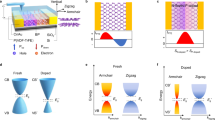
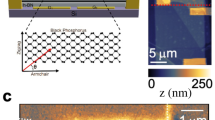
Abstract
A light field carrying multidimensional optical information, including but not limited to polarization, intensity and wavelength, is essential for numerous applications such as environmental monitoring, thermal imaging, medical diagnosis and free-space communications. Simultaneous acquisition of this multidimensional information could provide comprehensive insights for understanding complex environments but remains a challenge. Here we demonstrate a multidimensional optical information detection device based on zero-bias double twisted black arsenic–phosphorus homojunctions, where the photoresponse is dominated by the photothermoelectric effect. By using a bipolar and phase-offset polarization photoresponse, the device operated in the mid-infrared range can simultaneously detect both the polarization angle and incident intensity information through direct measurement of the photocurrents in the double twisted black arsenic–phosphorus homojunctions. The device’s responsivity makes it possible to retrieve wavelength information, typically perceived as difficult to obtain. Moreover, the device exhibits an electrically tunable polarization photoresponse, enabling precise distinction of polarization angles under low-intensity light exposure. These demonstrations offer a promising approach for simultaneous detection of multidimensional optical information, indicating potential for diverse photonic applications.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
$29.99 / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available within the main text and Supplementary Information. Any other relevant data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request. Source data are provided with this paper.
References
Rubin, N. A. et al. Matrix Fourier optics enables a compact full-Stokes polarization camera. Science 365, eaax1839 (2019).
He, C. et al. Polarisation optics for biomedical and clinical applications: a review. Light Sci. Appl. 10, 194 (2021).
Hakkel, K. D. et al. Integrated near-infrared spectral sensing. Nat. Commun. 13, 103 (2022).
Ren, Z., Zhang, Z., Wei, J., Dong, B. & Lee, C. Wavelength-multiplexed hook nanoantennas for machine learning enabled mid-infrared spectroscopy. Nat. Commun. 13, 3859 (2022).
Zou, K. et al. High-capacity free-space optical communications using wavelength- and mode-division-multiplexing in the mid-infrared region. Nat. Commun. 13, 7662 (2022).
Ou, K. et al. Mid-infrared polarization-controlled broadband achromatic metadevice. Sci. Adv. 6, eabc0711 (2020).
Tang, X., Ackerman, M. M., Chen, M. & Guyot-Sionnest, P. Dual-band infrared imaging using stacked colloidal quantum dot photodiodes. Nat. Photon. 13, 277–282 (2019).
Yuan, S., Naveh, D., Watanabe, K., Taniguchi, T. & Xia, F. A wavelength-scale black phosphorus spectrometer. Nat. Photon. 15, 601–607 (2021).
Yoon, H. H. et al. Miniaturized spectrometers with a tunable van der Waals junction. Science 378, 296–299 (2022).
Deng, W. et al. Electrically tunable two-dimensional heterojunctions for miniaturized near-infrared spectrometers. Nat. Commun. 13, 4627 (2022).
Shen, D. et al. High-performance mid-IR to deep-UV van der Waals photodetectors capable of local spectroscopy at room temperature. Nano Lett. 22, 3425–3432 (2022).
Chen, Y. et al. Unipolar barrier photodetectors based on van der Waals heterostructures. Nat. Electron. 4, 357–363 (2021).
Liu, W. et al. Graphene charge-injection photodetectors. Nat. Electron. 5, 281–288 (2022).
Chen, Y. et al. Momentum-matching and band-alignment van der Waals heterostructures for high-efficiency infrared photodetection. Sci. Adv. 8, eabq1781 (2022).
Adinolfi, V. & Sargent, E. H. Photovoltage field-effect transistors. Nature 542, 324–327 (2017).
Zhang, B. Y. et al. Broadband high photoresponse from pure monolayer graphene photodetector. Nat. Commun. 4, 1811 (2013).
Yuan, H. et al. Polarization-sensitive broadband photodetector using a black phosphorus vertical p–n junction. Nat. Nanotechnol. 10, 707–713 (2015).
Wu, S. et al. Ultra-sensitive polarization-resolved black phosphorus homojunction photodetector defined by ferroelectric domains. Nat. Commun. 13, 3198 (2022).
Dai, M. et al. High-performance, polarization-sensitive, long-wave infrared photodetection via photothermoelectric effect with asymmetric van der Waals contacts. ACS Nano 16, 295–305 (2022).
Semkin, V. A. et al. Zero-bias photodetection in 2D materials via geometric design of contacts. Nano Lett. 23, 5250–5256 (2023).
Ma, C. et al. Intelligent infrared sensing enabled by tunable moire quantum geometry. Nature 604, 266–272 (2022).
Xiong, Y. et al. Twisted black phosphorus-based van der Waals stacks for fiber-integrated polarimeters. Sci. Adv. 8, eabo0375 (2022).
Deng, W. et al. Switchable unipolar-barrier van der Waals heterostructures with natural anisotropy for full linear polarimetry detection. Adv. Mater. 34, 2203766 (2022).
Dai, M. et al. On-chip mid-infrared photothermoelectric detectors for full-Stokes detection. Nat. Commun. 13, 4560 (2022).
Wei, J. et al. Zero-bias mid-infrared graphene photodetectors with bulk photoresponse and calibration-free polarization detection. Nat. Commun. 11, 6404 (2020).
Wei, J. et al. Geometric filterless photodetectors for mid-infrared spin light. Nat. Photon. 17, 171–178 (2022).
Dai, M. et al. Long-wave infrared photothermoelectric detectors with ultrahigh polarization sensitivity. Nat. Commun. 14, 3421 (2023).
Liu, M. et al. High yield growth and doping of black phosphorus with tunable electronic properties. Mater. Today 36, 91–101 (2020).
Amani, M., Regan, E., Bullock, J., Ahn, G. H. & Javey, A. Mid-wave infrared photoconductors based on black phosphorus–arsenic alloys. ACS Nano 11, 11724–11731 (2017).
Yuan, S. et al. Air-stable room-temperature mid-infrared photodetectors based on hBN/black arsenic phosphorus/hBN heterostructures. Nano Lett. 18, 3172–3179 (2018).
Long, M. et al. Room temperature high-detectivity mid-infrared photodetectors based on black arsenic phosphorus. Sci. Adv. 3, e1700589 (2017).
Karki, B., Rajapakse, M., Sumanasekera, G. U. & Jasinski, J. B. Structural and thermoelectric properties of black arsenic–phosphorus. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 3, 8543–8551 (2020).
Wang, F. et al. A two-dimensional mid-infrared optoelectronic retina enabling simultaneous perception and encoding. Nat. Commun. 14, 1938 (2023).
Xu, X., Gabor, N. M., Alden, J. S., van der Zande, A. M. & McEuen, P. L. Photo-thermoelectric effect at a graphene interface junction. Nano Lett. 10, 562–566 (2010).
Wang, F., Pei, K., Li, Y., Li, H. & Zhai, T. 2D homojunctions for electronics and optoelectronics. Adv. Mater. 33, 2005303 (2021).
Xu, B., Mao, N., Zhao, Y., Tong, L. & Zhang, J. Polarized Raman spectroscopy for determining crystallographic orientation of low-dimensional materials. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 12, 7442–7452 (2021).
Zou, B. et al. Unambiguous determination of crystal orientation in black phosphorus by angle-resolved polarized Raman spectroscopy. Nanoscale Horiz. 6, 809–818 (2021).
Liu, B. et al. Black arsenic–phosphorus: layered anisotropic infrared semiconductors with highly tunable compositions and properties. Adv. Mater. 27, 4423–4429 (2015).
Wei, J. X., Xu, C., Dong, B. W., Qiu, C. W. & Lee, C. K. Mid-infrared semimetal polarization detectors with configurable polarity transition.Nat. Photon. 15, 614–621 (2021).
Liu, Y. et al. Approaching the Schottky–Mott limit in van der Waals metal–semiconductor junctions. Nature 557, 696–700 (2018).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Singapore Ministry of Education (MOE-T2EP50120-0009 (Q.J.W.)), the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR) (A18A7b0058 (Q.J.W.), M22K2c0080 (Q.J.W.) and A2090b0144 (Q.J.W.)), the National Medical Research Council (NMRC) (award number MOH-000927 (Q.J.W.)) and the National Research Foundation Singapore (award number NRF-CRP22-2019-0007 (Q.J.W.)).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Q.J.W. supervised the project. F.W. designed and fabricated the devices. F.W., S.Z., W.C. and J.H. performed the device characterizations. S.Z., W.C., R.D., C.W., M.D., F.S. and Y.J. provided experimental testing support. F.W. analysed the data and drafted the manuscript. Q.J.W. revised the manuscript. All authors have discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Nanotechnology thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary Figs. 1–25, Notes 1–4 and Table 1.
Source data
Source Data Fig. 2
Source data for the plot in Fig. 2.
Source Data Fig. 3
Source data for the plot in Fig. 3.
Source Data Fig. 4
Source data for the plot in Fig. 4.
Source Data Fig. 5
Source data for the plot in Fig. 5.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Zhu, S., Chen, W. et al. Multidimensional detection enabled by twisted black arsenic–phosphorus homojunctions. Nat. Nanotechnol. 19, 455–462 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-023-01593-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-023-01593-y