Abstract
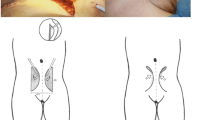
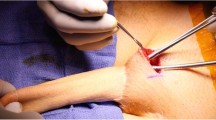
Phalloplasty is the gold-standard treatment for cis-men with penile insufficiency, which is often secondary to congenital conditions. The study-objective is to evaluate the functional outcomes and surgical complications in this population. A retrospective database comprised of cis-men undergoing a phalloplasty at a tertiary referral center from 2004 to 2019 was created. Phalloplasty was performed with various flaps. The tube-within-tube-technique was used for urethroplasty when possible. Complications <30 days postoperative were categorized according to Clavien–Dindo. Functional outcomes were assessed by bladder emptying and ability to achieve orgasm. Thirty patients were included. Nineteen of them needed urethroplasty, the remaining 11 patients had a catheterizable stoma. Within 30 days postoperative, 3 patients (10%) developed partial-flap necrosis (Clavien-Dindo III), 1 patient (3.3%) developed graft failure (Clavien-Dindo III), 2 patients (6.6%) developed infected hematomas (Clavien–Dindo III) and 1 phalloplasty (3.3%) was complicated by hematuria (Clavien-Dindo II). In the long-term, 10 patients (33%) developed fistulae, 6 (20%) requiring urethroplasty. Seven patients (23%) had urethral strictures, all needing urethroplasty or urethrotomy. Sixteen patients (84%) emptied their bladder per urethra, the three remaining necessitated conversion to perineostomy. Median (IQR) Qmax on uroflow was 15.7 (11.9–19.2)mL/s with median (IQR) voiding volume of 259 (137–307) mL and median (IQR) residual volume of 11.5 (0–20) ml on ultrasound. All patients but 1 (97%) reported ability to achieve orgasm. RFFA and ALT result in phalli with great ability to achieve orgasm but urethral complications are frequent.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lumen N, Monstrey S, Selvaggi G, Ceulemans P, De Cuypere G, Van Laecke E, et al. Phalloplasty: a valuable treatment for males with penile insufficiency. Urology. 2008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2007.08.066.
Diamond DA, Burns JP, Huang L, Rosoklija I, Retik AB. Gender assignment for newborns with 46XY cloacal exstrophy: A 6-year followup survey of pediatric urologists. J Urol. 2011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2011.03.101.
Sopko NA, Tuffaha SH, Lough D, Brandacher G, Lee WPA, Bivalacqua TJ, et al. Penile allotransplantation for complex genitourinary reconstruction. J Urol. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2016.10.134.
Tuffaha SH, Cooney DS, Sopko NA, Bivalacqua TJ, Lough DM, Cooney CM, et al. Penile transplantation: an emerging option for genitourinary reconstruction. Transpl Int. 2017. https://doi.org/10.1111/tri.12928.
Rasper AM, Terlecki RP. Ushering in the era of penile transplantation. Transl Androl Urol. 2017. https://doi.org/10.21037/tau.2016.11.02.
Monstrey S, Hoebeke P, Dhont M, Selvaggi G, Hamdi M, Van Landuyt K, et al. Radial forearm phalloplasty: a review of 81 cases. Eur J Plast Surg. 2005. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00238-005-0743-1.
Lumen N, Monstrey S, Ceulemans P, van Laecke E, Hoebeke P. Reconstructive surgery for severe penile inadequacy: phalloplasty with a free radial forearm flap or a pedicled anterolateral thigh flap. Adv Urol. 2008. https://doi.org/10.1155/2008/704343.
Monstrey S, Hoebeke P, Selvaggi G, Ceulemans P, Van Landuyt K, Blondeel P, et al. Penile reconstruction: is the radial forearm flap really the standard technique? Plast Reconstr Surg. 2009. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0b013e3181aeeb06.
Descamps MJL, Hayes PM, Hudson DA. Phalloplasty in complete aphallia: pedicled anterolateral thigh flap. J Plast Reconstr Aesthetic Surg. 2009. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjps.2007.04.014.
Sengezer M, Öztürk S, Deveci M, Odabaşi Z. Long-term follow-up of total penile reconstruction with sensate osteocutaneous free fibula flap in 18 biological male patients. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2004. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.PRS.0000131883.27191.86.
Djordjevic ML, Bumbasirevic MZ, Vukovic PM, Sansalone S, Perovic SV. Musculocutaneous latissimus dorsi free transfer flap for total phalloplasty in children. J Pediatr Urol. 2006. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpurol.2006.05.003.
The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union. Regulation (EU) 2916/679 (General Data Protection Regulation). Off J Eur Union. 2016;119:1–88.
Chen H, Tian J. Resurfacing large skin defects of the face and neck by optimizing the utilization of expanded forehead axial-pattern flap and cervicofacial local flap. J Craniofac Surg. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000005376.
Garaffa G, Christopher NA, Ralph DJ. Total phallic reconstruction in female-to-male transsexuals. Eur Urol. 2010. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2009.05.018.
Chang TS, Hwang WY. Forearm flap in one-stage reconstruction of the penis. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1984. https://doi.org/10.1097/00006534-198408000-00014.
Tuinder SMH, Beugels J, Lataster A, de Haan W, Piatkowski A, Saint-Cyr M, et al. The lateral thigh perforator flap for autologous breast reconstruction: a prospective analysis of 138 flaps. In: Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000004072.
Schober JM, Meyer-Bahlburg HFL, Dolezal C. Self-ratings of genital anatomy, sexual sensitivity and function in men using the “Self-Assessment of Genital Anatomy and Sexual Function, Male” questionnaire. BJU Int. 2009. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2008.08166.x.
De Cuypere G, T’Sjoen G, Beerten R, Selvaggi G, De Sutter P, Hoebeke P, et al. Sexual and physical health after sex reassignment surgery. Arch Sex Behav. 2005;34:679–90.
Wierckx K, Van Caeneghem E, Elaut E, Dedecker D, Van de Peer F, Toye K, et al. Quality of life and sexual health after sex reassignment surgery in transsexual men. J Sex Med. 2011;8:3379–88.
Remington AC, Morrison SD, Massie JP, Crowe CS, Shakir A, Xilson SC, et al. Outcomes after phalloplasty: do transgender patients and multiple urethral procedures carry a higher rate of complication? Plast Reconstr Surg. 2018. https://doi.org/10.1097/PRS.0000000000004061.
Franco I, Shei-Dei Yang S, Chang SJ, Nussenblatt B, Franco JA. A quantitative approach to the interpretation of uroflowmetry in children. Neurourol Urodyn. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1002/nau.22813.
Jun MS, Santucci RA. Urethral stricture after phalloplasty. Transl Androl Urol. 2019. https://doi.org/10.21037/tau.2019.05.08.
Lumen N, Monstrey S, Goessaert AS, Oosterlinck W, Hoebeke P. Urethroplasty for strictures after phallic reconstruction: A single-institution experience. Eur Urol. 2011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2010.11.015.
D’Ancona C, Haylen B, Oelke M, Abranches-Monteiro L, Arnold E, Goldman H, et al. The International Continence Society (ICS) report on the terminology for adult male lower urinary tract and pelvic floor symptoms and dysfunction. Neurourol Urodyn. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1002/nau.23897.
Tam CA, Elliott SP, Voelzke BB, Myers JB, Vanni AJ, Smith TG 3rd, et al. The International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) is an inadequate tool to screen for urethral stricture recurrence after anterior urethroplasty. Urology. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2016.04.006.
Bronselaer G, Callens N, De Sutter P, De Cuyepere G, T’Sjoen G, Cools M, et al. Self-assessment of genital anatomy and sexual function within a Belgian, Dutch-speaking female population: a validation study. J Sex Med. 2013. https://doi.org/10.1111/jsm.12326.
Acknowledgements
The Ghent University Hospital’s Department of Urology is accredited by the European Reference Network (ERN) in the eUrogen sub-section (urologic rare diseases), specifically for the EEC complex, making the Department a European referral center.
Funding
This research was made possible thanks to the Research Fund for Pediatric Urology ‘Gianni Eggermont fonds ter bevordering van de kinderurologie’.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sinatti, C., Wolff, D., Buncamper, M. et al. Phalloplasty in cis-men with penile insufficiency: evaluation of outcomes and surgical complications. Int J Impot Res 33, 178–183 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-020-00385-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41443-020-00385-5
This article is cited by
-
Functional and surgical outcomes after phalloplasty in cis men
World Journal of Urology (2022)
-
Out of the dark, into the light: sexuality and fertility in pediatric urological conditions
International Journal of Impotence Research (2021)