sensitivity analysis showed that the pooled results were not significantly affected by a single study. For the anxiety scores, the results were stable at post-treatment, with the SMD (95% CI) changing from 0.84 (0.48, 1.19) to 1.06 (0.66, 1.46). However, the results at the 6-month follow-up were unstable, with the SMD (95% CI) changing from 1.19 (− 0.15, 2.53) to 1.25 (0.08, 2.42).
The Egger test was used to evaluate the publication bias between the studies (Table 3). The included studies that investigated depression and anxiety after follow-up had a significant publication bias (P < 0.05). However, the results of the trim-and-fill method suggested that the program did not fill in the fictitious negative results to enhance the symmetry of the funnel plot; further, the meta-analysis results did not change, indicating that the original pooled results were stable. The included studies that investigated the other outcome indicators did not have a significant publication bias (P > 0.05).
Qualitative analysis
Duffy et al.54 reported differences in the depression rates between patients with cancer who underwent CBT and TAU at the 6-month follow-up, with the rate in the CBT group decreasing from 68 to 21% and that in the TAU group from 70 to 24%, showing no significant difference between the two groups (P > 0.05). Savard et al.51 suggested that CBT significantly influenced the depression and anxiety scores at the end of the intervention (P < 0.05).
Discussion
This study analyzed the efficacy of CBT for anxiety and depression across 15 RCTs that included 1979 cancer survivors. The analysis showed that CBT can significantly reduce depression and anxiety in cancer survivors during the intervention period and until 6 months of follow-up, as measured by the depression and anxiety scores, when compared with TAU. The observed effects persisted until the 6-month follow-up, suggesting that CBT provided significant, lasting improvements in depression and anxiety. However, more high-quality RCTs are required to confirm these findings. Additionally, there was no finding that the geographical location, treatment time and treatment form of the included studies affected the heterogeneity.
In a previous meta-analysis and systematic review, with pooled samples of approximately 50,000 long-term cancer survivors, the prevalence of depression and anxiety was 12% and 18%, respectively16. Although antidepressants are effective for the treatment of anxiety and depression, they yield poor tolerance, rebound insomnia, and adverse side effects after discontinuation55. Given the effects of depression and anxiety on symptom burden and quality of life, evidence supporting effective interventions with minimal side effects and long-term benefits is needed for cancer survivors with anxiety and depression. Evidence from RCTs has indicated that several behavioral approaches, such as mindfulness-based approaches, hypnosis, and self-management strategies, are effective in improving anxiety and depression in cancer survivors56,57,58. However, most studies have been conducted in breast cancer survivors; thus, these interventions need to be further tested in different groups of survivors.
CBT has been demonstrated to be effective in the treatment of depression and anxiety, with well-maintained effects over a 3-month follow-up period59. Currently, CBT is recommended as the first-line treatment for depression and anxiety by the National Institute for Health and Care Excellence in the United Kingdom. However, among cancer survivors, the majority of CBT-related studies have focused on those with insomnia60,61, with less attention paid to those with depression and anxiety. A recent meta-analysis examined the effect of CBT on the quality of life and psychological health (depression, anxiety, and stress) of patients and survivors of breast cancer. It revealed that CBT is effective in improving the psychological symptoms of both patients and survivors, with meaningful clinical effect sizes62. In our study, the beneficial effects of CBT on depression and anxiety in the cancer survivors were maintained until the 6-month follow-up, which suggests the durability of this treatment. Our results are consistent with a previous finding that “individual CBT has short-term effects (< 8 months)” on both depression and anxiety among cancer survivors63. Therefore, further research is needed before CBT can be used in the long-term.
It's worth noting that, among the included literatures, several studies were based on internet CBT39,41,48. Traditional CBT usually proceeds through face-to-face sessions with a professional in an individual or small-group format and therefore requires significant manpower, time, and cost64,65. Internet-based CBT programs is a promising therapeutic alternative that can spread widely within a very short period. They are more accessible and effective than traditional face-to-face interventions in terms of manpower and cost66. Internet CBT may provide access to standardized, evidence-based therapy without physical and/or geographical barriers67. It has been reported that internet CBT can achieve comparable outcomes to face-to-face CBT for mild to severe anxiety and depression in the general population68. Therefore, internet CBT has potential to revolutionize the delivery of CBT, improving the accessibility and availability of CBT content for cancer survivors.
The methodological quality of the included articles herein was moderate; thus, the findings may have the potential to serve as a basis for clinical practice guidelines69. Although we applied strict inclusion and exclusion criteria to minimize heterogeneity, there were still high levels of heterogeneity found, which may be attributed to the different methods used to deliver CBT. A subgroup analysis was then used to analyze the potential sources of heterogeneity. The analysis revealed that the geographical location and treatment time were not sources of significant heterogeneity. Importantly, a treatment time of more than 6 weeks was associated with the treatment effect of CBT on both depression and anxiety. Thus, a treatment time of more than 6 weeks is recommended to ensure the efficacy of CBT. Specifically, the subgroup analysis was only performed on the post-treatment changes, since there were fewer than five included studies that conducted 3-, 6-, and 12-month follow-ups. Therefore, the effects of follow-up deserve further attention. Taken together, these findings support recommendations for the use of CBT in survivors of cancer.
Study strengths and limitations
This study has several strengths. A wide range of databases were searched without restrictions on time scales or language. Strict inclusion and exclusion criteria were used to minimize heterogeneity. The high level of heterogeneity may be attributed to the differences in how CBT was delivered. Study selection and quality assessment were independently completed by two reviewers. The control group was limited to TAU, which can objectively evaluate the intervention effect of CBT. Additionally, the methodological quality of the included studies was moderate, and the control of selection bias, reporting bias, and loss-to-follow-up bias was reasonable. Importantly, although there was significant publication bias for some outcome indicators, the results of both the trim-and-fill method and the one-by-one elimination method suggested the high stability of the pooled results.
This study has some limitations, which might have influenced the results. First, the heterogeneity of the included studies was large, and no significant source of heterogeneity was found in the subgroup analysis. Second, the CBT intervention approaches were inconsistent among the included studies, which is an important source of clinical heterogeneity. Currently, there is no appropriate quantitative method to evaluate the impact on the results of the meta-analysis. Finally, for some outcome indicators, the number of included studies was small, and the sensitivity analysis results were unstable, requiring more large-sample studies to verify the results.
Clinical implications
Depression and anxiety are highly prevalent concern, affecting cancer survivors and patients. A suite of interventions incorporating cognitive, behavioral, and educational components has been developed for depression and other psychological symptoms70. It has been suggested that behavioral interventions are valid for quality of life in cancer patients, and CBT is moderately efficacious for anxiety, depression, and stress symptoms71,72. Our study described a statistically significant effect of CBT on depression and distress among cancer survivors, and the results concluded that CBT was an effective intervention in improving depression and distress in cancer survivors during the intervention period and until 6 months of follow-up. Current interventions are often face to face and specialist led. The present mata-analysis included several studies based on internet CBT39,41,48, which has potential to revolutionize the delivery of CBT, improving the accessibility and availability of CBT content for cancer survivors. For future studies, it is necessary to address whether intervention effects appear after a continuous intervention.
Conclusions
This systematic review provided a detailed summary of the evidence on the effect of CBT interventions on depression and anxiety among cancer survivors and evaluated dynamic data at 3–12 months of follow-up. Compared with TAU, CBT significantly improved the depression and anxiety scores of the cancer survivors, and this improvement was maintained until the 6-month follow-up. It is recommended that more large-sample, high-quality RCTs be conducted for verification.
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed in this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
References
Mullan, F. Seasons of survival: Reflections of a physician with cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 313, 270–273. https://doi.org/10.1056/nejm198507253130421 (1985).
Sanft, T. et al. Survivorship, Version 2.2019: Featured updates to the NCCN guidelines. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. JNCCN 17, 784 (2019).
Kaffe, E. et al. Hepatocyte autotaxin expression promotes liver fibrosis and cancer. Hepatology 65, 1369–1383. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.28973 (2017).
Miller, K. D. et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 69, 363–385. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21565 (2019).
Zeng, H. et al. Changing cancer survival in China during 2003–15: A pooled analysis of 17 population-based cancer registries. Lancet Glob. Health 6, e555–e567. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2214-109x(18)30127-x (2018).
Bluethmann, S. M., Mariotto, A. B. & Rowland, J. H. Anticipating the “Silver Tsunami”: Prevalence trajectories and comorbidity burden among older cancer survivors in the United States. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 25, 1029–1036. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.epi-16-0133 (2016).
Miller, K. D. et al. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J. Clin. 66, 271–289. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21349 (2016).
Cancer survivors—United States, 2007. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 60, 269–272 (2011).
Stanton, A. L. Psychosocial concerns and interventions for cancer survivors. J. Clin. Oncol. 24, 5132–5137. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2006.06.8775 (2006).
Stoneham, S. J. AYA survivorship: The next challenge. Cancer 126, 2116–2119. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.32774 (2020).
Sánchez-Jiménez, A. et al. Physical impairments and quality of life of colorectal cancer survivors: A case–control study. Eur. J. Cancer Care 24, 642–649. https://doi.org/10.1111/ecc.12218 (2015).
Gonzalez-Saenz de Tejada, M. et al. Association between social support, functional status, and change in health-related quality of life and changes in anxiety and depression in colorectal cancer patients. Psychooncology 26, 1263–1269. https://doi.org/10.1002/pon.4303 (2017).
Simard, S. et al. Fear of cancer recurrence in adult cancer survivors: A systematic review of quantitative studies. J. Cancer survivorship Res. Pract. 7, 300–322. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11764-013-0272-z (2013).
Walker, J. et al. Prevalence, associations, and adequacy of treatment of major depression in patients with cancer: A cross-sectional analysis of routinely collected clinical data. Lancet Psychiatry 1, 343–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/s2215-0366(14)70313-x (2014).
Greer, J. A. et al. Anxiety disorders in long-term survivors of adult cancers. Psychosomatics 52, 417–423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psym.2011.01.014 (2011).
Mitchell, A. J., Ferguson, D. W., Gill, J., Paul, J. & Symonds, P. Depression and anxiety in long-term cancer survivors compared with spouses and healthy controls: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 14, 721–732. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(13)70244-4 (2013).
Krebber, A. M. et al. Prevalence of depression in cancer patients: A meta-analysis of diagnostic interviews and self-report instruments. Psychooncology 23, 121–130. https://doi.org/10.1002/pon.3409 (2014).
Linden, W., Vodermaier, A., Mackenzie, R. & Greig, D. Anxiety and depression after cancer diagnosis: Prevalence rates by cancer type, gender, and age. J. Affect. Disord. 141, 343–351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2012.03.025 (2012).
DiMatteo, M. R. & Haskard-Zolnierek, K. B. Impact of depression on treatment adherence and survival from cancer. In Depression and Cancer 101–124 (2011).
Robson, A., Scrutton, F., Wilkinson, L. & MacLeod, F. The risk of suicide in cancer patients: A review of the literature. Psychooncology 19, 1250–1258. https://doi.org/10.1002/pon.1717 (2010).
Mols, F., Husson, O., Roukema, J. A. & van de Poll-Franse, L. V. Depressive symptoms are a risk factor for all-cause mortality: Results from a prospective population-based study among 3,080 cancer survivors from the PROFILES registry. J. Cancer Survivorship Res. Pract. 7, 484–492. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11764-013-0286-6 (2013).
Soodan, S. & Arya, A. Understanding the pathophysiology and management of the anxiety disorders. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Res. 4, 251–278 (2015).
Yi, J. C. & Syrjala, K. L. Anxiety and depression in cancer survivors. Med. Clin. N. Am. 101, 1099–1113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcna.2017.06.005 (2017).
Choo, C. C. & Chew, P. K. H. Health-related quality of life in pediatric patients with leukemia in Singapore: A cross-sectional pilot study. IJERPH 16, 2069. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16122069 (2019).
Moorey, S. & Greer, S. Oxford Guide to CBT for People with Cancer (OUP, 2011).
Kaplan, C. A., Thompson, A. E. & Searson, S. M. Cognitive behaviour therapy in children and adolescents. Arch. Dis. Child. 73, 472–475. https://doi.org/10.1136/adc.73.5.472 (1995).
Choo, C. Adapting cognitive behavioral therapy for children and adolescents with complex symptoms of neurodevelopmental disorders and conduct disorders. J. Psychol. Abnorm. Children 3, 1–3 (2014).
DeRubeis, R., Webb, C., Tang, T., Beck, A. & Dobson, K. Handbook of Cognitive–Behavioral Therapies (Guilford Publications, 2010).
Addison, S. et al. Effects of tandem cognitive behavioral therapy and healthy lifestyle interventions on health-related outcomes in cancer survivors: A systematic review. J. Cancer Survivorship Res. Pract. 1, 24. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11764-021-01094-8 (2021).
Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J. & Altman, D. G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Ann. Intern. Med. 151, 264–269. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00135 (2009).
Tarsilla, M. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions. J. Multidiscip. Eval. 6, 142–148 (2008).
Higgins, J. P., Thompson, S. G., Deeks, J. J. & Altman, D. G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 327, 557–560. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557 (2003).
Cheung, M. W., Ho, R. C., Lim, Y. & Mak, A. Conducting a meta-analysis: Basics and good practices. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 15, 129–135. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1756-185X.2012.01712.x (2012).
Aurelio, T. Assessing the influence of a single study in the meta-anyalysis estimate. Stata Tech. Bull. 8, 15 (1999).
Egger, M., Davey-Smith, G., Schneider, M. & Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 315, 629–634 (1997).
Duval, S. & Tweedie, R. Trim and fill: A simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics 56, 455–463 (2015).
Fenlon, D. et al. Effectiveness of nurse-led group CBT for hot flushes and night sweats in women with breast cancer: Results of the MENOS4 randomised controlled trial. Psychooncology 29, 1514–1523. https://doi.org/10.1002/pon.5432 (2020).
Groarke, A., Curtis, R. & Kerin, M. Cognitive-behavioural stress management enhances adjustment in women with breast cancer. Br. J. Health. Psychol. 18, 623–641. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjhp.12009 (2013).
Ham, K. et al. Preliminary results from a randomized controlled study for an app-based cognitive behavioral therapy program for depression and anxiety in cancer patients. Front. Psychol. 10, 1592. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.01592 (2019).
Jelvehzadeh, F. & Dogaheh, E. R. The effect of a group cognitive behavioral therapy on the quality of life and emotional disturbance of women with breast cancer. Support. Care Cancer 30, 305–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-021-06421-4 (2022).
Murphy, M. J., Newby, J. M. & Butow, P. Randomised controlled trial of internet-delivered cognitive behaviour therapy for clinical depression and/or anxiety in cancer survivors (iCanADAPT Early). J. Psychosom. Obstet. Gynecol. 29, 76–85. https://doi.org/10.1002/pon.5267 (2020).
Qiu, J. et al. A randomized controlled trial of group cognitive behavioral therapy for Chinese breast cancer patients with major depression. J. Psychosom. Obstet. Gynaecol. 34, 60–67. https://doi.org/10.3109/0167482x.2013.766791 (2013).
Savard, J. et al. Randomized clinical trial on cognitive therapy for depression in women with metastatic breast cancer: Psychological and immunological effects. Palliat. Support. Care 4, 219–237. https://doi.org/10.1017/s1478951506060305 (2006).
Savard, J., Simard, S., Ivers, H. & Morin, C. M. Randomized study on the efficacy of cognitive-behavioral therapy for insomnia secondary to breast cancer, part I: Sleep and psychological effects. J. Clin. Oncol. 23, 6083–6096. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2005.09.548 (2005).
Serfaty, M. & King, M. Manualised cognitive-behavioural therapy in treating depression in advanced cancer: The CanTalk RCT. Health Technol. Assess. 23, 1–106. https://doi.org/10.3310/hta23190 (2019).
Sheikhzadeh, M., Zanjani, Z. & Baari, A. Efficacy of mindfulness-based cognitive therapy and cognitive behavioral therapy for anxiety, depression, and fatigue in cancer patients: A randomized clinical trial. Iran. J. Psychiatry 16, 271–280. https://doi.org/10.18502/ijps.v16i3.6252 (2021).
Trask, P. C., Paterson, A. G., Griffith, K. A., Riba, M. B. & Schwartz, J. L. Cognitive-behavioral intervention for distress in patients with melanoma: Comparison with standard medical care and impact on quality of life. Cancer 98, 854–864. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.11579 (2003).
van de Wal, M., Thewes, B., Gielissen, M., Speckens, A. & Prins, J. Efficacy of blended cognitive behavior therapy for high fear of recurrence in breast, prostate, and colorectal cancer survivors: The SWORD study, a randomized controlled trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 35, 2173–2183. https://doi.org/10.1200/jco.2016.70.5301 (2017).
Yang, Y. et al. The effectiveness of computer-assisted Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (cCBT) for psychological outcomes in patients with laryngectomy: Randomized controlled trial. J. Affect. Disord. 300, 59–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2021.12.068 (2022).
Jelvehzadeh, F., Dogaheh, E. R., Bernstein, C., Shakiba, S. & Ranjbar, H. The effect of a group cognitive behavioral therapy on the quality of life and emotional disturbance of women with breast cancer. Support Care Cancer 30, 305–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-021-06421-4 (2022).
Savard, J., Ivers, H., Savard, M. H. & Morin, C. M. Is a video-based cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia as efficacious as a professionally administered treatment in breast cancer? Results of a randomized controlled trial. Sleep 37, 1305–1314. https://doi.org/10.5665/sleep.3918 (2014).
Murphy, M. J. et al. Randomised controlled trial of internet-delivered cognitive behaviour therapy for clinical depression and/or anxiety in cancer survivors (iCanADAPT Early). Psychooncology 29, 76–85. https://doi.org/10.1002/pon.5267 (2020).
Serfaty, M. et al. Manualised cognitive-behavioural therapy in treating depression in advanced cancer: The CanTalk RCT. Health Technol. Assess. 23, 1–106. https://doi.org/10.3310/hta23190 (2019).
Duffy, S. A. et al. A tailored smoking, alcohol, and depression intervention for head and neck cancer patients. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 15, 2203–2208. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965.Epi-05-0880 (2006).
Singer, S., Das-Munshi, J. & Brähler, E. Prevalence of mental health conditions in cancer patients in acute care—A meta-analysis. Ann. Oncol. 21, 925–930. https://doi.org/10.1093/annonc/mdp515 (2010).
Carlson, L. E. et al. Randomized-controlled trial of mindfulness-based cancer recovery versus supportive expressive group therapy among distressed breast cancer survivors (MINDSET): Long-term follow-up results. Psychooncology 25, 750–759. https://doi.org/10.1002/pon.4150 (2016).
Johnson, A. J., Marcus, J., Hickman, K., Barton, D. & Elkins, G. Anxiety reduction among breast-cancer survivors receiving hypnotic relaxation therapy for hot flashes. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Hypn. 64, 377–390. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207144.2016.1209042 (2016).
Kanera, I. M. & Willems, R. A. Use and appreciation of a tailored self-management ehealth intervention for early cancer survivors: Process evaluation of a randomized controlled trial. J. Med. Internet Res. 18, e229. https://doi.org/10.2196/jmir.5975 (2016).
Cohen, J. Statistical Power Analysis for the Behavioral Sciences (Routledge, 2013).
Peoples, A. R. et al. Cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia reduces depression in cancer survivors. J. Clin. Sleep Med. JCSM 15, 129–137. https://doi.org/10.5664/jcsm.7586 (2019).
Garland, S. N. et al. Acupuncture versus cognitive behavioral therapy for insomnia in cancer survivors: A randomized clinical trial. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 111, 1323–1331. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djz050 (2019).
Ye, M. et al. A meta-analysis of the efficacy of cognitive behavior therapy on quality of life and psychological health of breast cancer survivors and patients. Psycho‐oncology 27, 1695–1703. https://doi.org/10.1002/pon.4687 (2018).
Osborn, R. L., Demoncada, A. C. & Feuerstein, M. Psychosocial interventions for depression, anxiety, and quality of life in cancer survivors: Meta-analyses. Int. J. Psychiatry Med. 36, 13–34. https://doi.org/10.2190/eufn-rv1k-y3tr-fk0l (2006).
Beatty, L., Koczwara, B. & Wade, T. Evaluating the efficacy of a self-guided Web-based CBT intervention for reducing cancer-distress: A randomised controlled trial. Support. Care Cancer 24, 1043–1051. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-015-2867-6 (2016).
Mohr, D. C. et al. Effect of telephone-administered vs face-to-face cognitive behavioral therapy on adherence to therapy and depression outcomes among primary care patients: A randomized trial. JAMA 307, 2278–2285. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2012.5588 (2012).
Donker, T. et al. Internet-delivered interpersonal psychotherapy versus internet-delivered cognitive behavioral therapy for adults with depressive symptoms: Randomized controlled noninferiority trial. J. Med. Internet Res. 15, e82. https://doi.org/10.2196/jmir.2307 (2013).
Andersson, G. & Titov, N. Advantages and limitations of Internet-based interventions for common mental disorders. World Psychiatry 13, 4–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/wps.20083 (2014).
Andersson, G., Cuijpers, P., Carlbring, P., Riper, H. & Hedman, E. Guided Internet-based vs face-to-face cognitive behavior therapy for psychiatric and somatic disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World Psychiatry 13, 288–295. https://doi.org/10.1002/wps.20151 (2014).
Guyatt, G. H. et al. Going from evidence to recommendations. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 336, 1049–1051. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.39493.646875.AE (2008).
Stagl, J. M. et al. Long-term psychological benefits of cognitive-behavioral stress management for women with breast cancer: 11-year follow-up of a randomized controlled trial. Cancer 121, 1873–1881. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.29076 (2015).
Carlisi, C. O. et al. Comparative multimodal meta-analysis of structural and functional brain abnormalities in autism spectrum disorder and obsessive-compulsive disorder. Biol. Psychiatry 82, 83–102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.10.006 (2017).
Playdon, M. C. et al. Weight gain after breast cancer diagnosis and all-cause mortality: Systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 107, djv275. https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djv275 (2015).
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of Hunan Province (2020RC3067), Clinical medical technology innovation guided project (2020SK51112) and Natural Science Foundation of Changsha Science and Technology Bureau (Kq2001024).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.Z., X.L., F.T. carried out the conception and design of the research. R.Z., W.P., H.Y., F.L. and D.Y. participated in the acquisition of data. X.H., M.W., L.J. and L.Y. carried out the analysis and interpretation of data. L.Z., X.L. participated in the design of the study, prepare and revise the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L., Liu, X., Tong, F. et al. Cognitive behavioral therapy for anxiety and depression in cancer survivors: a meta-analysis. Sci Rep 12, 21466 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-25068-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-25068-7
This article is cited by
-
Trajectories and predictors of anxiety and depression among older cancer survivors: a nationally representative cohort study
Journal of Cancer Survivorship (2024)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.