Abstract
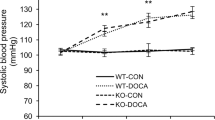
Hypertension-induced renal injury is characterized by robust inflammation and tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Jumonji domain containing-3 (JMJD3) is closely linked with inflammatory response and fibrogenesis. Here we examined the effect of myeloid JMJD3 ablation on kidney inflammation and fibrosis in deoxycorticosterone acetate (DOCA)/salt hypertension. Our results showed that JMJD3 is notably induced in the kidneys with hypertensive injury. DOCA/salt stress causes an elevation in blood pressure that was no difference between myeloid specific JMJD3-deficient mice and wild-type control mice. Compared with wild-type control mice, myeloid JMJD3 ablation ameliorated kidney function and injury of mice in response to DOCA/salt challenge. Myeloid JMJD3 ablation attenuated collagen deposition, extracellular matrix proteins expression, and fibroblasts activation in injured kidneys following DOCA/salt treatment. Furthermore, myeloid JMJD3 ablation blunts inflammatory response in injured kidneys after DOCA/salt stress. Finally, myeloid JMJD3 ablation precluded myeloid myofibroblasts activation and protected against macrophages to myofibroblasts transition in injured kidneys. These beneficial effects were accompanied by reduced expression of interferon regulator factor 4. In summary, JMJD3 ablation in myeloid cells reduces kidney inflammation and fibrosis in DOCA salt-induced hypertension. Inhibition of myeloid JMJD3 may be a novel potential therapeutic target for hypertensive nephropathy.

Myeloid JMJD3 deficiency reduces inflammatory response, myeloid fibroblasts activation, macrophages to myofibroblasts transition, and delays kidney fibrosis progression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Udani S, Lazich I, Bakris GL. Epidemiology of hypertensive kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011;7:11–21.
Elijovich F, Laffer CL, Sahinoz M, Pitzer A, Ferguson JF, Kirabo A. The gut microbiome, inflammation, and salt-sensitive hypertension. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2020;22:79.
Slagman MC, Kwakernaak AJ, Yazdani S, Laverman GD, van den Born J, Titze J, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor C levels are modulated by dietary salt intake in proteinuric chronic kidney disease patients and in healthy subjects. Nephrol Dial Transpl. 2012;27:978–82.
Lu X, Crowley SD. Inflammation in salt-sensitive hypertension and renal damage. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2018;20:103.
Liu ML, Song HX, Tian XX, Liu YX, Liu D, Hou ZW, et al. Recombinant cellular repressor of E1A-stimulated genes protects against renal fibrosis in dahl salt-sensitive rats. Am J Nephrol. 2020;51:401–10.
Krishnan SM, Ling YH, Huuskes BM, Ferens DM, Saini N, Chan CT, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of the NLRP3 inflammasome reduces blood pressure, renal damage, and dysfunction in salt-sensitive hypertension. Cardiovasc Res. 2019;115:776–87.
Zhang X, Liu L, Yuan X, Wei Y, Wei X. JMJD3 in the regulation of human diseases. Protein Cell. 2019;10:864–82.
Huang M, Wang Q, Long F, Di Y, Wang J, Zhun Zhu Y, et al. Jmjd3 regulates inflammasome activation and aggravates DSS-induced colitis in mice. FASEB j. 2020;34:4107–19.
Davis FM, Tsoi LC, Melvin WJ, denDekker A, Wasikowski R, Joshi AD, et al. Inhibition of macrophage histone demethylase JMJD3 protects against abdominal aortic aneurysms. J Exp Med. 2021;218:e20201839.
Long F, Wang Q, Yang D, Zhu M, Wang J, Zhu Y, et al. Targeting JMJD3 histone demethylase mediates cardiac fibrosis and cardiac function following myocardial infarction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;528:671–77.
Lai J, Ge M, Shen S, Yang L, Jin T, Cao D, et al. Activation of NFKB-JMJD3 signaling promotes bladder fibrosis via boosting bladder smooth muscle cell proliferation and collagen accumulation. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019;1865:2403–10.
Bergmann C, Brandt A, Merlevede B, Hallenberger L, Dees C, Wohlfahrt T, et al. The histone demethylase Jumonji domain-containing protein 3 (JMJD3) regulates fibroblast activation in systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77:150–58.
Liang H, Liu B, Gao Y, Nie J, Feng S, Yu W, et al. Jmjd3/ IRF4 axis aggravates myeloid fibroblast activation and M2 macrophage to myofibroblast transition in renal fibrosis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:978262.
Wilde E, Aubdool AA, Thakore P, Baldissera L Jr, Alawi KM, Keeble J, et al. Tail-cuff technique and its influence on central blood pressure in the mouse. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017;6:e005204.
Liang H, Zhang Z, Yan J, Wang Y, Hu Z, Mitch WE, et al. The IL-4 receptor α has a critical role in bone marrow-derived fibroblast activation and renal fibrosis. Kidney Int. 2017;92:1433–43.
Chen M, Wen X, Gao Y, Liu B, Zhong C, Nie J, et al. IRF-4 deficiency reduces inflammation and kidney fibrosis after folic acid-induced acute kidney injury. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;100:108142.
Liang H, Ma Z, Peng H, He L, Hu Z, Wang Y. CXCL16 deficiency attenuates renal injury and fibrosis in salt-sensitive hypertension. Sci Rep. 2016;6:28715.
Sun YB, Qu X, Caruana G, Li J. The origin of renal fibroblasts/myofibroblasts and the signals that trigger fibrosis. Differentiation. 2016;92:102–07.
Yan J, Zhang Z, Jia L, Wang Y. Role of bone marrow-derived fibroblasts in renal fibrosis. Front Physiol. 2016;7:61.
Wei J, Xu Z, Yan X. The role of the macrophage-to-myofibroblast transition in renal fibrosis. Front Immunol. 2022;13:934377.
Wang YY, Jiang H, Pan J, Huang XR, Wang YC, Huang HF, et al. Macrophage-to-myofibroblast transition contributes to interstitial fibrosis in chronic renal allograft injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;28:2053–67.
Satoh T, Takeuchi O, Vandenbon A, Yasuda K, Tanaka Y, Kumagai Y, et al. The Jmjd3-Irf4 axis regulates M2 macrophage polarization and host responses against helminth infection. Nat Immunol. 2010;11:936–44.
Ming-Chin Lee K, Achuthan AA, De Souza DP, Lupancu TJ, Binger KJ, Lee MKS, et al. Type I interferon antagonism of the JMJD3-IRF4 pathway modulates macrophage activation and polarization. Cell Rep. 2022;39:110719.
Tang J, Liu N, Zhuang S. Role of epidermal growth factor receptor in acute and chronic kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2013;83:804–10.
Liu Y. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of renal fibrosis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2011;7:684–96.
Djudjaj S, Boor P. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of kidney fibrosis. Mol Asp Med. 2019;65:16–36.
He C, Larson-Casey JL, Gu L, Ryan AJ, Murthy S, Carter AB. Cu,Zn-superoxide dismutase-mediated redox regulation of jumonji domain containing 3 modulates macrophage polarization and pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016;55:58–71.
Oh J, Matkovich SJ, Riek AE, Bindom SM, Shao JS, Head RD, et al. Macrophage secretion of miR-106b-5p causes renin-dependent hypertension. Nat Commun. 2020;11:4798.
Krämer S, Binder E, Loof T, Wang-Rosenke Y, Martini S, Khadzhynov D, et al. The lymphocyte migration inhibitor FTY720 attenuates experimental hypertensive nephropathy. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2009;297:F218–27.
Tang PM, Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Lan HY. Macrophages: versatile players in renal inflammation and fibrosis. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2019;15:144–58.
Sato Y, Yanagita M. Resident fibroblasts in the kidney: a major driver of fibrosis and inflammation. Inflamm Regen. 2017;37:17.
Srivastava SP, Hedayat AF, Kanasaki K, Goodwin JE. microRNA crosstalk influences epithelial-to-mesenchymal, endothelial-to-mesenchymal, and macrophage-to-mesenchymal transitions in the kidney. Front Pharm. 2019;10:904.
Wang JJ, Wang X, Xian YE, Chen ZQ, Sun YP, Fu YW, et al. The JMJD3 histone demethylase inhibitor GSK-J1 ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation in a mastitis model. J Biol Chem. 2022;298:102017.
Alexaki VI, Fodelianaki G, Neuwirth A, Mund C, Kourgiantaki A, Ieronimaki E, et al. DHEA inhibits acute microglia-mediated inflammation through activation of the TrkA-Akt1/2-CREB-Jmjd3 pathway. Mol Psychiatry. 2018;23:1410–20.
Wu W, Qin M, Jia W, Huang Z, Li Z, Yang D, et al. Cystathionine-γ-lyase ameliorates the histone demethylase JMJD3-mediated autoimmune response in rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Mol Immunol. 2019;16:694–705.
Wynn TA. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of fibrosis. J Pathol. 2008;214:199–210.
Humphreys BD. Mechanisms of renal fibrosis. Annu Rev Physiol. 2018;80:309–26.
Haimei Z, Ying G, Wenqiang Y, Jiping L, Chaoqun Z, Xi S, et al. Pharmacological inhibition of STING/ TBK1 signaling attenuates myeloid fibroblast activation and macrophage to myofibroblast transition in renal fibrosis. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:940716.
Nikolic-Paterson DJ, Wang S, Lan HY. Macrophages promote renal fibrosis through direct and indirect mechanisms. Kidney Int Suppl. 2014;4:34–38.
Xuan D, Han Q, Tu Q, Zhang L, Yu L, Murry D, et al. Epigenetic modulation in periodontitis: interaction of adiponectin and JMJD3-IRF4 axis in macrophages. J Cell Physiol. 2016;231:1090–6.
Achuthan A, Cook AD, Lee MC, Saleh R, Khiew HW, Chang MW, et al. Granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor induces CCL17 production via IRF4 to mediate inflammation. J Clin Investig. 2016;126:3453–66.
Yu C, Xiong C, Tang J, Hou X, Liu N, Bayliss G, et al. Histone demethylaseJMJD3 protects against renal fibrosis by suppressing TGFb and notch signaling and preserving PTEN expression. Theranostics. 2021;11:2706–21.
Neele AE, Prange KH, Hoeksema MA, van der Velden S, Lucas T, Dimmeler S, et al. Macrophage Kdm6b controls the pro-fibrotic transcriptome signature of foam cells. Epigenomics. 2017;9:383–91.
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. Chaoqun Zhong for her assistance with the schematic diagram.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81871539), Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (No. 2021A1515011481) and Special Fund of Foshan Summit Plan (2019C001, 2019D004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YG and HL conceived and designed the research. YG, BL, and WY performed the experiments. YG, BL, JS, and JN analyzed the data. BL, JS, SW, and ZC interpreted the results of experiments. WY and HL drafted the manuscript. HL edited and revised the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, Y., Yu, W., Song, J. et al. JMJD3 ablation in myeloid cells confers renoprotection in mice with DOCA/salt-induced hypertension. Hypertens Res 46, 1934–1948 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-023-01312-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-023-01312-z