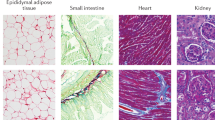
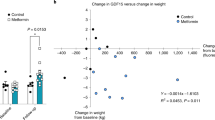
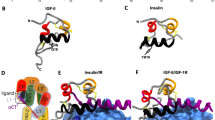
Abstract
The acid-labile subunit (ALS) of the insulin-like growth factor (IGF) binding protein (IGFBP) complex, encoded in humans by IGFALS, has a vital role in regulating the endocrine transport and bioavailability of IGF-1 and IGF-2. Accordingly, ALS has a considerable influence on postnatal growth and metabolism. ALS is a leucine-rich glycoprotein that forms high-affinity ternary complexes with IGFBP-3 or IGFBP-5 when they are occupied by either IGF-1 or IGF-2. These complexes constitute a stable reservoir of circulating IGFs, blocking the potentially hypoglycaemic activity of unbound IGFs. ALS is primarily synthesized by hepatocytes and its expression is lower in non-hepatic tissues. ALS synthesis is strongly induced by growth hormone and suppressed by IL-1β, thus potentially serving as a marker of growth hormone secretion and/or activity and of inflammation. IGFALS mutations in humans and Igfals deletion in mice cause modest growth retardation and pubertal delay, accompanied by decreased osteogenesis and enhanced adipogenesis. In hepatocellular carcinoma, IGFALS is described as a tumour suppressor; however, its contribution to other cancers is not well delineated. This Review addresses the endocrine physiology and pathology of ALS, discusses the latest cell and proteomic studies that suggest emerging cellular roles for ALS and outlines its involvement in other disease states.
Key points
-
The insulin-like growth factor (IGF) acid-labile subunit (ALS), encoded by IGFALS, forms a circulating ternary complex with IGF binding protein (IGFBP)-3 or IGFBP-5, and IGF-1 or IGF-2.
-
This ternary complex acts as a reservoir of IGF-1 and IGF-2 in the bloodstream and has a central role in regulating their endocrine transport and tissue bioavailability.
-
Owing to the induction of its expression by growth hormone and suppression by IL-1β, ALS might serve as a marker of growth hormone secretion and/or activity and of inflammation.
-
Mutation, deletion or inactivation of the gene that encodes ALS in humans and mice decreases circulating levels of IGF-1 and IGFBP-3, causing moderate growth deficiency and abnormalities in bone and carbohydrate metabolism.
-
As a marker of inflammation and sepsis, ALS levels are low in critical illness, cardiovascular disease and COVID-19; in some conditions, ALS levels might predict disease progression and mortality.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bürgi, H., Müller, W. A., Humbel, R. E., Labhart, A. & Froesch, E. R. Non-suppressible insulin-like activity of human serum. I. Physicochemical properties, extraction and partial purification. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 121, 349–359 (1966).
Zapf, J., Waldvogel, M. & Froesch, E. R. Binding of nonsuppressible insulin-like activity to human serum. Evidence for a carrier protein. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 168, 638–645 (1975).
Hintz, R. L. & Liu, F. Demonstration of specific plasma protein binding sites for somatomedin. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 45, 988–995 (1977).
Wilkins, J. R. & D’Ercole, A. J. Affinity-labeled plasma somatomedin-C/insulin-like growth factor I binding proteins. Evidence of growth hormone dependence and subunit structure. J. Clin. Invest. 75, 1350–1358 (1985).
Furlanetto, R. W. The somatomedin C binding protein: evidence for a heterologous subunit structure. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 51, 12–19 (1980).
Hintz, R. L. Plasma forms of somatomedin and the binding protein phenomenon. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 13, 31–42 (1984).
Martin, J. L. & Baxter, R. C. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein from human plasma. Purification and characterization. J. Biol. Chem. 261, 8754–8760 (1986).
Wood, W. I. et al. Cloning and expression of the growth hormone-dependent insulin-like growth factor-binding protein. Mol. Endocrinol. 2, 1176–1185 (1988).
Baxter, R. C. Characterization of the acid-labile subunit of the growth hormone-dependent insulin-like growth factor binding protein complex. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 67, 265–272 (1988).
Baxter, R. C., Martin, J. L. & Beniac, V. A. High molecular weight insulin-like growth factor binding protein complex. Purification and properties of the acid-labile subunit from human serum. J. Biol. Chem. 264, 11843–11848 (1989).
Leong, S. R., Baxter, R. C., Camerato, T., Dai, J. & Wood, W. I. Structure and functional expression of the acid-labile subunit of the insulin-like growth factor-binding protein complex. Mol. Endocrinol. 6, 870–876 (1992).
Baxter, R. C. & Martin, J. L. Structure of the Mr 140,000 growth hormone-dependent insulin-like growth factor binding protein complex: determination by reconstitution and affinity-labeling. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 86, 6898–6902 (1989).
Cohen, K. L. & Nissley, S. P. The serum half-life of somatomedin activity: evidence for growth hormone dependence. Acta Endocrinol. 83, 243–258 (1976).
Franklin, R. C., Rennie, G. C., Burger, H. G. & Cameron, D. P. Changes in NSILA-S in response to somatotropin administration and hypophysectomy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 47, 91–96 (1978).
Baxter, R. C. & Martin, J. L. Radioimmunoassay of growth hormone-dependent insulin-like growth factor binding protein in human plasma. J. Clin. Invest. 78, 1504–1512 (1986).
Baxter, R. C. Circulating levels and molecular distribution of the acid-labile (alpha) subunit of the high molecular weight insulin-like growth factor-binding protein complex. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 70, 1347–1353 (1990).
Bella, J., Hindle, K. L., McEwan, P. A. & Lovell, S. C. The leucine-rich repeat structure. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 65, 2307–2333 (2008).
Matsushima, N., Takatsuka, S., Miyashita, H. & Kretsinger, R. H. Leucine rich repeat proteins: sequences, mutations, structures and diseases. Protein Pept. Lett. 26, 108–131 (2019).
Janosi, J. B. et al. The acid-labile subunit of the serum insulin-like growth factor-binding protein complexes. Structural determination by molecular modeling and electron microscopy. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 23328–23332 (1999).
David, A., Kelley, L. A. & Sternberg, M. J. A new structural model of the acid-labile subunit: pathogenetic mechanisms of short stature-causing mutations. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 49, 213–220 (2012).
Kim, H. et al. Structural basis for assembly and disassembly of the IGF/IGFBP/ALS ternary complex. Nat. Commun. 13, 4434 (2022).
Swanson, L. E. et al. Drosophila convoluted/dALS is an essential gene required for tracheal tube morphogenesis and apical matrix organization. Genetics 181, 1281–1290 (2009).
Rotwein, P. Large-scale analysis of variation in the insulin-like growth factor family in humans reveals rare disease links and common polymorphisms. J. Biol. Chem. 292, 9252–9261 (2017).
Janosi, J. B., Firth, S. M., Bond, J. J., Baxter, R. C. & Delhanty, P. J. N-linked glycosylation and sialylation of the acid-labile subunit. Role in complex formation with insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein-3 and the IGFs. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 5292–5298 (1999).
Holman, S. R. & Baxter, R. C. Insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3: factors affecting binary and ternary complex formation. Growth Regul. 6, 42–47 (1996).
Lee, C. Y. & Rechler, M. M. Purified rat acid-labile subunit and recombinant human insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein-3 can form a 150-kilodalton binary complex in vitro in the absence of IGFs. Endocrinology 136, 4982–4989 (1995).
Choi, K. Y. & Lee, D. H. Interaction between acid-labile subunit and insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 expressed in Xenopus oocytes. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 35, 186–193 (2002).
Firth, S. M., Ganeshprasad, U. & Baxter, R. C. Structural determinants of ligand and cell surface binding of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 2631–2638 (1998).
Twigg, S. M. & Baxter, R. C. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein 5 forms an alternative ternary complex with IGFs and the acid-labile subunit. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 6074–6079 (1998).
Twigg, S. M., Kiefer, M. C., Zapf, J. & Baxter, R. C. Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 5 complexes with the acid-labile subunit. Role of the carboxyl-terminal domain. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 28791–28798 (1998).
Chin, E., Zhou, J., Dai, J., Baxter, R. C. & Bondy, C. A. Cellular localization and regulation of gene expression for components of the insulin-like growth factor ternary binding protein complex. Endocrinology 134, 2498–2504 (1994).
Kim, J. W. et al. Isolation of the cDNA encoding the acid labile subunit (ALS) of the 150 kDa IGF-binding protein complex in cattle and ALS regulation during the transition from pregnancy to lactation. J. Endocrinol. 189, 583–593 (2006).
Lee, C. Y. et al. Molecular cloning of the porcine acid-labile subunit (ALS) of the insulin-like growth factor-binding protein complex and detection of ALS gene expression in hepatic and non-hepatic tissues. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 26, 135–144 (2001).
Landi, E. et al. Expression of acid-labile subunit (ALS) in developing and adult zebrafish and its role in dorso-ventral patterning during development. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 299, 113591 (2020).
Chen, W. et al. The matrisome genes from hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma unveiled. Hepatol. Commun. 5, 1571–1585 (2021).
Naba, A. et al. The extracellular matrix: tools and insights for the ‘omics’ era. Matrix Biol. 49, 10–24 (2016).
Ouni, E., Vertommen, D., Chiti, M. C., Dolmans, M. M. & Amorim, C. A. A draft map of the human ovarian proteome for tissue engineering and clinical applications. Mol. Cell Proteom. 18, S159–S173 (2019).
Wilczak, N. et al. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I binding to a cell membrane associated IGF binding protein-3 acid-labile subunit complex in human anterior pituitary gland. J. Neurochem. 82, 430–438 (2002).
Lewitt, M. S. et al. Regulation of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 ternary complex formation in pregnancy. J. Endocrinol. 159, 265–274 (1998).
Lo, H. C. et al. Relation of cord serum levels of growth hormone, insulin-like growth factors, insulin-like growth factor binding proteins, leptin, and interleukin-6 with birth weight, birth length, and head circumference in term and preterm neonates. Nutrition 18, 604–608 (2002).
Juul, A. et al. The acid-labile subunit of human ternary insulin-like growth factor binding protein complex in serum: hepatosplanchnic release, diurnal variation, circulating concentrations in healthy subjects, and diagnostic use in patients with growth hormone deficiency. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 83, 4408–4415 (1998).
Stadler, S. et al. Monoclonal anti-acid-labile subunit oligopeptide antibodies and their use in a two-site immunoassay for ALS measurement in humans. J. Immunol. Methods 252, 73–82 (2001).
Frystyk, J. et al. Developmental changes in serum levels of free and total insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I), IGF-binding protein-1 and -3, and the acid-labile subunit in rats. Endocrinology 139, 4286–4292 (1998).
Baxter, R. C. & Dai, J. Purification and characterization of the acid-labile subunit of rat serum insulin-like growth factor binding protein complex. Endocrinology 134, 848–852 (1994).
Hwang, D. L., Lee, P. D. & Cohen, P. Quantitative ontogeny of murine insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF-binding protein-3 and the IGF-related acid-labile subunit. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 18, 65–74 (2008).
Baxter, R. C. Signaling pathways of the insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. Endocr. Rev. 44, 753–778 (2023).
Santos-Lozano, A. et al. Successful aging: insights from proteome analyses of healthy centenarians. Aging 12, 3502–3515 (2020).
Dai, J. & Baxter, R. C. Regulation in vivo of the acid-labile subunit of the rat serum insulin-like growth factor-binding protein complex. Endocrinology 135, 2335–2341 (1994).
Lee, C. Y., Cohen, F. J., Wu, H. B., Ooi, G. T. & Rechler, M. M. The absence of 150-kDa insulin-like growth factor complexes in fetal rat serum is not due to a lack of functional acid-labile subunit. Horm. Metab. Res. 31, 182–185 (1999).
Schreiter, T. et al. Transcriptome-wide analysis of human liver reveals age-related differences in the expression of select functional gene clusters and evidence for a PPP1R10-governed ‘aging cascade’. Pharmaceutics 13, 2009 (2021).
Mandel, S. H., Moreland, E., Rosenfeld, R. G. & Gargosky, S. E. The effect of GH therapy on the immunoreactive forms and distribution of IGFBP-3, IGF-I, the acid-labile subunit, and growth rate in GH-deficient children. Endocrine 7, 351–360 (1997).
Gargosky, S. E., Tapanainen, P. & Rosenfeld, R. G. Administration of growth hormone (GH), but not insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I), by continuous infusion can induce the formation of the 150-kilodalton IGF-binding protein-3 complex in GH-deficient rats. Endocrinology 134, 2267–2276 (1994).
Scharf, J., Ramadori, G., Braulke, T. & Hartmann, H. Synthesis of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins and of the acid-labile subunit in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes, of Kupffer cells, and in cocultures: regulation by insulin, insulinlike growth factor, and growth hormone. Hepatology 23, 818–827 (1996).
Olivecrona, H. et al. Acute and short-term effects of growth hormone on insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins: serum levels and hepatic messenger ribonucleic acid responses in humans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 84, 553–560 (1999).
Dai, J., Scott, C. D. & Baxter, R. C. Regulation of the acid-labile subunit of the insulin-like growth factor complex in cultured rat hepatocytes. Endocrinology 135, 1066–1072 (1994).
Ooi, G. T., Cohen, F. J., Tseng, L. Y., Rechler, M. M. & Boisclair, Y. R. Growth hormone stimulates transcription of the gene encoding the acid-labile subunit (ALS) of the circulating insulin-like growth factor-binding protein complex and ALS promoter activity in rat liver. Mol. Endocrinol. 11, 997–1007 (1997).
Ooi, G. T., Hurst, K. R., Poy, M. N., Rechler, M. M. & Boisclair, Y. R. Binding of STAT5a and STAT5b to a single element resembling a gamma-interferon-activated sequence mediates the growth hormone induction of the mouse acid-labile subunit promoter in liver cells. Mol. Endocrinol. 12, 675–687 (1998).
Sos, B. C. et al. Abrogation of growth hormone secretion rescues fatty liver in mice with hepatocyte-specific deletion of JAK2. J. Clin. Invest. 121, 1412–1423 (2011).
Barreca, A. et al. Functions and regulation of the acid-labile subunit of the 150 K complex. Prog. Growth Factor. Res. 6, 231–239 (1995).
Scharf, J. G., Braulke, T., Hartmann, H. & Ramadori, G. Regulation of the components of the 150 kDa IGF binding protein complex in cocultures of rat hepatocytes and Kupffer cells by 3′,5′-cyclic adenosine monophosphate. J. Cell Physiol. 186, 425–436 (2001).
Delhanty, P. J. & Baxter, R. C. The regulation of acid-labile subunit gene expression and secretion by cyclic adenosine 3′,5′-monophosphate. Endocrinology 139, 260–265 (1998).
Delhanty, P. J. Interleukin-1 beta suppresses growth hormone-induced acid-labile subunit mRNA levels and secretion in primary hepatocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 243, 269–272 (1998).
Barreca, A., Ketelslegers, J. M., Arvigo, M., Minuto, F. & Thissen, J. P. Decreased acid-labile subunit (ALS) levels by endotoxin in vivo and by interleukin-1beta in vitro. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 8, 217–223 (1998).
Hynes, R. O. & Naba, A. Overview of the matrisome — an inventory of extracellular matrix constituents and functions. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 4, a004903 (2012).
Fernqvist-Forbes, E., Ekberg, K., Lindgren, B. F. & Brismar, K. Splanchnic exchange of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1), IGF-I and acid-labile subunit (ALS) during normo- and hyper-insulinaemia in healthy subjects. Clin. Endocrinol. 51, 327–332 (1999).
Juul, A. et al. Serum levels of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3) in healthy infants, children, and adolescents: the relation to IGF-I, IGF-II, IGFBP-1, IGFBP-2, age, sex, body mass index, and pubertal maturation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 80, 2534–2542 (1995).
Van den Berghe, G. et al. Reactivation of pituitary hormone release and metabolic improvement by infusion of growth hormone-releasing peptide and thyrotropin-releasing hormone in patients with protracted critical illness. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 84, 1311–1323 (1999).
Lewitt, M. S., Saunders, H., Phuyal, J. L. & Baxter, R. C. Complex formation by human insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-3 and human acid-labile subunit in growth hormone-deficient rats. Endocrinology 134, 2404–2409 (1994).
Lewitt, M. S., Saunders, H. & Baxter, R. C. Bioavailability of insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) in rats determined by the molecular distribution of human IGF-binding protein-3. Endocrinology 133, 1797–1802 (1993).
Zapf, J., Hauri, C., Waldvogel, M. & Froesch, E. R. Acute metabolic effects and half-lives of intravenously administered insulin-like growth factors I and II in normal and hypophysectomized rats. J. Clin. Invest. 77, 1768–1775 (1986).
Firth, S. M., McDougall, F., McLachlan, A. J. & Baxter, R. C. Impaired blockade of insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I)-induced hypoglycemia by IGF binding protein-3 analog with reduced ternary complex-forming ability. Endocrinology 143, 1669–1676 (2002).
Payet, L. D., Firth, S. M. & Baxter, R. C. The role of the acid-labile subunit in regulating insulin-like growth factor transport across human umbilical vein endothelial cell monolayers. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 89, 2382–2389 (2004).
Xu, S. et al. Insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) and IGF-binding proteins in human skin interstitial fluid. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 80, 2940–2945 (1995).
Hughes, S. C., Mason, H. D., Franks, S. & Holly, J. M. The insulin-like growth factors (IGFs) in follicular fluid are predominantly bound in the ternary complex. J. Endocrinol. 155, R1–R4 (1997).
Khosravi, M. J., Diamandi, A., Mistry, J., Krishna, R. G. & Khare, A. Acid-labile subunit of human insulin-like growth factor-binding protein complex: measurement, molecular, and clinical evaluation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 82, 3944–3951 (1997).
Labarta, J. I. et al. Immunoblot studies of the acid-labile subunit (ALS) in biological fluids, normal human serum and in children with GH deficiency and GH receptor deficiency before and after long-term therapy with GH or IGF-I respectively. Clin. Endocrinol. 47, 657–666 (1997).
Wandji, S. A., Gadsby, J. E., Simmen, F. A., Barber, J. A. & Hammond, J. M. Porcine ovarian cells express messenger ribonucleic acids for the acid-labile subunit and insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 during follicular and luteal phases of the estrous cycle. Endocrinology 141, 2638–2647 (2000).
Moon, J. S. & Choi, Y. H. Multiplex PCR for the rapid detection of insulin-like growth factor in the Pacific oyster, Crassostrea gigas: a useful indicator for growth assessment. Mol. Biol. Rep. 46, 1023–1031 (2019).
Hetz, J. A. et al. Growth axis maturation is linked to nutrition, growth and developmental rate. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 411, 38–48 (2015).
Arquier, N. et al. Drosophila ALS regulates growth and metabolism through functional interaction with insulin-like peptides. Cell Metab. 7, 333–338 (2008).
Ueki, I. et al. Inactivation of the acid labile subunit gene in mice results in mild retardation of postnatal growth despite profound disruptions in the circulating insulin-like growth factor system. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 6868–6873 (2000).
Yakar, S. et al. Circulating levels of IGF-1 directly regulate bone growth and density. J. Clin. Invest. 110, 771–781 (2002).
Yakar, S. et al. The ternary IGF complex influences postnatal bone acquisition and the skeletal response to intermittent parathyroid hormone. J. Endocrinol. 189, 289–299 (2006).
Fritton, J. C. et al. The insulin-like growth factor-1 binding protein acid-labile subunit alters mesenchymal stromal cell fate. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 4709–4714 (2010).
Courtland, H. W. et al. Low levels of plasma IGF-1 inhibit intracortical bone remodeling during aging. Age 35, 1691–1703 (2013).
Swindell, W. R. Gene expression profiling of long-lived dwarf mice: longevity-associated genes and relationships with diet, gender and aging. BMC Genomics 8, 353 (2007).
Mariño, G. et al. Insulin-like growth factor 1 treatment extends longevity in a mouse model of human premature aging by restoring somatotroph axis function. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 107, 16268–16273 (2010).
Kim, Y. W. et al. Harnessing the paradoxical phenotypes of APOE ɛ2 and APOE ɛ4 to identify genetic modifiers in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 17, 831–846 (2021).
Domené, H. M. et al. Deficiency of the circulating insulin-like growth factor system associated with inactivation of the acid-labile subunit gene. N. Engl. J. Med. 350, 570–577 (2004).
Hwa, V. et al. Total absence of functional acid labile subunit, resulting in severe insulin-like growth factor deficiency and moderate growth failure. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 91, 1826–1831 (2006).
Firth, S. M., Yan, X. & Baxter, R. C. D440N mutation in the acid-labile subunit of insulin-like growth factor complexes inhibits secretion and complex formation. Mol. Endocrinol. 25, 307–314 (2011).
Domené, H. M. et al. Human acid-labile subunit deficiency: clinical, endocrine and metabolic consequences. Horm. Res. 72, 129–141 (2009).
Fofanova-Gambetti, O. V. et al. Impact of heterozygosity for acid-labile subunit (IGFALS) gene mutations on stature: results from the international acid-labile subunit consortium. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 95, 4184–4191 (2010).
van Duyvenvoorde, H. A. et al. Homozygous and heterozygous expression of a novel mutation of the acid-labile subunit. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 159, 113–120 (2008).
Hess, O. et al. A novel mutation in IGFALS, c.380T>C (p.L127P), associated with short stature, delayed puberty, osteopenia and hyperinsulinaemia in two siblings: insights into the roles of insulin growth factor-1 (IGF1). Clin. Endocrinol. 79, 838–844 (2013).
Domené, H. M. et al. Heterozygous IGFALS gene variants in idiopathic short stature and normal children: impact on height and the IGF system. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 80, 413–423 (2013).
Işık, E. et al. Clinical and biochemical characteristics and bone mineral density of homozygous, compound heterozygous and heterozygous carriers of three novel IGFALS mutations. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 176, 657–667 (2017).
Kumar, A. et al. Pathogenic/likely pathogenic variants in the SHOX, GHR and IGFALS genes among Indian children with idiopathic short stature. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 33, 79–88 (2020).
Franzoni, A. et al. Novel IGFALS mutations with predicted pathogenetic effects by the analysis of AlphaFold structure. Endocrine 79, 292–295 (2023).
Domené, S. & Domené, H. M. The role of acid-labile subunit (ALS) in the modulation of GH-IGF-I action. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 518, 111006 (2020).
Högler, W. et al. IGFALS gene dosage effects on serum IGF-I and glucose metabolism, body composition, bone growth in length and width, and the pharmacokinetics of recombinant human IGF-I administration. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 99, E703–E712 (2014).
Grandone, A. et al. Clinical features of a new acid-labile subunit (IGFALS) heterozygous mutation: anthropometric and biochemical characterization and response to growth hormone administration. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 81, 67–72 (2014).
Haluzik, M. et al. Insulin resistance in the liver-specific IGF-1 gene-deleted mouse is abrogated by deletion of the acid-labile subunit of the IGF-binding protein-3 complex: relative roles of growth hormone and IGF-1 in insulin resistance. Diabetes 52, 2483–2489 (2003).
de Boer, H. et al. Monitoring of growth hormone replacement therapy in adults, based on measurement of serum markers. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 81, 1371–1377 (1996).
Thorén, M. et al. Serum insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I), IGF-binding protein-1 and -3, and the acid-labile subunit as serum markers of body composition during growth hormone (GH) therapy in adults with GH deficiency. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 82, 223–228 (1997).
Drake, W. M. et al. Optimizing growth hormone replacement therapy by dose titration in hypopituitary adults. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 83, 3913–3919 (1998).
Marzullo, P. et al. Usefulness of different biochemical markers of the insulin-like growth factor (IGF) family in diagnosing growth hormone excess and deficiency in adults. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86, 3001–3008 (2001).
Fukuda, I. et al. Acid-labile subunit in growth hormone excess and deficiency in adults: evaluation of its diagnostic value in comparison with insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF-binding protein-3. Endocr. J. 49, 379–386 (2002).
Barrios, V. et al. Diagnostic interest of acid-labile subunit measurement in relationship to other components of the IGF system in pediatric patients with growth or eating disorders. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 144, 245–250 (2001).
Ertl, D. A. et al. Diagnostic value of serum acid-labile subunit alone and in combination with IGF-I and IGFBP-3 in the diagnosis of growth hormone deficiency. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 93, 371–379 (2020).
Yuen, K. C. J. et al. Diagnosis and testing for growth hormone deficiency across the ages: a global view of the accuracy, caveats, and cut-offs for diagnosis. Endocr. Connect. 12, e220504 (2023).
Arosio, M. et al. Diagnostic value of the acid-labile subunit in acromegaly: evaluation in comparison with insulin-like growth factor (IGF) I, and IGF-binding protein-1, -2, and -3. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 86, 1091–1098 (2001).
Morrison, K. M., Wu, Z., Bidlingmaier, M. & Strasburger, C. J. Findings and theoretical considerations on the usefulness of the acid-labile subunit in the monitoring of acromegaly. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 11, S61–S63 (2001).
Giustina, A. et al. Multidisciplinary management of acromegaly: a consensus. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 21, 667–678 (2020).
Wallace, J. D. et al. Responses of the growth hormone (GH) and insulin-like growth factor axis to exercise, GH administration, and GH withdrawal in trained adult males: a potential test for GH abuse in sport. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 84, 3591–3601 (1999).
Equey, T. et al. Application of the athlete biological passport approach to the detection of growth hormone doping. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 107, 649–659 (2022).
Neumann, O. et al. Methylome analysis and integrative profiling of human HCCs identify novel protumorigenic factors. Hepatology 56, 1817–1827 (2012).
Udali, S. et al. DNA methylation and gene expression profiles show novel regulatory pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin. Epigenet. 7, 43 (2015).
Marquardt, J. U. et al. Sequential transcriptome analysis of human liver cancer indicates late stage acquisition of malignant traits. J. Hepatol. 60, 346–353 (2014).
Yu, J., Zhang, H., Zhang, Y. & Zhang, X. Integrated analysis of the altered lncRNA, microRNA, and mRNA expression in HBV-positive hepatocellular carcinoma. Life 12, 701 (2022).
Ge, S. et al. Identification of the diagnostic biomarker VIPR1 in hepatocellular carcinoma based on machine learning algorithm. J. Oncol. 2022, 2469592 (2022).
Ye, J. et al. Prognosis-related molecular subtypes and immune features associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers 14, 5721 (2022).
Huang, J. et al. Novel potential biomarkers for severe alcoholic liver disease. Front. Immunol. 13, 1051353 (2022).
Mucci, L. A. et al. Plasma levels of acid-labile subunit, free insulin-like growth factor-I, and prostate cancer risk: a prospective study. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 19, 484–491 (2010).
Ma, C. et al. Circulating insulin-like growth factor 1-related biomarkers and risk of lethal prostate cancer. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 6, pkab091 (2022).
Johansson, M. et al. Genetic and plasma variation of insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in relation to prostate cancer incidence and survival. Prostate 69, 1281–1291 (2009).
Cao, Y. et al. Insulin-like growth factor pathway genetic polymorphisms, circulating IGF1 and IGFBP3, and prostate cancer survival. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 106, dju085 (2014).
Chen, J. et al. High-resolution bisulfite-sequencing of peripheral blood DNA methylation in early-onset and familial risk breast cancer patients. Clin. Cancer Res. 25, 5301–5314 (2019).
Wang, F., Tang, C., Gao, X. & Xu, J. Identification of a six-gene signature associated with tumor mutation burden for predicting prognosis in patients with invasive breast carcinoma. Ann. Transl. Med. 8, 453 (2020).
Zhao, Y., Zhang, Y., Dai, C., Hong, K. & Guo, Y. A signature constructed with mitophagy-related genes to predict the prognosis and therapy response for breast cancer. Aging 14, 6169–6186 (2022).
Canzian, F. et al. Polymorphisms of genes coding for insulin-like growth factor 1 and its major binding proteins, circulating levels of IGF-I and IGFBP-3 and breast cancer risk: results from the EPIC study. Br. J. Cancer 94, 299–307 (2006).
Deming, S. L. et al. Genetic variation in IGF1, IGF-1R, IGFALS, and IGFBP3 in breast cancer survival among Chinese women: a report from the Shanghai Breast Cancer Study. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 104, 309–319 (2007).
Taverne, C. W. et al. Common genetic variation of insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 1 (IGFBP-1), IGFBP-3, and acid labile subunit in relation to serum IGF-I levels and mammographic density. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 123, 843–855 (2010).
Daughaday, W. H. & Trivedi, B. Measurement of derivatives of proinsulin-like growth factor-II in serum by a radioimmunoassay directed against the E-domain in normal subjects and patients with nonislet cell tumor hypoglycemia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 75, 110–115 (1992).
Zapf, J., Futo, E., Peter, M. & Froesch, E. R. Can ‘big’ insulin-like growth factor II in serum of tumor patients account for the development of extrapancreatic tumor hypoglycemia? J. Clin. Invest. 90, 2574–2584 (1992).
Dynkevich, Y. et al. Tumors, IGF-2, and hypoglycemia: insights from the clinic, the laboratory, and the historical archive. Endocr. Rev. 34, 798–826 (2013).
Baxter, R. C. & Daughaday, W. H. Impaired formation of the ternary insulin-like growth factor-binding protein complex in patients with hypoglycemia due to nonislet cell tumors. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 73, 696–702 (1991).
Daughaday, W. H., Trivedi, B. & Baxter, R. C. Abnormal serum IGF-II transport in non-islet cell tumor hypoglycemia results from abnormalities of both IGF binding protein-3 and acid labile subunit and leads to elevation of serum free IGF-II. Endocrine 3, 425–428 (1995).
Teale, J. D., Blum, W. F. & Marks, V. Alleviation of non-islet cell tumour hypoglycaemia by growth hormone therapy is associated with changes in IGF binding protein-3. Ann. Clin. Biochem. 29, 314–323 (1992).
Baxter, R. C. et al. Regulation of the insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins by glucocorticoid and growth hormone in nonislet cell tumor hypoglycemia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 80, 2700–2708 (1995).
Katz, L. E. et al. The effect of growth hormone treatment on the insulin-like growth factor axis in a child with nonislet cell tumor hypoglycemia. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 81, 1141–1146 (1996).
Bond, J. J., Meka, S. & Baxter, R. C. Binding characteristics of pro-insulin-like growth factor-II from cancer patients: binary and ternary complex formation with IGF binding proteins-1 to -6. J. Endocrinol. 165, 253–260 (2000).
Boisclair, Y. R., Wang, J., Shi, J., Hurst, K. R. & Ooi, G. T. Role of the suppressor of cytokine signaling-3 in mediating the inhibitory effects of interleukin-1beta on the growth hormone-dependent transcription of the acid-labile subunit gene in liver cells. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 3841–3847 (2000).
Kong, S. E., Firth, S. M., Baxter, R. C. & Delhanty, P. J. Regulation of the acid-labile subunit in sustained endotoxemia. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 283, E692–E701 (2002).
Baxter, R. C., Hawker, F. H., To, C., Stewart, P. M. & Holman, S. R. Thirty-day monitoring of insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins in intensive care unit patients. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 8, 455–463 (1998).
Van den Berghe, G. et al. A paradoxical gender dissociation within the growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor I axis during protracted critical illness. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 85, 183–192 (2000).
Flannery, B. M., Amuzie, C. J. & Pestka, J. J. Evaluation of insulin-like growth factor acid-labile subunit as a potential biomarker of effect for deoxynivalenol-induced proinflammatory cytokine expression. Toxicology 304, 192–198 (2013).
Ruiz-Sanmartín, A. et al. Characterization of a proteomic profile associated with organ dysfunction and mortality of sepsis and septic shock. PLoS ONE 17, e0278708 (2022).
Salie, M. T. et al. Data-independent acquisition mass spectrometry in severe rheumatic heart disease (RHD) identifies a proteomic signature showing ongoing inflammation and effectively classifying RHD cases. Clin. Proteom. 19, 7 (2022).
Xu, G. et al. Virus-inducible IGFALS facilitates innate immune responses by mediating IRAK1 and TRAF6 activation. Cell Mol. Immunol. 18, 1587–1589 (2021).
Lee, J. S. et al. Longitudinal proteomic profiling provides insights into host response and proteome dynamics in COVID-19 progression. Proteomics 21, e2000278 (2021).
Richard, V. R. et al. Early prediction of COVID-19 patient survival by targeted plasma multi-omics and machine learning. Mol. Cell Proteom. 21, 100277 (2022).
Kimura, Y. et al. Identification of serum prognostic biomarkers of severe COVID-19 using a quantitative proteomic approach. Sci. Rep. 11, 20638 (2021).
Völlmy, F. et al. A serum proteome signature to predict mortality in severe COVID-19 patients. Life Sci. Alliance 4, e202101099 (2021).
Calvet, J. et al. Biomarker candidates for progression and clinical management of COVID-19 associated pneumonia at time of admission. Sci. Rep. 12, 640 (2022).
Fischer, F. et al. Associations of insulin-like growth factors, insulin-like growth factor binding proteins and acid-labile subunit with coronary heart disease. Clin. Endocrinol. 61, 595–602 (2004).
Prentice, R. L. et al. Novel proteins associated with risk for coronary heart disease or stroke among postmenopausal women identified by in-depth plasma proteome profiling. Genome Med. 2, 48 (2010).
Chen, H. et al. Systemic biomarkers and unique pathways in different phenotypes of heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Biomolecules 12, 1419 (2022).
Heyse, W. et al. Identification of patient subtypes based on protein expression for prediction of heart failure after myocardial infarction. iScience 26, 106171 (2023).
Wysokinski, W. E. et al. Impact of atrial fibrillation on platelet gene expression. Eur. J. Haematol. 98, 615–621 (2017).
Bereket, A. et al. Regulation of the acid-labile subunit of the insulin-like growth factor ternary complex in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and severe burns. Clin. Endocrinol. 44, 525–532 (1996).
Lai, Y. C., Li, H. Y., Wu, T. J., Jeng, C. Y. & Chuang, L. M. Correlation of circulating acid-labile subunit levels with insulin sensitivity and serum LDL cholesterol in patients with type 2 diabetes: findings from a prospective study with rosiglitazone. PPAR Res. 2014, 917823 (2014).
Kershaw, N. J. et al. SOCS3 binds specific receptor-JAK complexes to control cytokine signaling by direct kinase inhibition. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 20, 469–476 (2013).
Woolson, H. D., Thomson, V. S., Rutherford, C., Yarwood, S. J. & Palmer, T. M. Selective inhibition of cytokine-activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase by cyclic AMP via Epac1-dependent induction of suppressor of cytokine signalling-3. Cell Signal. 21, 1706–1715 (2009).
Cocolakis, E. et al. Smad signaling antagonizes STAT5-mediated gene transcription and mammary epithelial cell differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 283, 1293–1307 (2008).
Bianchi, M., Meng, C. & Ivashkiv, L. B. Inhibition of IL-2-induced Jak-STAT signaling by glucocorticoids. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 97, 9573–9578 (2000).
Wei, S. & Qiu, Y. MiR-210-5p regulates STAT3 activation by targeting STAT5A in the differentiation of dermal fibroblasts. 3 Biotech 11, 243 (2021).
D’Alessandro, A. et al. Serum proteomics in COVID-19 patients: altered coagulation and complement status as a function of IL-6 level. J. Proteome Res. 19, 4417–4427 (2020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The author declares no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Reviews Endocrinology thanks Horacio Domene, Briony Forbes and Shoshana Yakar for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Related links
Human Gene Mutation Database: www.hgmd.cf.ac.uk
The Human Protein Atlas: www.proteinatlas.org/
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Baxter, R.C. Endocrine and cellular physiology and pathology of the insulin-like growth factor acid-labile subunit. Nat Rev Endocrinol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-024-00970-4
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41574-024-00970-4