Abstract
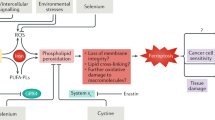
Ferroptosis, a regulated form of cell death triggered by iron-dependent lipid peroxidation, has emerged as a promising therapeutic strategy for cancer treatment, particularly in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the mechanisms underlying the regulation of ferroptosis in HCC remain to be unclear. In this study, we have identified a novel regulatory pathway of ferroptosis involving the inhibition of Apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1 (APE1), a key enzyme with dual functions in DNA repair and redox regulation. Our findings demonstrate that inhibition of APE1 leads to the accumulation of lipid peroxidation and enhances ferroptosis in HCC. At the molecular level, the inhibition of APE1 enhances ferroptosis which relies on the redox activity of APE1 through the regulation of the NRF2/SLC7A11/GPX4 axis. We have identified that both genetic and chemical inhibition of APE1 increases AKT oxidation, resulting in an impairment of AKT phosphorylation and activation, which leads to the dephosphorylation and activation of GSK3β, facilitating the subsequent ubiquitin-proteasome-dependent degradation of NRF2. Consequently, the downregulation of NRF2 suppresses SLC7A11 and GPX4 expression, triggering ferroptosis in HCC cells and providing a potential therapeutic approach for ferroptosis-based therapy in HCC. Overall, our study uncovers a novel role and mechanism of APE1 in the regulation of ferroptosis and highlights the potential of targeting APE1 as a promising therapeutic strategy for HCC and other cancers.

This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data needed to evaluate the conclusions in the paper are present in the paper. Additional data related to this paper may be requested from the corresponding author.
References
Faivre S, Rimassa L, Finn RS. Molecular therapies for HCC: Looking outside the box. J Hepatol. 2020;72:342–52.
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, et al. Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell. 2012;149:1060–72.
Jiang L, Kon N, Li T, Wang SJ, Su T, Hibshoosh H, et al. Ferroptosis as a p53-mediated activity during tumour suppression. Nature. 2015;520:57–62.
Wang W, Green M, Choi JE, Gijon M, Kennedy PD, Johnson JK, et al. CD8(+) T cells regulate tumour ferroptosis during cancer immunotherapy. Nature. 2019;569:270–4.
Lang X, Green MD, Wang W, Yu J, Choi JE, Jiang L, et al. Radiotherapy and Immunotherapy Promote Tumoral Lipid Oxidation and Ferroptosis via Synergistic Repression of SLC7A11. Cancer Discov. 2019;9:1673–85.
Kagan VE, Mao G, Qu F, Angeli JP, Doll S, Croix CS, et al. Oxidized arachidonic and adrenic PEs navigate cells to ferroptosis. Nat Chem Biol. 2017;13:81–90.
Koppula P, Zhuang L, Gan B. Cystine transporter SLC7A11/xCT in cancer: ferroptosis, nutrient dependency, and cancer therapy. Protein Cell. 2021;12:599–620.
Yang WS, SriRamaratnam R, Welsch ME, Shimada K, Skouta R, Viswanathan VS, et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell. 2014;156:317–31.
Chen J, Li X, Ge C, Min J, Wang F. The multifaceted role of ferroptosis in liver disease. Cell Death Differ. 2022;29:467–80.
Liao H, Shi J, Wen K, Lin J, Liu Q, Shi B, et al. Molecular Targets of Ferroptosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2021;8:985–96.
Chen Q, Zheng W, Guan J, Liu H, Dan Y, Zhu L, et al. SOCS2-enhanced ubiquitination of SLC7A11 promotes ferroptosis and radiosensitization in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Differ. 2023;30:137–51.
Wang Q, Bin C, Xue Q, Gao Q, Huang A, Wang K, et al. GSTZ1 sensitizes hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib-induced ferroptosis via inhibition of NRF2/GPX4 axis. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12:426.
Bhakat KK, Mantha AK, Mitra S. Transcriptional regulatory functions of mammalian AP-endonuclease (APE1/Ref-1), an essential multifunctional protein. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2009;11:621–38.
Demple B, Herman T, Chen DS. Cloning and expression of APE, the cDNA encoding the major human apurinic endonuclease: definition of a family of DNA repair enzymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1991;88:11450–4.
Li M, Wilson DM 3rd. Human apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease 1. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2014;20:678–707.
Kelley MR, Georgiadis MM, Fishel ML. APE1/Ref-1 role in redox signaling: translational applications of targeting the redox function of the DNA repair/redox protein APE1/Ref-1. Curr Mol Pharm. 2012;5:36–53.
Nishi T, Shimizu N, Hiramoto M, Sato I, Yamaguchi Y, Hasegawa M, et al. Spatial redox regulation of a critical cysteine residue of NF-kappa B in vivo. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:44548–56.
Logsdon DP, Grimard M, Luo M, Shahda S, Jiang Y, Tong Y, et al. Regulation of HIF1alpha under Hypoxia by APE1/Ref-1 Impacts CA9 Expression: Dual Targeting in Patient-Derived 3D Pancreatic Cancer Models. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016;15:2722–32.
Ando K, Hirao S, Kabe Y, Ogura Y, Sato I, Yamaguchi Y, et al. A new APE1/Ref-1-dependent pathway leading to reduction of NF-kappaB and AP-1, and activation of their DNA-binding activity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36:4327–36.
Seo YR, Kelley MR, Smith ML. Selenomethionine regulation of p53 by a ref1-dependent redox mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2002;99:14548–53.
Caston RA, Gampala S, Armstrong L, Messmann RA, Fishel ML, Kelley MR. The multifunctional APE1 DNA repair-redox signaling protein as a drug target in human disease. Drug Discov Today. 2021;26:218–28.
Lu X, Zhao H, Yuan H, Chu Y, Zhu X. High nuclear expression of APE1 correlates with unfavorable prognosis and promotes tumor growth in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Mol Histol. 2021;52:219–31.
Li E, Xia M, Du Y, Long K, Ji F, Pan F, et al. METTL3 promotes homologous recombination repair and modulates chemotherapeutic response in breast cancer by regulating the EGF/RAD51 axis. Elife. 2022;11:e75231.
Yang F, Hu Z, Guo Z. Small-Molecule Inhibitors Targeting FEN1 for Cancer Therapy. Biomolecules. 2022;12:1007.
Ji F, Zhang F, Zhang M, Long K, Xia M, Lu F, et al. Targeting the DNA damage response enhances CD70 CAR-T cell therapy for renal carcinoma by activating the cGAS-STING pathway. J Hematol Oncol. 2021;14:152.
Long K, Gu L, Li L, Zhang Z, Li E, Zhang Y, et al. Small-molecule inhibition of APE1 induces apoptosis, pyroptosis, and necroptosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2021;12:503.
Zhao H, Ding Y, Zhang L. SIRT1/APE1 promotes the viability of gastric cancer cells by inhibiting p53 to suppress ferroptosis. Open Med (Wars). 2023;18:20220620.
Yue R, Zhou M, Li X, Xu L, Lu C, Dong Z, et al. GSH/APE1 Cascade-Activated Nanoplatform for Imaging Therapy Resistance Dynamics and Enzyme-Mediated Adaptive Ferroptosis. ACS Nano. 2023;17:13792–810.
Kobayashi T, Kishigami S, Sone M, Inokuchi H, Mogi T, Ito K. Respiratory chain is required to maintain oxidized states of the DsbA-DsbB disulfide bond formation system in aerobically growing Escherichia coli cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:11857–62.
Sriramajayam K, Peng D, Lu H, Zhou S, Bhat N, McDonald OG, et al. Activation of NRF2 by APE1/REF1 is redox-dependent in Barrett’s related esophageal adenocarcinoma cells. Redox Biol. 2021;43:101970.
Tang D, Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G. Ferroptosis: molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell Res. 2021;31:107–25.
Habib E, Linher-Melville K, Lin HX, Singh G. Expression of xCT and activity of system xc(-) are regulated by NRF2 in human breast cancer cells in response to oxidative stress. Redox Biol. 2015;5:33–42.
Yuan S, Wei C, Liu G, Zhang L, Li J, Li L, et al. Sorafenib attenuates liver fibrosis by triggering hepatic stellate cell ferroptosis via HIF-1alpha/SLC7A11 pathway. Cell Prolif. 2022;55:e13158.
Feng H, Liu Y, Gan Y, Li M, Liu R, Liang Z, et al. AdipoR1 Regulates Ionizing Radiation-Induced Ferroptosis in HCC cells through Nrf2/xCT Pathway. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:8091464.
Hayes JD, Dinkova-Kostova AT. The Nrf2 regulatory network provides an interface between redox and intermediary metabolism. Trends Biochem Sci. 2014;39:199–218.
Rada P, Rojo AI, Evrard-Todeschi N, Innamorato NG, Cotte A, Jaworski T, et al. Structural and functional characterization of Nrf2 degradation by the glycogen synthase kinase 3/beta-TrCP axis. Mol Cell Biol. 2012;32:3486–99.
Sharma M, Chuang WW, Sun Z. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt stimulates androgen pathway through GSK3beta inhibition and nuclear beta-catenin accumulation. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:30935–41.
Murata H, Ihara Y, Nakamura H, Yodoi J, Sumikawa K, Kondo T. Glutaredoxin exerts an antiapoptotic effect by regulating the redox state of Akt. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:50226–33.
Yao F, Deng Y, Zhao Y, Mei Y, Zhang Y, Liu X, et al. A targetable LIFR-NF-kappaB-LCN2 axis controls liver tumorigenesis and vulnerability to ferroptosis. Nat Commun. 2021;12:7333.
Gao R, Kalathur RKR, Coto-Llerena M, Ercan C, Buechel D, Shuang S, et al. YAP/TAZ and ATF4 drive resistance to Sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma by preventing ferroptosis. EMBO Mol Med. 2021;13:e14351.
Lei G, Zhang Y, Koppula P, Liu X, Zhang J, Lin SH, et al. The role of ferroptosis in ionizing radiation-induced cell death and tumor suppression. Cell Res. 2020;30:146–62.
Viswanathan VS, Ryan MJ, Dhruv HD, Gill S, Eichhoff OM, Seashore-Ludlow B, et al. Dependency of a therapy-resistant state of cancer cells on a lipid peroxidase pathway. Nature. 2017;547:453–7.
Wu J, Minikes AM, Gao M, Bian H, Li Y, Stockwell BR, et al. Intercellular interaction dictates cancer cell ferroptosis via NF2-YAP signalling. Nature. 2019;572:402–6.
Gao M, Yi J, Zhu J, Minikes AM, Monian P, Thompson CB, et al. Role of Mitochondria in Ferroptosis. Mol Cell. 2019;73:354–63.e353.
Ma X, Dang C, Min W, Diao Y, Hui W, Wang X, et al. Downregulation of APE1 potentiates breast cancer cells to olaparib by inhibiting PARP-1 expression. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2019;176:109–17.
Bersuker K, Hendricks JM, Li Z, Magtanong L, Ford B, Tang PH, et al. The CoQ oxidoreductase FSP1 acts parallel to GPX4 to inhibit ferroptosis. Nature. 2019;575:688–92.
Doll S, Proneth B, Tyurina YY, Panzilius E, Kobayashi S, Ingold I, et al. ACSL4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular lipid composition. Nat Chem Biol. 2017;13:91–8.
Liu J, Ren Z, Yang L, Zhu L, Li Y, Bie C, et al. The NSUN5-FTH1/FTL pathway mediates ferroptosis in bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8:99.
Dodson M, Castro-Portuguez R, Zhang DD. NRF2 plays a critical role in mitigating lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 2019;23:101107.
Cuadrado A. Structural and functional characterization of Nrf2 degradation by glycogen synthase kinase 3/beta-TrCP. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015;88:147–57.
Park MS, Kim CS, Joo HK, Lee YR, Kang G, Kim SJ, et al. Cytoplasmic localization and redox cysteine residue of APE1/Ref-1 are associated with its anti-inflammatory activity in cultured endothelial cells. Mol Cells. 2013;36:439–45.
Di Maso V, Avellini C, Croce LS, Rosso N, Quadrifoglio F, Cesaratto L, et al. Subcellular localization of APE1/Ref-1 in human hepatocellular carcinoma: possible prognostic significance. Mol Med. 2007;13:89–96.
Lu GS, Li M, Xu CX, Wang D. APE1 stimulates EGFR-TKI resistance by activating Akt signaling through a redox-dependent mechanism in lung adenocarcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2018;9:1111.
Whitaker AM, Freudenthal BD. APE1: A skilled nucleic acid surgeon. DNA Repair. 2018;71:93–100.
Li M, Yang X, Lu X, Dai N, Zhang S, Cheng Y, et al. APE1 deficiency promotes cellular senescence and premature aging features. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018;46:5664–77.
Liu J, Kang R, Tang D. Signaling pathways and defense mechanisms of ferroptosis. FEBS J. 2022;289:7038–50.
Chen PH, Tseng WH, Chi JT. The Intersection of DNA Damage Response and Ferroptosis-A Rationale for Combination Therapeutics. Biology. 2020;9:187.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (32171407 and 82373183) and the Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.D., Y.Z., and X.Y. performed study concept and design; Z.H., Y.D., Z.G., L.H. and F.P. performed development of methodology and writing, review and revision of the paper; Y.D., Y.Z., X.Y., Z.H. and Z.G. provided acquisition, analysis and interpretation of data, and statistical analysis; F.P., Z.H., L.H. and Z.G. provided technical and material support. All authors read and approved the final paper.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval
This research was approved by the Ethics Committee of Nanjing Normal University. All animal experiments were performed according to procedures approved by the Laboratory Animal Care Committee at Nanjing Normal University, in accordance with the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Du, Y., Zhou, Y., Yan, X. et al. APE1 inhibition enhances ferroptotic cell death and contributes to hepatocellular carcinoma therapy. Cell Death Differ 31, 431–446 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-024-01270-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-024-01270-0