Abstract
A contribution of DNA methylation to defense against invading nucleic acids and maintenance of genome integrity is uncontested; however, our understanding of the extent of involvement of this epigenetic mark in genome-wide gene regulation and plant developmental control is incomplete. Here, we knock out all five known DNA methyltransferases in Arabidopsis, generating DNA methylation-free plants. This quintuple mutant exhibits a suite of developmental defects, unequivocally demonstrating that DNA methylation is essential for multiple aspects of plant development. We show that CG methylation and non-CG methylation are required for a plethora of biological processes, including pavement cell shape, endoreduplication, cell death, flowering, trichome morphology, vasculature and meristem development, and root cell fate determination. Moreover, we find that DNA methylation has a strong dose-dependent effect on gene expression and repression of transposable elements. Taken together, our results demonstrate that DNA methylation is dispensable for Arabidopsis survival but essential for the proper regulation of multiple biological processes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
DNA methylation at the C-5 position of cytosine residues is a conserved epigenetic modification involved in transposon silencing, genome stability, and regulation of gene expression in many eukaryotes1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13. In plants, DNA methylation occurs in three sequence contexts: CG, CHG, and CHH, where H is any nucleotide except G. Plants have evolved different DNA methyltransferases for the establishment and maintenance of DNA methylation depending on the cytosine sequence contexts13,14. CG methylation is maintained by METHYLTRANSFERASE 1 (MET1), an orthologue of the mammalian DNA methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1), which recognizes hemi-methylated CG dinucleotides following DNA replication and methylates the unmodified cytosine in te daughter strand15,16. Maintenance of CHG methylation is catalyzed by CHROMOMETHYLASE 3 (CMT3) and, to a lesser extent, by CMT2 and is tightly linked to dimethylation of lysine 9 on histone 3 (H3K9me2)17,18,19. The asymmetric CHH methylation is maintained by two different types of DNA methyltransferases, CMT2 and DOMAINS REARRANGED METHYLTRANSFERASE 1/2 (DRM1/2, homologs of DNMT3), depending on the genomic regions: CHH methylation in heterochromatin is maintained by CMT2, whereas CHH methylation in euchromatin or at the edge of long transposable elements (TEs) is mediated by DRM1/2 through the RNA-directed DNA methylation (RdDM) pathway20,21,22,23,24. RdDM is also important for de novo DNA methylation in all three sequence contexts1,2,21,23,25,26,27,28. Even though the roles of these five DNA methyltransferases have been extensively studied, whether they are sufficient to maintain DNA methylation throughout the entire genome or, on the contrary, the contribution of other yet-to-be-described DNA methyltransferases is required, is unresolved.
Heavy DNA methylation occurs in heterochromatic regions, which are enriched with TEs and other repetitive DNA sequences29,30,31. Extensive hypomethylation in heterochromatic regions causes genome-wide TE transcriptional activation and induces TE transposition after continuous selfing20,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39. Thus, DNA methylation plays an important role in repressing invading nucleic acids (transposable elements, viruses, and transgenes). In contrast to TEs, which are methylated in their body region in all three sequence contexts, gene-associated DNA methylation can occur in the promoter region or in introns, or within the transcribed gene body only in the CG context. DNA methylation in different positions within genic sequences seems to play different functions: (1) in promoters, DNA methylation usually inhibits gene transcription, although the opposite effect has occasionally been observed29,40,41; (2) genes with DNA methylation in their body in the CG context are generally constitutively expressed29,42,43; and (3) DNA methylation in the introns of several genes has been shown to promote polyadenylation of their full-length transcripts44,45,46,47,48,49, but whether intronic DNA methylation has a general effect on transcript processing is still uncertain. In order to fully assess the genome-wide contribution of DNA methylation to gene expression, the generation of stable DNA methylation-free plant materials is required. Although mutant Arabidopsis plants displaying a nearly complete loss of either CG or non-CG methylation are available19,29, mutants with full erasure of DNA methylation have not been reported.
DNA methylation is critical for development in animals: e.g., null mutation in DNMT1 or DNMT3a/3b in mice leads to embryonic lethality13. However, loss of function of MET1, DRM1/2, CMT2, or CMT3 does not result in obvious developmental abnormalities in Arabidopsis, with the exception of the late flowering phenotype displayed by met115,50. The drm1 drm2 cmt3 cmt2 quadruple mutant, which loses almost all non-CG methylation, has curled leaves and a slightly reduced rosette size19,51,52. Simultaneous mutations in both met1 and some of the non-CG methyltransferases produces serious developmental defects, including extremely slow growth and late flowering, reduced plant size, and sterility53,54. Nevertheless, the lack of a met1 drm1 drm2 cmt3 cmt2 quintuple mutant has precluded conclusive studies regarding the contribution of DNA methylation to the regulation of different aspects of plant development.
Here, we generate the elusive Arabidopsis quintuple mutant in which the genes encoding all known functional DNA methyltransferases (MET1, DRM1, DRM2, CMT3, and CMT2) have been mutated (hereafter referred to as mddcc). mddcc plants exhibit extreme growth retardation and small size, display a suite of severe developmental defects, and do not undergo floral transition. We report the genome-wide analysis of DNA methylation, RNA expression, and TE movement in this mutant, demonstrating that: (i) DNA methylation in all contexts is completely eliminated in mddcc; (ii) DNA methylation exhibits a strong dose effect in terms of the regulation of gene expression and TE silencing; and (iii) CG and non-CG methylation act redundantly in the control of multiple biological processes, including flowering, trichome morphology, vasculature and meristem development, and root cell differentiation, likely through affecting the expression of genes encoding central regulators of these processes. Our findings extend prior knowledge on the importance of DNA methylation for global gene expression and development in plants and establish a framework for the future investigation of the contribution of this epigenetic mark to specific biological processes.
Results
MET1, DRM1, DRM2, CMT3, and CMT2 maintain the entire DNA methylation of the Arabidopsis genome
To determine whether the five known DNA methyltransferases maintain the entire DNA methylation of Arabidopsis plants, we combined the power of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated genome editing with traditional genetics to knock out the corresponding protein-coding genes55. First, we crossed cmt2 to the drm1 drm2 cmt3 (ddc) triple mutant and isolated the drm1 drm2 cmt3 cmt2 (ddcc) quadruple mutant; then, we used a CRISPR/Cas9 system with two sgRNAs targeting the first exon of MET1 to generate a met1 mutation in the ddcc background. Cas9-free met1/+ drm1 drm2 cmt3 cmt2 seeds were obtained in the T2 generation, and met1 drm1 drm2 cmt3 cmt2 (mddcc) individuals were isolated from the progeny of these plants. We named the met1 allele generated in the quadruple mutant background met1-8 (Fig. 1a and Supplementary Fig. 1a). In parallel, the same CRISPR/Cas9 vector was used to produce a met1 single mutant; the allele generated in the WT background was named met1-9 (Fig. 1a and Supplementary Fig. 1a). met1-8 results in a frameshift mutation that creates a premature stop codon in the first exon of MET1 (Fig. 1a and Supplementary Fig. 1a). In met1-9, a 531 bp fragment was deleted from the MET1 gene, causing a deletion of 177 aa in the N-terminal part of MET1 (Fig. 1a).
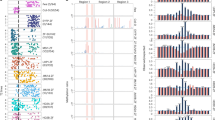
a Diagrams of the MET1 gene showing the mutation sites in met1-8 (upper) and met1-9 (lower) mutants. Purple bars indicate the position of the sgRNAs used. b Genome-wide distribution of DNA methylation in all three sequence contexts in the indicated mutants. Wireframes are zoom-in of the indicated regions. Biological replicates were combined as one sample. Independent biological replicates are shown in Supplementary Fig. 2a. It should be noted that the lines of the WT overlap with those of ddcc in the mCG row. c Screenshot of DNA methylation levels over one representative locus in the indicated mutants. Orange and blue bars indicate TEs and genes, respectively. TEs and genes oriented 5′–3′ and 3′–5′ are shown above and below the line, respectively. Biological replicates were combined as one sample. Independent biological replicates are shown in Supplementary Fig. 2b. d Comparison of the DNA methylation levels between nuclear and chloroplast genomes in the indicated genotypes. Biological replicates were combined as one sample. Independent biological replicates are shown in Supplementary Fig. 2c. The horizontal line within the box represents the median; the whiskers represent minimum and maximum values; and the lower and upper boundaries of the box represent the 25th and 75th percentiles, respectively.
To examine the DNA methylation levels in ddcc, met1-9, and mddcc mutants, we carried out whole-genome bisulfite sequencing (Supplementary Table 1). As expected, almost all CG and non-CG methylation is eliminated in met1-9 and ddcc mutants, respectively (Fig. 1b, c and Supplementary Fig. 1b–d and Fig. 2a, b). A more detailed observation of DNA methylation levels across chromosomes revealed that a low level of CG and non-CG methylation remains at pericentromeric regions in met1-9 and ddcc relative to mddcc, respectively, indicating that MET1 and DRM1/DRM2/CMT2/CMT3 can contribute to some extent to maintaining non-CG and CG methylation, respectively (Fig. 1b and Supplementary Fig. 2a). To investigate whether genomic DNA methylation is completely erased in mddcc, we compared the DNA methylation levels of the nuclear genome with those of the methylation-free chloroplast genome. Noticeably, the DNA methylation of the nuclear genome in mddcc was as low as that of the chloroplast genome in any mutant background in all three sequence contexts (Fig. 1d and Supplementary Fig. 2c), indicating that MET1, DRM1, DRM2, CMT3, and CMT2 are responsible for the maintenance of the entire DNA methylation in the Arabidopsis genome, and implying that additional yet-to-be-described DNA methyltransferases do not contribute genome-wide to this epigenetic modification (Fig. 1d and Supplementary Fig. 2c). Thus, the mddcc mutant is a DNA methylation-free Arabidopsis genotype.
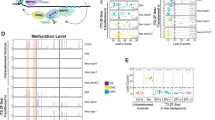
a Numbers of differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in the indicated mutants relative to WT. b, c Venn diagrams showing the overlap among up-regulated genes (b) or down-regulated genes (c) in ddcc, met1-9, and mddcc mutants. d Flow diagram indicating the criteria for gene classification according to the DNA methylation status in the WT background. Genes with no detectable expression (FPKM < 0.5) in any genotype were excluded. FPKM: fragments per kilobase of exon model per million mapped fragments. e Heat maps showing the expression and DNA methylation patterns of the indicated groups of up-regulated in DNA methyltransferase-deficient mutants. Based on their expression pattern, DEGs methylated in the WT were classified in the following categories: Redundancy (expression increased only in mddcc); Dosage I (expression mildly increased upon loss of CG methylation (in met1-9), and further increased upon loss of non-CG methylation (in mddcc)); Dosage II (expression mildly increased upon loss of non-CG methylation (in ddcc), and further increased upon loss of CG methylation (in mddcc)); and Dosage III (expression weakly increased upon loss of either CG or non-CG methylation (in both met1-9 and ddcc) and further increased upon complete loss of DNA methylation (in mddcc)). f Proportion of DEGs in the gbM, teM, pM, dM, or UM categories in the indicated genotypes. Down: down-regulated; up: up-regulated. Numbers over the bars indicate the total number of genes in each category. Bottom, we randomly selected the same numbers of genes to perform the overlap analysis. g Relative proportion of different categories of methylated genes. The number of genes in each category is indicated. h Proportion of gene types in the indicated DEG subsets. Numbers above the bars indicate the total number of DEGs. i Snapshots of expression and DNA methylation levels over two Intron-teM genes in the indicated mutants. Structure of genes are shown in the bottom. + and − indicate forward and reverse strands in the genome, respectively. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
DNA methylation regulates gene expression in a dose-dependent manner
We performed strand-specific RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) in WT, ddcc, met1-9, and mddcc (Supplementary Fig. 3a and Supplementary Table 2). By analyzing differentially expressed genes relative to WT (DEGs; fold change >2, p-adjusted < 0.01), we found that, in contrast to met1-9, which shows thousands of DEGs, there are just ~300 DEGs in ddcc (Fig. 2a), suggesting that the impact of CG methylation on gene transcription directly and indirectly is much stronger than that of non-CG methylation. Furthermore, the mddcc mutant shows a substantially higher number of DEGs than met1-9 (Fig. 2a), supporting a partial functional redundancy between CG and non-CG methylation in the regulation of gene expression. The subsets of DEGs in ddcc, met1-9, and mddcc highly overlap with one another (Fig. 2b, c). To confirm our identified DEGs, we randomly selected 25 up-regulated and 25 down-regulated genes in the mddcc mutant for validation by qPCR; the results obtained are consistent with the RNA-seq data, as shown in Supplementary Fig. 4. Gene ontology (GO) analysis showed that defense- and response to stimuli-related GO terms are enriched in the subset of up-regulated genes in ddcc, met1-9, and mddcc, whereas metabolic process-related GO terms are enriched in the subset of down-regulated genes in met1-9 and mddcc (Supplementary Fig. 5a, b). Interestingly, cell division-related GO terms are specifically enriched in the mddcc-unique down-regulated genes (Supplementary Fig. 5b).
To perform a more detailed analysis of the function of DNA methylation in the regulation of gene expression, we first classified the 17,930 genes with detectable expression (genes with no detectable expression in any genotype were excluded) into five main categories based on their methylation level in the WT background: 3463 (19.3%) genes with gene body methylation only in the CG context (gbM genes), 292 (1.6%) genes with gene body methylation in non-CG contexts (teM genes, TE-like methylated genes), 3773 (21.0%) genes with methylation in their promoters (pM genes), 2367 (13.2%) genes with methylation in their 3′ downstream regions (dM genes), and 8035 (44.8%) unmethylated genes (UM genes) (Fig. 2d). The proportion of DEGs among gbM genes is low (Fig. 2f). A significant proportion of DEGs was found among dM genes, suggesting that DNA methylation in the 3′ downstream of genes also plays a role in regulating gene expression (Fig. 2f). The proportion of up-regulated genes in the teM subset is significantly higher than that of down-regulated genes, indicating that non-CG gene body methylation plays a major role in gene repression (Fig. 2f). Unexpectedly, a similar number of up- and down-regulated genes could be identified in each of the gbM, pM, and dM subsets (Fig. 2f). Thus, our results confirm the accepted repressive effect of DNA methylation on gene expression but also hint at a broad activating function of DNA methylation. Admittedly, we cannot exclude that the downregulation of methylated genes in these mutants is an indirect consequence of the upregulation of methylated genes or derives from additional side effects of the depletion of this epigenetic mark.
Interestingly, using heatmaps to compare the gene expression level of overlapping DEGs among ddcc, met1-9, and mddcc mutants (Fig. 2b, c, e and Supplementary Fig 3b, c), we found that DNA methylation in the methylated genes (gbM, teM, pM, and dM) affects gene expression in multiple ways. According to the behavior of DEGs in the different mutant backgrounds, we could distinguish the following effects of DNA methylation on gene expression: Redundancy, when the expression is increased/decreased only in mddcc; Dosage I, when the expression is mildly increased/decreased upon loss of CG methylation (in met1-9), and is further increased/decreased upon loss of non-CG methylation (in mddcc); Dosage II, when the expression is mildly increased/decreased upon loss of non-CG methylation (in ddcc), and is further increased/decreased upon loss of CG methylation (in mddcc); Dosage III, when the expression is weakly increased/decreased upon loss of either CG or non-CG methylation (in both met1-9 and ddcc) and is further increased/decreased upon complete loss of DNA methylation (in mddcc); Silenced/Activated by mCG, when the degree of gene up- or down-regulation in met1-9 is comparable to that in mddcc; and Silenced by non-mCG, when the degree of gene up-regulation is similar between ddcc and mddcc (Fig. 2e, Supplementary Fig 3b, c, and Supplementary Figs. 6–8). The number of genes regulated by a Dosage effect is significantly higher than that of genes regulated by Redundancy, Silenced/Activated by mCG, and Silenced by non-mCG genes (Fig. 2g), suggesting that either DNA methylation regulates gene expression mainly in a dose-dependent manner, or CG and non-CG methylation exert a redundant effect on gene expression. Compared to Dosage I regulation, which is the most common dosage effect, Dosage II and III cases are rare (Fig. 2g), indicating that CG methylation plays a major role in regulating gene expression under normal conditions, whereas the main function of non-CG methylation is to prevent misexpression of genes when CG methylation is absent. Of note, consistent with previous results56, we found that CHG and CHH methylation of methylated DEGs in met1-9 was mildly decreased relative to the WT. Therefore, changes in non-CG methylation could also contribute to the changes in gene expression detected in met1-9 (Supplementary Fig. 9).
It should be noted that a substantial proportion of DEGs in ddcc, met1-9, and mddcc are UM genes (Fig. 2h). The expression changes in these genes could be indirectly caused by changes in the expression of methylated genes, although the possibility that the differential expression of these genes results from the loss of trace levels of DNA methylation cannot be ruled out (Fig. 2e and Supplementary Fig. 3b, c).
It has been previously shown that DNA methylation in an intron promotes the polyadenylation of the full length transcript for several genes, as exemplified by intronic DNA methylation in the IBM1 gene44,46,47. Consistent with the previous results, 3′ transcripts of the IBM1 gene are dramatically decreased in ddcc, met1-9, and mddcc relative to WT (Supplementary Fig. 10). To investigate the extent to which DNA methylation in introns promotes the accumulation of 3′ transcripts, we selected a subset of 173 teM genes with heavy methylation in introns, which we called Intron-teM genes (Fig. 2d). A whole gene can be divided in two parts (5′ and 3′) by a methylated intron. After excluding genes with low levels of 5′ transcripts (see the “Methods” section), we retained 52 Intron-teM genes, 9 of which showed a dramatic decrease in 3′ transcripts in mddcc compared to WT (Supplementary Table 3, Log2 [(mddcc 3′/5′)/(Col-0 3′/5′)] < −1). Intronic DNA methylation in Intron-teM genes promoting the stability of 3′ transcripts also shows various patterns of regulation, including Redundancy, when a downregulation of 3′ transcripts is found only in the complete absence of DNA methylation (Fig. 2i); Dosage, when the decrease in 3′ transcripts correlates with the quantitative loss of intronic DNA methylation (Fig. 2i); mCG, when the degree of downregulation of 3′ transcripts is comparable between met1-9 and mddcc mutants (Supplementary Fig. 10); and mCG-and-non-mCG, when the degree of downregulation of 3′ transcripts is comparable among ddcc, met1-9, and mddcc mutants (Supplementary Fig. 10). Our findings suggest that intronic DNA methylation is required for the proper expression of some Intron teM genes by promoting the production of their full-length transcripts, although the number of teM genes for which 3′ transcripts are decreased in mddcc is limited.
CG and non-CG methylation jointly repress TE expression and transposition
We identified differentially expressed TEs (DETs) in the DNA methyltransferase mutants relative to WT (DET; fold change > 2, p-adjusted < 0.01). As expected, most DETs are up-regulated in these mutants (Fig. 3a), and the results support that methylation in the CG context has a major role in suppressing TE expression, with non-CG methylation acting redundantly with CG methylation to repress a subset of TEs (Fig. 3a). Consistent with what is observed in genic regions, the effect of DNA methylation on TE expression displays various patterns, including Redundancy, Dosage I, Dosage II, Dosage III, Silenced by mCG, and Silenced by non-mCG (Fig. 3b, c and Supplementary Fig. 11). Thus, CG and non-CG methylation collaborate to repress TE expression in various ways, and there is a dose/effect relationship between DNA methylation and TE expression.
a Number of differentially expressed TEs (DETs) in the indicated mutants relative to WT. b Venn diagram showing the overlap among up-regulated TEs in ddcc, met1-9, and mddcc mutants. c Heat maps showing the expression and DNA methylation patterns of TEs in the indicated groups. Based on the expression patterns of TEs, TEs were classified into the following categories: Redundancy, Dosage I, Dosage II, and Dosage III (for details, see Fig. 2e). d–f Circle plots showing TE transposition in different mddcc individual plants. Arrows start and end represent the original and inserted sites of transposed TEs, respectively. The red/green/blue arrows indicate that the transposed TE belongs to the ATCOPIA21, ATENSPM3, or VANDAL21 subfamily, respectively. g–i Products of PCR amplification with paired primers flanking new insertion sites or a transposon-specific primer and a primer flanking the new insertion site in the indicated genotypes. Black arrows indicate primers. Upper panels: screenshots from Integrative Genomic Viewer (IGV) showing split-reads for TE insertions. Lower panels, coordinate lines indicate the sequence contexts of the new insertion sites. j Snapshots of expression and DNA methylation levels over transposed TEs in the indicated mutants. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
To examine whether reactivation of TEs in these mutants may result in TE transposition, we performed DNA sequencing (DNA-seq) in WT, ddcc, met1-9, and mddcc mutants (Supplementary Fig. 12a and Supplementary Table 4). By analyzing the DNA-seq data, 1, 1 and 12 putative TE transposition events were identified in ddcc, met1-9, and mddcc, respectively (Supplementary Table 5); however, only 11 TE transposition events, all in mddcc, could be confirmed by PCR (Fig. 3d–i and Supplementary Fig. 12). The 11 transposition events involved 5 TEs (Fig. 3j and Supplementary Table 5); these transposed TEs (AT1TE42210, AT2TE20205, AT5TE65370, and AT1TE49860) show the highest expression levels in mddcc, suggesting that the high degree of TE transcriptional activation only partially correlates with transpositional activation. Interestingly, we found that only a partial and antisense transcript of AT2TE42810 is increased in mddcc relative to met1-9, implying that the activation of this part of the locus may be more important than the other part for AT2TE42810 transposition (Fig. 3j). Consistent with previous results showing that mutations in MET1 cause transposition of a limited number of TEs only after continuous selfing35, we did not find any transposed TEs in the met1-9 mutant, which is newly generated by CRISPR-Cas9 (Supplementary Table 5). Of note, in the mddcc mutant, the 11 transposition events were identified in the first homozygous generation. Our findings confirm prior results indicating that CG and non-CG methylation act redundantly to prevent TEs transposition.
Expression of antisense transcripts and non-annotated transcripts in DNA methyltransferase-deficient mutants
DNA methylation (both CG and non-CG) in gene bodies has been proposed to suppress the expression of intragenic antisense transcripts57,58,59; however, mutation in MET1, which results in a substantial loss of gene body methylation, causes overexpression of only a handful of intragenic antisense transcripts29. We hypothesized that CG and non-CG methylation may act redundantly to suppress the expression of intragenic antisense transcripts. To test this idea, we identified antisense transcripts with significantly altered expression (fold change > 4, p-adjusted < 0.01) in ddcc, met1-9, and mddcc mutants compared to WT. The numbers of misexpressed antisense transcripts in met1-9 and mddcc mutants are low, but higher than those in ddcc. The observed increase in mddcc relative to met1-9 is minor (Fig. 4a, b). As expected, most of the genes with up-regulated antisense transcripts harbor heavy DNA methylation in WT plants (Fig. 4c, d). These results support a role of CG and non-CG methylation in the gene bodies in suppressing antisense transcription on a restricted number of loci.
a Numbers of differentially expressed antisense (AS) transcripts in the indicated mutants relative to WT. b Venn diagram showing the overlap among up-regulated AS transcripts in ddcc, met1-9, and mddcc mutants. c Heat maps showing the expression and DNA methylation patterns of the antisense transcripts in the indicated groups. d Snapshots of expression and DNA methylation levels over three antisense transcript genes in the indicated mutants. e Number of differentially expressed non-annotated transcripts in the indicated mutants relative to WT. f Venn diagram showing the overlap among up-regulated non-annotated transcripts in ddcc, met1-9, and mddcc mutants. g Heat maps showing the expression and DNA methylation patterns of the non-annotated transcripts in the indicated groups. h Snapshots of expression and DNA methylation levels over three non-annotated transcripts in the indicated mutants.
Additionally, we searched for non-annotated transcripts with different expression levels (fold change > 2, p-adjusted < 0.01) in ddcc, met1-9, and mddcc mutants relative to WT. Interestingly, we identified 46 non-annotated transcribed elements in the mddcc mutant (Fig. 4e, f). The vast majority of loci of up-regulated non-annotated transcripts display dense DNA methylation in WT plants (Fig. 4g, h). This finding suggests that additional transcribed elements, whose expression is blocked by DNA methylation, exist in the Arabidopsis genome.
DNA methylation is required for normal Arabidopsis development but dispensable for its survival
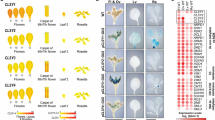
To investigate the significance of DNA methylation for plant development, we phenotyped the ddcc, met1-9, and mddcc mutants throughout their life cycle. While seedling size in ddcc and met1-9 is similar to that in WT (Fig. 5a), mddcc seedlings are extremely small (Fig. 5a). The reduction in size is even more pronounced when mddcc plants are grown in soil, where they display a range of phenotype severities (Fig. 5b). This phenotypic variability among mddcc individual plants may be caused by TE transposition in these plants (Fig. 3 and Supplementary Fig. 12). Noticeably, although mddcc plants grow slowly and exhibit severe developmental alterations, their survival span is longer than that of other genotypes in long-day conditions (Supplementary Fig. 13), leading to the conclusion that DNA methylation is necessary for Arabidopsis development but dispensable for its survival. Nevertheless, we found that the mddcc mutant never flowered (Fig. 5c and Supplementary Fig. 13), which correlates with the aberrant expression of genes involved in floral development (Fig. 5d). Previous studies have demonstrated that the loss of DNA methylation at the FWA promoter in met1 mutants causes ectopic FWA expression, which results in late flowering60. Since the expression levels of FWA are comparable between met1-9 and mddcc (Fig. 5e), other genes must underlie this phenotypic difference between the two mutants.
a Phenotypes of 11-day-old seedlings of the indicated genotypes on 1/2 MS media. Scale bar, 1 cm. b Phenotypes of 35-day-old plants of the indicated genotypes. After growing for 14 days on 1/2 MS media, the plants were transplanted into soil for 21 days of growth. Based on the rosette radius, the phenotypes of the mddcc mutant were classified into Weak, Medium and Strong, as indicated; the bar plot shows the relative abundance of each of these categories. c The mddcc mutant never flowers. Left, bar pot showing the flowering times of the indicated genotypes grown in long-day conditions. The data are the means ± SD of the biological repeats (n = 13). Right, phenotypes of 84-day-old and 125-day-old mddcc plants. After growing for 14 days on 1/2 MS media, the plants were transplanted into soil for 70 or 111 days of growth. Scale bar, 1 cm. d Heat maps showing the expression and DNA methylation patterns of flower development-related genes (upper panel), cytoskeleton organization-related genes (middle panel), and trichome differentiation-related genes (lower panel) in the indicated genotypes. Flower development-related genes (see Supplementary Data 1) were selected from the overlap between GO:0009908 (flower development) and DEGs in mddcc. Cytoskeleton organization-related genes (see Supplementary Data 1) were selected from microtubule-related GO terms over-represented in the subset of down-regulated genes common to met1-9 and mddcc (Fig. 2c). Trichome differentiation-related genes (see Supplementary Data 1) were identified from the overlap between GO:0010026 (trichome differentiation) and down-regulated genes in mddcc. e Snapshots of expression and DNA methylation levels over AT4G25530 (FWA) in the indicated mutants. f Representative images of pavement cell morphology of cotyledons from 11-day-old WT, ddcc, met1-9, and mddcc seedlings. Cell outlines were visualized with PI. Scale bar: 100 μm. Experiments were independently repeated two times with similar results. g Trichome branch number in WT, ddcc, met1-9, and mddcc. The numbers above the bars indicate the total number of trichomes analyzed. Trichomes were observed from the first true leaf of 11-day-old plants. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
Intriguingly, mutation in MET1 is sufficient to alter pavement cell shape from irregular (jigsaw-puzzle shape)61 to regular (lacking interdigitation of lobes) (Fig. 5f and Supplementary Fig. 14a), and to cause spontaneous cell death (Supplementary Fig. 14c). Consistently, cytoskeleton organization-related genes with pivotal roles in controlling pavement cell shape62,63 and cell death-related genes are sharply down-regulated and up-regulated, respectively, in both met1-9 and mddcc mutants (Fig. 5d and Supplementary Fig. 14d). In addition, CG methylation affects endoreduplication in nuclei isolated from cotyledons from 11-day-old seedling, since the distribution of DNA content in nuclei from met1 and mddcc, which peaks at 8 °C, is different from that in nuclei from WT and ddcc, which peaks at 16 °C instead (Supplementary Fig. 14b)61. In contrast to WT, ddcc, and met1, where trichomes generally have three branches, the majority of trichomes in mddcc have two branches (Fig. 5g and Supplementary Fig. 14e), indicating that CG and non-CG methylation redundantly contribute to trichome development. In addition, DNA methylation is essential for proper vascular development, since vasculature is dramatically reduced in the mddcc mutant (Supplementary Fig. 15a–c). Gene expression analyses support our findings, since multiple genes involved in trichome differentiation and vascular development are drastically misexpressed in mddcc (Fig. 5d and Supplementary Fig. 15d). Given the extreme developmental defects of the mddcc mutant, we wondered whether DNA methylation might be required for meristem activity. While the shoot apical meristem (SAM) in both met1-9 and ddcc mutants is comparable to that in WT (Supplementary Fig. 16a, b), the SAM in the mddcc mutant is severely reduced (Supplementary Fig. 16a, b), implying that CG and non-CG methylation are redundantly involved in the development of the SAM. In line with this observation, misregulation of genes involved in SAM development is maximal in the mddcc mutant (Supplementary Fig. 16c).
Root length is slightly reduced in ddcc and met1 compared to the WT, but is drastically decreased in mddcc (Fig. 6a). To examine the activity of the RAM, we applied the thymidine analog 5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine (EdU) to visualize cell proliferation in this area64,65. We found that the EdU signal, a proxy for DNA replication and cell division, is dramatically decreased in met1-9, and is virtually undetectable in mddcc (Fig. 6b), demonstrating that CG methylation contributes to cell proliferation in the RAM, with non-CG methylation acting partially redundantly. Remarkably, we found that xylem differentiation and root hair differentiation occur prematurely in mddcc, being frequently observed directly at the root tip (Fig. 6c–e and Supplementary Fig. 17); this phenotype suggests that CG and non-CG methylation act redundantly to either inhibit root cell differentiation and/or promote meristem maintenance.
a Quantification of root length of 9-day-old WT, ddcc, met1-9, and mddcc seedlings. The data are the means ± SD of the biological repeats. b Representative images of EdU labeling in the RAM of roots of 11-day-old WT, ddcc, met1-9, and mddcc seedlings. Images framed with a red dotted line show a higher exposure version of the images on the left. Scale bar: 50 μm. Experiments were independently repeated two times with similar results. c Distance from the QC to xylem lignification in roots of 9-day-old WT, ddcc, met1-9, and mddcc mutants. The data are the means ± SD of the biological repeats. d Cleared roots stained with calcofluor white (blue) and basic fuchsin (red). White arrowheads indicate the site of appearance of the first protoxylem cells; red arrowheads indicate root hairs. Scale bar: 100 μm. Experiments were independently repeated two times with similar results. e Representative images of root meristems from 9-day-old WT, ddcc, met1-9, and mddcc seedlings. Cell outlines were visualized with calcofluor white. Blue and white arrowheads indicate the QC and the cortex transition boundary, respectively. Scale bars: 100 μm. Experiments were independently repeated two times with similar results. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.
Discussion
The mechanisms regulating DNA methylation in plants have been extensively studied in the model species Arabidopsis in the past decades1,2,4,5,6,7,8,9,12,13,14,28,66. However, DNA methylation-free mutant plants have not been available thus far, and consequently it remained unclear to what extent this epigenetic modification was required for plant growth and development. Here, we mutated all known functional DNA methyltransferases in Arabidopsis, generating a quintuple mutant devoid of DNA methylation (Fig. 1). Our results demonstrate that DNA methylation in Arabidopsis is mediated entirely by the five previously identified DNA methyltransferase enzymes. The extremely low levels of DNA methylation in mddcc are likely attributable to non-conversion of unmethylated cytosines (Supplementary Table 1). In Arabidopsis, there are three MET1 homologs (AT4G14140, AT4G13610, and AT4G08990), of which the potential function in DNA methylation is unexplored. Considering that these homologous genes are expressed in seedlings67 and that DNA methylation is completely erased in mddcc, it seems likely that the encoded proteins do not play a prevalent role in maintaining DNA methylation, although we cannot exclude that they may maintain DNA methylation in endosperm since their expression levels are up-regulated in endosperm relative to other tissues68. Of note, a function of these or other yet-to-be-identified DNA methyltransferases in very limited specific cells or at certain developmental stages, of which the contribution might have been diluted in our experimental approach, can nevertheless not be ruled out at this point.
It is notable that complete removal of DNA methylation in Arabidopsis is not lethal, rendering individuals infertile yet viable. In contrast, null mutations in single DNA methyltransferases result in seedling or embryonic lethality in rice or maize69,70. Compared to Arabidopsis, these plants have much higher contents of TEs in their genomes71, and consequently much higher probabilities of essential genes being affected by nearby TEs and thus by DNA methylation around the TEs. Even though DNA methylation is present in the genomes of all vertebrates and plants, there are species without DNA methylation, as exemplified by Drosophila melanogaster, Caenorhabditis elegans, and Tribolium castaneum13,72. It seems that these species have evolved other mechanisms to replace the central function of DNA methylation, namely the silencing of TEs73. While our manuscript was under review, Liang et al. reported that an mddcc mutant is embryonically lethal74. It should be pointed out that their failure to obtain a viable mddcc mutant likely results from the fact that their selected ddcc alleles (drm1-2 drm2-2 cmt3-11 cmt2-7), as well as the process employed for the generation of the quintuple mutant74 (CRISPR/Cas9-mediated mutation of MET1 in the WT background and subsequent crossing with the ddcc mutant), are different from the ones used in this work (drm1-2 drm2-2 cmt3-11 cmt2-3; CRISPR/Cas9-mediated mutation of MET1 directly in the ddcc background (see the “Methods” section)).
The DNA methylation-free mddcc mutant has enabled a comprehensive assessment of the full impact of DNA methylation on the regulation of gene expression, TE silencing, and plant development. Our results indicate that the degree of functional redundancy between CG methylation and non-CG methylation in the regulation of gene expression is limited (Fig. 2), and that DNA methylation dosage is determinant (Fig. 2g). Unexpectedly, we found that nearly half of the differentially expressed, methylation-associated genes (with the exception of teM genes) are down-regulated in mddcc (Fig. 2f), pointing to a possibly broader role of DNA methylation than previously assumed in the promotion of gene expression. Recently discovered DNA methylation reader complexes which promote gene expression support this assumption75,76,77,78,79. Also surprising is the observation that half of the DEGs in mddcc belong to the unmethylated (UM) category (Fig. 2h); it is conceivable that the altered expression of these genes is a byproduct of changes in the expression of DNA methylation-associated genes, or, alternatively, is regulated by distant DNA methylation through chromosomal interactions80.
Our results also revealed that DNA methylation in introns at Intron-teM genes promotes the accumulation of full-length transcripts (Fig. 2i and Supplementary Fig. 10). This role is in agreement with the recent discovery of a protein complex that promotes distal polyadenylation of intron-methylated genes45,46,47,48,49,81. It seems likely that DNA methylation-associated heterochromatic histone modifications may recruit this protein complex to Intron-teM genes to facilitate the production of full-length transcripts.
In contrast to gbM, dM, and pM genes, the expression of most teM genes is up-regulated in mddcc (Fig. 2f), suggesting that DNA methylation acts to restrain gene expression when gene bodies carry heavy non-CG methylation. Across all mutants, few DEGs belong to the gbM gene category (Fig. 2f), supporting that either CG methylation in gbM genes has a limited role in regulating gene expression, or that the role of gbM in regulating gene expression is limited, and the affected transcripts did not reach the threshold to be considered DEGs in our analyses. In a recent preprint, Shahzad et al. showed that gene body methylation tends to have a modest positive effect on gene expression in natural accessions and that natural variation in this trait is associated with environmental variables, suggesting a role in adaptive evolution59. In mouse cells, CG methylation in gene bodies prevents cryptic transcription initiation82. However, results obtained in Arabidopsis do not support a similar function in plants83.
Interestingly, we found that the proportion of DEGs in dM genes is similar to that in pM genes; how DNA methylation at 3′ downstream sequences regulates gene expression is poorly understood. Conceivably, DNA methylation in these regions may affect transcription termination or transcript processing, hence affecting transcript stability, or may even impact promoter function through the formation of chromatin loops84,85.
The subset of up-regulated genes in the DNA methylation-deficient mutants is highly enriched in defense-related GO terms (Supplementary Fig. 5a, c), which suggests a general role of DNA methylation in this process. This is consistent with recent studies showing that DNA demethylases are required for the expression of defense-related genes and for plant resistance against fungal and bacterial pathogens86,87,88,89.
It should be noted that the age of the plants used for the transcriptomic analysis is genotype-dependent: while 2-week-old plants were used for the WT, met1, and ddcc, 5-week-old plants were used for the quintuple mddcc mutant. The justification for this experimental design lies on the extremely slow pace of growth and development exhibited by the latter, which renders 5-week-old mddcc plants more similar to 2-week-old plants of the other genotypes analyzed. To exclude the possibility that DEGs identified in mddcc in this study are mainly caused by the difference in sampling time, we compared the expression levels of these DEGs between 5-week-old mddcc and 5-week-old WT plants. We found that more than half of these DEGs are similarly up/down-regulated in 5-week-old mddcc compared to 5-week-old WT plants (Supplementary Fig. 19). Most of those DEGs that are not similarly up/down-regulated in 5-week-old mddcc compared to 5-week-old WT plants display the corresponding changes in 2-week-old met1 plants relative to 2-week-old wild-type plants (Supplementary Fig. 19), suggesting that the expression of these genes can be regulated by DNA methylation rather than purely developmental stage-dependent. In parallel, we compared the expression levels of selected previously described DEGs potentially involved in specific phenotypes of the mddcc mutant, finding that the majority of very highly up-regulated DEGs are also up-regulated in 5-week-old mddcc relative to 5-week-old WT plants, despite the differences in developmental stage (Supplementary Fig. 20). Taken together, these results indicate that the transcript differences identified between the mddcc mutant and WT are, at least to a large extent, not artifactual due to the age difference. Nevertheless, an effect of the sampling time on the transcript differences observed cannot be excluded. Moreover, the difference in the development of mddcc mutant compared to other genotypes could have unintended secondary effects, which must be considered when interpreting the results. Of note, the analysis of expression of TEs, antisense, and non-annotated transcripts may be also affected by the factors mentioned above (sampling time and developmental stage).
Our results indicate that non-CG methylation fully compensates the loss of CG methylation in terms of transposition, even though this compensation is only partial in terms of TE expression. Interestingly, RdDM has been shown to preferentially target the extremities of long TEs (e.g. ONSEN and other COPIA LTR-retroelements), which is sufficient to prevent their transposition even when they are transcriptionally active90,91. While 12 TE subfamilies were identified as mobilized in a ddm1-derived epi-RIL population38, only three of them were found as transposing in this work; nevertheless, it is worth noting that these three subfamilies account for 98% of the transposition events in the ddm1-derived epi-RIL. The detection of additional, lowly represented mobilized TE subfamilies in the mddcc mutant might have been hampered by the limited number of individuals included in the analyses. TE transposition occurs in the first homozygous generation of mddcc, providing direct evidence that DNA methylation plays a crucial role in protecting genome stability. DNA methylation is known to strongly impact meiotic recombination frequencies92,93,94. It would be of interest to investigate in the future whether the DNA methylation-free mutants may exhibit changes in genomic structural rearrangements.
Choi et al. proposed that DNA methylation and other factors jointly suppress the expression of antisense transcripts95; however, according to our results, DNA methylation would have a strong contribution in this process, yet on a limited number of loci (Fig. 4a–d). Interestingly, we found that dozens of non-annotated transcripts are expressed in the mddcc mutant (Fig. 4e–h). These non-annotated transcripts may represent unidentified genes or non-coding RNAs normally masked by DNA methylation. Whether these putative novel transcripts have biological functions in plants is at this point an open question.
Strikingly, the mddcc mutant displays extremely reduced size and a number of obvious developmental defects, fails to flower (Fig. 5 and Supplementary Fig. 13), and both the SAM and RAM and the formation of the vasculature are dramatically affected in these plants (Fig. 6 and Supplementary Figs. 15 and 16). Our results therefore suggest that meristem activity is redundantly regulated by CG and non-CG methylation. This notion is supported by the fact that DNA methylation dynamically changes during SAM development96,97,98. In contrast, pavement cell shape, cell death, and endoreduplication are specifically controlled by CG methylation (Fig. 5f and Supplementary Fig. 14a–c). Absence of both CG and non-CG methylation in the mddcc mutant causes premature cell differentiation in roots; a role of this epigenetic modification in cell differentiation is consistent with the finding that the RAM displays widespread cell type-specific patterns of DNA methylation99. Loci encoding crucial regulators of some of the biological processes severely affected in the DNA methyltransferases-deficient mutants analyzed in this work show altered methylation patterns and gene expression levels (Supplementary Data 1). For example, the positive regulator of cell death ACCELERATED CELL DEATH 6 (ACD6) loses DNA methylation in its promoter in met1 and mddcc, and is concomitantly up-regulated (Supplementary Fig. 18). It has been demonstrated that over-expression of ACD6 causes spontaneous cell death100. Therefore, the CG methylation-dependent cell death regulation (Supplementary Fig. 14c) could potentially function, at least in part, via modulating ACD6 expression. Loss of methylation in the promoter of E2Fc, encoding a core inhibitor of cell division101,102, correlates with a substantial increase in its expression (Supplementary Fig. 18), which may underlie the observed defects in cell proliferation in met1-9 and mddcc (Fig. 6b).
In summary, our results demonstrate that CG and non-CG methylation act together to protect genome stability and regulate gene expression, ultimately controlling a suite of important developmental processes and reproduction.
Methods
Plant materials and growth conditions
All plants were grown under long-day condition (16 h light/8 h dark). For seedling growth, Arabidopsis seeds were plated on 1/2 Murashige and Skoog (MS) medium with 0.6% agar, 0.7% agar, 1.0% or 1.2% agar and 1.5% sucrose and stratified for 7 days at 4 °C in darkness before being transferred to the growth chamber (16 h light/8 h dark, 22 °C). For experiments with adult plants, 14-day-old seedlings were transplanted to soil in the growth chamber. All mutant lines used in this study are in the Columbia-0 (Col-0) background. The ddcc mutant used in this study was generated by genetic crossing (cmt2 × ddc) and subsequent PCR-based genotyping in F2 populations. The mddcc and met1-9 mutants used in this study were generated by CRISPR/Cas9 system in ddcc and WT background, respectively (see below).
Generation of ddcc, met1-9, and mddcc mutants
We crossed the cmt220 mutant to the ddc103 triple mutant and obtained the ddcc mutant by genotyping the F2 populations. Primer sequences are listed in Supplementary Data 2.
The constructs for CRISPR-Cas9-mediated genome editing were designed as previously described55. Briefly, the expression of Cas9 was controlled by the UBQ1 promoter. The UBQ1 terminator was placed at the end of Cas9 ORF. The nuclear localization signal (NLS) was fused to both the N and C termini of Cas9. The sgRNAs were driven by Pol III-dependent gene promoters, including U6, U3b, and 7SL. Two sgRNAs were designed to target the first exon of the MET1 gene. The CRISPR-Cas9 construct was transformed into WT and the ddcc mutant backgrounds. The T1 transformants were analyzed by sequencing the sgRNAs target regions in the MET1 gene, which were amplified by PCR using the primers listed in Supplementary Data 2. Then, we isolated homozygous met1-9 mutants without the CRISPR-Cas9 constructs from the mutated T2 populations in the WT background. Heterozygous met1 mutants (met1/+) without the CRISPR-Cas9 construct were isolated from the mutated T2 populations in the ddcc background. The mddcc mutant was isolated by genotyping the progenies of met1/+ drm1 drm2 cmt3 cmt2 plants. Primer sequences are listed in Supplementary Data 2.
PCR assay
To confirm new transposon insertions, PCR was performed with a transposon-specific primer and a primer flanking the new insertion or with two primers flanking the new insertion. The DNeasy Plant Mini Kit (Qiagen) was used for DNA extraction. All PCR reactions were carried out using Ex-Taq enzyme (Takara). Primer sequences are listed in Supplementary Data 2.
Real-time quantitative RT-PCR
For real-time RT-PCR analysis, total RNA was subjected to reverse transcription using the TransScript One-Step gDNA Removal and cDNA Synthesis SuperMix kit (TransGen Biotech). The cDNA was used as template in a PCR reaction with Green Premix Ex Taq (Tli RNaseH Plus) (TaKaRa). All the reactions were carried out on a CFX96TM Real-Time System (Bio-Rad). The constitutively expressed EF1α was used as an endogenous control for normalization. Primer sequences are listed in Supplementary Data 2.
Flow cytometry
Cotyledons of 11-day-old plants were chopped with a razor blade in 1 mL Galbraith’s buffer104 (45 mM MgCl2, 30 mM sodium citrate, 20 mM MOPS, 0.1% (v/v) Triton x-100, pH = 7.0). The lysate was filtered through a 40-μm cell strainer (BD Falcon) and incubated at 4 °C for 5 min. The eluate was transferred to a 15 mL tube, 2 μl DAPI solution (1 mg/mL) were added, and the mixture was incubated on ice for 10 min. Then, ploidy was analyzed by using a BD FASCAria III flow cytometer. The FACS data were analyzed by FlowJo 7.6. The Flow cytometry gating strategy is shown in Supplementary Fig. 21.
Confocal microscopy
For visualizing pavement cells, cotyledons from 4-day-old or 11-day-old seedlings were detached and incubated with propidium iodide (PI) solution (10 μg/mL) for 10 min. Then, samples were imaged by confocal microscopy (LEICA SMD FLCS). PI was excited with a 538 nm laser; emission was detected between 600 and 640 nm.
Histological analysis
11-day-old seedlings or cotyledon and hypocotyl of 11-day-old pants were infiltrated with FAA solution (50% (v/v) ethanol, 5% (v/v) acetic acid, 3.7% formaldehyde) through vacuum infiltration for 15 min, and incubated with this FAA solution overnight at 4 °C (12–16 h). After fixation, samples were dehydrated in a graded ethanol series (1 h 50% ethanol, 1 h 60% ethanol, 1 h 70% ethanol); samples were then stored in 70% ethanol overnight. Next, samples were again dehydrated and infiltrated with Histo-Clear II (HS-202) according the following steps: 85% ethanol for 1 h at 4 °C; 95% ethanol for 1 h at 4 °C; 100% ethanol for 30 min at room temperature (RT); 100% ethanol for 30 min at RT; 100% ethanol for 1 h at RT; 100% ethanol for 1 h at RT; 25% Histo-Clear II/75% ethanol for 30 min at RT; 50% Histo-Clear II/50% ethanol with eosin (1.25%) for 30 min at RT; 75% Histo-Clear II/25% ethanol for 30 min at RT; 100% Histo-Clear II for 1 h at RT; 100% Histo-Clear II for 1 h at RT; 100% Histo-Clear II with 1/4 volume paraffin (REF. 39601095, Leica) overnight at RT. In the next 4 days, the samples were repeatedly infiltrated with paraffin, and then embedded. A series of 6 μm-thick longitudinal sections were made with a Leica RM 2235 microtome. Sections were transferred to microscopic slides, stained for 15 min in 0.1% toluidine blue solution, and rinsed with water. The slides were sealed by neutral balsam and visualized under a microscope (BX53F, Olympus).
Examination of cell death
Cell death was determined by trypan blue staining, following a published method105. Plant cotyledons were placed in TB staining solution (0.02 g of trypan blue and 10 g of phenol dissolved in 30 mL of mixed solution (1/3 (v/v) glycerol, 1/3 (v/v) lactic acid, 1/3 (v/v) water); this solution was further diluted with ethanol in 1:2 (v/v)) and boiled for 2 min. Then, the tubes were placed in the fume hood for 1 h with gentle shaking at RT. Then, the nonspecific staining was removed with the destaining solution (250% (m/v) chloral hydrate, pH = 1.2). Plant tissues were then kept in 10% (v/v) glycerol for imaging. Imaging was done using an SZX7 microscope (OLYMPUS).
Analysis of trichomes
The first true leaf of 11-day-old plants were selected to do this assay. Quantification of trichome branching was done manually by counting the number of branches under the microscopy (SZX7, Olympus). At least 23 plants per genotypes were observed.
Imaging leaf vein
Leaf vein patterning was imaging according to a previously described procedure with minor modifications106. Briefly, cotyledons were fixed in 100% ethanol:acetic acid (6:1, v/v) overnight at 4 °C. They were then washed once in 100% ethanol and again in 70% (v/v) ethanol, followed by clearing in chloral hydrate solution (chloral hydrate/glycerol/water (8:1:3)) for 1 h at RT. Then, cotyledons were rinsed twice in water. Cotyledons were cleared again in 85% (w/v) lactic acid for at least 3 days at RT. Cotyledons were placed in lactic acid and observed using IX73 microscopy (OLYMPUS).
Root imaging
Root apices of 9-day-old seedlings were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, treated with ClearSee solution107, and stained with calcofluor-white and basic fuchsin. Confocal images were taken with a Leica TCS SP8 point scanning confocal microscope with the following settings: for calcofluor-white, Ex: 405 nm, Em: 425-475 nm; for basic fuchsin, Ex: 561 nm, Em: 600–650 nm. ImageJ was used for imaging analysis.
5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine staining
11-day-old seedlings were incubated with 5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine (EdU) (1 μM) (Cat#C10350, Invitrogen) for 30 min in liquid 1/2 MS medium. Then, samples were fixed with 1× PBS solution containing 4% formaldehyde and 0.1% Triton x-100 for 30 min at 4 °C. After fixation, samples were washed with 1× PBS 3 times with rotation for 5 min at RT, then conjugated to Alexa Fluor 488 with the Click-iT EdU Alexa Fluor 488 HCS Assay (Cat#C10350, Invitrogen) for 30 min in the dark at RT. Samples were then washed with 1× PBS 3 times with rotation for 10 min at RT and imaged using a stereomicroscope (Leica DM6B).
DNA-seq and identification of non-reference TE insertions
The DNeasy Plant Mini Kit (Qiagen) was used for DNA extraction. Library construction and sequencing were performed at the PSC Genomics Core Facility. Identification of non-reference TE insertions with target site duplications (TSDs) was conducted using SPLITREADER with some modifications108. In brief, after trimming low-quality sequences and adapters using Trimmomatic, clean read pairs were mapped to the reference genome using Bowtie2 with the parameter “-very-sensitive”. Subsequently, unmapped reads from both pairs, including discordantly mapped reads, were extracted and merged together. Those unmapped reads were remapped to a collection of 5′ and 3′ TE extremities (300 bp) sequence with parameters “–local–very-sensitive” (TE families like ARNOLDY2, ATCOPIA62, ATCOPIA95, TA12, and TAG1 families were excluded, since they do not contain copies with intact extremities in the TAIR10 reference genome108) and reads with soft-clipped mapping (with one end ≥20 nt mapped to the TE extremity) were selected. Those selected reads were further recursively soft-clipped by 1 nt and mapped to the reference genome using Bowtie2 with parameters “–mp 13–rdg 8,5–rfg 8,5 --local --very-sensitive” until the soft-clipped read length reached 20 nt. For reads simultaneously clipped-mapped to the TE reference and the reference genome, we further require that the other pair of the clipped read was also mapped and met one of the following criteria: (a) the other pair was properly mapped (insertion size <3000 bp and on the opposite strand) on the reference genome; (b) the other pair was properly mapped on the same TE reference; (c) the other pair is also clipped-mapped for the same TE reference and reference genome on the opposite strand. Around the TSD insertion sites, read clusters composed of four or more reads clipped from the same extremity and overlapping with read clusters composed of reads clipped from the other extremity were taken to indicate the presence of a bona fide TE insertion only if the size of the overlap was more than 3 bp and <20 bp. Putative non-reference TE insertions overlapping with aberrant genomic regions (3 kb away from the centromeric region based on Repbase annotation109, 3 kb away from the extremities of each chromosome and regions within 500 bp of “NNNN” sequence) or spanning the corresponding donor TE sequence were filtered out.
Whole-genome bisulfite sequencing and analysis
Genomic DNA was extracted from the aerial part of 2-week-old (WT, met1-9, and ddcc) or 5-week-old (mddcc) plants using DNeasy Plant Maxi Kit (Qiagen). Bisulfite treatment (EpiTect Plus Bisulfite Kits, Qiagen), library construction (Ultra II DNA Library Prep Kit, NEB), and sequencing (Illumina Hiseq x10) were performed at the PSC Genomics Core Facility.
For data analysis, reads containing adapters and low-quality reads (q < 20) were trimmed using cutadapt110 and Trimmomatic111, respectively, and clean reads that were shorter than 45nt were discarded. The remaining clean reads were mapped to the Arabidopsis TAIR 10 genome using BSMAP(2.90)112 with default parameters. In order to reduce the effect of RNA-DNA hybrids that interfere with bisulfite treatment, the reads were also mapped to the genome using bowtie2, and the reads with 0/1 mismatch both in BSAMP and bowite2 were filtered. Then methratio.py script was used to extract methylation ratio from filtered mapping results; the option -r was used to remove potential PCR duplicates. Cytosine positions with at least 4 reads coverage were retained for further analysis.
Defining DNA methylation-associated genes
Genes were classified into six groups using a modified version of the binomial test113. This approach tests for enrichment of C, CG, CHG, and CHH against a background level calculated from the whole genome. The total number of C counts and the total number of C+T counts within gene bodies (transcribed regions) of each gene were computed. The total number of C and C+T at all cytosine positions within each 500 bp bin of each gene promoter (2 kb) and downstream region (2 kb) were also computed, and the region with maximum DNA methylation level was selected for further analysis. A one-tailed binomial test was then applied to each gene for each context testing against the background methylation level in gene body, gene promoter, and gene downstream region, respectively. To control for false positives at the extremes, q values were calculated from P values by adjusting for multiple testing using the Benjamini–Hochberg false discovery rate.
gbM genes were defined by a gene body with a CG methylation q value <0.01 and CHG and CHH methylation q values ≥ 0.01. teM genes were defined by CHG or CHH methylation q values < 0.01. According to the CHG or CHH methylation q values < 0.01 of exon or intron, teM genes were divided into Intron teM genes and Other-teM genes. In addition to gbM and teM genes, genes could be classified into pM genes and dM genes. pM genes were defined by a gene promoter with a C methylation q value < 0.01. dM genes were defined by a downstream region with a C methylation q value < 0.01 and promoter with a C methylation q value ≥ 0.01. Other genes were classified as unmethylated (UM) genes. You can find the categories of genes in the Supplementary Data 3.
mRNA-sequencing data analysis
Total RNA was extracted from the aerial part of 2-week-old WT, met1-9, and ddcc, or 5-week-old WT (removing the inflorescence) and mddcc using RNeasy Plant Mini Kit (Qiagen) and RNase-Free DNase Set (Qiagen). Library construction (RiboMinus Plant Kit, Invitrogen; Ultra II Directional RNA Library Prep Kit, NEB) and sequencing (Illumina Hiseq x10) were performed at the PSC Genomics Core Facility.
For RNA-seq data processing, quality control was performed using FastQC (www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc). RNA-Seq reads were trimmed using cutadapt110 and Trimmomatic111 before alignment. The trimmed reads were aligned to the Arabidposis TAIR10 genome using STAR (v2.5.3)114 with parameters “--outSAMmultNmax 1” and “--outSAMstrandField intronMotif” for running Cufflinks to assemble. The tool htseq-count of Python package HTSeq115 was used to count the mapped fragments for each gene and TE with “--stranded=reverse” for differentially expressed genes analysis and “--stranded = yes” for differentially expressed antisense transcription of genes.
In order to identify non-annotated transcripts, cufflinks was used to assemble transcriptomes from the results of STAR. Cuffmerge were used to merge all assemblies into a master transcriptome, which was compared to known gene transcripts. The transcripts with “class_code = u” were selected as non-annotated transcripts. The non-annotated transcripts overlapping with transposons elements were removed. The tool htseq-count of Python package HTSeq115 was used to count the mapped fragments for each non-annotated transcript with “--stranded = reverse” for differentially expressed non-annotated transcripts analysis.
The output count table was used as the input for DESeq2116 to compute the differentially expressed genes/TE/antisense transcripts/non-annotated transcripts.
To identify Intron-teM genes with down-regulated expression downstream of their methylated intron in mutants relative to WT, the gene region upstream of the intron with the maximum non-CG methylation level was designated as the 5′ part (5′), the gene region downstream of the intron was designated as the 3′ part (3′), and the numbers of mapped reads in 5′ and 3′ were calculated using featureCounts with parameters -M -p -s 2, separately. The Intron-teM genes in which the 5′ reads in WT were ≥10, were retained for the following analysis. The reads ratio of 3′/5′ was used to monitor expression changes in the 3′ of Intron-teM genes, and the 3′ down-regulated Intron-teM genes were determined using Log2[(3′/5′ counts ratio in mutant)/(3′/5′ counts ratio in WT)] < −1. Using this approach, we obtained 52 Intron-teM genes, 10 of which showed 3′ down-regulation in these mutants compared with the WT (Supplementary Table 3).
GO-enrichment analysis
GO-enrichment analysis of genes was performed using agriGO v.2117 (http://systemsbiology.cau.edu.cn/agriGOv2/classification_analysis.php?category=Plant&&family=Brassicaceae).
Reporting summary
Further information on research design is available in the Nature Research Reporting Summary linked to this article.
Data availability
All data supporting the findings of this study are available within the manuscript and its supplementary files. All high-throughput sequencing data generated in this study have been deposited in GEO with accessions codes GSE169497. Mutant seeds used to isolate the mddcc quintuple mutant are available at the Arabidopsis Biological Resource Center (ABRC) (stock numbers CS72761). Source data are provided with this paper.
References
Zhang, H., Lang, Z. & Zhu, J. K. Dynamics and function of DNA methylation in plants. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 19, 489–506 (2018).
Law, J. A. & Jacobsen, S. E. Establishing, maintaining and modifying DNA methylation patterns in plants and animals. Nat. Rev. Genet. 11, 204–220 (2010).
Jullien, P. E., Susaki, D., Yelagandula, R., Higashiyama, T. & Berger, F. DNA methylation dynamics during sexual reproduction in Arabidopsis thaliana. Curr. Biol. 22, 1825–1830 (2012).
Bond, D. M. & Baulcombe, D. C. Small RNAs and heritable epigenetic variation in plants. Trends Cell Biol. 24, 100–107 (2014).
Pikaard, C. S., Mittelsten & Scheid, O. Epigenetic regulation in plants. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 6, a019315 (2014).
Heard, E. & Martienssen, R. A. Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance: myths and mechanisms. Cell 157, 95–109 (2014).
Deaton, A. M. & Bird, A. CpG islands and the regulation of transcription. Genes Dev. 25, 1010–1022 (2011).
Quadrana, L. & Colot, V. Plant transgenerational epigenetics. Annu. Rev. Genet. 50, 467–491 (2016).
Schmitz, R. J., Lewis, Z. A. & Goll, M. G. DNA methylation: shared and divergent features across Eukaryotes. Trends Genet. 35, 818–827 (2019).
Quante, T. & Bird, A. Do short, frequent DNA sequence motifs mould the epigenome? Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 17, 257–262 (2016).
He, X. J., Chen, T. & Zhu, J. K. Regulation and function of DNA methylation in plants and animals. Cell Res. 21, 442–465 (2011).
Zhong, X. Comparative epigenomics: a powerful tool to understand the evolution of DNA methylation. N. Phytol. 210, 76–80 (2016).
Goll, M. G. & Bestor, T. H. Eukaryotic cytosine methyltransferases. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 74, 481–514 (2005).
Chen, T. & Li, E. Structure and function of eukaryotic DNA methyltransferases. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 60, 55–89 (2004).
Kankel, M. W. et al. Arabidopsis MET1 cytosine methyltransferase mutants. Genetics 163, 1109–1122 (2003).
Finnegan, E. J. & Dennis, E. S. Isolation and identification by sequence homology of a putative cytosine methyltransferase from Arabidopsis thaliana. Nucleic Acids Res. 21, 2383–2388 (1993).
Lindroth, A. M. et al. Requirement of CHROMOMETHYLASE3 for maintenance of CpXpG methylation. Science 292, 2077–2080 (2001).
Du, J. et al. Dual binding of chromomethylase domains to H3K9me2-containing nucleosomes directs DNA methylation in plants. Cell 151, 167–180 (2012).
Stroud, H. et al. Non-CG methylation patterns shape the epigenetic landscape in Arabidopsis. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 21, 64–72 (2014).
Zemach, A. et al. The Arabidopsis nucleosome remodeler DDM1 allows DNA methyltransferases to access H1-containing heterochromatin. Cell 153, 193–205 (2013).
Cuerda-Gil, D. & Slotkin, R. K. Non-canonical RNA-directed DNA methylation. Nat. Plants 2, 16163 (2016).
Haag, J. R. & Pikaard, C. S. Multisubunit RNA polymerases IV and V: purveyors of non-coding RNA for plant gene silencing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 12, 483–492 (2011).
Matzke, M. A. & Mosher, R. A. RNA-directed DNA methylation: an epigenetic pathway of increasing complexity. Nat. Rev. Genet. 15, 394–408 (2014).
He, L. et al. Pathway conversion enables a double-lock mechanism to maintain DNA methylation and genome stability. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 118, e2107320118 (2021).
Bond, D. M. & Baulcombe, D. C. Epigenetic transitions leading to heritable, RNA-mediated de novo silencing in Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 112, 917–922 (2015).
Singh, J., Mishra, V., Wang, F., Huang, H. Y. & Pikaard, C. S. Reaction mechanisms of Pol IV, RDR2, and DCL3 drive RNA channeling in the siRNA-directed DNA methylation pathway. Mol. Cell 75, 576–589 (2019). e575.
Borges, F. & Martienssen, R. A. The expanding world of small RNAs in plants. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 16, 727–741 (2015).
He, X. J., Ma, Z. Y. & Liu, Z. W. Non-coding RNA transcription and RNA-directed DNA methylation in Arabidopsis. Mol. Plant. 7, 1406–1414 (2014).
Zhang, X. et al. Genome-wide high-resolution mapping and functional analysis of DNA methylation in Arabidopsis. Cell 126, 1189–1201 (2006).
Henderson, I. R. & Jacobsen, S. E. Epigenetic inheritance in plants. Nature 447, 418–424 (2007).
Underwood, C. J., Henderson, I. R. & Martienssen, R. A. Genetic and epigenetic variation of transposable elements in Arabidopsis. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 36, 135–141 (2017).
Miura, A. et al. Mobilization of transposons by a mutation abolishing full DNA methylation in Arabidopsis. Nature 411, 212–214 (2001).
Tsukahara, S. et al. Bursts of retrotransposition reproduced in Arabidopsis. Nature 461, 423–426 (2009).
Lippman, Z. et al. Role of transposable elements in heterochromatin and epigenetic control. Nature 430, 471–476 (2004).
Mirouze, M. et al. Selective epigenetic control of retrotransposition in Arabidopsis. Nature 461, 427–430 (2009).
Wang, Z. & Baulcombe, D. C. Transposon age and non-CG methylation. Nat. Commun. 11, 1221 (2020).
Lee, S. C. et al. Arabidopsis retrotransposon virus-like particles and their regulation by epigenetically activated small RNA. Genome Res. 30, 576–588 (2020).
Quadrana, L. et al. Transposition favors the generation of large effect mutations that may facilitate rapid adaption. Nat. Commun. 10, 3421 (2019).
Kato, M., Miura, A., Bender, J., Jacobsen, S. E. & Kakutani, T. Role of CG and non-CG methylation in immobilization of transposons in Arabidopsis. Curr. Biol. 13, 421–426 (2003).
Lei, M. et al. Regulatory link between DNA methylation and active demethylation in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 112, 3553–3557 (2015).
Williams, B. P., Pignatta, D., Henikoff, S. & Gehring, M. Methylation-sensitive expression of a DNA demethylase gene serves as an epigenetic rheostat. PLoS Genet. 11, e1005142 (2015).
Takuno, S. & Gaut, B. S. Gene body methylation is conserved between plant orthologs and is of evolutionary consequence. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 110, 1797–1802 (2013).
Niederhuth, C. E. et al. Widespread natural variation of DNA methylation within angiosperms. Genome Biol. 17, 194 (2016).
Rigal, M., Kevei, Z., Pelissier, T. & Mathieu, O. DNA methylation in an intron of the IBM1 histone demethylase gene stabilizes chromatin modification patterns. Embo J. 31, 2981–2993 (2012).
To, T. K., Saze, H. & Kakutani, T. DNA methylation within transcribed regions. Plant Physiol. 168, 1219–1225 (2015).
Wang, X. et al. RNA-binding protein regulates plant DNA methylation by controlling mRNA processing at the intronic heterochromatin-containing gene IBM1. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 110, 15467–15472 (2013).
Saze, H. et al. Mechanism for full-length RNA processing of Arabidopsis genes containing intragenic heterochromatin. Nat. Commun. 4, 2301 (2013).
Duan, C. G. et al. A protein complex regulates RNA processing of intronic heterochromatin-containing genes in Arabidopsis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 114, E7377–E7384 (2017).
Zhang, Y. Z. et al. Genome-wide distribution and functions of the AAE complex in epigenetic regulation in Arabidopsis. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 63, 707–722 (2021).
Saze, H., Mittelsten Scheid, O. & Paszkowski, J. Maintenance of CpG methylation is essential for epigenetic inheritance during plant gametogenesis. Nat. Genet 34, 65–69 (2003).
Henderson, I. R. & Jacobsen, S. E. Tandem repeats upstream of the Arabidopsis endogene SDC recruit non-CG DNA methylation and initiate siRNA spreading. Genes Dev. 22, 1597–1606 (2008).
Tian, W. et al. SDC mediates DNA methylation-controlled clock pace by interacting with ZTL in Arabidopsis. Nucleic Acids Res. 49, 3764–3780 (2021).
Zhang, X. & Jacobsen, S. E. Genetic analyses of DNA methyltransferases in Arabidopsis thaliana. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 71, 439–447 (2006).
Mathieu, O., Reinders, J., Caikovski, M., Smathajitt, C. & Paszkowski, J. Transgenerational stability of the Arabidopsis epigenome is coordinated by CG methylation. Cell 130, 851–862 (2007).
Zhang, Z. et al. A multiplex CRISPR/Cas9 platform for fast and efficient editing of multiple genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Rep. 35, 1519–1533 (2016).
Lister, R. et al. Highly integrated single-base resolution maps of the epigenome in Arabidopsis. Cell 133, 523–536 (2008).
Tran, R. K. et al. DNA methylation profiling identifies CG methylation clusters in Arabidopsis genes. Curr. Biol. 15, 154–159 (2005).
Zilberman, D., Gehring, M., Tran, R. K., Ballinger, T. & Henikoff, S. Genome-wide analysis of Arabidopsis thaliana DNA methylation uncovers an interdependence between methylation and transcription. Nat. Genet. 39, 61–69 (2007).
Shahzad, Z., Moore, J. D. & Zilberman, D. Gene body methylation mediates epigenetic inheritance of plant traits. Preprint at bioRxiv https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.03.15.435374 (2021).
Soppe, W. J. et al. The late flowering phenotype of fwa mutants is caused by gain-of-function epigenetic alleles of a homeodomain gene. Mol. Cell 6, 791–802 (2000).
Vassileva, V., Hollwey, E., Todorov, D. & Meyer, P. Leaf epidermal profiling as a phenotyping tool for DNA methylation mutants. Genet. Plant Physiol. 6, 3–13 (2016).
Chen, J., Wang, F., Zheng, S., Xu, T. & Yang, Z. Pavement cells: a model system for non-transcriptional auxin signalling and crosstalks. J. Exp. Bot. 66, 4957–4970 (2015).
Sapala, A., Runions, A. & Smith, R. S. Mechanics, geometry and genetics of epidermal cell shape regulation: different pieces of the same puzzle. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 47, 1–8 (2018).
Kotogany, E., Dudits, D., Horvath, G. V. & Ayaydin, F. A rapid and robust assay for detection of S-phase cell cycle progression in plant cells and tissues by using ethynyl deoxyuridine. Plant Methods 6, 5 (2010).
Kazda, A., Akimcheva, S., Watson, J. M. & Riha, K. Cell Proliferation analysis using EdU labeling in whole plant and histological samples of Arabidopsis. Methods Mol. Biol. 1370, 169–182 (2016).
Kawashima, T. & Berger, F. Epigenetic reprogramming in plant sexual reproduction. Nat. Rev. Genet. 15, 613–624 (2014).
Winter, D. et al. An “Electronic Fluorescent Pictograph” browser for exploring and analyzing large-scale biological data sets. PLoS ONE 2, e718 (2007).
Hsieh, T. F. et al. Regulation of imprinted gene expression in Arabidopsis endosperm. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 108, 1755–1762 (2011).
Hu, L. et al. Mutation of a major CG methylase in rice causes genome-wide hypomethylation, dysregulated genome expression, and seedling lethality. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 111, 10642 (2014).
Fu, F. F., Dawe, R. K. & Gent, J. I. Loss of RNA-directed DNA methylation in maize chromomethylase and DDM1-type nucleosome remodeler mutants. Plant Cell 30, 1617–1627 (2018).
Huang, C. R. L., Burns, K. H. & Boeke, J. D. Active transposition in genomes. Annu. Rev. Genet. 46, 651–675 (2012).
Zemach, A., McDaniel, I. E., Silva, P. & Zilberman, D. Genome-wide evolutionary analysis of eukaryotic DNA methylation. Science 328, 916–919 (2010).
Lee, J. Y. et al. Conserved dual-mode gene regulation programs in higher eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res. 49, 2583–2597 (2021).
Liang, W. et al. Deciphering the synergistic and redundant roles of CG and non-CG DNA methylation in plant development and transposable element silencing. N. Phytol. 233, 722–737 (2022).
Harris, C. J. et al. A DNA methylation reader complex that enhances gene transcription. Science 362, 1182 (2018).
Miao, W. et al. Roles of IDM3 and SDJ1/2/3 in establishment and/or maintenance of DNA methylation in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell Physiol. 62, 1409–1422 (2021).
Li, S. et al. SUVH1, a Su(var)3-9 family member, promotes the expression of genes targeted by DNA methylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 44, 608–620 (2015).
Zhao, Q. Q., Lin, R. N., Li, L., Chen, S. & He, X. J. A methylated-DNA-binding complex required for plant development mediates transcriptional activation of promoter methylated genes. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 61, 120–139 (2019).
Xiao, X. et al. A group of SUVH methyl-DNA binding proteins regulate expression of the DNA demethylase ROS1 in Arabidopsis. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 61, 110–119 (2019).
Rowley, M. J., Rothi, M. H., Bohmdorfer, G., Kucinski, J. & Wierzbicki, A. T. Long-range control of gene expression via RNA-directed DNA methylation. PLoS Genet. 13, e1006749 (2017).
Lei, M. et al. Arabidopsis EDM2 promotes IBM1 distal polyadenylation and regulates genome DNA methylation patterns. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 111, 527–532 (2014).
Neri, F. et al. Intragenic DNA methylation prevents spurious transcription initiation. Nature 543, 72–77 (2017).
Le, N. T. et al. Epigenetic regulation of spurious transcription initiation in Arabidopsis. Nat. Commun. 11, 3224 (2020).
Zhao, L. et al. Chromatin loops associated with active genes and heterochromatin shape rice genome architecture for transcriptional regulation. Nat. Commun. 10, 3640 (2019).
Lupianez, D. G. et al. Disruptions of topological chromatin domains cause pathogenic rewiring of gene–enhancer interactions. Cell 161, 1012–1025 (2015).
Zeng, W. et al. Roles of DEMETER in regulating DNA methylation in vegetative tissues and pathogen resistance. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 63, 691–706 (2020).
Halter, T. et al. The Arabidopsis active demethylase ROS1 cis-regulates defence genes by erasing DNA methylation at promoter-regulatory regions. eLife 10, e62994 (2021).
Schumann, U. et al. DEMETER plays a role in DNA demethylation and disease response in somatic tissues of Arabidopsis. Epigenetics 14, 1074–1087 (2019).
Wang, L. et al. A virus-encoded protein suppresses methylation of the viral genome through its interaction with AGO4 in the Cajal body. eLife 9, e55542 (2020).
Ito, H. et al. An siRNA pathway prevents transgenerational retrotransposition in plants subjected to stress. Nature 472, 115–119 (2011).
Baduel, P. et al. Genetic and environmental modulation of transposition shapes the evolutionary potential of Arabidopsis thaliana. Genome Biol. 22, 138 (2021).
Yelina, N. E. et al. DNA methylation epigenetically silences crossover hot spots and controls chromosomal domains of meiotic recombination in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev. 29, 2183–2202 (2015).
Underwood, C. J. et al. Epigenetic activation of meiotic recombination near Arabidopsis thaliana centromeres via loss of H3K9me2 and non-CG DNA methylation. Genome Res. 28, 519–531 (2018).
Zhao, M. et al. The mop1 mutation affects the recombination landscape in maize. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 118, e2009475118 (2021).
Choi, J., Lyons, D. B., Kim, M. Y., Moore, J. D. & Zilberman, D. DNA methylation and histone H1 jointly repress transposable elements and aberrant intragenic transcripts. Mol. Cell 77, 310–323 (2020). e317.
Bouyer, D. et al. DNA methylation dynamics during early plant life. Genome Biol. 18, 179 (2017).
Higo, A. et al. DNA methylation is reconfigured at the onset of reproduction in rice shoot apical meristem. Nat. Commun. 11, 4079 (2020).
Gutzat, R. et al. Arabidopsis shoot stem cells display dynamic transcription and DNA methylation patterns. EMBO J. 39, e103667 (2020).
Kawakatsu, T. et al. Unique cell-type-specific patterns of DNA methylation in the root meristem. Nat. Plants 2, 16058 (2016).
Lu, H., Rate, D. N., Song, J. T. & Greenberg, J. T. ACD6, a novel ankyrin protein, is a regulator and an effector of salicylic acid signaling in the Arabidopsis defense response. Plant Cell 15, 2408–2420 (2003).
Inze, D. & De Veylder, L. Cell cycle regulation in plant development. Annu. Rev. Genet. 40, 77–105 (2006).
del Pozo, J. C., Boniotti, M. B. & Gutierrez, C. Arabidopsis E2Fc functions in cell division and is degraded by the ubiquitin-SCF(AtSKP2) pathway in response to light. Plant Cell 14, 3057–3071 (2002).
Chan, S. W. et al. RNAi, DRD1, and histone methylation actively target developmentally important non-CG DNA methylation in arabidopsis. PLoS Genet. 2, e83 (2006).
Galbraith, D. W. et al. Rapid flow cytometric analysis of the cell cycle in intact plant tissues. Science 220, 1049–1051 (1983).
Li, B. et al. FATTY ACID DESATURASE5 is required to induce autoimmune responses in gigantic chloroplast mutants of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 32, 3240–3255 (2020).
Baylis, T., Cierlik, I., Sundberg, E. & Mattsson, J. SHORT INTERNODES/STYLISH genes, regulators of auxin biosynthesis, are involved in leaf vein development in Arabidopsis thaliana. N. Phytol. 197, 737–750 (2013).
Ursache, R., Andersen, T. G., Marhavy, P. & Geldner, N. A protocol for combining fluorescent proteins with histological stains for diverse cell wall components. Plant J. 93, 399–412 (2018).
Quadrana, L. et al. The Arabidopsis thaliana mobilome and its impact at the species level. eLife 5, e15716 (2016).
Bao, W., Kojima, K. K. & Kohany, O. Repbase Update, a database of repetitive elements in eukaryotic genomes. Mob. DNA 6, 11 (2015).
Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J. 17, 1 (2011).
Bolger, A. M., Lohse, M. & Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 30, 2114–2120 (2014).
Xi, Y. & Li, W. BSMAP: whole genome bisulfite sequence MAPping program. BMC Bioinforma. 10, 232 (2009).
Bewick, A. J. et al. On the origin and evolutionary consequences of gene body DNA methylation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 113, 9111–9116 (2016).
Dobin, A. et al. STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 29, 15–21 (2013).
Anders, S., Pyl, P. T. & Huber, W. HTSeq—a Python framework to work with high-throughput sequencing data. Bioinformatics 31, 166–169 (2015).
Love, M. I., Huber, W. & Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15, 550 (2014).
Tian, T. et al. agriGO v2.0: a GO analysis toolkit for the agricultural community, 2017 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 45, W122–W129 (2017).
Acknowledgements
We thank the Core Facility for Genomics and Plant Cell biology at Shanghai Center for Plant Stress Biology (PSC), Chinese Academy of Sciences, for technical support. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32100458 to L.H.) and the Chinese Academy of Sciences (to J.-K.Z.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
L.H. and J.-K.Z. designed the research. L.H. performed most experiments. H.H. carried out bioinformatics analyses, with the exception of TE insertion analysis. M.B. performed the root-related assays. L.H. and Y.Y. performed trichome-related assay. C.Z. performed TE insertion analysis. J.M. performed EdU-labeling assay. L.H. and L.Z. performed RNA sequencing. L.H., R.L.-D., and J.-K.Z analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Peer review
Peer review information
Nature Communications thanks Tzung-Fu Hsieh and the other, anonymous, reviewer(s) for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Peer reviewer reports are available.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Source data
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
He, L., Huang, H., Bradai, M. et al. DNA methylation-free Arabidopsis reveals crucial roles of DNA methylation in regulating gene expression and development. Nat Commun 13, 1335 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-28940-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-28940-2
This article is cited by
-
Increased DNA methylation contributes to the early ripening of pear fruits during domestication and improvement
Genome Biology (2024)
-
BSXplorer: analytical framework for exploratory analysis of BS-seq data
BMC Bioinformatics (2024)
-
Epigenetic variation in early and late flowering plants of the rubber-producing Russian dandelion Taraxacum koksaghyz provides insights into the regulation of flowering time
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Methylation in cornea and corneal diseases: a systematic review
Cell Death Discovery (2024)
-
High allelic diversity in Arabidopsis NLRs is associated with distinct genomic features
EMBO Reports (2024)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.