Abstract
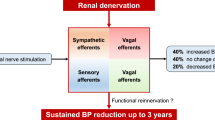
Renal nerves have critical roles in regulating blood pressure and fluid volume, and their dysfunction is closely related with cardiovascular diseases. Renal nerves are composed of sympathetic efferent and sensory afferent nerves. Activation of the efferent renal sympathetic nerves induces renin secretion, sodium absorption, and increased renal vascular resistance, which lead to increased blood pressure and fluid retention. Afferent renal sensory nerves, which are densely innervated in the renal pelvic wall, project to the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus in the brain to modulate sympathetic outflow to the periphery, including the heart, kidneys, and arterioles. The effects of renal denervation on the cardiovascular system are mediated by both efferent denervation and afferent denervation. The first half of this review focuses on basic research using animal models of hypertension and heart failure, and addresses the therapeutic effects of renal denervation for hypertension and heart failure, including underlying mechanisms. The second half of this review focuses on clinical research related to catheter-based renal denervation in patients with hypertension. Randomized sham-controlled trials using second-generation devices, endovascular radiofrequency-based devices and ultrasound-based devices are reviewed and their results are assessed. This review summarizes the basic and clinical evidence of renal denervation to date, and discusses future prospects and potential developments in renal denervation therapy for cardiovascular diseases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bohm M, Kario K, Kandzari DE, Mahfoud F, Weber MA, Schmieder RE, et al. Efficacy of catheter-based renal denervation in the absence of antihypertensive medications (SPYRAL HTN-OFF MED Pivotal): a multicentre, randomised, sham-controlled trial. Lancet. 2020;395:1444–51.
Kandzari DE, Bohm M, Mahfoud F, Townsend RR, Weber MA, Pocock S, et al. Effect of renal denervation on blood pressure in the presence of antihypertensive drugs: 6-month efficacy and safety results from the SPYRAL HTN-ON MED proof-of-concept randomised trial. Lancet. 2018;391:2346–55.
Azizi M, Schmieder RE, Mahfoud F, Weber MA, Daemen J, Davies J, et al. Endovascular ultrasound renal denervation to treat hypertension (RADIANCE-HTN SOLO): a multicentre, international, single-blind, randomised, sham-controlled trial. Lancet. 2018;391:2335–45.
Azizi M, Sanghvi K, Saxena M, Gosse P, Reilly JP, Levy T, et al. Ultrasound renal denervation for hypertension resistant to a triple medication pill (RADIANCE-HTN TRIO): a randomised, multicentre, single-blind, sham-controlled trial. Lancet. 2021;397:2476–86.
Foss JD, Wainford RD, Engeland WC, Fink GD, Osborn JW. A novel method of selective ablation of afferent renal nerves by periaxonal application of capsaicin. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2015;308:R112–22.
Banek CT, Knuepfer MM, Foss JD, Fiege JK, Asirvatham-Jeyaraj N, Van Helden D, et al. Resting afferent renal nerve discharge and renal inflammation: elucidating the role of afferent and efferent renal nerves in deoxycorticosterone acetate salt hypertension. Hypertension. 2016;68:1415–23.
Ong J, Kinsman BJ, Sved AF, Rush BM, Tan RJ, Carattino MD, et al. Renal sensory nerves increase sympathetic nerve activity and blood pressure in 2-kidney 1-clip hypertensive mice. J Neurophysiol. 2019;122:358–67.
Milanez MIO, Veiga AC, Martins BS, Pontes RB, Bergamaschi CT, Campos RR, et al. Renal sensory activity regulates the gamma-aminobutyric acidergic inputs to the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus in Goldblatt hypertension. Front Physiol. 2020;11:601237.
Solano-Flores LP, Rosas-Arellano MP, Ciriello J. Fos induction in central structures after afferent renal nerve stimulation. Brain Res. 1997;753:102–19.
Osborn JW, Foss JD. Renal nerves and long-term control of arterial pressure. Compr Physiol. 2017;7:263–320.
Zheng H, Patel KP. Integration of renal sensory afferents at the level of the paraventricular nucleus dictating sympathetic outflow. Auton Neurosci. 2017;204:57–64.
Shen XZ, Li Y, Li L, Shah KH, Bernstein KE, Lyden P, et al. Microglia participate in neurogenic regulation of hypertension. Hypertension. 2015;66:309–16.
Shi P, Diez-Freire C, Jun JY, Qi Y, Katovich MJ, Li Q, et al. Brain microglial cytokines in neurogenic hypertension. Hypertension. 2010;56:297–303.
Li Y, Wei B, Liu X, Shen XZ, Shi P. Microglia, autonomic nervous system, immunity and hypertension: is there a link? Pharmacol Res. 2020;155:104451.
Veiga AC, Milanez MIO, Ferreira GR, Lopes NR, Santos CP, De Angelis K, et al. Selective afferent renal denervation mitigates renal and splanchnic sympathetic nerve overactivity and renal function in chronic kidney disease-induced hypertension. J Hypertens. 2020;38:765–73.
Foss JD, Fiege J, Shimizu Y, Collister JP, Mayerhofer T, Wood L, et al. Role of afferent and efferent renal nerves in the development of AngII-salt hypertension in rats. Physiol Rep. 2018;6:e13602.
Ott C, Mahfoud F, Mancia G, Narkiewicz K, Ruilope LM, Fahy M, et al. Renal denervation in patients with versus without chronic kidney disease: results from the global SYMPLICITY Registry with follow-up data of 3 years. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfab154. [Epub ahead of print]
Johns EJ, Kopp UC, DiBona GF. Neural control of renal function. Compr Physiol. 2011;1:731–67.
Katsurada K, Ogoyama Y, Imai Y, Patel KP, Kario K. Renal denervation based on experimental rationale. Hypertens Res. 2021;44:1385–94.
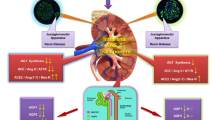
Zheng H, Katsurada K, Liu X, Knuepfer MM, Patel KP. Specific afferent renal denervation prevents reduction in neuronal nitric oxide synthase within the paraventricular nucleus in rats with chronic heart failure. Hypertension. 2018;72:667–75.
Katsurada K, Nandi SS, Zheng H, Liu X, Sharma NM, Patel KP. GLP-1 mediated diuresis and natriuresis are blunted in heart failure and restored by selective afferent renal denervation. Cardiovascular Diabetol. 2020;19:57.
DiBona GF, Herman PJ, Sawin LL. Neural control of renal function in edema-forming states. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 1988;254:R1017–24.
Zheng H, Li YF, Zucker IH, Patel KP. Exercise training improves renal excretory responses to acute volume expansion in rats with heart failure. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2006;291:F1148–56.
Katsurada K, Nandi SS, Sharma NM, Zheng H, Liu X, Patel KP. Does glucagon-like peptide-1 induce diuresis and natriuresis by modulating afferent renal nerve activity? Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2019;317:F1010–21.
Zheng H, Liu X, Katsurada K, Patel KP. Renal denervation improves sodium excretion in rats with chronic heart failure: effects on expression of renal ENaC and AQP2. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019;317:H958–68.
Zheng H, Liu X, Sharma NM, Li Y, Pliquett RU, Patel KP. Urinary proteolytic activation of renal epithelial Na+ channels in chronic heart failure. Hypertension. 2016;67:197–205.
Kwon TH, Nielsen J, Knepper MA, Frokiaer J, Nielsen S. Angiotensin II AT1 receptor blockade decreases vasopressin-induced water reabsorption and AQP2 levels in NaCl-restricted rats. Am J Physiol Ren. Physiol 2005;288:F673–84.
Katsurada K, Nandi SS, Sharma NM, Patel KP. Enhanced expression and function of renal SGLT2 (Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2) in heart failure: role of renal nerves. Circ Heart Fail. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.121.008365.
Sharp TE 3rd, Polhemus DJ, Li Z, Spaletra P, Jenkins JS, Reilly JP, et al. Renal denervation prevents heart failure progression via inhibition of the renin-angiotensin system. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018;72:2609–21.
Liu X, Patel KP, Zheng H. Role of renal sympathetic nerves in GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1) receptor agonist exendin-4-mediated diuresis and natriuresis in diet-induced obese rats. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021;10:e022542.
Bhatt DL, Kandzari DE, O’Neill WW, D’Agostino R, Flack JM, Katzen BT, et al. A controlled trial of renal denervation for resistant hypertension. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:1393–401.
Kandzari DE, Mahfoud F, Bhatt DL, Bohm M, Weber MA, Townsend RR, et al. Confounding factors in renal denervation trials: revisiting old and identifying new challenges in trial design of device therapies for hypertension. Hypertension. 2020;76:1410–7.
Kario K, Kim BK, Aoki J, Wong AY, Lee YH, Wongpraparut N, et al. Renal denervation in Asia: consensus statement of the Asia renal denervation consortium. Hypertension. 2020;75:590–602.
Weber MA, Mahfoud F, Schmieder RE, Kandzari DE, Tsioufis KP, Townsend RR, et al. Renal denervation for treating hypertension: current scientific and clinical evidence. JACC Cardiovasc Interv. 2019;12:1095–105.
Townsend RR, Walton A, Hettrick DA, Hickey GL, Weil J, Sharp ASP, et al. Review and meta-analysis of renal artery damage following percutaneous renal denervation with radiofrequency renal artery ablation. EuroIntervention. 2020;16:89–96.
Mahfoud F, Bohm M, Schmieder R, Narkiewicz K, Ewen S, Ruilope L, et al. Effects of renal denervation on kidney function and long-term outcomes: 3-year follow-up from the Global SYMPLICITY Registry. Eur Heart J. 2019;40:3474–82.
Mahfoud F, Mancia G, Schmieder R, Narkiewicz K, Ruilope L, Schlaich M, et al. Renal denervation in high-risk patients with hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2020;75:2879–88.
Kario K, Yokoi Y, Okamura K, Fujihara M, Ogoyama Y, Yamamoto E, et al. Catheter-based ultrasound renal denervation in patients with resistant hypertension: the randomized, controlled REQUIRE trial. Hypertens Res. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-021-00754-7. [Epub ahead of print]
Ogoyama Y, Tada K, Abe M, Nanto S, Shibata H, Mukoyama M, et al. Effects of renal denervation on blood pressures in patients with hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized sham-controlled trials. Hypertens Res. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-021-00761-8. [Epub ahead of print]
Bohm M, Mahfoud F, Townsend RR, Kandzari DE, Pocock S, Ukena C, et al. Ambulatory heart rate reduction after catheter-based renal denervation in hypertensive patients not receiving anti-hypertensive medications: data from SPYRAL HTN-OFF MED, a randomized, sham-controlled, proof-of-concept trial. Eur Heart J. 2019;40:743–51.
Mahfoud F, Townsend RR, Kandzari DE, Kario K, Schmieder RE, Tsioufis K, et al. Changes in plasma renin activity after renal artery sympathetic denervation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2021;77:2909–19.
Kario K, Kagitani H, Hayashi S, Hanamura S, Ozawa K, Kanegae H. A Japan nationwide web-based survey of patient preference for renal denervation for hypertension treatment. Hypertens Res. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-021-00760-9. [Epub ahead of print]
de Jong MR, Adiyaman A, Gal P, Smit JJ, Delnoy PP, Heeg JE, et al. Renal nerve stimulation-induced blood pressure changes predict ambulatory blood pressure response after renal denervation. Hypertension. 2016;68:707–14.
Qian PC, Barry MA, Lu J, Pouliopoulos J, Mina A, Bandodkar S, et al. Transvascular pacing of aorticorenal ganglia provides a testable procedural endpoint for renal artery denervation. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 2019;12:1109–20.
Tsioufis KP, Feyz L, Dimitriadis K, Konstantinidis D, Tousoulis D, Voskuil M, et al. Safety and performance of diagnostic electrical mapping of renal nerves in hypertensive patients. EuroIntervention. 2018;14:e1334–42.
Singh RR, McArdle ZM, Iudica M, Easton LK, Booth LC, May CN, et al. Sustained decrease in blood pressure and reduced anatomical and functional reinnervation of renal nerves in hypertensive sheep 30 months after catheter-based renal denervation. Hypertension. 2019;73:718–27.
Mulder J, Hokfelt T, Knuepfer MM, Kopp UC. Renal sensory and sympathetic nerves reinnervate the kidney in a similar time-dependent fashion after renal denervation in rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2013;304:R675–82.
Kario K, Yamamoto E, Tomita H, Okura T, Saito S, Ueno T, et al. Sufficient and persistent blood pressure reduction in the final long-term results from SYMPLICITY HTN-Japan- safety and efficacy of renal denervation at 3 years. Circ J. 2019;83:622–9.
Kario K, Ito S, Itoh H, Rakugi H, Okuda Y, Yamakawa S. Effect of esaxerenone on nocturnal blood pressure and natriuretic peptide in different dipping phenotypes. Hypertens Res. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-021-00756-5. [Epub ahead of print]
Kario K, Williams B. Nocturnal hypertension and heart failure: mechanisms, evidence, and new treatments. Hypertension. 2021;78:564–77.
Kario K, Hoshide S, Mizuno H, Kabutoya T, Nishizawa M, Yoshida T, et al. Nighttime blood pressure phenotype and cardiovascular prognosis: practitioner-based nationwide JAMP study. Circulation. 2020;142:1810–20.
Narita K, Hoshide S, Kario K. Association of treatment-resistant hypertension defined by home blood pressure monitoring with cardiovascular outcome. Hypertens Res. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-021-00757-4. [Epub ahead of print]
Kario K, Sakima A, Ohya Y. STEP to estimate cardiovascular events by home blood pressure in the era of digital hypertension. Hypertens Res. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-021-00764-5. [Epub ahead of print]
Kario K, Hettrick DA, Prejbisz A, Januszewicz A. Obstructive sleep apnea-induced neurogenic nocturnal hypertension: a potential role of renal denervation? Hypertension. 2021;77:1047–60.
Kario K, Weber MA, Mahfoud F, Kandzari DE, Schmieder RE, Kirtane AJ, et al. Changes in 24-hour patterns of blood pressure in hypertension following renal denervation therapy. Hypertension. 2019;74:244–9.
Steinberg JS, Shabanov V, Ponomarev D, Losik D, Ivanickiy E, Kropotkin E, et al. Effect of renal denervation and catheter ablation vs catheter ablation alone on atrial fibrillation recurrence among patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation and hypertension: the ERADICATE-AF randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2020;323:248–55.
Younis A, Steinberg JS. Renal denervation for patients with atrial fibrillation. Curr Cardiol Rep. 2021;23:126.
Kario K, Hoshide S, Narita K, Okawara Y, Kanegae H. Investigators’ network. Cardiovascular prognosis in drug-resistant hypertension stratified by 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure: the JAMP study. Hypertension. 2021;78:1781–90.
Kario K, Wang TD. Perspectives of renal denervation from hypertension to heart failure in Asia. Hypertens Res. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-021-00751-w. [Epub ahead of print]
Sharp TE 3rd, Lefer DJ. Renal denervation to treat heart failure. Annu Rev Physiol. 2021;83:39–58.
Lian Z, Yu SR, Song JX, Lee CY, Li SF, Cui YX, et al. Efficacy and safety of catheter-based renal denervation for heart failure with reduced ejection fraction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Auton Res. 2020;30:521–30.
Kresoja KP, Rommel KP, Fengler K, von Roeder M, Besler C, Lucke C, et al. Renal sympathetic denervation in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction. Circ Heart Fail. 2021;14:e007421.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
K. Kario received speaker fees and works as a consultant to JIMRO Co., Ltd., Medtronic Co. Inc. and Terumo Co. Inc. SN received a consultant fee from JIMRO Co., Ltd. KS was supported by grants from Daiichi Sankyo and Nippon Boehringer Ingelheim. The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katsurada, K., Shinohara, K., Aoki, J. et al. Renal denervation: basic and clinical evidence. Hypertens Res 45, 198–209 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-021-00827-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-021-00827-7
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Beneficial effects of renal denervation on heart, kidneys, and adipose tissue beyond antihypertensive effect: is it independent of systemic sympathetic activity?
Hypertension Research (2024)
-
Brain sodium exposure: inducing stroke onset independent of blood pressure elevation in stroke-prone spontaneously hypertensive rats
Hypertension Research (2024)
-
The effects of renal denervation on blood pressure, cardiac hypertrophy, and sympathetic activity during the established phase of hypertension in spontaneously hypertensive rats
Hypertension Research (2024)
-
Renal denervation in patients with chronic kidney disease: an approach using CO2 angiography
Hypertension Research (2024)
-
Does renal denervation require cardiovascular outcome-driven data?
Hypertension Research (2024)