Abstract
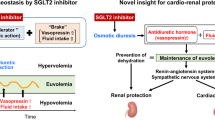
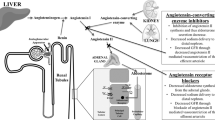
Hypertension in chronic kidney disease (CKD) is the most commonly observed comorbidity and is a risk factor for end-stage renal disease (ESRD) as well as cardiovascular disease (CVD) and mortality. Therefore, suitable blood pressure (BP) control in CKD patients is very important in preventing both CVD and ESRD. We herein describe the recommendations of target BP and the pharmacological drug options from the evidence-based clinical practice guidelines for CKD in 2018 by the Japanese Society of Nephrology (JSN CKD 2018) and recent advances in the management of hypertension in CKD, including sodium-glucose cotransporter (SGLT) 2 inhibitors, mineralocorticoid receptor blockers, and renal denervation. In particular, SGLT2 inhibitors are a new class of “antihypertensive drugs” that have a homeostatic mechanism that regulates body fluid volume in addition to diuretic action, which may be closely associated with their cardiorenal protective properties.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Muntner P, Anderson A, Charleston J, Chen Z, Ford V, Makos G, et al. Hypertension awareness, treatment, and control in adults with CKD: results from the Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) Study. Am J Kidney Dis. 2010;55:441–51.
Toto RD. Treatment of hypertension in chronic kidney disease. Semin Nephrol. 2005;25:435–9.
Townsend RR, Taler SJ. Management of hypertension in chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2015;11:555–63.
Japanese Society of Nephrology. Essential points from Evidence-based Clinical Practice Guidelines for Chronic Kidney Disease 2018. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2019;23:1–15.
Cushman WC, Evans GW, Byington RP, Goff DC Jr, Grimm RH Jr, Cutler JA, et al. Effects of intensive blood-pressure control in type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 2010;362:1575–85.
Bangalore S, Kumar S, Lobach I, Messerli FH. Blood pressure targets in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus/impaired fasting glucose: observations from traditional and Bayesian random-effects meta-analyses of randomized trials. Circulation. 2011;123:2799–810.
Wright JT Jr, Williamson JD, Whelton PK, Snyder JK, Sink KM, Rocco MV, et al. A randomized trial of intensive versus standard blood-pressure control. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:2103–16.
Hirayama A, Konta T, Kamei K, Suzuki K, Ichikawa K, Fujimoto S, et al. Blood pressure, proteinuria, and renal function decline: associations in a large community-based population. Am J Hypertens. 2015;28:1150–6.
Imai E, Ito S, Haneda M, Harada A, Kobayashi F, Yamasaki T, et al. Effects of blood pressure on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes and overt nephropathy: a post hoc analysis (ORIENT-blood pressure). Nephrol Dial Transpl. 2016;31:447–54.
Xie X, Liu Y, Perkovic V, Li X, Ninomiya T, Hou W, et al. Renin-angiotensin system inhibitors and kidney and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with CKD: a Bayesian network meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Am J Kidney Dis. 2016;67:728–41.
Brenner BM, Cooper ME, de Zeeuw D, Keane WF, Mitch WE, Parving HH, et al. Effects of losartan on renal and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:861–9.
Nistor I, De Sutter J, Drechsler C, Goldsmith D, Soler MJ, Tomson C, et al. Effect of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockade in adults with diabetes mellitus and advanced chronic kidney disease not on dialysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nephrol Dial Transpl. 2018;33:12–22.
Hsu TW, Liu JS, Hung SC, Kuo KL, Chang YK, Chen YC, et al. Renoprotective effect of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockade in patients with predialysis advanced chronic kidney disease, hypertension, and anemia. JAMA Intern Med. 2014;174:347–54.
Rocco MV, Sink KM, Lovato LC, Wolfgram DF, Wiegmann TB, Wall BM, et al. Effects of intensive blood pressure treatment on acute kidney injury events in the systolic blood pressure intervention trial (SPRINT). Am J Kidney Dis. 2018;71:352–61.
Obi Y, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Shintani A, Kovesdy CP, Hamano T. Estimated glomerular filtration rate and the risk-benefit profile of intensive blood pressure control amongst nondiabetic patients: a post hoc analysis of a randomized clinical trial. J Intern Med. 2018;283:314–27.
Vallon V. Glucose transporters in the kidney in health and disease. Pflugers Arch. 2020. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-020-02361-w. Online ahead of print.
Vallon V, Thomson SC. The tubular hypothesis of nephron filtration and diabetic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2020;16:317–36.
Kario K, Ferdinand KC, O’Keefe JH. Control of 24-hour blood pressure with SGLT2 inhibitors to prevent cardiovascular disease. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 2020;S0033-0620:30074-8.
Kario K, Okada K, Kato M, Nishizawa M, Yoshida T, Asano T, et al. 24-hour blood pressure-lowering effect of an SGLT-2 inhibitor in patients with diabetes and uncontrolled nocturnal hypertension: results from the randomized, placebo-controlled SACRA study. Circulation. 2019;139:2089–97.
Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, Bluhmki E, Hantel S, et al. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:2117–28.
Wanner C, Inzucchi SE, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, von Eynatten M, Mattheus M, et al. Empagliflozin and progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:323–34.
Neal B, Perkovic V, Mahaffey KW, de Zeeuw D, Fulcher G, Erondu N, et al. Canagliflozin and cardiovascular and renal events in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2017;377:644–57.
Wiviott SD, Raz I, Bonaca MP, Mosenzon O, Kato ET, Cahn A, et al. Dapagliflozin and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:347–57.
Perkovic V, Jardine MJ, Neal B, Bompoint S, Heerspink HJL, Charytan DM, et al. Canagliflozin and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes and nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:2295–306.
McMurray JJV, Solomon SD, Inzucchi SE, Kober L, Kosiborod MN, Martinez FA, et al. Dapagliflozin in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction. N Engl J Med. 2019;381:1995–2008.
Zelniker TA, Wiviott SD, Raz I, Im K, Goodrich EL, Bonaca MP, et al. SGLT2 inhibitors for primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Lancet. 2019;393:31–9.
Cherney DZ, Kanbay M, Lovshin JA. Renal physiology of glucose handling and therapeutic implications. Nephrol Dial Transpl. 2020;35:i3–12.
Wilcox CS. Antihypertensive and renal mechanisms of SGLT2 (sodium-glucose linked transporter 2) inhibitors. Hypertension. 2020;75:894–901.
Lambers, Heerspink HJ, de Zeeuw D, Wie L, Leslie B, List J. Dapagliflozin a glucose-regulating drug with diuretic properties in subjects with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2013;15:853–62.
Kawasoe S, Maruguchi Y, Kajiya S, Uenomachi H, Miyata M, Kawasoe M, et al. Mechanism of the blood pressure-lowering effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in obese patients with type 2 diabetes. BMC Pharm Toxicol. 2017;18:23.
Faucon AL, Flamant M, Metzger M, Boffa JJ, Haymann JP, Houillier P, et al. Extracellular fluid volume is associated with incident end-stage kidney disease and mortality in patients with chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2019;96:1020–9.
Tai R, Ohashi Y, Mizuiri S, Aikawa A, Sakai K. Association between ratio of measured extracellular volume to expected body fluid volume and renal outcomes in patients with chronic kidney disease: a retrospective single-center cohort study. BMC Nephrol. 2014;15:189.
Hung SC, Lai YS, Kuo KL, Tarng DC. Volume overload and adverse outcomes in chronic kidney disease: clinical observational and animal studies. J Am Heart Assoc. 2015;4:e001918.
Kanai Y, Lee WS, You G, Brown D, Hediger MA. The human kidney low affinity Na+/glucose cotransporter SGLT2. Delineation of the major renal reabsorptive mechanism for D-glucose. J Clin Invest. 1994;93:397–404.
Vallon V, Platt KA, Cunard R, Schroth J, Whaley J, Thomson SC, et al. SGLT2 mediates glucose reabsorption in the early proximal tubule. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011;22:104–12.
Ansary TM, Nakano D, Nishiyama A. Diuretic effects of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and their influence on the renin-angiotensin system. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:629.
Masuda T, Ohara K, Murakami T, Imai T, Nakagawa S, Okada M, et al. Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibition with dapagliflozin ameliorates extracellular volume expansion in diabetic kidney disease patients. POJ Diabetes Obes. 2017;1:1–8.
Ohara K, Masuda T, Murakami T, Imai T, Yoshizawa H, Nakagawa S, et al. Effects of the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor dapagliflozin on fluid distribution: a comparison study with furosemide and tolvaptan. Nephrology (Carlton). 2019;24:904–11.
Masuda T, Muto S, Fukuda K, Watanabe M, Ohara K, Koepsell H, et al. Osmotic diuresis by SGLT2 inhibition stimulates vasopressin-induced water reabsorption to maintain body fluid volume. Physiol Rep. 2020;8:e14360.
Masuda T, Watanabe Y, Fukuda K, Watanabe M, Onishi A, Ohara K, et al. Unmasking a sustained negative effect of SGLT2 inhibition on body fluid volume in the rat. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol. 2018;315:F653–64.
Ohara K, Masuda T, Morinari M, Okada M, Miki A, Nakagawa S, et al. The extracellular volume status predicts body fluid response to SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin in diabetic kidney disease. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2020;12:37.
Schork A, Saynisch J, Vosseler A, Jaghutriz BA, Heyne N, Peter A, et al. Effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on body composition, fluid status and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in type 2 diabetes: a prospective study using bioimpedance spectroscopy. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2019;18:46.
Yasui A, Lee G, Hirase T, Kaneko T, Kaspers S, von Eynatten M, et al. Empagliflozin induces transient diuresis without changing long-term overall fluid balance in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Ther. 2018;9:863–71.
Gilbert RE, Thorpe KE. Acute kidney injury with sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors: a meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2019;21:1996–2000.
Donnan JR, Grandy CA, Chibrikov E, Marra CA, Aubrey-Bassler K, Johnston K, et al. Comparative safety of the sodium glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 2019;9:e022577.
Braam B, Lai CF, Abinader J, Bello AK. Extracellular fluid volume expansion, arterial stiffness and uncontrolled hypertension in patients with chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfz020. Online ahead of print.
Shibata S, Ishizawa K, Uchida S. Mineralocorticoid receptor as a therapeutic target in chronic kidney disease and hypertension. Hypertens Res. 2017;40:221–5.
Azushima K, Morisawa N, Tamura K, Nishiyama A. Recent research advances in renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system receptors. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2020;22:22.
Nishiyama A. Pathophysiological mechanisms of mineralocorticoid receptor-dependent cardiovascular and chronic kidney disease. Hypertens Res. 2019;42:293–300.
Pitt B, Zannad F, Remme WJ, Cody R, Castaigne A, Perez A, et al. The effect of spironolactone on morbidity and mortality in patients with severe heart failure. Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study Investigators. N Engl J Med. 1999;341:709–17.
Pitt B, Remme W, Zannad F, Neaton J, Martinez F, Roniker B, et al. Eplerenone, a selective aldosterone blocker, in patients with left ventricular dysfunction after myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med. 2003;348:1309–21.
Ando K, Ohtsu H, Uchida S, Kaname S, Arakawa Y, Fujita T. Anti-albuminuric effect of the aldosterone blocker eplerenone in non-diabetic hypertensive patients with albuminuria: a double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014;2:944–53.
Shibata S, Nagase M, Yoshida S, Kawarazaki W, Kurihara H, Tanaka H, et al. Modification of mineralocorticoid receptor function by Rac1 GTPase: implication in proteinuric kidney disease. Nat Med. 2008;14:1370–6.
Shibata S, Mu S, Kawarazaki H, Muraoka K, Ishizawa K, Yoshida S, et al. Rac1 GTPase in rodent kidneys is essential for salt-sensitive hypertension via a mineralocorticoid receptor-dependent pathway. J Clin Invest. 2011;121:3233–43.
Yamada M, Takei M, Suzuki E, Takakusa H, Kotsuma M, Washio T, et al. Pharmacokinetics, distribution, and disposition of esaxerenone, a novel, highly potent and selective non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist, in rats and monkeys. Xenobiotica. 2017;47:1090–103.
Arai K, Homma T, Morikawa Y, Ubukata N, Tsuruoka H, Aoki K, et al. Pharmacological profile of CS-3150, a novel, highly potent and selective non-steroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharm. 2015;761:226–34.
Ito S, Shikata K, Nangaku M, Okuda Y, Sawanobori T. Efficacy and safety of esaxerenone (CS-3150) for the treatment of type 2 diabetes with microalbuminuria: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase II trial. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2019;14:1161–72.
Ito S, Itoh H, Rakugi H, Okuda Y, Yoshimura M, Yamakawa S. Double-blind randomized phase 3 study comparing esaxerenone (CS-3150) and eplerenone in patients with essential hypertension (ESAX-HTN study). Hypertension. 2020;75:51–58.
Kario K, Kim BK, Aoki J, Wong AY, Lee YH, Wongpraparut N, et al. Renal denervation in Asia: consensus statement of the Asia renal denervation consortium. Hypertension. 2020;75:590–602.
Bohm M, Kario K, Kandzari DE, Mahfoud F, Weber MA, Schmieder RE, et al. Efficacy of catheter-based renal denervation in the absence of antihypertensive medications (SPYRAL HTN-OFF MED Pivotal): a multicentre, randomised, sham-controlled trial. Lancet. 2020;395:1444–51.
Kario K, Yamamoto E, Tomita H, Okura T, Saito S, Ueno T, et al. Sufficient and persistent blood pressure reduction in the final long-term results from SYMPLICITY HTN-Japan- safety and efficacy of renal denervation at 3 years. Circ J. 2019;83:622–9.
Ott C, Mahfoud F, Schmid A, Toennes SW, Ewen S, Ditting T, et al. Renal denervation preserves renal function in patients with chronic kidney disease and resistant hypertension. J Hypertens. 2015;33:1261–6.
Kiuchi MG, Schlaich MP, Chen S, Villacorta H, Ho JK, Carnagarin R, et al. Relevance of targeting the distal renal artery and branches with radiofrequency renal denervation approaches—a secondary analysis from a hypertensive CKD patient cohort. J Clin Med. 2019;8:581.
Mahfoud F, Bohm M, Schmieder R, Narkiewicz K, Ewen S, Ruilope L, et al. Effects of renal denervation on kidney function and long-term outcomes: 3-year follow-up from the Global SYMPLICITY Registry. Eur Heart J. 2019;40:3474–82.
Duni A, Dounousi E, Pavlakou P, Eleftheriadis T, Liakopoulos V. Hypertension in chronic kidney disease: novel insights. Curr Hypertens Rev. 2020;16:45–54.
Acknowledgements
We thank Keiko Fukuda and Minami Watanabe for their valuable technical support.
Funding
This study was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists 15K21321 (to TM), Jichi Medical University Young Investigator Awards (to TM), and a Grant-in-Aid for Research on Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease, Practical Research Project for Renal Diseases from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED to DN).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masuda, T., Nagata, D. Recent advances in the management of secondary hypertension: chronic kidney disease. Hypertens Res 43, 869–875 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-020-0491-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-020-0491-4
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Fluid homeostasis induced by sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors: novel insight for better cardio-renal outcomes in chronic kidney disease
Hypertension Research (2023)
-
Urinary free cortisol excretion is associated with lumbar bone density in patients with adrenal Cushing’s syndrome
Hypertension Research (2022)
-
Update on Hypertension Research in 2021
Hypertension Research (2022)