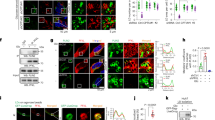
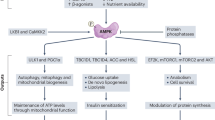
Abstract
Adipogenesis significantly contributes to healthy adipose tissue expansion in obesity. Increasing adipocyte number or function to alleviate adipose tissue overload could serve as a therapeutic strategy for both lipodystrophy and obesity-related metabolic syndrome. Inorganic pyrophosphatase (PPA1) is an enzyme that catalyzes the hydrolysis of pyrophosphate (PPi) and is involved in many biochemical reactions, but its function in adipose tissue has not been studied previously. In this study, we demonstrated that adipose-specific PPA1 knockout (PPA1AKO) mice showed lipodystrophy and spontaneously developed hepatic steatosis and severe insulin resistance under normal chow diet feeding. PPA1 deficiency suppressed the differentiation of primary adipocyte precursors and 3T3-L1 cells. Notably, PPA1 overexpression can restore inhibited adipogenesis in preadipocytes isolated from db/db mice and type 2 diabetes patients. Mechanistic studies have revealed that PPA1 acts as a positive regulator of early adipocyte differentiation by promoting CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteinβ and δ (C/EBPβ and δ) protein stability. Moreover, the function of PPA1 in adipogenesis is independent of its PPi catalytic activity. Collectively, our in vivo and in vitro findings demonstrated that PPA1 is a novel critical upstream regulator of adipogenesis, controlling adipose tissue development and whole-body metabolic homeostasis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw RNA-sequencing data reported in this paper have been deposited in the Figshare database (https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.25679760). All datasets analyzed in the study are available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request. Raw western blots are available in the Supplemental file.
References
Hirsch J, Han PW. Cellularity of rat adipose tissue: effects of growth, starvation, and obesity. J Lipid Res. 1969;10:77–82.
Kloting N, Bluher M. Adipocyte dysfunction, inflammation and metabolic syndrome. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2014;15:277–87.
Sun K, Tordjman J, Clement K, Scherer PE. Fibrosis and adipose tissue dysfunction. Cell Metab. 2013;18:470–7.
Hardy OT, Perugini RA, Nicoloro SM, Gallagher-Dorval K, Puri V, Straubhaar J, et al. Body mass index-independent inflammation in omental adipose tissue associated with insulin resistance in morbid obesity. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2011;7:60–7.
Kloting N, Fasshauer M, Dietrich A, Kovacs P, Schon MR, Kern M, et al. Insulin-sensitive obesity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010;299:E506–15.
Vishvanath L, Gupta RK. Contribution of adipogenesis to healthy adipose tissue expansion in obesity. J Clin Invest. 2019;129:4022–31.
Ghaben AL, Scherer PE. Adipogenesis and metabolic health. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2019;20:242–58.
Quinn K, Chauhan S, Purcell SM. Lipodystrophies. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024.
Mann JP, Savage DB. What lipodystrophies teach us about the metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest. 2019;129:4009–21.
Zammouri J, Vatier C, Capel E, Auclair M, Storey-London C, Bismuth E, et al. Molecular and Cellular Bases of Lipodystrophy Syndromes. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021;12:803189.
Mota de Sa P, Richard AJ, Hang H, Stephens JM. Transcriptional regulation of adipogenesis. Compr Physiol. 2017;7:635–74.
White U, Fitch MD, Beyl RA, Hellerstein MK, Ravussin E. Adipose depot-specific effects of 16 weeks of pioglitazone on in vivo adipogenesis in women with obesity: a randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia. 2021;64:159–67.
McLaughlin TM, Liu T, Yee G, Abbasi F, Lamendola C, Reaven GM, et al. Pioglitazone increases the proportion of small cells in human abdominal subcutaneous adipose tissue. Obes (Silver Spring). 2010;18:926–31.
Sarjeant K, Stephens JM. Adipogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2012;4:a008417.
Lee JE, Ge K. Transcriptional and epigenetic regulation of PPARgamma expression during adipogenesis. Cell Biosci. 2014;4:29.
Cao Z, Umek RM, McKnight SL. Regulated expression of three C/EBP isoforms during adipose conversion of 3T3-L1 cells. Genes Dev. 1991;5:1538–52.
Yeh WC, Cao Z, Classon M, McKnight SL. Cascade regulation of terminal adipocyte differentiation by three members of the C/EBP family of leucine zipper proteins. Genes Dev. 1995;9:168–81.
Tanaka T, Yoshida N, Kishimoto T, Akira S. Defective adipocyte differentiation in mice lacking the C/EBPbeta and/or C/EBPdelta gene. EMBO J. 1997;16:7432–43.
Guo L, Huang JX, Liu Y, Li X, Zhou SR, Qian SW, et al. Transactivation of Atg4b by C/EBPbeta promotes autophagy to facilitate adipogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 2013;33:3180–90.
Tang QQ, Otto TC, Lane MD. Mitotic clonal expansion: a synchronous process required for adipogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:44–9.
Tezuka Y, Okada M, Tada Y, Yamauchi J, Nishigori H, Sanbe A. Regulation of neurite growth by inorganic pyrophosphatase 1 via JNK dephosphorylation. PLoS One. 2013;8:e61649.
Polewski MD, Johnson KA, Foster M, Millan JL, Terkeltaub R. Inorganic pyrophosphatase induces type I collagen in osteoblasts. Bone. 2010;46:81–90.
Luo D, Liu D, Shi W, Jiang H, Liu W, Zhang X, et al. PPA1 promotes NSCLC progression via a JNK- and TP53-dependent manner. Oncogenesis. 2019;8:53.
Mishra DR, Chaudhary S, Krishna BM, Mishra SK. Identification of critical elements for regulation of inorganic pyrophosphatase (PPA1) in MCF7 Breast Cancer Cells. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0124864.
Tomonaga T, Matsushita K, Yamaguchi S, Oh-Ishi M, Kodera Y, Maeda T, et al. Identification of altered protein expression and post-translational modifications in primary colorectal cancer by using agarose two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10:2007–14.
Chen G, Gharib TG, Huang CC, Thomas DG, Shedden KA, Taylor JM, et al. Proteomic analysis of lung adenocarcinoma: identification of a highly expressed set of proteins in tumors. Clin Cancer Res. 2002;8:2298–305.
Yin Y, Wu Y, Zhang X, Zhu Y, Sun Y, Yu J, et al. PPA1 regulates systemic insulin sensitivity by maintaining adipocyte mitochondria function as a novel PPARgamma target gene. Diabetes. 2021;70:1278–91.
Stern JH, Rutkowski JM, Scherer PE. Adiponectin, leptin, and fatty acids in the maintenance of metabolic homeostasis through adipose tissue crosstalk. Cell Metab. 2016;23:770–84.
Cavalcanti-de-Albuquerque JP, Bober J, Zimmer MR, Dietrich MO. Regulation of substrate utilization and adiposity by Agrp neurons. Nat Commun. 2019;10:311.
Chhabra KH, Adams JM, Fagel B, Lam DD, Qi N, Rubinstein M, et al. Hypothalamic POMC deficiency improves glucose tolerance despite insulin resistance by increasing glycosuria. Diabetes. 2016;65:660–72.
Lahti R, Kolakowski LF Jr., Heinonen J, Vihinen M, Pohjanoksa K, Cooperman BS. Conservation of functional residues between yeast and E. coli inorganic pyrophosphatases. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990;1038:338–45.
Vihinen M, Lundin M, Baltscheffsky H. Computer modeling of two inorganic pyrophosphatases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992;186:122–8.
Gustafson B, Hammarstedt A, Hedjazifar S, Smith U. Restricted adipogenesis in hypertrophic obesity: the role of WISP2, WNT, and BMP4. Diabetes. 2013;62:2997–3004.
Tchoukalova YD, Votruba SB, Tchkonia T, Giorgadze N, Kirkland JL, Jensen MD. Regional differences in cellular mechanisms of adipose tissue gain with overfeeding. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:18226–31.
Cristancho AG, Lazar MA. Forming functional fat: a growing understanding of adipocyte differentiation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011;12:722–34.
Farmer SR. Transcriptional control of adipocyte formation. Cell Metab. 2006;4:263–73.
Hattori T, Ohoka N, Inoue Y, Hayashi H, Onozaki K. C/EBP family transcription factors are degraded by the proteasome but stabilized by forming dimer. Oncogene. 2003;22:1273–80.
Li H, Xiao N, Li Z, Wang Q. Expression of Inorganic Pyrophosphatase (PPA1) Correlates with Poor Prognosis of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2017;241:165–73.
Niu H, Zhou W, Xu Y, Yin Z, Shen W, Ye Z, et al. Silencing PPA1 inhibits human epithelial ovarian cancer metastasis by suppressing the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 2017;8:76266–78.
Siersbaek R, Nielsen R, Mandrup S. Transcriptional networks and chromatin remodeling controlling adipogenesis. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2012;23:56–64.
Lim GE, Albrecht T, Piske M, Sarai K, Lee JTC, Ramshaw HS, et al. 14-3-3zeta coordinates adipogenesis of visceral fat. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7671.
Tang QQ, Otto TC, Lane MD. CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta is required for mitotic clonal expansion during adipogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2003;100:850–5.
Audano M, Pedretti S, Caruso D, Crestani M, De Fabiani E, Mitro N. Regulatory mechanisms of the early phase of white adipocyte differentiation: an overview. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022;79:139.
Tang QQ, Lane MD. Adipogenesis: from stem cell to adipocyte. Annu Rev Biochem. 2012;81:715–36.
Guo L, Li X, Tang QQ. Transcriptional regulation of adipocyte differentiation: a central role for CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP) beta. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:755–61.
Liu Y, Zhang YD, Guo L, Huang HY, Zhu H, Huang JX, et al. Protein inhibitor of activated STAT 1 (PIAS1) is identified as the SUMO E3 ligase of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta (C/EBPbeta) during adipogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 2013;33:4606–17.
Chung SS, Ahn BY, Kim M, Choi HH, Park HS, Kang S, et al. Control of adipogenesis by the SUMO-specific protease SENP2. Mol Cell Biol. 2010;30:2135–46.
Ramji DP, Foka P. CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins: structure, function and regulation. Biochem J. 2002;365:561–75.
Lechner S, Mitterberger MC, Mattesich M, Zwerschke W. Role of C/EBPbeta-LAP and C/EBPbeta-LIP in early adipogenic differentiation of human white adipose-derived progenitors and at later stages in immature adipocytes. Differentiation. 2013;85:20–31.
Wang P, Zhou Y, Mei Q, Zhao J, Huang L, Fu Q. PPA1 regulates tumor malignant potential and clinical outcome of colon adenocarcinoma through JNK pathways. Oncotarget. 2017;8:58611–24.
Tchoukalova YD, Harteneck DA, Karwoski RA, Tarara J, Jensen MD. A quick, reliable, and automated method for fat cell sizing. J Lipid Res. 2003;44:1795–801.
Bahrami-Nejad Z, Zhao ML, Tholen S, Hunerdosse D, Tkach KE, van Schie S, et al. A transcriptional circuit filters oscillating circadian hormonal inputs to regulate fat cell differentiation. Cell Metab. 2018;27:854–68.e8.
Shamsi F, Tseng YH. Protocols for generation of immortalized human brown and white preadipocyte cell lines. Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1566:77–85.
Heinonen JK, Lahti RJ. A new and convenient colorimetric determination of inorganic orthophosphate and its application to the assay of inorganic pyrophosphatase. Anal Biochem. 1981;113:313–7.
Acknowledgements
We thank all the lab members for insightful discussion during this study.
Funding
This work was supported by National Key R&D Program of China (2022YFA0806102), National Natural Science Foundation of China (82270874, 82370855, 81970709).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YY and HYL conceived the project and wrote the manuscript. YYW and YS designed and performed most experiments. YQS performed in vivo studies and analyzed the data. YH and JTW performed in vitro experiments. XH contributed to the discussion and critically reviewed and edited the manuscript. All authors revised and approved the final version of the manuscript. XH is the guarantor of this work and, as such, had full access to all the data in the study and takes responsibility for the integrity of the data and the accuracy of the data analysis.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics
All animal experiments were approved and complied with the guidelines of the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the Nanjing Medical University, China (Permit Number: IACUC-NJMU 14030178). Human specimens were supplied by the Southeast University Affiliated Zhongda Hospital and written informed consent was obtained from the patients (Permit number: 2020ZDSYLL144-P01 by the Independent Ethics Committee of Southeast University Affiliated Zhongda Hospital).
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, Y., Sun, Y., Song, Y. et al. PPA1 promotes adipogenesis by regulating the stability of C/EBPs. Cell Death Differ (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-024-01309-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-024-01309-2