Abstract
Development of earth-abundant electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution and oxidation reactions in strong acids represents a great challenge for developing high efficiency, durable, and cost effective electrolyzers and fuel cells. We report herein that hafnium oxyhydroxide with incorporated nitrogen by treatment using an atmospheric nitrogen plasma demonstrates high catalytic activity and stability for both hydrogen evolution and oxidation reactions in strong acidic media using earth-abundant materials. The observed properties are especially important for unitized regenerative fuel cells using polymer electrolyte membranes. Our results indicate that nitrogen-modified hafnium oxyhydroxide could be a true alternative for platinum as an active and stable electrocatalyst, and furthermore that nitrogen plasma treatment may be useful in activating other non-conductive materials to form new active electrocatalysts.
Similar content being viewed by others
Introduction
Renewable hydrogen technologies provide prospective routes to change the fossil-fuel-dominated economy through multiple high efficiency processes, specifically the production of H2 from water electrolysis and generation of electricity in H2 fuel cells1. Major impediments to the application of current water electrolyzers and fuel cells are the rates of electrochemical reactions involved, such as the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) and hydrogen oxidation reaction (HOR), which often exhibit slow kinetics, except on platinum group metals (PGMs: Pt, Pd, and Ir), due to overpotentials for electron transfer at the electrode–electrolyte interface2. PGMs and their alloys are employed as active electrocatalysts due to their unique activity and durability under harsh acidic conditions but are limited in their application due to their scarcity and cost3,4,5. In contrast, under alkaline conditions, earth-abundant materials have been shown to be sufficiently stable to feasibly replace precious metals6,7,8. Although the use of high pH electrolytes addresses the need for non-precious metal electrocatalysts, other technical challenges remain. For instance, anion exchange membranes in alkaline membrane fuel cells have lower ion conductivity and suffer from more severe degradation than proton-exchange membranes (PEMs) in PEM fuel cells9. In electrolyzers, acidic PEM electrolysis technologies have been recognized to be superior to alkaline systems in numerous aspects, including their compact system design, lack of liquid electrolyte, high current density and energy efficiency, and high gas purity10,11.
The search for cost-effective, earth-abundant electrocatalytic materials for PEM electrolysis with high activity and stability has identified several classes of inorganic materials that are highly active for hydrogen evolution in acidic media12,13,14. Transition metal carbides such as WC and Mo2C are promising non-precious metal alternatives to Pt for HER15. Their good HER activity has been attributed to the strong hybridization between metal and carbon orbitals that lead to electronic structural characteristics resembling those of Pt metal16. Metal chalcogenides represent a large group of inorganic HER-active materials; however, since the active sites of these materials have been shown to be located at edge sites and defects, their morphology often dictates the number of active sites, electrical conductivity, and stability17,18,19. For example, on the most well-studied metal chalcogenide for HER, i.e., two-dimensional MoS2, edge S sites are active for forming sulfur hydride species that are the key intermediates for H2 production20. Metal phosphides are another emerging class of catalysts that effectively catalyze HER21,22. Cobalt phosphide has demonstrated the highest HER performance in acidic media of this class23,24. However, despite exhibiting promising HER catalytic activity and durability in acidic media, all of these inorganic compounds are unavoidably vulnerable in practice to surface oxidation during synthesis or during exposure to air and electrolytes. Furthermore, those materials cannot be utilized to catalyze HOR in acids due to oxide formation and their intrinsic instability in strong acids at anodic potentials25,26. So far, electrocatalysts composed of earth-abundant elements are not comparable to PGMs for HER and HOR under acidic electrochemical conditions.
One other class of materials, transition metal oxynitrides (e.g., MNxOy, M = Ti, Ta, Hf) have been tested as catalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction27 and oxygen evolution reaction28. Despite the high stability of these materials in acids, so far they have shown unsatisfactory catalytic performance for these reactions. In this paper, we report that processing Hf oxide with an atmospheric N2 plasma forms an acid-insoluble hafnium oxynitride material. We propose that under electrochemical environments this material is transformed into an active oxynitride hydroxide that is capable of functioning both as a highly active HER and HOR electrocatalyst in strong acid conditions. The zero onset potentials and high current densities demonstrate that this material is a promising alternative to Pt. This material demonstrates the excellent HOR and HER activities in acids using non-PGM catalysts, opening new opportunities to develop technologically and economically viable unitized regenerative fuel cell (URFC) systems and cost-effective PEM electrolyzers.
Results
Electrochemistry and electrocatalytic activity
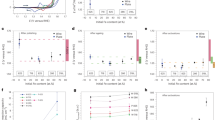
Hf thin films were prepared by physical vapor deposition using Ar+ ion sputtering of 20 nm of Hf on both sides of roughened Au substrates that were prepared following the reported electrochemical procedure29 and discussed further in Methods and in Supplementary Notes 1 and 2. Gold foil was chosen as a substrate because it is stable over a large potential range without showing measureable HER and HOR activity during the electrochemical polarization experiments, and roughened Au improved the physical stability of the HfOxthin films during H2 generation and enabled improved characterization using surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS). The Hf film was oxidized by air exposure and then exposed to a N2 plasma in a dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) reactor (Supplementary Figure 1) to incorporate nitrogen to form a hafnium oxynitride (HfNxOy) material. The surface composition and morphology (Supplementary Figure 2) of the N-modified sample were measured by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and scanning electron microscopy (SEM). The samples were then electrochemically cycled over the range −200 to 1600 mV (vs reversible hydrogen electrode (RHE)) in an aqueous solution of 0.1 M HClO4 prior to testing for HER and HOR performance under acidic conditions. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) using one of these HfNxOy samples is presented in Fig. 1, along with CV data from a roughened Au foil and a similarly prepared, but without N-modification, HfOx sample for comparison. Large current at negative potentials in the cathodic scan direction for HfNxOy is due to the HER, while the positive current in the anodic scan direction is due to the HOR. We observe a near-zero onset potential for both HER and HOR, which was formerly a unique property of PGM-based electrocatalysts. In addition, the large anodic current caused by HOR mirrors the electrochemical behavior of precious metals, such as Pt, Pd, and Ir.
Cyclic voltammetry (CV) of N-modified Hf oxide, Hf oxide, and a roughened Au foil in acidic media hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) current from a roughened Au foil becomes visible only at −100 mV, demonstrating that the HER and hydrogen oxidation reaction activity of the HfNxOy in the potential range of −100 to 800 mV does not arise from the exposed Au substrate. Scan rate: 50 mV s−1 in 0.1 M HClO4. The CV data are corrected for the current-resistance loss. The stable CV data shown above were from the 20th scans
At high anodic potentials, anodic peaks from 1300 to 1600 mV and cathodic peaks from 1400 to 900 mV from the HfOx and HfNxOy thin film samples are similar to those of the roughened Au foil sample despite detection of only 0.3 at.% Au from analysis using XPS. This is indicative of incomplete conformal coating of the rough Au surface by Hf during deposition, presumably because of shadowing of some of the Au substrate from the Hf atom flux by the rough surface features. The uncoated roughened Au sample did not show any HOR activity. HfOx showed some HOR activity, but it was significantly lower than that of the HfNxOy. Supplementary Figures 3 and 4 show electrochemical analysis of other surfaces for comparison, including uncoated Au (smooth and rough) and HfOx films supported on smooth Au (both N-modified and unmodified). All these N-unmodified surfaces showed significantly lower activity than HfNxOy. Given these results, we conclude that the N-modification of HfOx by plasma treatment is critical to the observed enhanced performance of HfNxOy. Next, we will focus our discussion on the superior catalytic performance and toward determining the chemical nature of the active phase of HfNxOy.
To accurately measure the hydrogen evolution and hydrogen oxidation activity and to define the zero potential on the RHE scale, electrochemical polarization scans were carried out in H2-purged 0.1 M HClO4 solutions and then compared to control scans using a Pt foil sample. The scanning rate was at 5 mV s−1. The HER/HOR plots shown in Fig. 2 have been corrected for the current-resistance loss from the ohmic resistance of the electrolyte obtained by impedance measurements.
Catalytic activity of HfNxOy. a Comparative electrochemical behavior of Pt foil and thin film HfNxOy electrodes in acidic media highlighting the high activity of HfNxOy for hydrogen evolution and oxidation reactions. Inset: Tafel plots. b Expanded view of the activity near zero potential. Inset: Mass activity. Scan rate: 5 mV s−1 in H2-purged 0.1 M HClO4. The non-faradaic current at 5 mV s−1 scan rate is negligible, which is shown in Supplementary Figure 5
Pt foil was used to benchmark HER and HOR activity as it demonstrates excellent activity in acidic media30. As shown in Supplementary Figure 6, a 20-nm Pt film deposited on similarly roughened Au was prepared and measured for HER and HOR activity. Although the Hupdpeak area of the 20-nm Pt film sample was larger by a factor of two than that of the Pt foil sample, the Pt foil sample showed higher HER and HOR activity. Thus this Pt foil sample was used to benchmark HER and HOR activity in this study. As shown in Fig. 2a, the current polarity follows the scanning potential, switching from HER to HOR at zero potential vs RHE. Further increases in positive potential caused the HOR current to plateau due to the H2 diffusion limit in the electrolyte. The current drop at higher potential (>900 mV) is caused by surface oxidation, which removes metallic Pt sites for the reaction. Interestingly, the HfNxOy thin film exhibits similar catalytic activity as Pt foil. The onset potential for the HfNxOy thin film for both HER and HOR is zero, as for Pt, highlighting the excellent catalytic activity of the HfNxOy material. In the HER potential region, the overpotential at 10 mA cm−2 is −75 mV vs RHE, which is only 35 mV more negative than that of Pt foil. The HER activity normalized to the mass of Hf is shown as an inset in Fig. 2b and reached 400 mA per mg Hf at −75 mV. The exchange current density for HER of the HfNxOy film reached 0.40 mA cm−2 (compared to 0.66 mA cm−2 for Pt foil) or 29 mA per mg Hf. The HER Tafel plots with steady-state current density in the range of 50 < η < 100 mV are shown as an inset in Fig. 2a. The Tafel slope is an important indicator of the rate-determining step of an electrochemical process. The Tafel slope of Pt was calculated to be 27 mV dec−1, consistent with previous studies24,31. The Tafel slope obtained for HfNxOy was 72 mV dec−1, indicating a different reaction mechanism for HER on the HfNxOy film. Turning our attention now to the HOR activity, we note that a polarization scan using a solid electrode in the current electrochemical set-up is not applicable for extracting the true kinetic parameters of HOR since the HOR kinetics of Pt in acid are extremely fast32,33. However, we still can see that the HfNxOy film demonstrates good HOR activity, with the current reaching to the H2-diffusion limited level at the overpotential of 50 mV, which is only 20 mV more positive than that of Pt foil. The most surprising observation, which differentiates this HfNxOy film from other non-precious metal inorganic HER catalysts, is that HfNxOy exhibits substantial HOR activity under acidic conditions. This remarkable HER and HOR activity of HfNxOy (approaching that of Pt) under acidic conditions makes this material a true potential alternative for Pt.
Chemical nature of the HfNxOy thin film
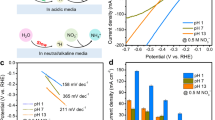
The surface composition and oxidation states of the HfNxOy thin film was analyzed by high-resolution X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (HRXPS). The results are summarized in Figure 3a–c and Table 1. In addition, SERS spectra of these films was obtained before and after electrochemical cycling between −200 and 1600 mV in 0.1 M HClO4, as shown in Fig. 3d. The combination of HRXPS and SERS helps to elucidate the chemical nature of these HfNxOy films and the changes induced by electrochemical measurements.
Characterization of HfNxOy by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and Raman spectroscopy. XPS and Raman spectra were obtained for HfNxOy before (bottom or red spectra) and after (top or black spectra) electrochemical measurement (250 cyclic voltammetric (CV) scans, −200 to 1600 mV) in acidic media. XPS regional spectra are shown for: a, Hf 4f; b, N 1s; and c, O 1s. The corresponding XPS survey scan is shown in Supplementary Figure 7a. The Raman spectrum, shown in d, for “after CV scanning” was obtained for the wet sample after CV scans without rinsing or drying
In Fig. 3a–c, spectra of the HfNxOy thin film are obtained before (bottom curves) and after (top curves) electrochemical measurements. Figure 3a shows a Hf 4f7/2 peak at 16.4 eV binding energy (BE), assigned to a low oxidation state Hf2+ initially and 16.8 eV BE (not full oxidation to Hf4+at 17.4 eV)34 after electrochemical testing. Figure 3b confirmed that the N2 plasma treatment led to an incorporation of N atoms into the as-grown Hf oxide film, resulting in two N 1s peaks at 399.7 and 404.0 eV BE. The high BE peak, assigned to nitrate (NO3−) species, was not stable in acid solution and was not present after electrochemical reactions. A corresponding change was observed by Raman spectroscopy, as shown in Fig. 3d, where multiple peaks in the range of 1350–1500 cm−1 corresponding to nitrate species disappeared after electrochemical reactions. In Fig. 3b, the 399.7 eV peak is assigned to the N 1s peak from oxynitride (O-Hf-N) species, which were also identified by the Raman spectrum in Fig. 3d that shows an intense peak at 2160 cm−135. This Raman peak significantly decreased after electrochemical measurements, which could be due to dissolution of the hafnium oxynitride. However, the small (25%) reduction in the N 1s XPS intensity at 399.7 eV indicates good stability of the N-containing material. This small reduction could be caused by the degradation of the surface oxynitride material, while the bulk of the N-containing material could be intact or transformed into other N-containing species, e.g., hydroxynitride, under electrochemical conditions. This interpretation is supported by the broad Raman peaks at 930 and 1250 cm−1 in Fig. 3d that may be assigned to vibrations related to Hf-N species36,37. There is also a broad shoulder in the N 1s region <400 eV that we assign to nitride-like nitrogen since peaks from metal nitrides occur near 397 eV. This nitride-like material could exist in the deeper parts of the bulk, assisting the electrical conductivity of the thin film.
The O 1s peaks (Fig. 3c) can be decomposed into three components: 530.1 eV from oxidic species (O2−), 531.6 eV from hydroxide species (OH−), and 533.1 eV from adsorbed or coordinated H2O. After electrochemical reaction, we observed an increase in the 531.6 eV peak intensity and assigned as corresponding to an increase in OH− concentration. The presence of Hf hydroxide was also supported by the Raman peaks at 1550–1600 cm−138. The multiple peaks in this region may be due to different local bonding environments. The atomic ratio of Hf:N determined by XPS was 4:1. It has been reported for HfOx that 25% doping with N strongly decreased (0.89 eV) the bandgap, while 50% doping with N transformed the material to a metallic oxynitride35. Thus we propose that one of the critical roles of N incorporation is to increase the electrical conductivity of the material, which is very important for Hf-based electrocatalysts because pristine Hf oxide is highly insulating. The broad peaks in the Raman spectra indicate that this film of HfNxOy does not have long-range order. Thus the combination of XPS and Raman analysis indicates that the N2 plasma treatment of Hf oxide incorporates N into Hf oxide (possibly oxyhydroxide) to form a material with an overall, near surface composition of roughly Hf1N0.25O2(OH)0.85, as determined from XPS (subject to the well-known limitations of assuming a uniform composition throughout the probed region and thus yielding only an average composition preferentially weighted by the surface layers).
Chemical and physical durability in strong acidic media
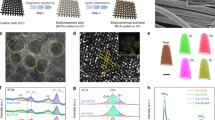
Physical and chemical durability is highly important for electrocatalysts during synthesis, storage, and after regeneration using high anodic potentials. We tested the electrochemical stability of these HfNxOy thin film electrodes in acid by CV cycling in large potential ranges (tested at both −300 to 1500 mV and −200 to 1600 mV vs RHE). These testing conditions are in stark contrast to the mild testing conditions commonly reported for non-precious metal HER catalysts such as WC, MoS2, and CoP, that unlike HfOx are unable to survive high anodic potentials in strongly acidic media. The reproducibility of the CV data observed even after 1000 scans (−300 to 1500 mV, Supplementary Figures 8 and 9) indicates the high stability of these HfNxOy electrodes in strong acid media. These results are further supported by XPS survey spectra taken before and after electrochemical testing for a new sample (250 CV cycles, −200 to 1600 mV), as shown in Supplementary Figures 2 and 7. The structural integrity of one of these HfNxOy films was analyzed by SEM and atomic force microscopic (AFM) measurements, as shown in Fig. 4. The surface morphology was similar to that before electrochemical testing, showing features with similar sizes and shapes as the Au substrate particles. Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopic (EDX) mapping, as shown in Fig. 4b, enabled measurements of the distribution of Hf, O, and N in the films that showed that these elemental distributions were correlated. An SEM image obtained at a 45˚ tilt, as shown in the right inset of Fig. 4a, enables us to estimate the height of the Au particles to be 50–100 nm, which is consistent with the heights measured by AFM topography, as shown in Fig. 4c. The surface roughness factor (film surface area normalized to geometric area) based on the image in Fig. 4c (top left) was 1.5, which is slightly less than the electrochemical surface roughness factor of 2.25 that was determined by double-layer measurements as shown in Fig. 4d. This low surface roughness establishes that the catalytic performance of the HfNxOy film mainly was not from an increase in the surface area caused by using the roughened Au substrate. In conclusion, the excellent chemical and physical stability of the HfNxOy films observed here demonstrates a promising lead for developing stable electrocatalysts that can operate in strong acidic conditions.
Surface characterization of a HfNxOy film on a roughened Au surface by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM). a SEM image after electrochemical measurements (250 cyclic voltammetry scans, −200 to 1600 mV) in H2 purged 0.1 M HClO4. Inset: 45°-tilted SEM image of the surface revealing surface morphology; height of the structures marked by red lines are 120 nm. Scale bars: 500 nm. b SEM image and corresponding energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) images for hafnium, oxygen, and nitrogen; scale bars: 300 nm. c AFM mapping after electrochemical measurements showing (top left, scale bar 1 μm) a topography image and (top right, scale bar 200 nm) a phase image of the red square area and (lower left) line scan. An inset provides a table for the root mean square (RMS) roughness. d Double-layer charging currents of a HfNxOy film measured at 400–500 mV (vs reversible hydrogen electrode) plotted as a function of scan rate in 0.1 M HClO4. The capacitance of the HfNxOy film was 90 μF cm−2, which was 2.25 times larger than that obtained when using a smooth Au foil. See Supplementary Note 3 for more details on double-layer capacitance measurements
Discussion
In this study, we report on our measurements using a novel N-containing Hf oxide catalyst that demonstrates excellent performance for the HER and, to the best of our knowledge, an unprecedented high activity for the HOR using non-PGM catalysts under acidic conditions. We propose that a significant influence of N incorporation into Hf oxide, to promote the activity of the material, may arise from the increase in electrical conductivity of the film. Although pristine Hf oxide is well known to be highly stable in strong acids, it is an extremely insulating material and thus not useful as an electrocatalyst. N2 plasma treatment is an effective approach to induce N incorporation into hafnium oxide thin films. This plasma may also create new sites or defects due to interaction with plasma species. Based on Raman spectroscopy and surface characterization by XPS, we propose that the thin film after electrochemical measurements was an N-containing oxyhydroxide.
Lack of a highly active, stable, earth-abundant electrocatalyst for carrying out HER and HOR in strongly acidic conditions is a major technical challenge for developing economical PEM-based electrolyzers and fuel cells, and the discovery of this excellent performance by a catalyst formed by N-incorporation into Hf oxide provides a new strategy for replacing Pt metal as an electrocatalyst for HER and HOR in strong acidic media. The natural abundance of Hf is significantly higher than any of the active HER/HOR precious metals (Pt, Pd, Rh, Ru, and Ir), but the currently feasibly minable amount of Hf may not be sufficient for widespread practical use. Results reported herein have broad implications for using nitrogen incorporation (e.g., N2 plasma treatment) to activate other non-conductive compounds and films to form electrocatalysts. Specifically, similar research effort should be extended to Zr-based materials since Zr belongs to the same group as Hf but is much more abundant. In addition, little is known currently about the origin of the HER/HOR activity or the active sites of these HfNxOy thin films. Further work should explore possible support effects from the Au substrate and determine the optimal concentration of N modification for the best catalytic performance.
Methods
Synthesis of N-modified HfOx thin films
The Hf thin film was deposited on a 4 × 20 mm2 Au foil (Aldrich, 99.999%) using the VCR IBS/TM200S ion beam sputter at the PRISM Imaging and Analysis Center (IAC) at Princeton University. The sample stage was oriented perpendicular to the Hf target (ESPI, 99.9%) and rotated to obtain even Hf coverage on the Au substrates. The Ar pressure was set at 2 × 10−5 torr during deposition and the thickness of Hf was monitored by quartz crystal microbalance. After 1 h of deposition, the Au substrate was covered by a 20-nm Hf film. Upon opening the chamber, metallic Hf quickly oxidized forming Hf oxide from exposure to air. The Hf sample was then treated by a 500-torr N2 plasma for 1 h. The N2 plasma was generated in a home-made DBD cell, powered by a 20-kHz, 20-kV AC power supply. The DBD plasma set-up and discharge conditions are shown in Supplementary Figure 1. After plasma treatment, the composition, oxidation states, and morphology of the samples were analyzed by a range of surface characterization techniques, including HRXPS, Raman, and SEM.
Electrochemical measurement
A standard three-electrode electrochemical cell was used with a graphite counter electrode and a Ag/AgCl/Sat. KCl reference electrode (Pine Research Instrument, RREF0024). We used graphite as the counter electrode to avoid possible Pt contamination that can occur when using a Pt counter electrode. During HER/HOR polarization testing, the sample was scanned from −100 to 1300 mV vs RHE at 5 mV s−1 scan rate. This potential range was chosen to cover both HER and HOR and to assess the material stability at high anodic potentials. After electrochemical measurements in the potential range −200 to 1600 mV for 250 cycles, the samples were rinsed with pure water and the remaining water was quickly removed using a stream of nitrogen. The surface morphology, composition, and chemical states of the tested surfaces were analyzed by HRXPS, Raman, SEM, EDX, and AFM. Polarization curves are plotted with the x axis scaled to the RHE. The zero potential was determined by the onset of the HER/HOR scan using a Pt electrode and H2-purged 0.1 M HClO4. This allows for correction of the potential drift of the Ag/AgCl reference electrode and the pH shift of the solution between different measurements. The activity was normalized to the geometrical surface area of the electrode surfaces. The electrochemical surface area was also evaluated by double-layer analysis. A fresh sample of HfNxOy was also prepared to test for stability by scanning from −300 to 1500 mV for 1000 cycles.
High-resolution XPS
HRXPS analysis of the HfOx samples was conducted using a ThermoFisher K-Alpha X-ray Photoelectron Spectrometer at the PRISM IAC at Princeton University. This system is equipped with a monochromatic X-ray source and a focusing lens allowing for analysis areas from 30 to 400 µm in 5-µm steps. In this study, we selected a 400 µm X-ray spot for all XPS measurements. Survey spectra was taken at 200 eV pass energy and the high-resolution spectra for the O 1s, Hf 4f, and N 1s regions were recorded at 20 eV pass energy. The XPS system has been calibrated by recording a clean Au sample with the Fermi edge BE at 0 eV and Au 4f7/2 BE at 84.0 eV. The C 1s peaks of adventitious carbon present on the samples were used to calibrate the BEs of the XPS peaks for different samples. The C 1s peak position in these measurements was at 284.7 ± 0.1 eV BE. In addition, the Au signals from the substrate were also aligned together, with the Au 4f7/2 peak at 84.0 eV BE. Film surface and chemical compositions were determined using the CasaXPS (Casa Software Ltd.) fitting software.
High-resolution SEM (HR-SEM) and EDX
HR-SEM, performed on a Verios 460 Extreme High Resolution SEM (XHR-SEM) at the PRISM IAC, was utilized to characterize all the thin film samples, including smooth Au, rough Au, HfOx, and N-modified HfOx. An Oxford EDX spectrometer, installed inside the SEM chamber, was utilized for element mapping and analysis. The SEM images were obtained under a beam with 3–5 kV and 50 pA. We compared the surface morphologies of different electrodes by SEM (Supplementary Figure 10a–j). These surfaces included a smooth Au sample, a roughened Au sample, 20 nm HfOx film coated on smooth Au foils (modified or unmodified with N), and 20 nm HfOx film on coated on roughened Au foils (modified or unmodified with N) before and after electrochemical measurements.
Atomic force microscopy
A Bruker NanoMan AFM at the PRISM IAC was utilized for topographical imaging of the N-modified HfOx samples after the HER/HOR measurements in tapping mode. The surface roughness was determined by AFM mapping using a 100-μm2 area.
Raman spectroscopy
The Raman spectra of N-modified HfOx at room temperature were measured using a Horiba LabRAM Aramis micro-Raman system, which consisted of a double monochromator combined with an optical microscope. The objective lens possessed 50 magnification. For excitation of the Raman spectra, a 532-nm line of an argon-ion laser was used at a power level of 0.6 mW. The Raman spectroscopy was used to probe the local bonding structure of the catalysts and to examine the influence of electrochemical testing on catalyst structure. Since the N-modified HfOx thin film was supported on a roughened Au substrate, SERS spectra were obtained.
Data availability
The data that support the plots within this paper and other findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Tseng, P., Lee, J. & Friley, P. A hydrogen economy: opportunities and challenges. Energy 30, 2703–2720 (2005).
Ursua, A., Gandia, L. M. & Sanchis, P. Hydrogen production from water electrolysis: current status and future trends. Proc. IEEE 100, 410–426 (2012).
Greeley, J. et al. Alloys of platinum and early transition metals as oxygen reduction electrocatalysts. Nat. Chem. 1, 552–556 (2009).
Huang, S.-Y., Ganesan, P. & Popov, B. N. Electrocatalytic activity and stability of titania-supported platinum–palladium electrocatalysts for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell. ACS Catal. 2, 825–831 (2012).
Ioroi, T., Kitazawa, N., Yasuda, K., Yamamoto, Y. & Takenaka, H. Iridium oxide/platinum electrocatalysts for unitized regenerative polymer electrolyte fuel cells. J. Electrochem. Soc. 147, 2018–2022 (2000).
Safizadeh, F., Ghali, E. & Houlachi, G. Electrocatalysis developments for hydrogen evolution reaction in alkaline solutions–a review. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 40, 256–274 (2015).
Chen, Z., Higgins, D., Yu, A., Zhang, L. & Zhang, J. A review on non-precious metal electrocatalysts for PEM fuel cells. Energy Env. Sci. 4, 3167–3192 (2011).
Cai, P., Huang, J., Chen, J. & Wen, Z. Oxygen‐containing amorphous cobalt sulfide porous nanocubes as high‐activity electrocatalysts for the oxygen evolution reaction in an alkaline/neutral medium. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 4858–4861 (2017).
Merle, G., Wessling, M. & Nijmeijer, K. Anion exchange membranes for alkaline fuel cells: a review. J. Membr. Sci. 377, 1–35 (2011).
Badwal, S., Giddey, S. & Ciacchi, F. Hydrogen and oxygen generation with polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM)-based electrolytic technology. Ionics 12, 7–14 (2006).
Briguglio, N. & Antonucci, V. (eds) Overview of PEM Electrolysis for Hydrogen Production (CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 2016).
Wang, T. et al. Precious metal-free approach to hydrogen electrocatalysis for energy conversion: from mechanism understanding to catalyst design. Nano Energy 42, 68–89 (2017).
Feng, J. X. et al. Efficient hydrogen evolution electrocatalysis using cobalt nanotubes decorated with titanium dioxide nanodots. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 56, 2960–2964 (2017).
Feng, J.-X., Tong, S.-Y., Tong, Y.-X. & Li, G.-R. Pt-like hydrogen evolution electrocatalysis on PANI/CoP hybrid nanowires by weakening the shackles of hydrogen ions on the surfaces of catalysts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 140, 5118–5126 (2018).
Chen, W.-F., Muckerman, J. T. & Fujita, E. Recent developments in transition metal carbides and nitrides as hydrogen evolution electrocatalysts. Chem. Commun. 49, 8896–8909 (2013).
Kitchin, J. R., Nørskov, J. K., Barteau, M. A. & Chen, J. G. Trends in the chemical properties of early transition metal carbide surfaces: a density functional study. Catal. Today 105, 66–73 (2005).
Kibsgaard, J., Chen, Z., Reinecke, B. N. & Jaramillo, T. F. Engineering the surface structure of MoS2 to preferentially expose active edge sites for electrocatalysis. Nat. Mater. 11, 963–969 (2012).
Gao, M.-R., Xu, Y.-F., Jiang, J. & Yu, S.-H. Nanostructured metal chalcogenides: synthesis, modification, and applications in energy conversion and storage devices. Chem. Soc. Rev. 42, 2986–3017 (2013).
Voiry, D. et al. The role of electronic coupling between substrate and 2D MoS2 nanosheets in electrocatalytic production of hydrogen. Nat. Mater. 15, 1003–1009 (2016).
Xie, J. et al. Defect‐rich MoS2 ultrathin nanosheets with additional active edge sites for enhanced electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Adv. Mater. 25, 5807–5813 (2013).
Shi, Y. & Zhang, B. Recent advances in transition metal phosphide nanomaterials: synthesis and applications in hydrogen evolution reaction. Chem. Soc. Rev. 45, 1529–1541 (2016).
Popczun, E. J. et al. Nanostructured nickel phosphide as an electrocatalyst for the hydrogen evolution reaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 135, 9267–9270 (2013).
Tian, J., Liu, Q., Asiri, A. M. & Sun, X. Self-supported nanoporous cobalt phosphide nanowire arrays: an efficient 3D hydrogen-evolving cathode over the wide range of pH 0–14. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 136, 7587–7590 (2014).
Popczun, E. J., Read, C. G., Roske, C. W., Lewis, N. S. & Schaak, R. E. Highly active electrocatalysis of the hydrogen evolution reaction by cobalt phosphide nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 53, 5274–5430 (2014).
Barnett, C. J., Burstein, G. T., Kucernak, A. R. J. & Williams, K. R. Electrocatalytic activity of some carburised nickel, tungsten and molybdenum compounds. Electrochim. Acta 42, 2381–2388 (1997).
Mittermeier, T., Madkikar, P., Wang, X., Gasteiger, H. A. & Piana, M. Probing transition-metal silicides as PGM-free catalysts for hydrogen oxidation and evolution in acidic medium. Materials 10, 661–672 (2017).
Chisaka, M., Iijima, T., Yaguchi, T. & Sakurai, Y. Carbon-supported hafnium oxynitride as cathode catalyst for polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 56, 4581–4588 (2011).
Gebauer, C. et al. Performance of titanium oxynitrides in the electrocatalytic oxygen evolution reaction. Nano Energy 29, 136–148 (2016).
Yeo, B. S., Klaus, S. L., Ross, P. N., Mathies, R. A. & Bell, A. T. Identification of hydroperoxy species as reaction intermediates in the electrochemical evolution of oxygen on gold. ChemPhysChem 11, 1854–1857 (2010).
Sheng, W. et al. Correlating hydrogen oxidation and evolution activity on platinum at different pH with measured hydrogen binding energy. Nat. Commun. 6, 5848–5854 (2015).
Kita, H., Ye, S. & Gao, Y. Mass transfer effect in hydrogen evolution reaction on Pt single-crystal electrodes in acid solution. J. Electroanal. Chem. 334, 351–357 (1992).
Sheng, W., Gasteiger, H. A. & Shao-Horn, Y. Hydrogen oxidation and evolution reaction kinetics on platinum: acid vs alkaline electrolytes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 157, B1529–B1536 (2010).
Strmcnik, D. et al. Improving the hydrogen oxidation reaction rate by promotion of hydroxyl adsorption. Nat. Chem. 5, 300–306 (2013).
Yang, X., Xu, W., Li, M., Koel, B. & Chen, J. A new class of electrocatalysts of supporting Pt on an Engel–Brewer alloy substrate: a demonstration for oxidation of ethylene glycol. Chem. Commun. 50, 12981–12984 (2014).
Belosludtsev, A. et al. Structure and properties of Hf-ON films prepared by high-rate reactive HiPIMS with smoothly controlled composition. Ceram. Int. 43, 5661–5667 (2017).
Kura, C. et al. Enhanced hydrogen permeability of hafnium nitride nanocrystalline membranes by interfacial hydridic conduction. J. Mater. Chem. A 6, 2730–2741 (2018).
Wang, S., Zhang, Y., Sun, Y., Xu, Y. & Yang, M. Synthesis and characteristic of SiBCN/HfN ceramics with high temperature oxidation resistance. J. Alloy Compd. 685, 828–835 (2016).
Acton, O. et al. π-σ-Phosphonic acid organic monolayer–amorphous sol–gel hafnium oxide hybrid dielectric for low-voltage organic transistors on plastic. J. Mater. Chem. 19, 7929–7936 (2009).
Acknowledgements
This material is based upon work supported by the National Science Foundation under Grant No. CHE-1465082. F.Z. acknowledges financial support by the Simons Foundation (#377485) and John Templeton Foundation (#58851). The electron microscopy and Raman characterization was partially supported by the National Science Foundation MRSEC program through the Princeton Center for Complex Materials (DMR-1420541)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
X.Y. and B.E.K. conceived the central ideas and directed the project. X.Y. and F.Z. synthesized and characterized HfNxOy samples and studied their catalytic behavior in acidic electrolyte, including the durability test. Y.-W.Y., R.S.S. and Z.C. conducted the SEM, AFM, and Raman measurements. Y.J. designed the plasma reactor. All authors contributed to the analysis of the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Journal Peer Review Information: Nature Communications thanks the anonymous reviewers for their contribution to the peer review of this work. Peer reviewer reports are available.
Publisher’s note: Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/.
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Zhao, F., Yeh, YW. et al. Nitrogen-plasma treated hafnium oxyhydroxide as an efficient acid-stable electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution and oxidation reactions. Nat Commun 10, 1543 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09162-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09162-5
This article is cited by
-
Supported PbHfCd electrocatalysts over carbon-hydroxyapatite composite fabricated by precipitation and NaBH4 reduction methods for glucose electrooxidation
Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry (2023)
-
Production of a hybrid capacitive storage device via hydrogen gas and carbon electrodes coupling
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Development of a photoelectrochemically self-improving Si/GaN photocathode for efficient and durable H2 production
Nature Materials (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.