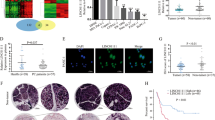
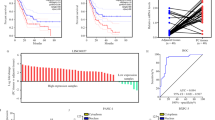
Abstract
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) represent an emerging field of tumor biology, playing essential roles in cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and metastasis. However, the overall functional and clinical significance of most lncRNAs in pancreatic cancer is not thoroughly understood. Here, we described most of the lncRNAs with aberrant expression patterns in pancreatic cancer as detected by microarray. Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction further verified that the expression of LINC00671 was decreased in pancreatic cancer cell lines and patient samples. Furthermore, lower LINC00671 expression was associated with reduced tumor differentiation, aggressiveness, and poor prognosis. Functionally, LINC00671 overexpression inhibited pancreatic cancer cell proliferation, invasion, and migration in vitro, and reduced tumor growth in vivo. LINC00671 is mainly located in the cytoplasm. RNA sequencing and bioinformatics analyses indicated that LINC00671 binds to multiple miRNAs and therefore could be involved in multiple tumor-associated pathways, such as the AMPK signaling pathway and PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Western blotting and immunohistochemistry further confirmed that LINC00671 overexpression suppressed the AKT, ERK, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition pathways. Overall, these results indicated that LINC00671 acts as a novel tumor suppressor in pancreatic cancer. Our findings may provide a new potential target for the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2019. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69:7–34.
Lai E, Puzzoni M, Ziranu P, Pretta A, Impera V, Mariani S, et al. New therapeutic targets in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 2019;81:101926.
Zhou W, Chen L, Li C, Huang R, Guo M, Ning S, et al. The multifaceted roles of long noncoding RNAs in pancreatic cancer: an update on what we know. Cancer Cell Int. 2020;20:41.
Tang Y, Cheung BB, Atmadibrata B, Marshall GM, Dinger ME, Liu PY, et al. The regulatory role of long noncoding RNAs in cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017;391:12–19.
Quinn JJ, Chang HY. Unique features of long non-coding RNA biogenesis and function. Nat Rev Genet. 2016;17:47–62.
Schmitt AM, Chang HY. Long noncoding RNAs in cancer pathways. Cancer Cell. 2016;29:452–63.
Bhan A, Soleimani M, Mandal SS. Long noncoding RNA and cancer: a new paradigm. Cancer Res. 2017;77:3965–81.
Sanchez Calle A, Kawamura Y, Yamamoto Y, Takeshita F, Ochiya T. Emerging roles of long non-coding RNA in cancer. Cancer Sci. 2018;109:2093–100.
Sun J, Zhang Z, Bao S, Yan C, Hou P, Wu N, et al. Identification of tumor immune infiltration-associated lncRNAs for improving prognosis and immunotherapy response of patients with non-small cell lung cancer. J Immunother Cancer. 2020;8:e000110.
Yang H, Liu P, Zhang J, Peng X, Lu Z, Yu S, et al. Long noncoding RNA MIR31HG exhibits oncogenic property in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and is negatively regulated by miR-193b. Oncogene. 2016;35:3647–57.
Li H, Wang X, Wen C, Huo Z, Wang W, Zhan Q, et al. Long noncoding RNA NORAD, a novel competing endogenous RNA, enhances the hypoxia-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition to promote metastasis in pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer. 2017;16:169.
Pellecchia S, Sepe R, Decaussin-Petrucci M, Ivan C, Shimizu M, Coppola C, et al. The long non-coding RNA Prader Willi/Angelman region RNA5 (PAR5) is downregulated in anaplastic thyroid carcinomas where it acts as a tumor suppressor by reducing EZH2 activity. Cancers. 2020;12:235.
Huang X, Zhi X, Gao Y, Ta N, Jiang H, Zheng J. LncRNAs in pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget. 2016;7:57379–90.
Lv Y, Huang S. Role of non-coding RNA in pancreatic cancer. Oncol Lett. 2019;18:3963–73.
Han T, Hu H, Zhuo M, Wang L, Cui JJ, Jiao F, et al. Long non-coding RNA: an emerging paradigm of pancreatic cancer. Curr Mol Med. 2016;16:702–9.
Wang G, Sheng W, Shi X, Li X, Zhou J, Dong M. Serine/arginine protein-specific kinase 2 promotes the development and progression of pancreatic cancer by downregulating Numb and p53. FEBS J. 2019;286:1668–82.
Jiang H, Hegde S, Knolhoff BL, Zhu Y, Herndon JM, Meyer MA, et al. Targeting focal adhesion kinase renders pancreatic cancers responsive to checkpoint immunotherapy. Nat Med. 2016;22:851–60.
Mello SS, Valente LJ, Raj N, Seoane JA, Flowers BM, McClendon J, et al. A p53 super-tumor suppressor reveals a tumor suppressive p53-Ptpn14-Yap axis in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Cell. 2017;32:460–73 e466.
Chan JJ, Tay Y. Noncoding RNA:RNA regulatory networks in cancer. Int J Mol Sci. 2018;19:1310.
Thomson DW, Dinger ME. Endogenous microRNA sponges: evidence and controversy. Nat Rev Genet. 2016;17:272–83.
Zheng J, Huang X, Tan W, Yu D, Du Z, Chang J, et al. Pancreatic cancer risk variant in LINC00673 creates a miR-1231 binding site and interferes with PTPN11 degradation. Nat Genet. 2016;48:747–57.
Pastushenko I, Blanpain C. EMT transition states during tumor progression and metastasis. Trends Cell Biol. 2019;29:212–26.
Saitoh M. Involvement of partial EMT in cancer progression. J Biochem. 2018;164:257–64.
Lu W, Kang Y. Epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity in cancer progression and metastasis. Dev Cell. 2019;49:361–74.
Tyagi N, Bhardwaj A, Singh AP, McClellan S, Carter JE, Singh S. p-21 activated kinase 4 promotes proliferation and survival of pancreatic cancer cells through AKT- and ERK-dependent activation of NF-kappaB pathway. Oncotarget. 2014;5:8778–89.
Sun Y, Li S, Yang L, Zhang D, Zhao Z, Gao J, et al. CDC25A facilitates chemo-resistance in ovarian cancer multicellular spheroids by promoting E-cadherin expression and arresting cell cycles. J Cancer. 2019;10:2874–84.
Liang X, Qi M, Wu R, Liu A, Chen D, Tang L, et al. Long non-coding RNA CUDR promotes malignant phenotypes in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma via activating AKT and ERK signaling pathways. Int J Oncol. 2018;53:2671–82.
Li J, Ji X, Wang H. Targeting long noncoding RNA HMMR-AS1 suppresses and radiosensitizes glioblastoma. Neoplasia. 2018;20:456–66.
Wang Y, Ding X, Hu H, He Y, Lu Z, Wu P, et al. Long non-coding RNA lnc-PCTST predicts prognosis through inhibiting progression of pancreatic cancer by downregulation of TACC-3. Int J Cancer. 2018;143:3143–54.
Deng SJ, Chen HY, Ye Z, Deng SC, Zhu S, Zeng Z, et al. Hypoxia-induced LncRNA-BX111 promotes metastasis and progression of pancreatic cancer through regulating ZEB1 transcription. Oncogene. 2018;37:5811–28.
Li N, Yang G, Luo L, Ling L, Wang X, Shi L, et al. lncRNA THAP9-AS1 promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma growth and leads to a poor clinical outcome via sponging miR-484 and interacting with YAP. Clin Cancer Res. 2020;26:1736–48.
Zhang B, Li C, Sun Z. Long non-coding RNA LINC00346, LINC00578, LINC00673, LINC00671, LINC00261, and SNHG9 are novel prognostic markers for pancreatic cancer. Am J Transl Res. 2018;10:2648–58.
Ohuchida K, Mizumoto K, Lin C, Yamaguchi H, Ohtsuka T, Sato N, et al. MicroRNA-10a is overexpressed in human pancreatic cancer and involved in its invasiveness partially via suppression of the HOXA1 gene. Ann Surg Oncol. 2012;19:2394–402.
Huang S, Guo H, Cao Y, Xiong J. MiR-708-5p inhibits the progression of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by targeting Sirt3. Pathol Res Pract. 2019;215:794–800.
Sadeghi H, Golalipour M, Yamchi A, Farazmandfar T, Shahbazi M. CDC25A pathway toward tumorigenesis: molecular targets of CDC25A in cell-cycle regulation. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120:2919–28.
Shen T, Huang S. The role of Cdc25A in the regulation of cell proliferation and apoptosis. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2012;12:631–9.
Li CY, Wang Q, Wang XM, Li GX, Shen S, Wei XL. Gambogic acid exhibits anti-metastatic activity on malignant melanoma mainly through inhibition of PI3K/Akt and ERK signaling pathways. Eur J Pharmacol. 2019;864:172719.
Xie S, Yu X, Li Y, Ma H, Fan S, Chen W, et al. Upregulation of lncRNA ADAMTS9-AS2 promotes salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma metastasis via PI3K/Akt and MEK/Erk signaling. Mol Ther. 2018;26:2766–78.
Zhang X, Lv QL, Huang YT, Zhang LH, Zhou HH. Akt/FoxM1 signaling pathway-mediated upregulation of MYBL2 promotes progression of human glioma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017;36:105.
Lin ZH, Wang L, Zhang JB, Liu Y, Li XQ, Guo L, et al. MST4 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis via activation of the p-ERK pathway. Int J Oncol. 2014;45:629–40.
Yang K, Li Y, Lian G, Lin H, Shang C, Zeng L, et al. KRAS promotes tumor metastasis and chemoresistance by repressing RKIP via the MAPK-ERK pathway in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer. 2018;142:2323–34.
Sheng W, Shi X, Lin Y, Tang J, Jia C, Cao R, et al. Musashi2 promotes EGF-induced EMT in pancreatic cancer via ZEB1-ERK/MAPK signaling. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020;39:16.
Sheng W, Chen C, Dong M, Wang G, Zhou J, Song H, et al. Calreticulin promotes EGF-induced EMT in pancreatic cancer cells via Integrin/EGFR-ERK/MAPK signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2017;8:e3147.
Guo YJ, Pan WW, Liu SB, Shen ZF, Xu Y, Hu LL. ERK/MAPK signalling pathway and tumorigenesis. Exp Ther Med. 2020;19:1997–2007.
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Kun Liu and Huimin Wang (Department of Hepatobiliary Surgery of Xijing Hospital) for collecting the tissue samples and the follow-up information
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 81672339, 81874051, and 81900571).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, S., Niu, K., Wang, J. et al. LINC00671 suppresses cell proliferation and metastasis in pancreatic cancer by inhibiting AKT and ERK signaling pathway. Cancer Gene Ther 28, 221–233 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-020-00213-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41417-020-00213-4
This article is cited by
-
The burgeoning importance of PIWI-interacting RNAs in cancer progression
Science China Life Sciences (2024)