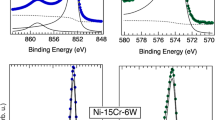
Abstract
Corrosion results in large costs and environmental impact but can be controlled by thin oxide films that passivate the metal surfaces and hinder further oxidation or dissolution in an aqueous environment. The structure, chemistry, and thickness of these oxide films play a significant role in determining their anti-corrosion properties and the early-stage oxidation dynamics affect the properties of the developed oxide. Here, we use in situ X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) to study the early-stage oxidation of a Ni-Cr-Mo alloy at room temperature and up to 400 °C. Cr and Mo begin to oxidize immediately after exposure to O2, and Cr3+, Mo4+, and Mo6+ oxides are formed. In contrast, Ni does not contribute significantly to the oxide film. A self-limiting oxide thickness, which did not depend on temperature below 400 °C, is observed. This is attributed to the consumption of available Cr and Mo near the surface, which results in an enrichment of metallic Ni under the oxide. The self-limited oxide thickness is 6–8 Å, which corresponds to 3–4 atomic layers of cations in the oxide. At 400 °C, sublimation of Mo6+ oxide is observed, resulting in the formation of an almost pure layer of Cr2O3 on the alloy surface. Lastly, a mechanism is presented that explains the formation of the bi-layer oxide structure observed for Ni-Cr-Mo alloys, which involves the enhanced migration of hexavalent Mo ions in the electric field, which drives mass transport during oxidation according to both the Cabrera Mott model and the Point Defect Model.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Corrosion of metallic materials results in substantial costs for society of around 4% of each nation’s GDP1,2. The production of metals is also responsible for 40% of global industrial CO2 emissions and uses 10% of global energy consumption3. Corrosion and degradation of metals hence lead to a significant environmental impact4,5,6. The utilization of reactive metals that spontaneously oxidize under ambient conditions is made possible due to the phenomena of passivity, where thin, stable oxide films on the metal surface hinder further oxidation and dissolution in the case of aqueous environments7,8,9. Studying the initial oxide formation and growth can then help us understand the factors governing the thickness, chemistry, and morphology of the thin oxide films, which are all important parameters when it comes to understanding the corrosion resistance of a material.
A model for the growth of thin oxide films on metal surfaces was developed by Cabrera and Mott in the 1940s10. It postulates that a potential drop occurs across the oxide film when electron tunneling results in the charge separation of metal cations at the metal/oxide interface and oxygen anions at the oxide surface. In the electric field caused by this potential, ions can then move across the oxide to facilitate the necessary mass transport for further oxide growth. This model also predicts the logarithmic oxide growth rate behavior that is often observed. For electrochemical oxide film growth, the Point Defect Model (PDM) was developed by Digby Macdonald in the 1980s11,12,13. Also, in the PDM, the growth of the oxide film is facilitated by the migration of ions across the oxide, only now driven by electrochemical potential.
Famous examples of alloys exhibiting passivity are stainless steel14,15,16 and aluminum alloys17,18,19. In harsh environments of high temperature, acidic solutions, and high Cl content, Ni-Cr-Mo alloys are commonly used. They are known for their excellent corrosion resistance20,21, attributed to the presence of thin passive oxide films of around 1 nm on the surface rich in Cr3+, Mo4+, and Mo6+22,23,24,25. Ni-Cr-Mo alloys have been studied in aqueous corrosive conditions26,27,28,29,30,31,32 and high-temperature oxidation33,34. The initial oxide growth that forms the passive film has been studied for stainless steel model systems35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42, Ni-Cr alloys43,44,45,46 and Ni-Cr- Mo alloys47. It has been observed that the oxide film on Ni-Cr-Mo alloys has a layered structure, with an inner layer rich in Cr3+ oxide and an outer layer rich in Mo6+ oxide22,25,48,49. However, the dynamics of the early-stage oxide formation that governs the oxide structure, thickness, and chemistry are not known for Ni-Cr-Mo alloys.
Here, we use in situ XPS to study the initial oxidation of a Ni-Cr-Mo (62.3 at% Ni, 26.3 at% Cr, and 9.7 at% Mo) polycrystalline surface after sputter removal of the oxide. Oxidation was performed in 1 × 10−8 mbar of O2 dosed in a UHV chamber at room temperature (RT), 150 °C, 300 °C, and 400 °C. It was found that for alloys such as Ni-Cr-Mo, where the base metal, Ni, does not contribute significantly to the oxide film, the oxide thickness is governed by the available amount of Cr and Mo near the surface. It was also found that at 400 °C, only Cr2O3 was present in the oxide film due to the sublimation of Mo6+ oxide. Cr and Mo both oxidize from the start of the O2 exposure. The origin of the bi-layer oxide model proposed in the literature for Ni-Cr-Mo alloys, with an inner layer rich in Cr2O3 and an outer layer rich in Mo6+ oxide, is hence explained by the enhanced migration of hexavalent Mo cations compared to trivalent Cr ions in the electric field that drives mass transport both in dry oxidation and electrochemical oxide growth.
Results
Quantitative analysis of in situ oxidation
Figure 1 shows an example of the deconvoluted spectra of the Cr 2p3/2, Mo 3d, and Ni 2p3/2 core levels measured in situ during O2 dosing at 1 × 10−8 mbar at RT. Deconvoluted spectra of the Cr 2p3/2, Mo 3d, and Ni 2p3/2 core levels measured at 150 °C, 300 °C, and 400 °C can be found in the supplementary information. All the spectra can also be found in the supplementary information. After sputtering to remove any oxide on the surface, only the metallic components are observed in the spectra at the bottom panel of Fig. 1. After dosing O2, the surface immediately oxidizes. In the Cr 2p3/2 core level spectra, Cr2O3 with its multiplet structure50,51,52 was formed on the surface, and it is clearly visible after 5.5 Langmuir (L) of O2 exposure. Upon increased exposure time to O2, the relative intensity of the Cr2O3 component further increases until around 20 L, after which not much change is observed. In the Mo 3d core level spectra, a component associated with Mo4+ oxide and Mo6+ oxide was observed upon exposure of the sample to O2, and the relative intensity of the oxide components increased upon increased cumulative O2 exposure until around 20 L. In the Ni 2p3/2 core level, a component associated with NiO could be seen upon exposure to O2. NiO has previously been observed on Ni-Cr surfaces upon low exposures of O243,45,46, but it is not found in the air-formed native oxide or electrochemically grown oxides on Ni-Cr-Mo alloys22,23,24,27. The small, oxidized Ni component could potentially also be associated with hydroxylated Ni from residual water vapor in the chamber.
Figure 2 shows the results of the quantitative analysis of the deconvoluted components from the XPS spectra that were performed to extract information about the oxide layer thickness and composition, as well as the composition of the metal underneath the oxide layer. In the analysis, a model of a single and homogeneous oxide overlayer was assumed to exist on the surface. The photoelectron intensity of each deconvoluted component could then be described in a system of equations, as shown in the supplementary information. By solving this system of equations for each set of spectra at increasing cumulative O2 exposure, the oxide thickness, oxide composition, and underlying metal composition can be determined. This can then be plotted against the O2 exposure, which is directly proportional to the oxidation time since a constant pressure of O2 was used. Figure 2a shows the oxide thickness as a function of oxygen exposure at different sample temperatures. At RT and 150 °C, an initial and rapid growth rate of the oxide can be seen, and the two curves exhibit practically identical behavior. At 300 °C, the initial oxide growth rate is less rapid than at RT and 150 °C, this has previously been observed also for stainless steel40. At 400 °C, an incubation period can be seen during the first 4 L of exposure, which is followed by a rapid oxide growth rate. At all oxidation temperatures, the oxide reaches a self-limiting thickness after around 20 L of exposure. Interestingly, the self-limiting oxide thickness is temperature-independent at 300 °C and below, where a thickness of around 6 Å is reached. At 400 °C, an oxide thickness of around 8 Å is reached.
Quantitative analysis of oxide thickness and composition, as well as the composition of the probed layer of underlying metal at varying sample temperatures as a function of O2 exposure. a Oxide thickness. b Cr2O3 content in the oxide film. c Mo4+ content in the oxide film. d Mo6+ content in the oxide film. e Ni2+ content in the oxide film. f Ni content in the metal under the oxide film. g Cr content in the metal under the oxide film. h Mo content in the metal under the oxide film.
Figure 2b–e shows the Cr2O3, Mo4+, Mo6+ and Ni2+ content in the oxide film as a function of O2 exposure. The Cr2O3 content in the oxide film increases during the initial stages of oxidation below 5 L and afterward reaches a steady value, as seen in Fig. 2b. It can also be seen that the Cr2O3 content in the oxide film increases with increasing temperature. At RT and 150 °C, the same is true for Mo6+ oxide, as shown in Fig. 2d, which also increases in the beginning at the initial stages of oxidation until a plateau is reached. At increasing sample temperature, the Mo6+ content in the oxide decreases. The Mo4+ oxide content is highest at the very beginning of oxidation after only 1 L of O2 exposure, as shown in Fig. 2c. It then decreases as the oxide film instead becomes enriched in Cr2O3 and Mo6+ oxide. The Ni content in the oxide film never exceeds 18% for the oxide grown at RT. At all elevated temperatures, the contribution of Ni in the oxide film was close to zero, which can also be seen from the fitted spectra in the supplementary information. Figure 2f–h shows the metal composition under the oxide film during oxidation. It can be seen that the Ni metal content underneath the oxide increases during oxidation, as shown in Fig. 2f, and reaches a steady value around 20 L where also the oxide reaches a self-limiting thickness. Both the metallic Cr and Mo content under the oxide film decrease during oxidation. This is consistent with the fact that Cr and Mo are oxidized to a greater extent while Ni is not. Thus, as Cr and Mo are consumed in the alloy near the surface during oxidation, metallic Ni is enriched under the oxide film, which goes in line with previous observations23,24.
Figure 3 shows the oxide and metal composition for the different temperatures at the beginning and end of the oxidation experiment. At all temperatures, the Mo4+ oxide content is higher after 2 L than after 44 L, as seen in Fig. 3a, b. At increasing oxygen exposure at RT, the oxide becomes enriched in Cr3+ oxide and Mo6+ oxide. However, after 44 L, at the end of the in situ experiment, the oxide composition is different from that after long-term aging in air, where further Cr3+ enrichment of up to 70 cation% is seen in the oxide23,24. The metal composition of the surface before oxidation, shown in Fig. 3c), does not vary significantly with temperature until 400 °C, where an enrichment of metallic Cr is seen. This can be attributed to the bulk diffusion of Cr, which becomes effective above 300 °C40. A slight enrichment of Mo compared to the expected bulk composition is also seen, which could be attributed to the preferential sputtering of the lighter elements Cr and Ni. However, after oxidation, the metal composition under the oxide is almost temperature-independent, as seen in Fig. 3d. Ni is enriched under the oxide, while Cr and Mo are depleted. By comparing the metal composition before oxidation in Fig. 3c to the oxide composition at the end of the in situ experiment seen in Fig. 3b, no strong correlation between the initial surface composition and the oxide composition can be seen. This highlights the complexity of oxidation of industrial alloys where temperature also plays a crucial role in determining the oxide composition.
Depth resolved analysis of oxide native oxide film
Figure 4 shows the depth-resolved variation of the Mo oxidation states in the air-formed film on the Ni-Cr-Mo alloy. It is known from Time Of Flight Secondary Ion Mass Spectrometry (TOF-SIMS) and XPS analysis that the oxide film on Ni-Cr-Mo alloys exhibits a layered structure with an inner layer rich in Cr3+ oxide and an outer layer rich in Mo6+ oxide22,25,48,49, as depicted in the schematic in Fig. 4a. It has also recently been shown that such a bi-layer oxide structure is also formed upon oxidation in pure O247. Mo 3d core level XPS spectra measured at different photon energies are shown in Fig. 4b. As seen, the ratio of the different components varies as a function of depth, where a higher photon energy means that the photoelectrons originate from deeper into the sample. The relative intensity of the Mo metal components is seen to decrease when the photon energy is decreased. The ratio of the different Mo oxidation states taken from the Mo 3d core level spectra is shown in Fig. 4c. As can be seen, Mo6+ is more enriched near the surface, which is consistent with previous observations. Since Mo6+ oxide and Cr3+ oxide formed at the same time during the in situ oxidation experiment, there seems to be a mechanism present that favors the migration of Mo6+ toward the oxide surface. It also needs to be considered that Cr2O3 can reduce Mo6+ into Mo4+53, which might affect the ratio of the different oxidation states as a function of depth. Mo5+ oxide is not observed during the oxidation experiments in pure O2 presented here, or even at high exposures as previously shown47. However, in air-formed oxides and electrochemically grown passive films, a component, usually associated to Mo5+ is commonly observed. This component could then potentially be associated to Mo4+ hydroxide, or incorporation of Mo in the Cr2O3 lattice54.
a Layered oxide model for Ni-Cr-Mo alloys proposed in the literature. b Mo 3d core level measured with varying photon energy to achieve depth profiling of an air-formed oxide on the Ni-Cr-Mo alloy. c Fraction of different Mo oxidation states measured at different depths. The x-axis is based on the mean free path of the photoelectrons, λ, calculated for Cr2O3 for simplicity.
Discussion
The temperature-independent self-limiting oxide thickness for the Ni-Cr-Mo alloy beyond 20 L of exposure observed in the present manuscript is different from what is observed for stainless steel38,40. In the case of stainless steel, the self-limiting oxide thickness increases with temperature, which is only observed for the Ni-Cr-Mo alloy at temperatures of 400 °C. At this temperature, bulk diffusion of Cr starts to activate38, and the initial sputter-cleaned surface exhibited a higher Cr content at 400 °C, as shown in Fig. 3c. For stainless steel, Cr plays a significant role in the formation of the protective oxide. However, the base metal Fe participates significantly in the oxide film on stainless steel16,38. The situation is different for Ni-Cr-Mo alloys since no NiO is observed originating from the base metal in either native air-formed oxides or electrochemically grown passive films22,23,27. What is observed for stainless steel is that Cr oxidizes rapidly at the expense of the depletion of metallic Cr near the surface, and only after that Fe is oxidized to further grow the oxide film38. Regarding Cr, the same is observed for the Ni-Cr-Mo alloy studied here, where rapid oxidation and depletion of metallic Cr near the surface are observed. However, once all accessible metallic Cr near the surface is depleted, the oxide cannot further grow on the Ni-Cr-Mo alloy since Ni does not significantly participate in the oxide film. The oxide thickness here seems to be governed by the accessible amount of Cr and Mo near the surface and not by the temperature until the temperature is high enough to drive sufficient bulk diffusion, which can supply the surface with Cr atoms from the bulk alloy. The self-limiting oxide thickness on Ni-Cr-Mo alloys exposed to air is around 1 nm22,23,24,55, which is significantly thinner than that generally found on stainless steel of 2–2.5 nm56,57,58,59,60. The difference in the self-limiting oxide thickness for stainless steel and Ni-Cr-Mo alloys can be explained by the fact that the accessible Cr near the surface defines the self-limiting oxide thickness for Ni-Cr-Mo alloys, which is not the case for stainless steel where Fe also participates in the oxide film.
Molybdenum also influences the oxidation behavior of the alloy surface. During the initial stages of oxidation, the Mo4+ oxide content on the surface is high. This rapid initial formation of Mo4+ oxide before the formation of Cr2O3 and Mo6+ oxide could indicate that Mo4+ oxide forms and acts as nucleation sites for further oxide growth, or that the nucleation barrier for Mo oxides is lower than that of Cr oxide. At higher oxygen exposure, the thermodynamic preference for Cr2O3 outweighs the nucleation barrier, resulting in Cr oxide enrichment. It has also been shown with Density Functional Theory (DFT) and experimentally that Mo can act as a catalyst to supply Cr at the surface with oxygen by lowering the adsorption energy of atomic oxygen at hollow sites between Cr and Mo atoms in an alloy compared to pure Cr21,44,61. At elevated temperatures, the behavior of Mo during oxidation of the Ni-Cr-Mo alloy changes. At 400 °C, the Mo content in the oxide film decreases during oxidation, and the oxide film gets rich in Cr2O3. At the same time, the Mo content in the metal underneath the oxide also decreases. If Mo simply did not participate in the oxide film, it should have been enriched under the oxide film, similarly to Ni, which was not observed. This indicates that Mo6+ oxide forms and sublimates at these temperatures, and it has previously been shown that Mo6+ oxide is not stable in oxide films on Ni-Cr-Mo alloys at temperatures of 300 °C and above during vacuum annealing55 and sublimation of MoO3 thin films are observed close to 400 °C62.
For stainless steel, a bilayer oxide model of a Cr-rich inner layer and a Fe-rich outer layer has been observed with both Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM)63,64 and TOF-SIMS65,66. It was shown with XPS that this is caused by the initial formation of a Cr oxide layer and the subsequent formation of the Fe layer on top38. It is, hence, the depletion of Cr near the surface that drives the formation of this bilayer oxide structure on stainless steel. The reason why Fe appears in the outer layer and not the inner layer is due to the fact that cations are responsible for the mass transport across the oxide film during growth67,68,69,70. Also, for Ni-Cr-Mo alloys, a bilayer structure is observed where Cr oxide is enriched at the metal oxide interface, and Mo6+ oxide is enriched at the oxide surface22,25,47,48,49. However, the mechanism that gives rise to the observed bi-layer oxide structure for Ni-Cr-Mo alloys seems to be different from that of Fe-Cr alloys, based on the observations in this manuscript. It is not driven by the initial depletion of Cr and subsequent oxidation of Mo to form Mo6+ since it was experimentally observed in Fig. 2 that both Cr and Mo start to oxidize at the same time when exposed to oxygen. Since cations are responsible for the mass transport during oxidation (and not oxygen anions), the Mo6+ ions somehow are transported and driven across the oxide faster or easier than the Cr3+ ions, assuming that no change in oxidation state occurs in the Mo cations during transport across the oxide film. This could be explained by two main factors. First, ion transport across the oxide film during growth is driven by the electric field across the oxide film, both in the case of dry oxidation according to the Cabrera-Mott model10 and according to the PDM of electrochemical oxide film growth12,13. The difference in charge of the cations, Cr3+ vs. Mo6+, results in a larger force experienced by the Mo6+ cation in the electric field, and hence the migration velocity should be higher, even when considering the higher mass of the Mo ion. The ionic radii is also significantly smaller for Mo6+, 41–73 pm depending on the coordination of the ion, compared to Cr3+ with an ionic radius of 62 pm71. Second, the concentration and availability of oxygen anions are greater at the oxide surface than at the metal/oxide interface. Since the hexavalent Mo cation needs to bind to more oxygen anions, this could result in a driving force “pulling” the Mo6+ ions across the oxide film to the oxide surface, where oxygen anions are readily available. It is also possible that Mo4+ and Mo5+ is further oxidized at the outermost surface by the high availability of oxygen.
The oxidation behavior at RT and at 400 °C is schematically summarized in Fig. 5a–d. At RT, the oxide free alloy surface exhibits the same composition as the bulk alloy. Once exposed to oxygen, Cr and Mo immediately start to oxidize and are consumed near the surface, resulting in the enrichment of metallic Ni under the oxide film. Once all Cr and Mo near the surface are consumed, a self-limiting oxide thickness is reached. Compared to Cr3+, the transport of Mo6+ cations to the oxide surface is favored resulting in a layered oxide structure. At 400 °C, metallic Cr is enriched at the oxide free surface due to diffusion of Cr from the bulk alloy. Upon exposure to oxygen, Cr and Mo are oxidized, and Ni is enriched under the oxide, and a self-limiting oxide is achieved upon depletion of Cr near the surface. At 400 °C, Mo6+ oxide is not stable and sublimates from the oxide surface, leaving an oxide film rich in Cr3+. At RT, the self-limiting oxide thickness is 6 Å, and at 400 °C, it is 8 Å. This can be compared to atomic models of crystalline Cr2O3 and MoO3, as shown in Fig. 5e, f. In Cr2O3, 13.58 Å corresponds to around 6 layers of cations. An oxide thickness of 6–8 Å is then equal to only 3–4 atomic layers of cations, as depicted in the schematics of Fig. 5b, d. For MoO3, 13.85 Å corresponds to 4 layers of cations. An oxide thickness of 6–8 Å, as measured for the Ni-Cr-Mo alloys, would then only correspond to 2 atomic layers of cations. The lack of strong chemical bonds between the layered structure of MoO3 could potentially explain the thermal instability of the Mo6+ oxide observed here.
Schematic atomic model of the oxidation behavior. a Clean alloy surface before oxidation at RT. b Alloy surface after oxidation at RT. c Clean alloy surface before oxidation at 400 °C with surface enrichment of Cr. d Alloy surface after oxidation at 400 °C. e Atomic structure of Cr2O3. Note that one unit cell, which corresponds to 13.58 Å, contains 6 layers of metal cations. f Atomic structure of MoO3. Note that one unit cell, which corresponds to 13.85 Å, contains 4 layers of metal cations. The structures are drawn using VESTA76 with atomic coordinates from refs. 77,78. The arrows denote the crystallographic axes of the unit cells.
Methods
Material
The material used in the present study was an industrial-grade Ni–Cr–Mo alloy (Ni alloy 59, UNS no: N06059) containing 62.3 at% Ni, 26.3 at% Cr, and 9.7 at% Mo. Minor alloying elements and the microstructure of the Ni-Cr-Mo polycrystal are shown in the supplementary material Supplementary Table 1 and Supplementary Fig. 1. The sample material was supplied in standard solution annealing condition with a representative microstructure.
XPS measurements
The in situ XPS experiments were performed at the EA01 endstation at the FlexPES beamline at the MAX IV synchrotron radiation source in Lund, Sweden72. The base pressure in the experimental chamber was around 5 × 10−10 mbar. The alloy sample was sputtered for 60 min by Ar+ ions with an energy of 1 keV at a pressure of 1.5 × 10−6 mbar of Ar, and the oxidation experiments were carried out right after without any annealing step to avoid altering the alloy composition of the surface due to thermally enhanced diffusion. Prior to each oxidation experiment, an XPS survey spectrum was measured with 1200 eV photon energy to exclude the presence of any contamination, as shown in the supplementary information Supplementary Fig. 2. During the in situ oxidationexperiment, O2 was dosed from a leak valve, and a pressure of 1 × 10−8 mbar was maintained in the chamber. While dosing O2, the Cr 2p3/2 Ni 2p3/2 O 1 s and Mo 3d core levels were measured in a sequence repeatedly with a photon energy of 975 eV and a pass energy of 100 eV. Measuring the sequence of core levels took 144 s, which corresponds to 1.1 L. All spectra were measured in normal emission using a DA30-L(W) hemispherical analyzer (Scienta Omicron, Sweden). Depth-resolved XPS was also performed on a Ni-Cr-Mo alloy sample that had been oxidized in air for several weeks. The sample with the native oxide was cleaned with acetone and ethanol and blow dried with nitrogen before inserting into the vacuum system at the beamline. To vary the probing depth, different photon energies were used such that kinetic energies of the photoelectrons of 100, 200, 400, and 600 eV were achieved.
Data analysis
The XPS data were fitted using the Python package LMFIT73. All fitting parameters are shown in the supplementary information. Asymmetric Voigt line profiles were used for the metallic components of the Ni, Cr, and Mo spectra74. All other components were fitted with a regular Voigt line profile. All spectra were background subtracted using a Shirley background75, and the binding energy scale was calibrated by defining the measured Fermi level as zero. Quantitative analysis of the oxide film thickness and composition was done by defining and solving a system of equations describing the intensity of each fitted component, as previously described27,56. Equations and parameters used for the quantitative analysis are shown in the supplementary information. The fitting procedure of the whole dataset was done automatically by restricting the peak positions and widths and only varying the intensity of the components. The line profile of the metallic components was determined by fitting the sputter-cleaned alloy surface.
Data availability
The data can be obtained from the authors upon reasonable request.
References
Koch, G. in Trends in Oil and Gas Corrosion Research and Technologies (ed A. M. El-Sherik) 3–30 (Woodhead Publishing, 2017).
Hou, B. et al. The cost of corrosion in China. npj mater. degrad. 1, 4, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41529-017-0005-2 (2017).
Raabe, D. The materials science behind sustainable metals and alloys. Chem. Rev. 123, 2436–2608, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00799 (2023).
Raabe, D., Tasan, C. C. & Olivetti, E. A. Strategies for improving the sustainability of structural metals. Nature 575, 64–74, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1702-5 (2019).
Bender, R. et al. Corrosion challenges towards a sustainable society. Mater. Corros. 73, 1730–1751, https://doi.org/10.1002/maco.202213140 (2022).
Zhong, X. et al. Global greenhouse gas emissions from residential and commercial building materials and mitigation strategies to 2060. Nat. Commun. 12, 6126, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-26212-z (2021).
Uhlig, H. H. Passivity in metals and alloys. Corros. Sci. 19, 777–791, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0010-938X(79)80075-X (1979).
Macdonald, D. D. Passivity–the key to our metals-based civilization. Pure Appl. Chem. 71, 951–978, https://doi.org/10.1351/pac199971060951 (1999).
Schmuki, P. From Bacon to barriers: a review on the passivity of metals and alloys. J. Solid State Electrochem. 6, 145–164 (2002).
Cabrera, N. & Mott, N. F. Theory of the oxidation of metals. Rep. Prog. Phys. 12, 163, https://doi.org/10.1088/0034-4885/12/1/308 (1949).
Lin, L. F., Chao, C. Y. & Macdonald, D. D. A point defect model for anodic passive films: II. Chemical breakdown and pit initiation. J. Electrochem. Soc. 128, 1194, https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2127592 (1981).
Macdonald, D. D. The point defect model for the passive state. J. Electrochem. Soc. 139, 3434, https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2069096 (1992).
Macdonald, D. D. The history of the Point Defect Model for the passive state: a brief review of film growth aspects. Electrochim. Acta 56, 1761–1772, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2010.11.005 (2011).
Clayton, C. R. & Lu, Y. C. A bipolar model of the passivity of stainless steel: the role of Mo addition. J. Electrochem. Soc. 133, 2465, https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2108451 (1986).
Brooks, A. R., Clayton, C. R., Doss, K. & Lu, Y. C. On the role of Cr in the passivity of stainless steel. J. Electrochem. Soc. 133, 2459, https://doi.org/10.1149/1.2108450 (1986).
Olsson, C. O. A. & Landolt, D. Passive films on stainless steels—chemistry, structure and growth. Electrochim. Acta 48, 1093–1104, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0013-4686(02)00841-1 (2003).
Bockris, J. O. M. & Kang, Y. The protectivity of aluminum and its alloys with transition metals. J. Solid State Electrochem. 1, 17–35, https://doi.org/10.1007/s100080050019 (1997).
Bockris, J. O. M. & Minevski, L. V. On the mechanism of the passivity of aluminum and aluminum alloys. J. Electroanal. Chem. 349, 375–414, https://doi.org/10.1016/0022-0728(93)80186-L (1993).
Evertsson, J. et al. The thickness of native oxides on aluminum alloys and single crystals. Appl. Surf. Sci. 349, 826–832, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.05.043 (2015).
Lloyd, A. C., Noël, J. J., McIntyre, S. & Shoesmith, D. W. Cr, Mo and W alloying additions in Ni and their effect on passivity. Electrochim. Acta 49, 3015–3027, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2004.01.061 (2004).
Lutton Cwalina, K., Demarest, C. R., Gerard, A. Y. & Scully, J. R. Revisiting the effects of molybdenum and tungsten alloying on corrosion behavior of nickel-chromium alloys in aqueous corrosion. Curr. Opin. Solid State Mater. Sci. 23, 129–141, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cossms.2019.03.002 (2019).
Wang, Z. et al. XPS and ToF-SIMS investigation of native oxides and passive films formed on Nickel alloys containing chromium and molybdenum. J. Electrochem. Soc. 168, 041503, https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/abf308 (2021).
Larsson, A. et al. Thickness and composition of native oxides and near-surface regions of Ni superalloys. J. Alloys Compd. 895, 162657, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.162657 (2022).
Eidhagen, J. et al. Synchrotron XPS and electrochemical study of aging effect on passive film of Ni alloys. J. Electrochem. Soc. 170, 021506, https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/acba4b (2023).
Morgan, A. M., Henderson, J. D., Kobe, B. A., Biesinger, M. C. & Noël, J. J. Investigating the structure of the oxide on Ni-Cr-Mo alloys while presenting a method for analysis of complex oxides using QUASES. Surf. Interface Anal. 55, 749–762, https://doi.org/10.1002/sia.7243 (2023).
Larsson, A. et al. The oxygen evolution reaction drives passivity breakdown for Ni-Cr-Mo alloys. Adv. Mater. n/a, 2304621, https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202304621 (2023).
Larsson, A. et al. In situ quantitative analysis of electrochemical oxide film development on metal surfaces using ambient pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy: Industrial alloys. Appl. Surf. Sci. 611, 155714, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.155714 (2023).
Li, X. et al. The contribution of Cr and Mo to the passivation of Ni22Cr and Ni22Cr10Mo alloys in sulfuric acid. Corros. Sci. 176, 109015, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2020.109015 (2020).
Henderson, J. D., Li, X., Shoesmith, D. W., Noël, J. J. & Ogle, K. Molybdenum surface enrichment and release during transpassive dissolution of Ni-based alloys. Corros. Sci. 147, 32–40, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2018.11.005 (2019).
Henderson, J. D. et al. Investigating the role of Mo and Cr during the activation and passivation of Ni-based alloys in acidic chloride solution. J. Electrochem. Soc. 168, 021509, https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/abe47a (2021).
Henderson, J. D. et al. Investigating the influence of Cr and Mo additions to commercial Ni-based alloys exposed to neutral and acidic chloride solutions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 167, 131512, https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/abbea7 (2020).
Li, X. & Ogle, K. The passivation of Ni-Cr-Mo alloys: time resolved enrichment and dissolution of Cr and Mo during passive-active cycles. J. Electrochem. Soc. 166, C3179, https://doi.org/10.1149/2.0201911jes (2019).
Yu, X.-x et al. In situ observations of early stage oxidation of Ni-Cr and Ni-Cr-Mo alloys. Corrosion 74, 939–946, https://doi.org/10.5006/2807%J.Corrosion (2018).
Yu, X.-x et al. Nonequilibrium solute capture in passivating oxide films. Phys. Rev. Lett. 121, 145701, https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.121.145701 (2018).
Lince, J. R., Didziulis, S. V., Shuh, D. K., Durbin, T. D. & Yarmoff, J. A. Interaction of O2 with the Fe0.84Cr0.16(001) surface studied by photoelectron spectroscopy. Surf. Sci. 277, 43–63, https://doi.org/10.1016/0039-6028(92)90611-9 (1992).
Ali-Löytty, H., Jussila, P., Hirsimäki, M. & Valden, M. Influence of CrN surface compound on the initial stages of high temperature oxidation of ferritic stainless steel. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 7783–7791, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.04.029 (2011).
Lampimäki, M., Lahtonen, K., Jussila, P., Hirsimäki, M. & Valden, M. Morphology and composition of nanoscale surface oxides on Fe–20Cr–18Ni{111} austenitic stainless steel. J. Electron. Spectrosc. Relat. Phenom. 154, 69–78, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elspec.2006.12.002 (2007).
Lynch, B., Wiame, F., Maurice, V. & Marcus, P. XPS study of oxide nucleation and growth mechanisms on a model FeCrNiMo stainless steel surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 575, 151681, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.151681 (2022).
Ma, L., Lynch, B., Wiame, F., Maurice, V. & Marcus, P. Nanoscale early oxidation mechanisms of model FeCrNi austenitic stainless steel surfaces at room temperature. Corros. Sci. 190, 109653, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2021.109653 (2021).
Ma, L., Wiame, F., Maurice, V. & Marcus, P. New insight on early oxidation stages of austenitic stainless steel from in situ XPS analysis on single-crystalline Fe–18Cr–13Ni. Corros. Sci. 140, 205–216, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2018.06.001 (2018).
Ma, L., Wiame, F., Maurice, V. & Marcus, P. Stainless steel surface structure and initial oxidation at nanometric and atomic scales. Appl. Surf. Sci. 494, 8–12, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.07.166 (2019).
Ma, L., Wiame, F., Maurice, V. & Marcus, P. Origin of nanoscale heterogeneity in the surface oxide film protecting stainless steel against corrosion. npj Mater. Degrad. 3, 29, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41529-019-0091-4 (2019).
Blades, W. H. & Reinke, P. Early-stage evolution of nanoscale oxides on Ni(111) and Ni-Cr(111) surfaces. Corros. Sci. 209, 110755, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2022.110755 (2022).
Volders, C. et al. Unraveling the role of tungsten as a minor alloying element in the oxidation NiCr alloys. npj Mater. Degrad. 6, 52, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41529-022-00265-x (2022).
Blades, W. H., Barone, M. R. & Reinke, P. Initial atomic-scale oxidation pathways on a Ni–15Cr(100) alloy surface. npj Mater. Degrad. 5, 17, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41529-021-00164-7 (2021).
Blades, W. H. & Reinke, P. From alloy to oxide: capturing the early stages of oxidation on Ni–Cr(100) alloys. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 10, 43219–43229, https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b15210 (2018).
Volders, C. et al. Oxidation of NiCr and NiCrMo alloys at low temperatures. Corrosion, https://doi.org/10.5006/4400 (2023).
Zhang, X., Zagidulin, D. & Shoesmith, D. W. Characterization of film properties on the NiCrMo Alloy C-2000. Electrochim. Acta 89, 814–822, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2012.11.029 (2013).
Henderson, J. D. et al. Investigating the transport mechanisms governing the oxidation of Hastelloy BC-1 by in situ ToF-SIMS. Corros. Sci. 159, 108138, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2019.108138 (2019).
Biesinger, M. C. et al. Resolving surface chemical states in XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides: Cr, Mn, Fe, Co and Ni. Appl. Surf. Sci. 257, 2717–2730, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2010.10.051 (2011).
Biesinger, M. C. et al. Quantitative chemical state XPS analysis of first row transition metals, oxides and hydroxides. J. Phys. Conference Ser. 100, 012025, https://doi.org/10.1088/1742-6596/100/1/012025 (2008).
Biesinger, M. C., Brown, C., Mycroft, J. R., Davidson, R. D. & McIntyre, N. S. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy studies of chromium compounds. Surf. Interface Anal. 36, 1550–1563, https://doi.org/10.1002/sia.1983 (2004).
Eissa, M. A., Elmasry, M. A. A. & Abadir, M. F. Thermal study of the Cr-Mo-O system in air. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 52, 587–594, https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010179908698 (1998).
Huang, X., Costa, D., Diawara, B., Maurice, V. & Marcus, P. Atomistic insights on enhanced passivity: DFT study of substitutional Mo on Cr2O3 and Fe2O3 surfaces. Corros. Sci. 224, 111543, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2023.111543 (2023).
Wang, Z. et al. Thermal stability of surface oxides on nickel alloys (NiCr and NiCrMo) investigated by XPS and ToF-SIMS. Appl. Surf. Sci. 576, 151836, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.151836 (2022).
Gardin, E., Zanna, S., Seyeux, A., Allion-Maurer, A. & Marcus, P. Comparative study of the surface oxide films on lean duplex and corresponding single phase stainless steels by XPS and ToF-SIMS. Corros. Sci. 143, 403–413, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2018.08.009 (2018).
Långberg, M. et al. Lateral variation of the native passive film on super duplex stainless steel resolved by synchrotron hard X-ray photoelectron emission microscopy. Corros. Sci. 174, 108841, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2020.108841 (2020).
Gardin, E., Zanna, S., Seyeux, A., Allion-Maurer, A. & Marcus, P. XPS and ToF-SIMS characterization of the surface oxides on lean duplex stainless steel – Global and local approaches. Corros. Sci. 155, 121–133, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2019.04.039 (2019).
Långberg, M. et al. Redefining passivity breakdown of super duplex stainless steel by electrochemical operando synchrotron near surface X-ray analyses. npj Mater. Degrad. 3, 22, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41529-019-0084-3 (2019).
Tardio, S., Abel, M.-L., Carr, R. H., Castle, J. E. & Watts, J. F. Comparative study of the native oxide on 316L stainless steel by XPS and ToF-SIMS. J. Vacuum Sci. Technol. A 33, https://doi.org/10.1116/1.4927319 (2015).
Samin, A. J. & Taylor, C. D. First-principles investigation of surface properties and adsorption of oxygen on Ni-22Cr and the role of molybdenum. Corros. Sci. 134, 103–111, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2018.02.017 (2018).
Guimond, S. et al. Well-ordered molybdenum oxide layers on Au(111): preparation and properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 117, 8746–8757, https://doi.org/10.1021/jp3113792 (2013).
Hamada, E. et al. Direct imaging of native passive film on stainless steel by aberration corrected STEM. Corros. Sci. 52, 3851–3854, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2010.08.025 (2010).
Zhang, B. et al. Unmasking chloride attack on the passive film of metals. Nat. Commun. 9, 2559, https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-04942-x (2018).
Wang, L., Seyeux, A. & Marcus, P. Thermal stability of the passive film formed on 316L stainless steel surface studied by ToF-SIMS. Corros. Sci. 165, 108395, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2019.108395 (2020).
Wang, Z., Seyeux, A., Zanna, S., Maurice, V. & Marcus, P. Chloride-induced alterations of the passive film on 316L stainless steel and blocking effect of pre-passivation. Electrochim. Acta 329, 135159, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2019.135159 (2020).
Seyeux, A. et al. ToF-SIMS investigation with 18O isotopic tracer of the ion transport mechanisms in surface oxides on nickel-chromium and nickel-chromium-molybdenum alloys. Electrochim. Acta 426, 140797, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2022.140797 (2022).
Wang, L. et al. Insight on passivity of high entropy alloys: thermal stability and ion transport mechanisms in the passive oxide film on CoCrFeMnNi surfaces. Corros. Sci. 188, 109540, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2021.109540 (2021).
Wang, L., Seyeux, A. & Marcus, P. Ion transport mechanisms in the oxide film formed on 316L stainless steel surfaces studied by ToF-SIMS with 18O2 isotopic tracer. J. Electrochem. Soc. 167, 101511, https://doi.org/10.1149/1945-7111/ab9c87 (2020).
Wang, L., Voyshnis, S., Seyeux, A. & Marcus, P. Ion transport mechanisms in the passive film formed on 304L stainless steel studied by ToF-SIMS with 18O isotopic tracer. Corros. Sci. 173, 108779, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.corsci.2020.108779 (2020).
Shannon, R. D. Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomic distances in halides and chalcogenides. Acta Cryst. A 32, 751–767, https://doi.org/10.1107/S0567739476001551 (1976).
Preobrajenski, A. et al. FlexPES: a versatile soft X-ray beamline at MAX IV Laboratory. J. Synchrotron Rad. 30, 831–840 (2023).
Newville, M. et al. LMFIT: non-linear least-square minimization and curve-fitting for Python. Astrophysics Source Code Library ascl: 1606.1014. https://ui.adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/2016ascl.soft06014N (2016).
Schmid, M., Steinrück, H.-P. & Gottfried, J. M. A new asymmetric Pseudo-Voigt function for more efficient fitting of XPS lines. Surf. Interface Anal. 46, 505–511, https://doi.org/10.1002/sia.5521 (2014).
Shirley, D. A. High-resolution X-ray photoemission spectrum of the valence bands of gold. Phys. Rev. B 5, 4709 (1972).
Momma, K. & Izumi, F. VESTA: a three-dimensional visualization system for electronic and structural analysis. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 41, 653–658 (2008).
HAAN, ΥD. Refinement of the a Al2O3, Ti2O3, V2O3 and Cr2O3 structures. Zeitschrift für Kristallographie-Crystalline Mater. 117, 235–237 (1962).
Andersson, G., Magneli, A., Sillén, L. G. & Rottenberg, M. On the crystal structure of molybdenum trioxide. Acta Chem. Scand. 4, 793–797 (1950).
Acknowledgements
Financial support is acknowledged from the Swedish Research Council (2018-03434 and 2020-06154) and the Swedish Foundation for Strategic Research under contract ID19-0032. We acknowledge MAX IV Laboratory for time on the Beamline FlexPES under Proposal 20210800 and 20220587. Research conducted at MAX IV, a Swedish national user facility, is supported by the Swedish Research council under contract 2018-07152, the Swedish Governmental Agency for Innovation Systems under contract 2018-04969, and Formas under contract 2019-02496.
Funding
Open access funding provided by Lund University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.L. conceptualized and participated in the experiments, analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript. S.G. participated in the experiments, helped with analyzing the data and reviewed the manuscript. A.G., V.K., J.E. and X.Y. participated in the experiments and reviewed the manuscript. E.F., S.A., A.G. and A.P. provided experimental support at the beamline and reviewed the manuscript. J.P. and H.O. acquired funding and reviewed the manuscript. E.L. acquired funding, helped to conceptualize the experiment and reviewed the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Larsson, A., Gericke, S., Grespi, A. et al. Dynamics of early-stage oxide formation on a Ni-Cr-Mo alloy. npj Mater Degrad 8, 39 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41529-024-00463-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41529-024-00463-9